吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 1155-1162.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220327
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于多尺度特征的行人重识别属性提取新方法
- 长春理工大学 电子信息工程学院,长春 130022
New method for extracting person re-identification attributes based on multi-scale features
- School of Electronic and Information Engineering,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
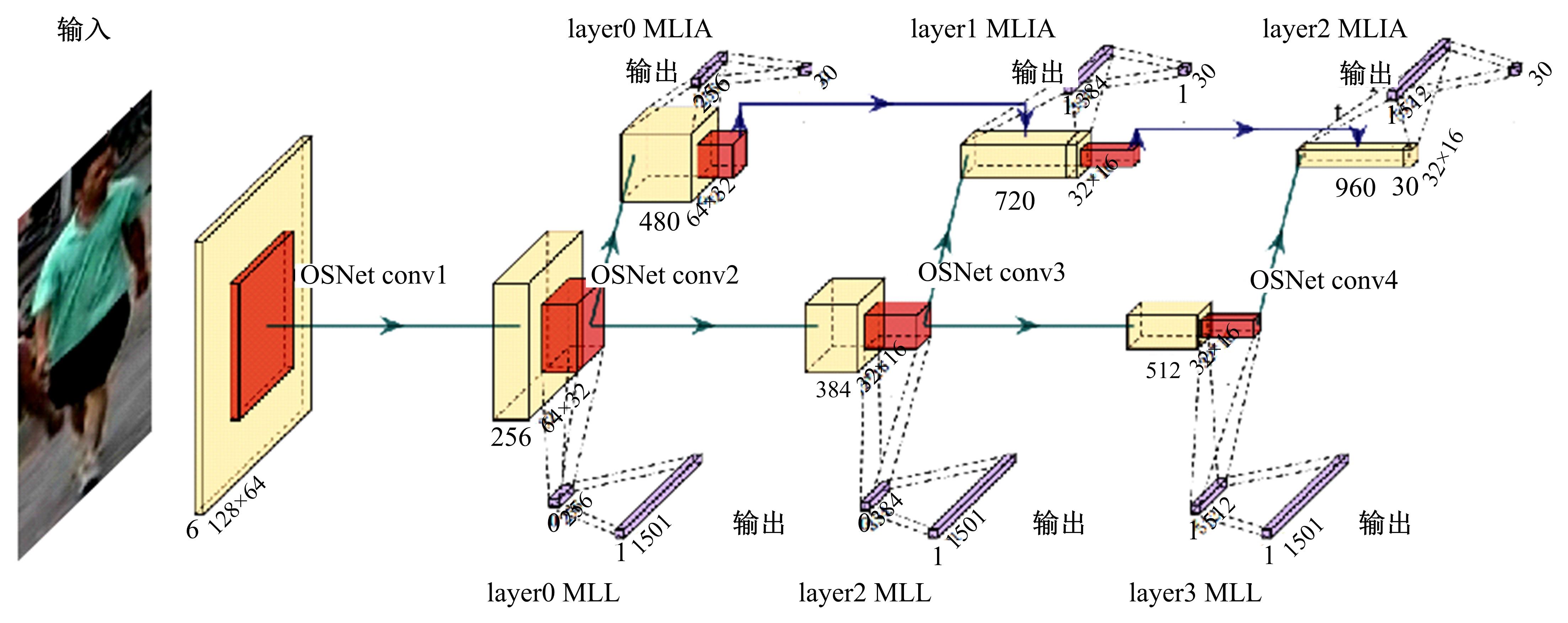
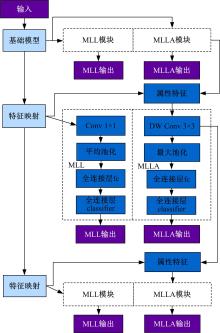
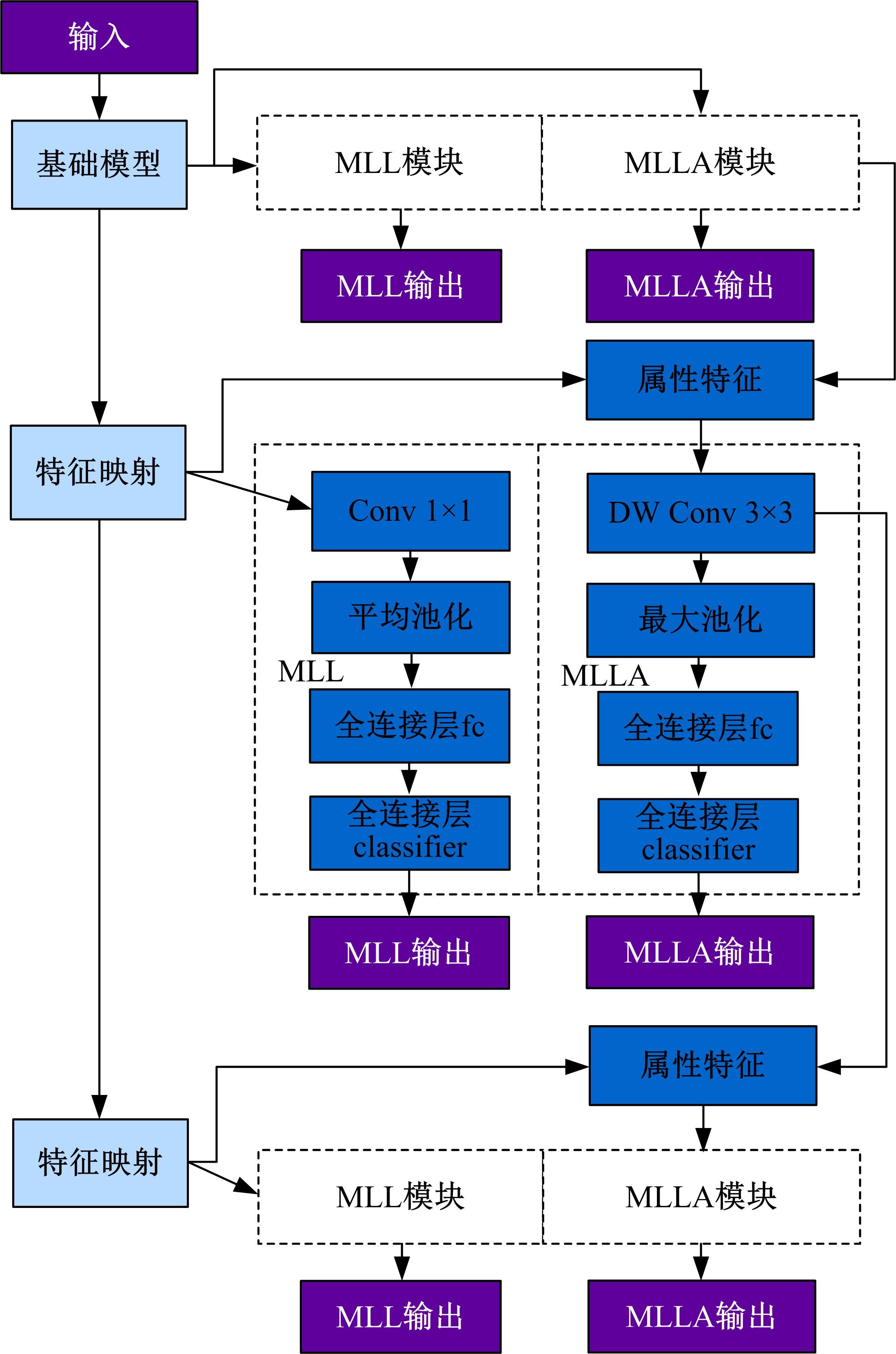
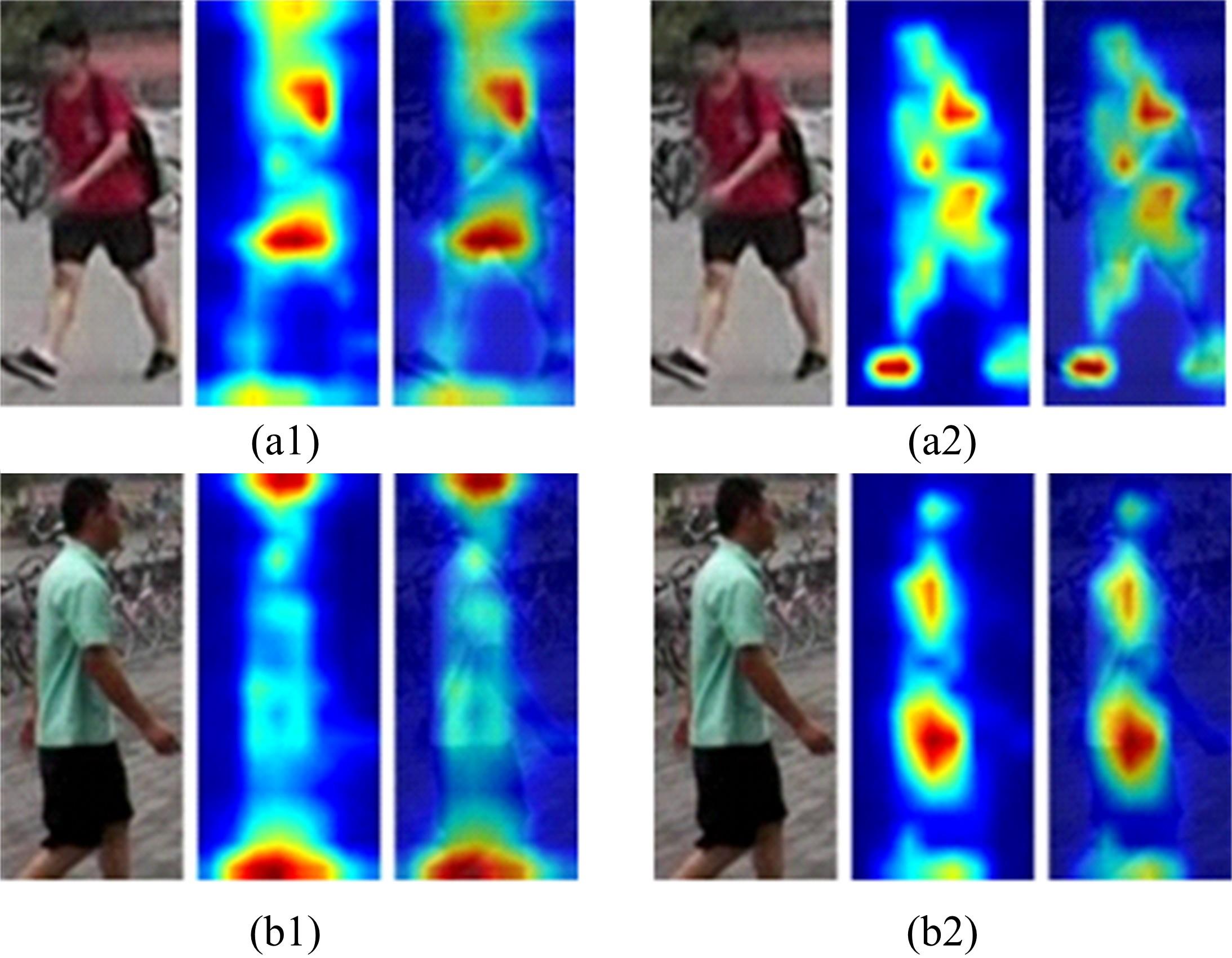
针对目前行人重识别存在背景混乱、遮挡干扰、姿势不对齐、解释性不足等问题,提出了一种基于多尺度特征的行人重识别属性提取新方法。通过中间层学习模块学习属性并按属性分组卷积,以增强模型的可解释性;通过选择对比中间的属性特征,减少干扰特征的影响。本文方法在3个常用的公开数据集上测试并与其他方法进行了对比,实验结果表明,该方法可以有效提取中间层的语义信息,并且在跨数据集上测试优于其他方法。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Alex K, Ilya S, Geoffrey E H. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. |
| 2 | Zhang Zhi-zheng, Lan Cui-ling, Zeng Wen-jun, et al. Relation-aware global attention for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 3186-3195. |
| 3 | Chen Guang-yi, Lin Chun-ze, Ren Liang-liang, et al. Self-critical attention learning for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 9637-9646. |
| 4 | Fang Peng-fei, Zhou Jie-ming, Kumar Roy Soumava, et al. Bilinear attention networks for person retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 8030-8039. |
| 5 | Sun Yi-fan, Zheng Liang, Yang Yi, et al. Beyond part models: person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline)[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 501-518. |
