吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 533-539.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220335
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于机器阅读理解的事件检测方法
- 1.国防科技大学 第六十三研究所,南京 210007
2.宿迁学院 信息工程学院,江苏 宿迁 223800
Event detection method as machine reading comprehension
Liu LIU1,2( ),Kun DING1(
),Kun DING1( ),Shan-shan LIU1,Ming LIU1
),Shan-shan LIU1,Ming LIU1
- 1.The Sixty-Third Research Institute,National University of Defense Technology,Nanjing 210007,China
2.School of Information Engineering,Suqian University,Suqian 223800,China
摘要:
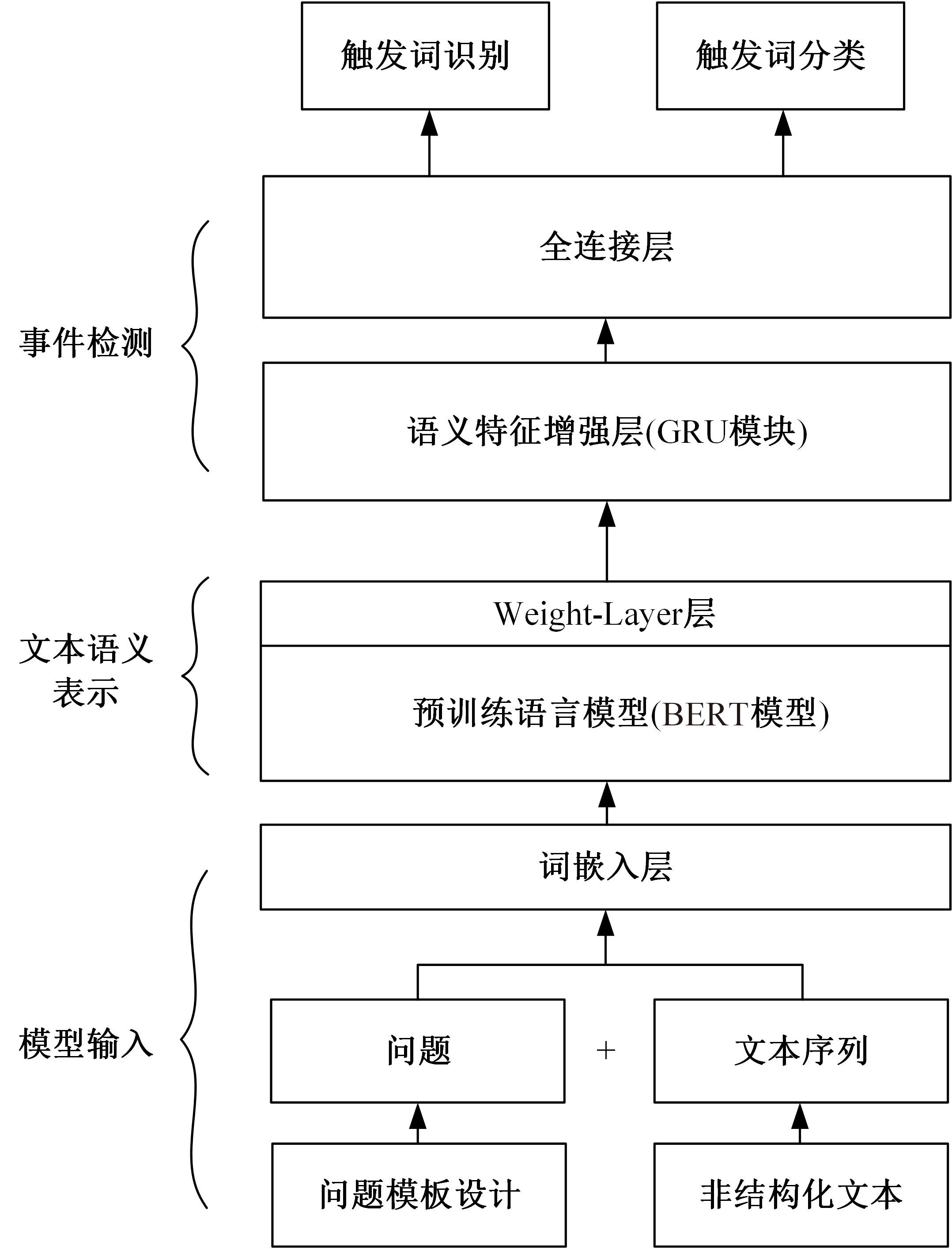
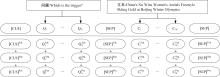
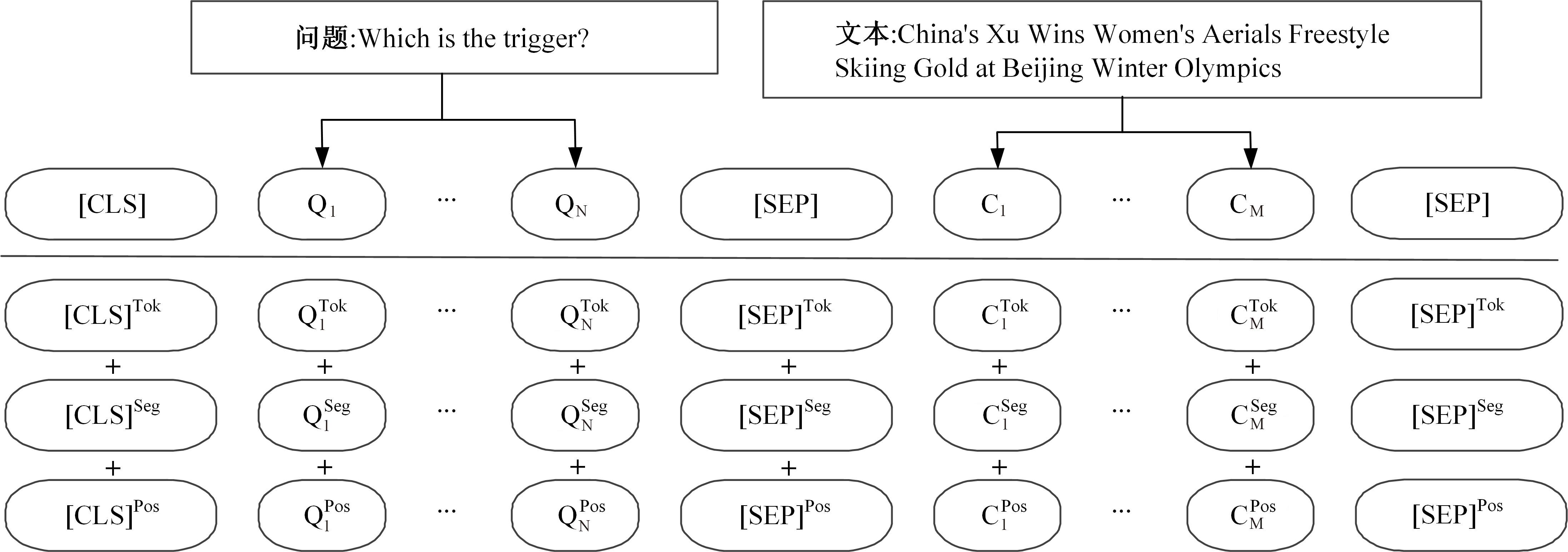
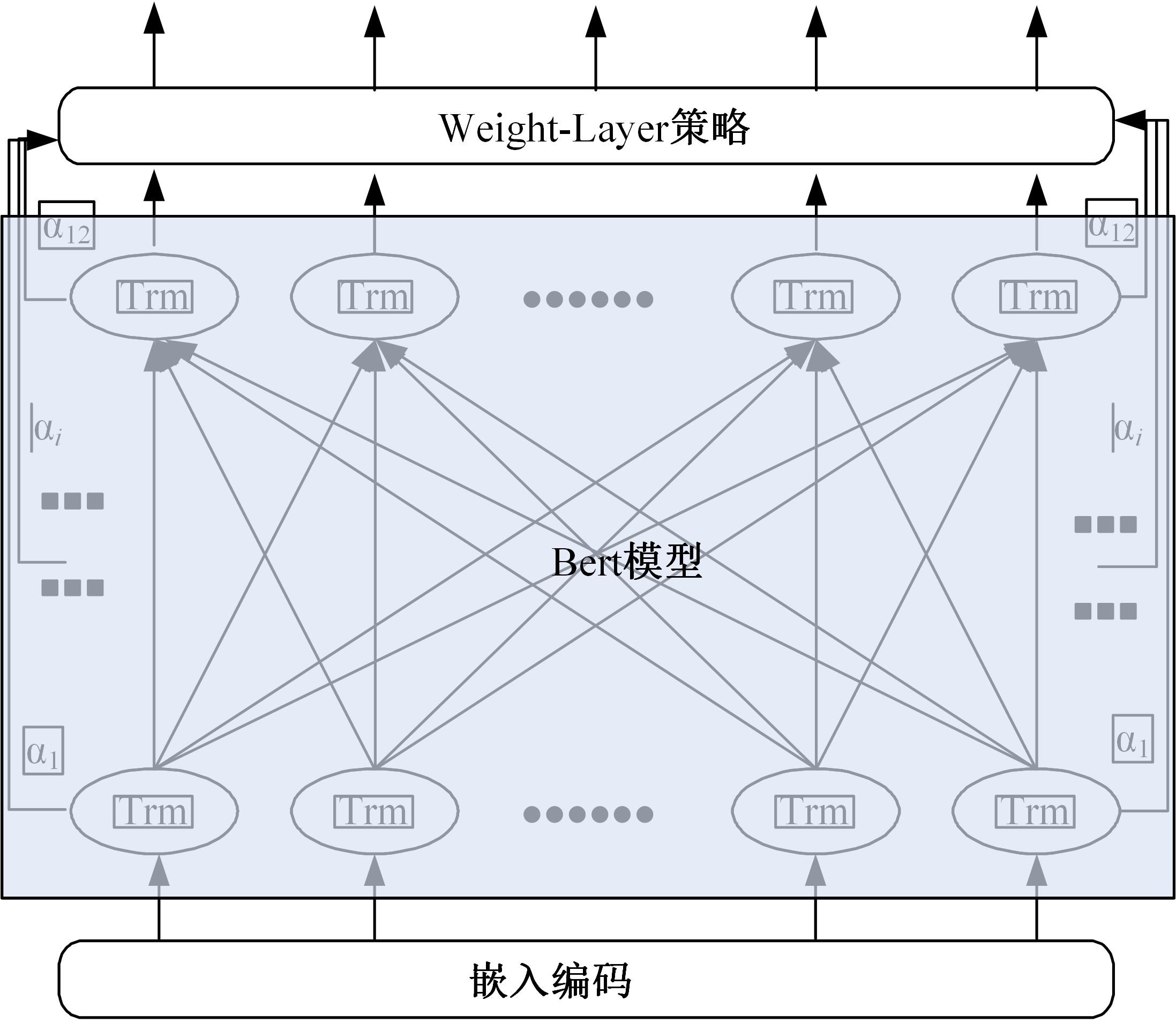
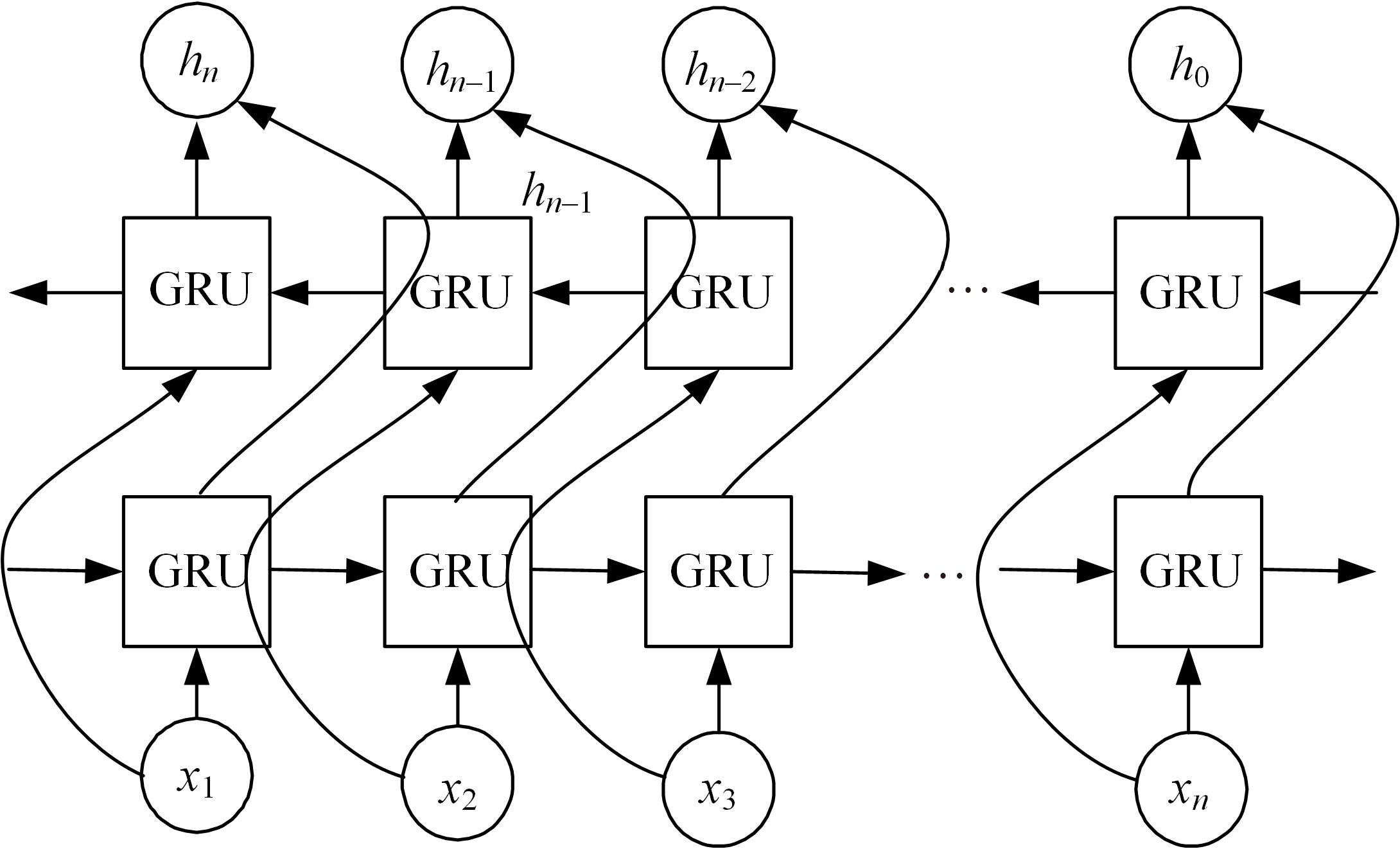
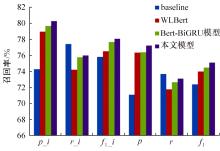
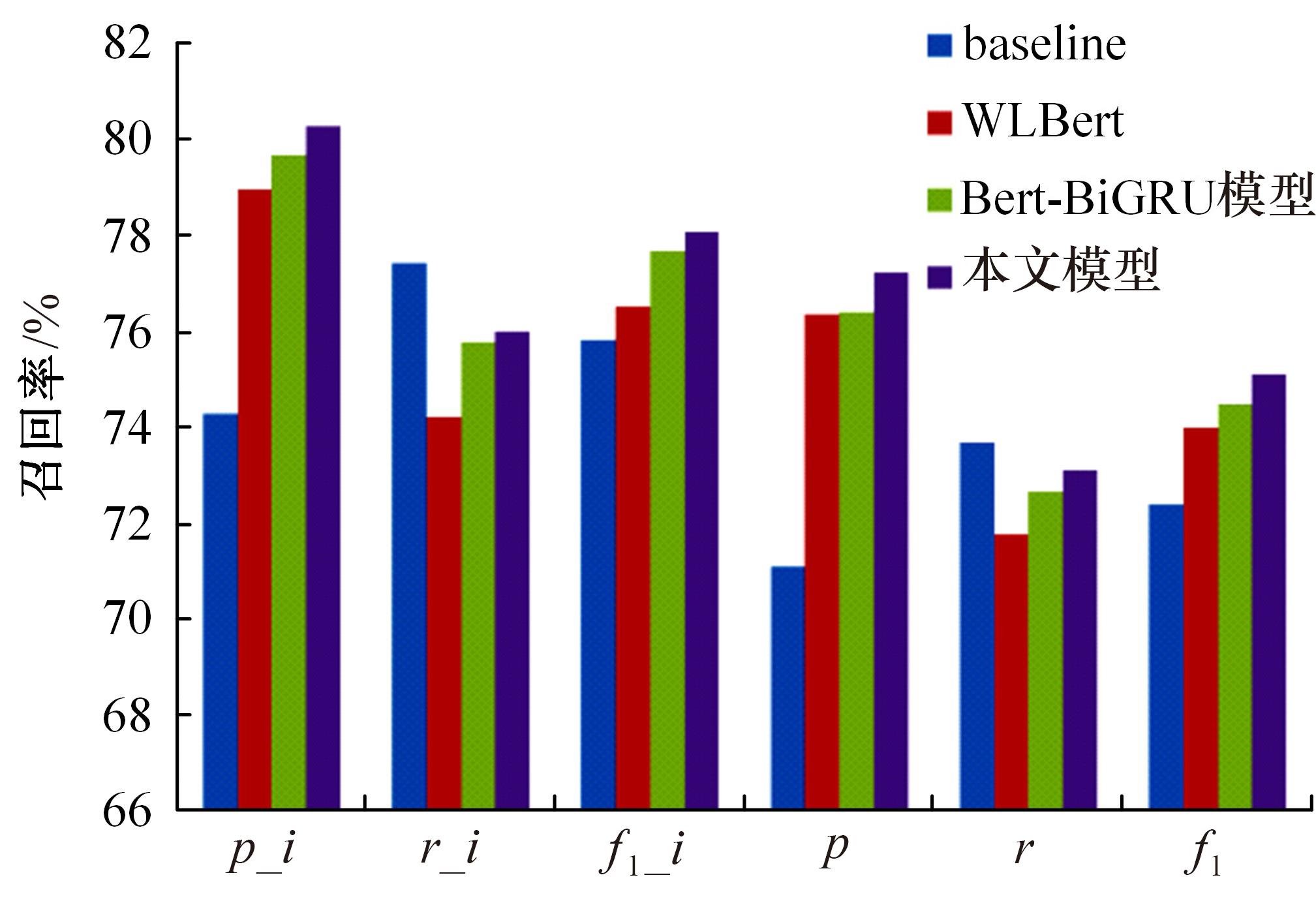
为提高事件检测任务的性能,将该任务重定义为一种提示范式,该范式使用问答对的形式将事件检测转化为机器阅读问题。同时,设计了一种名为WLBert-BiGRU的学习模型对问答对中的事件触发词进行预测,该模型使用Weight-Layers策略丰富Bert模型的语义表征能力,并使用双向门控循环单元神经网络(Bi-GRU)方法强化模型对事件触发词的识别能力。在ACE 2005数据集上的实验结果表明,本文方法在事件触发词识别和分类上的F1指标分别达到了78.1%和75.1%,较现有的工作平均提高了4.18%和4.3%。
中图分类号:
- TP391.1
