吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 550-557.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220409
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
基于改进混沌优化的选择性催化还原系统参数辨识方法
赵靖华1,2( ),杜世豪1,刘靓葳1,3,胡云峰2,孙耀2(
),杜世豪1,刘靓葳1,3,胡云峰2,孙耀2( ),解方喜2
),解方喜2
- 1.吉林师范大学 计算机学院,吉林 四平 136002
2.吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
3.长春金融高等专科学校 信息技术学院,长春 130028
Parameter identification for SCR systems based on improved chaos optimization algorithm
Jing-hua ZHAO1,2( ),Shi-hao DU1,Liang-wei LIU1,3,Yun-feng HU2,Yao SUN2(
),Shi-hao DU1,Liang-wei LIU1,3,Yun-feng HU2,Yao SUN2( ),Fang-xi XIE2
),Fang-xi XIE2
- 1.College of Computer,Jilin Normal University,Siping 136002,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
3.College of Information Technology,Changchun Finance College,Changchun 130028,China
摘要:
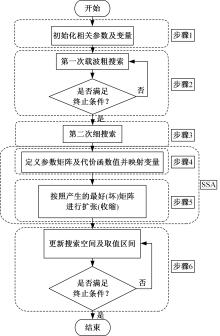
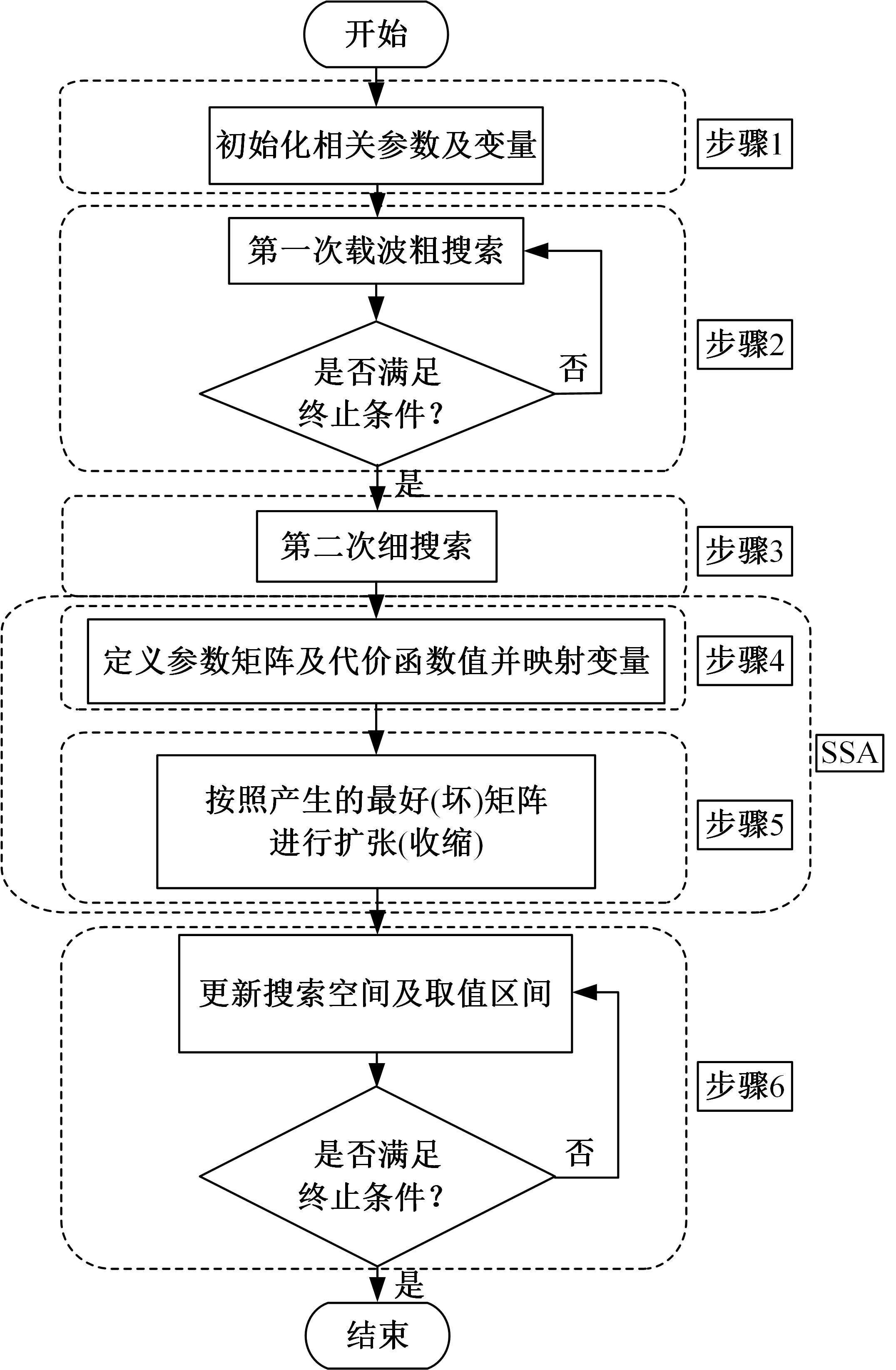
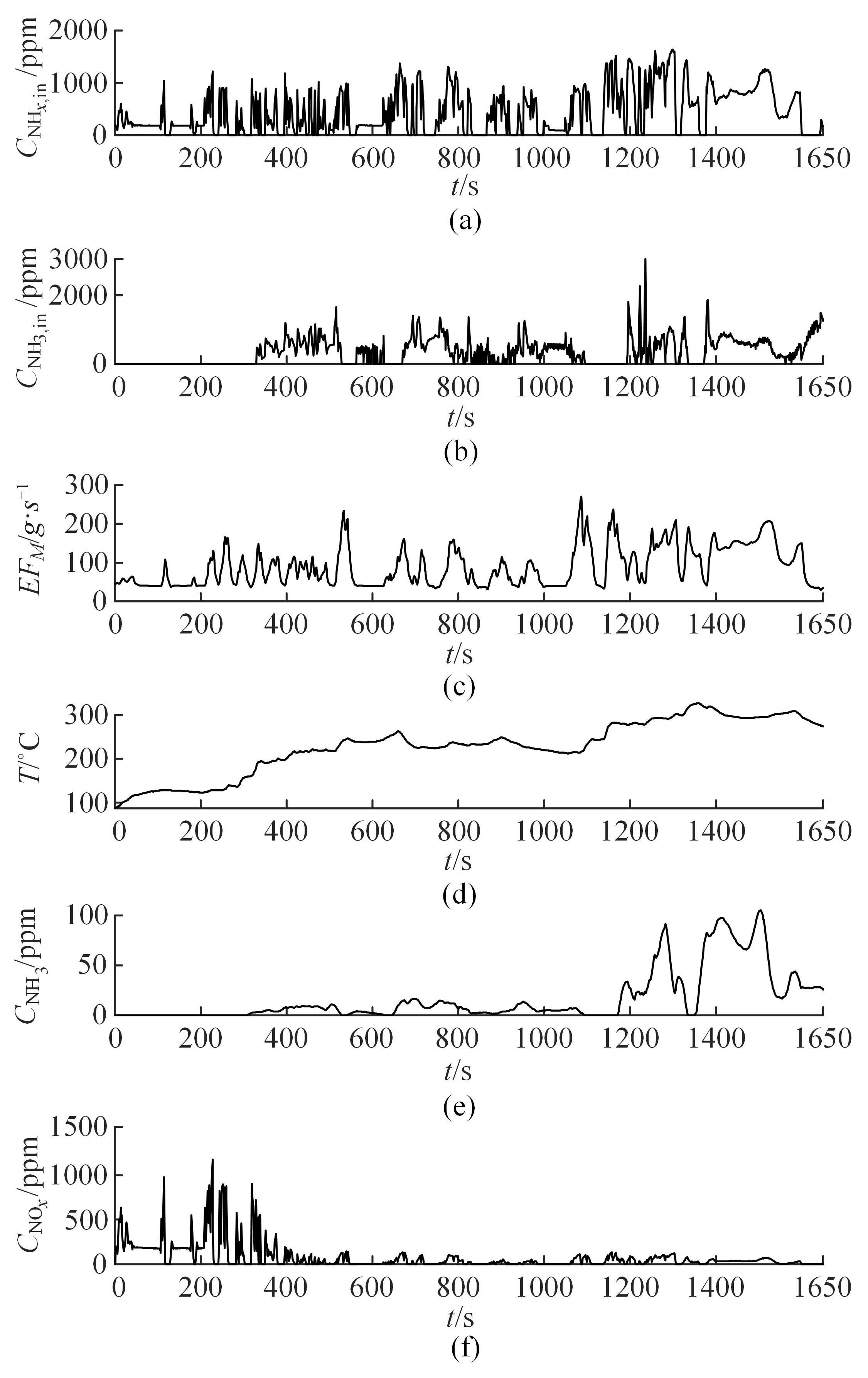