| 6 | Zhou Kai-yang, Yang Yong-xin, Cavallaro Andrea, et al. Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 3702-3712. |
| 7 | Chen Xiao-dong, Liu Xin-chen, Liu Wu, et al. Explainable person re-identification with attribute-guided metric distillation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Montreal, Canada, 2021: 11813-11822. |
| 8 | Divyansh G, Netra P, Thomas T, et al. Towards explainable person re-identification[C]//2021 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Orlando, USA, 2021: 1-8. |
| 9 | Chen Guang-yi, Gu Tian-pei, Lu Ji-wen, et al. Person re-identification via attention pyramid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 7663-7676. |
| 10 | Wang Guan-shuo, Yuan Yu-feng, Chen Xiong, et al. Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Korea(South), 2018: 274-282. |
| 11 | Feng Zheng, Cheng Deng, Xing Sun, et al. Pyramidal person re-identification via multi-loss dynamic training[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 8514-8522. |
| 12 | 本杰明•里贝特. 心智时间: 意识中的时间因素[M]: 李恒熙,李恒威,罗慧怡译.杭州: 浙江大学出版社, 2013:55-56. |
| 13 | Han Yi-zeng, Huang Gao, Song Shi-ji, et al. Dynamic neural networks: a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 44(11): 7436-7456. |
| 14 | Teerapittayanon S, McDanel B, Kung H T. Branchynet: fast inference via early exiting from deep neural networks[C]//The 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Cancun, Mexico, 2016: 2464-2469. |
| 15 | Hermans Alexander, Beyer Lucas, Leibe Bastian. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv 2017[J/OL].[2017-04-01]. . |