| 1 | Linguistic Data Consortium. ACE (Automatic Content Extra-ction) English Annotation Guidelines for Events Version 5.4. 3 [EB/OL].[2005-07-01]. |
| 2 | Du X, Cardie C. Event extraction by answering (almost) natural questions[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2020: 671-683. |
| 3 | 张婧丽. 基于知识扩展与信息融合的事件检测方法研究[D].苏州:苏州大学计算机科学与技术学院, 2020. |
| Zhang Jing-li. Research on event detection based on knowledge expansion and information fusion[D]. Suzhou: School of Computer Science and Technology, Soochow University, 2020. | |
| 4 | Grishman R, Westbrook D, Meyers A. Nyu's english ace 2005 system description[J]. Journal on Satisfiability, 2005, 51(11): 1927-1938. |
| 5 | Ahn D. The stages of event extraction[C]∥Proceedings of the Workshop on Annotating and Reasoning about Time and Events. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2006: 1-8. |
| 6 | Ji H, Grishman R. Refining event extraction through cross-document inference[C]∥Proceedings of the 46th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA: AcL, 2008: 254-262. |
| 7 | Liao S, Grishman R. Using document level cross-event inference to improve event extraction[C]∥Proceedings of the 48th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA: AcL, 2010: 789-797. |
| 8 | Hong Y, Zhang J, Ma B, et al. Using cross-entity inference to improve event extraction[C]∥Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2011: 1127-1136. |
| 9 | Li Q, Ji H, Huang L. Joint event extraction via structured prediction with global features[C]∥Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2013: 73-82. |
| 10 | 郭晓然, 罗平, 王维兰. 基于Transformer编码器的中文命名实体识别[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(3): 989-995. |
| Guo Xiao-ran, Luo Ping, Wang Wei-lan. Chinese named entity recognition based on Transformer encoder[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 989-995. | |
| 11 | Nguyen T H, Grishman R. Modeling skip-grams for event detection with convolutional neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2016: 886-891. |
| 12 | Chen Y, Xu L, Liu K, et al. Event extraction via dynamic multi-pooling convolutional neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2015: 167-176. |