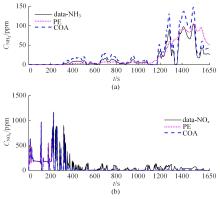
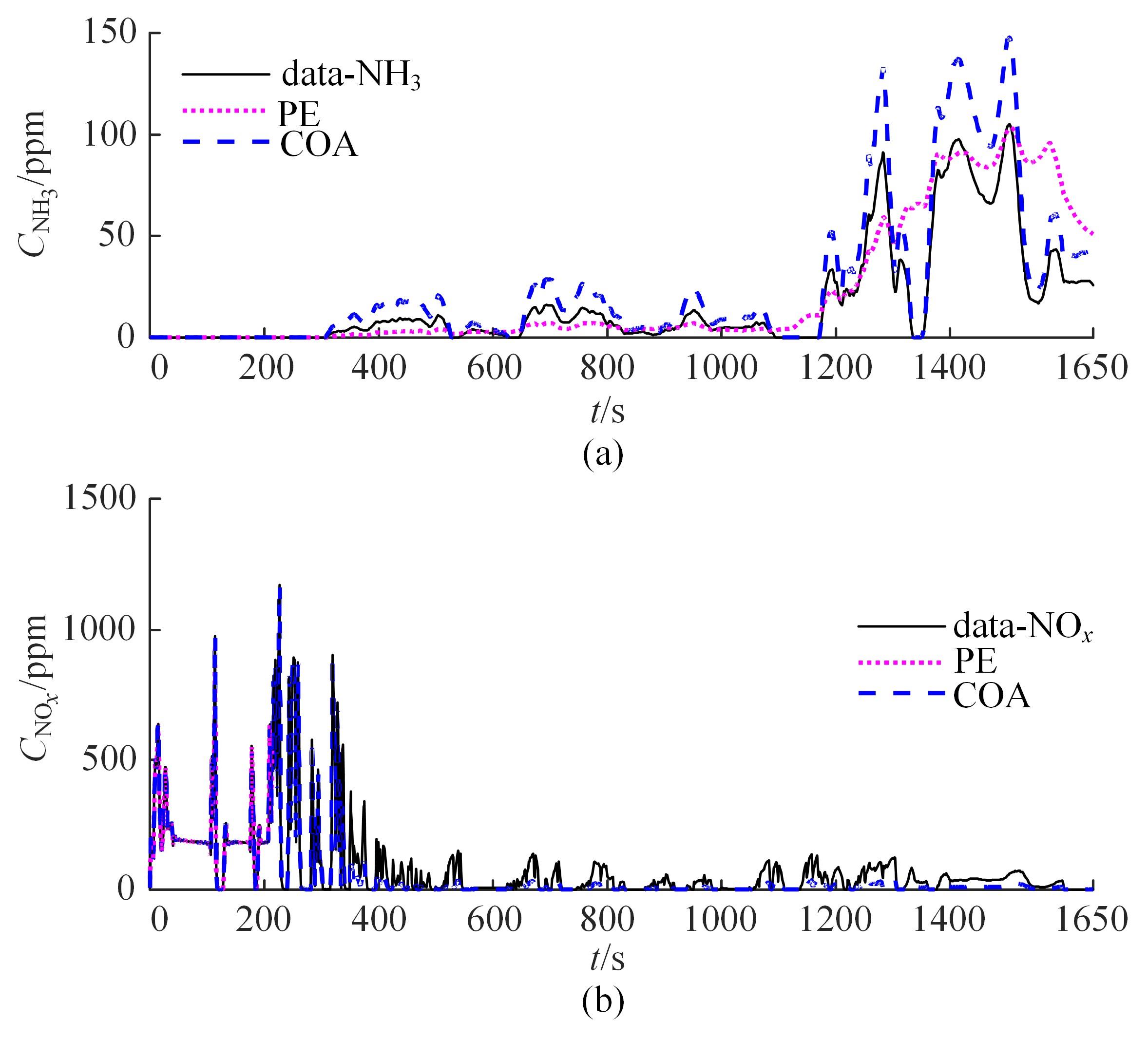
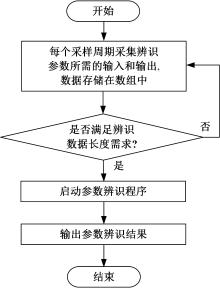
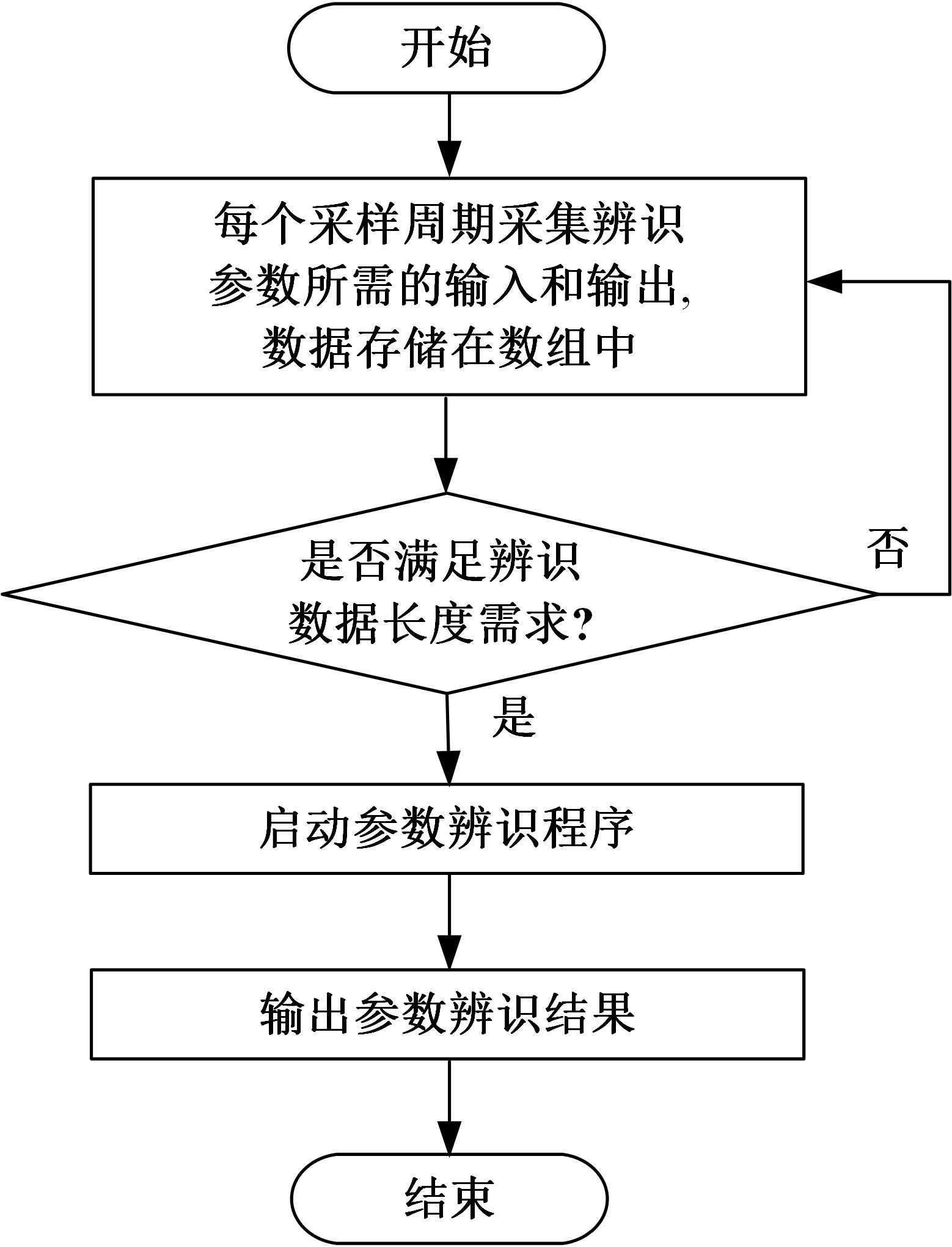
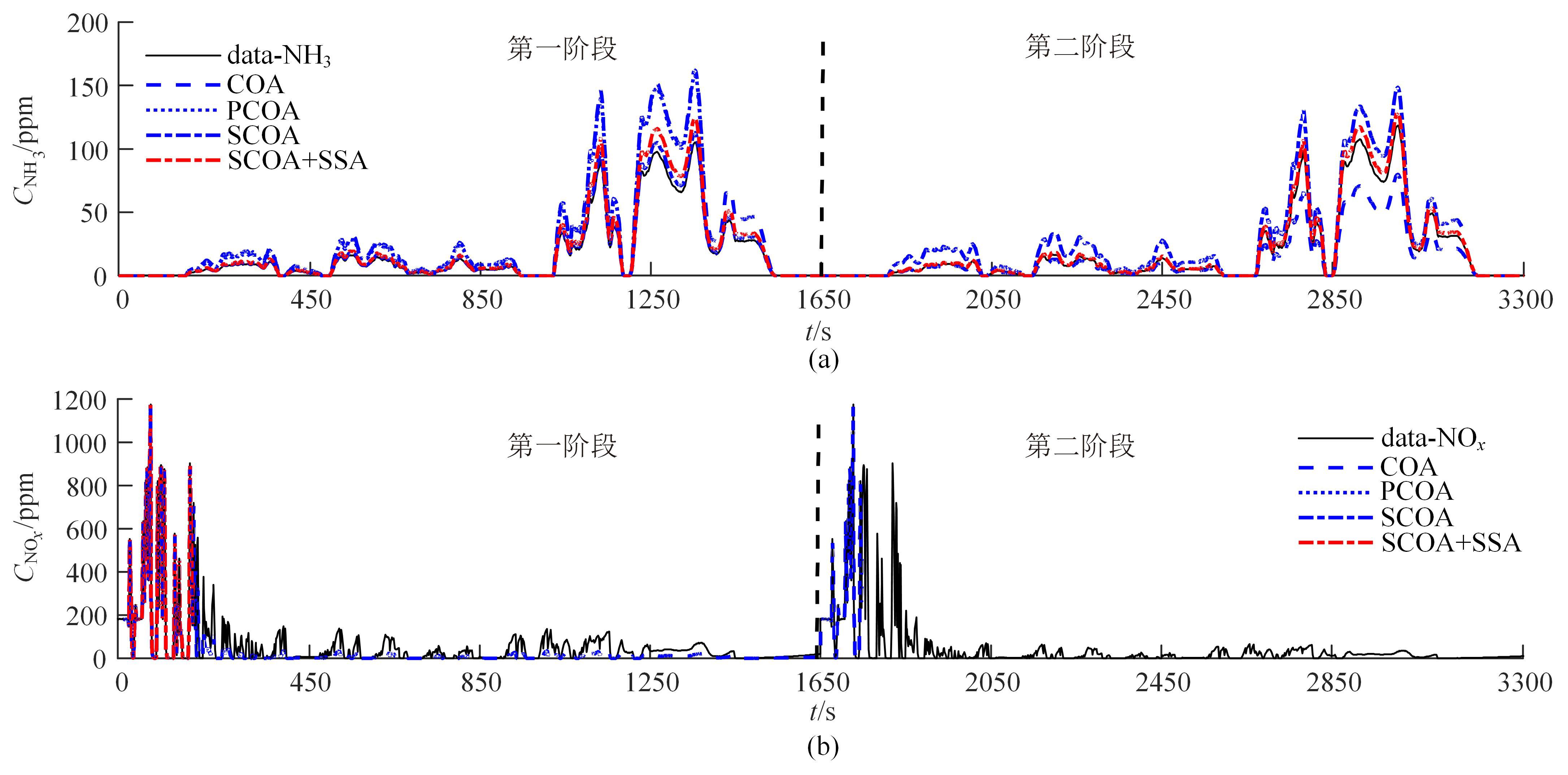
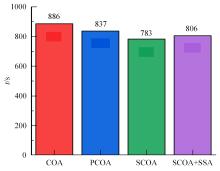