| 16 | Zheng Liang, Shen Li-yue, Tian Lu, et al. Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1116-1124. |
| 17 | Zhong Zhun, Zheng Liang, Cao Dong-lin, et al. Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1318-1327. |
| 18 | Ergys R, Francesco S, Roger Z, et al. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 17-35. |
| 19 | Lin Yu-tian, Zheng Liang, Zheng Zhe-dong, et al. Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 95: 151-161. |
| 20 | Jia Deng, Wei Dong, Socher Richard, et al. Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 248-255. |
| 21 | Hyunjong P, Bumsub H. Relation network for person re-identification[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(7): 11839-11847. |
| 22 | Sun Yi-fan, Xu Qin, Li Ya-li, et al. Perceive where to focus: learning visibility-aware part-level features for partial person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 393-402. |
| 23 | Tay C-P, Roy S, Yap K-H. Aanet: attribute attention network for person re-identifications[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 7134-7143. |
| 24 | Yang Wen-jie, Huang Hou-jing, Zhang Zhang, et al. Towards rich feature discovery with class activation maps augmentation for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1389-1398. |
| 25 | Chen Bing-hui, Deng Wei-hong, Hu Jia-ni. Mixed high-order attention network for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 371-381. |
| 26 | Chen Xue-song, Fu Can-miao, Zhao Yong, et al. Salience-guided cascaded suppression network for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 3300-3310. |