| 13 | Nguyen T H, Cho K, Grishman R. Joint event extraction via recurrent neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2016: 300-309. |
| 14 | Feng X, Qin B, Liu T. A language-independent neural network for event detection[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2018, 61(9): 1-12. |
| 15 | Peters M E, Neumann M, Iyyer M, et al. Deep contextualized word representations[C]∥Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. Stroudsburg: ACL, PA, 2018: 2227-2237. |
| 16 | Radford A, Narasimhan K, Salimans T, et al. Improving language understanding by generative pre-training [EB/OL]. [2022-03-25]. |
| 17 | Devlin J, Chang M W, Lee K, et al. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding [EB/OL]. [2022-03-25]. |
| 18 |
李健, 熊琦, 胡雅婷, 等.基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的中文命名实体识别方法[J/OL].[2022-05-12].DOI:10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210856 .
doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210856 |
|
Li Jian, Xiong Qi, Hu Ya-ting, et al. Chinese named entity recognition method based on transformer and hidden Markov model[J/OL]. [2022-05-12]. DOI:10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210856 .
doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210856 |
|
| 19 | Wadden D, Wennberg U, Luan Y, et al. Entity, relation, and event extraction with contextualized span representations[C]∥Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2019: 5784-5789. |
| 20 | Lin Y, Ji H, Huang F, et al. A joint neural model for information extraction with global features[C]∥Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2020: 7999-8009. |
| 21 | Nguyen T M, Nguyen T H. One for all: neural joint modeling of entities and events[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Menlo Park, CA, 2019: 6851-6858. |
| 22 | Zhang T, Ji H, Sil A. Joint entity and event extraction with generative adversarial imitation learning[J]. Data Intelligence, 2019, 1(2): 99-120. |
| [1] | 车翔玖,徐欢,潘明阳,刘全乐. 生物医学命名实体识别的两阶段学习算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2380-2387. |
| [2] | 李健,熊琦,胡雅婷,刘孔宇. 基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的中文命名实体识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [3] | 马月坤,郝益锋. 考虑特征稀疏特性的短文本命名实体快速识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3529-3535. |