| 27 | Zhao Shi-zhen, Gao Chang-xin, Zhang Jun, et al. Do not disturb me: person re-identification under the interference of other pedestrians[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 647-663. |
| [1] | 姜宇,潘家铮,陈何淮,符凌智,齐红. 基于分割方法的繁体中文报纸文本检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1146-1154. |
| [2] | 吴振宇,刘小飞,王义普. 基于DKRRT*-APF算法的无人系统轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 781-791. |
| [3] | 陶博,颜伏伍,尹智帅,武冬梅. 基于高精度地图增强的三维目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 802-809. |
| [4] | 薛珊,张亚亮,吕琼莹,曹国华. 复杂背景下的反无人机系统目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 891-901. |
| [5] | 潘弘洋,刘昭,杨波,孙庚,刘衍珩. 基于新一代通信技术的无人机系统群体智能方法综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 629-642. |
| [6] | 何颖,樊俊松,王巍,孙庚,刘衍珩. 无人机空地安全通信与航迹规划的多目标联合优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 913-922. |
| [7] | 郭鹏,赵文超,雷坤. 基于改进Jaya算法的双资源约束柔性作业车间调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 480-487. |
| [8] | 刘近贞,高国辉,熊慧. 用于脑组织分割的多尺度注意网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 576-583. |
| [9] | 祁贤雨,王巍,王琳,赵玉飞,董彦鹏. 基于物体语义栅格地图的语义拓扑地图构建方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 569-575. |
| [10] | 时小虎,吴佳琦,吴春国,程石,翁小辉,常志勇. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| [11] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [12] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [13] | 周丰丰,朱海洋. 基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法SEE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1834-1841. |
| [14] | 赵宏伟,张健荣,朱隽平,李海. 基于对比自监督学习的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1850-1856. |
| [15] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
|
||