| [4] | 刘春晖,王思长,郑策,陈秀连,郝春蕾. 基于深度学习的室内导航机器人避障规划算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3558-3564. |
| [5] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [6] | 王生生,姜林延,杨永波. 基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
| [7] | 田皓宇,马昕,李贻斌. 基于骨架信息的异常步态识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 725-737. |
| [8] | 刘勇,徐雷,张楚晗. 面向文本游戏的深度强化学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 666-674. |
| [9] | 雷景佩,欧阳丹彤,张立明. 基于知识图谱嵌入的定义域值域约束补全方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 154-161. |
| [10] | 李志华,张烨超,詹国华. 三维水声海底地形地貌实时拼接与可视化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 180-186. |
| [11] | 欧阳丹彤,张必歌,田乃予,张立明. 结合格局检测与局部搜索的故障数据缩减方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2144-2153. |
| [12] | 徐艳蕾,何润,翟钰婷,赵宾,李陈孝. 基于轻量卷积网络的田间自然环境杂草识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2304-2312. |
| [13] | 杨勇,陈强,曲福恒,刘俊杰,张磊. 基于模拟划分的SP⁃k⁃means-+算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1808-1816. |
| [14] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [15] | 董延华,刘靓葳,赵靖华,李亮,解方喜. 基于BPNN在线学习预测模型的扭矩实时跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1405-1413. |
|
||