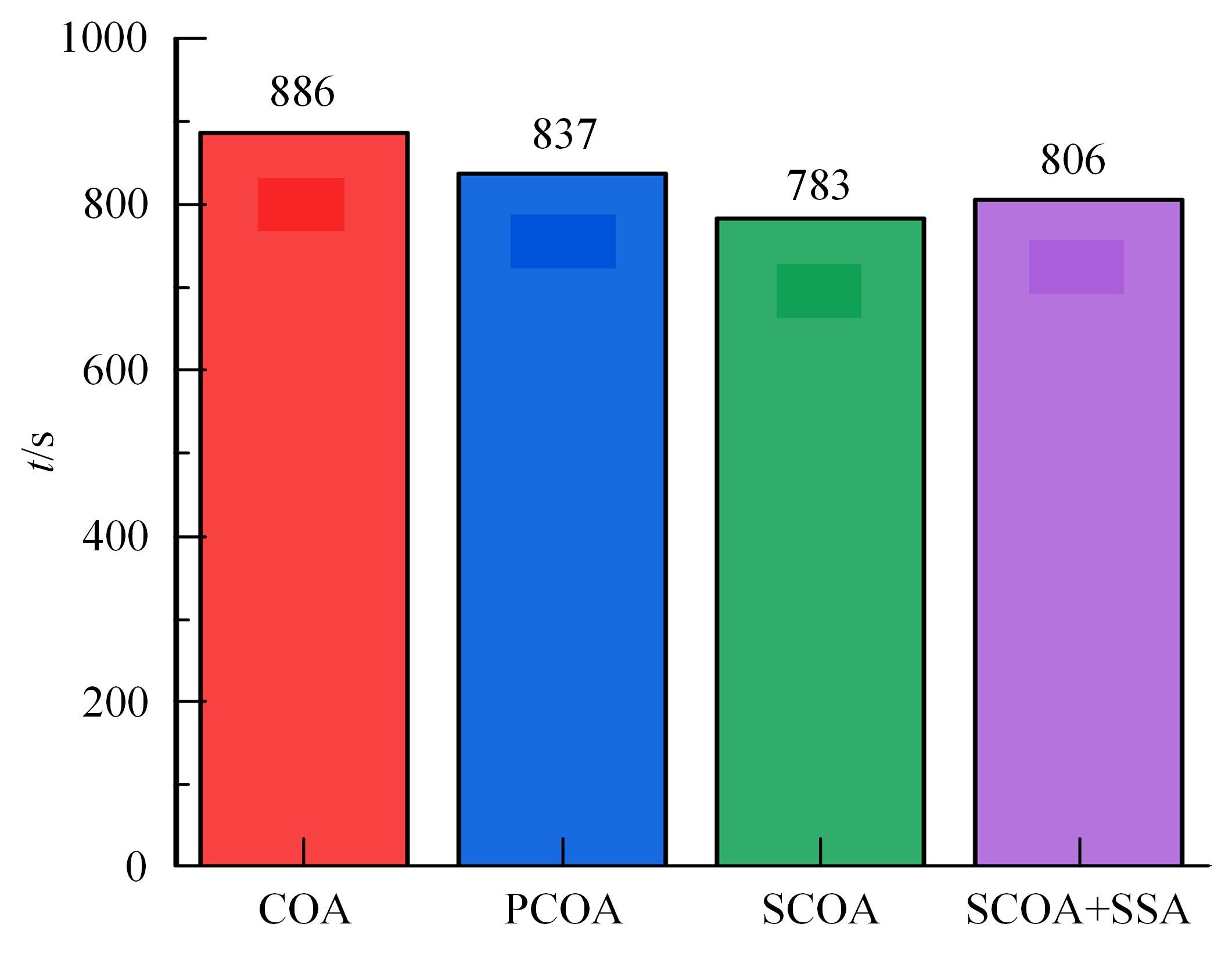
针对选择性催化还原系统(SCR)系统在工作过程中,模型参数会受到老化、损耗等影响发生偏移,特别是催化剂硫中毒会造成氨的最大吸附能力严重下降,导致SCR系统失效的问题,提出了融合加速混沌优化和单一搜索(SCOA+SSA)算法的参数在线辨识方法。该方法能同时辨识SCR系统化学反应动力学中8项关键参数。试验结果表明:该方法能在SCR系统中氨的最大吸附能力阶跃下降时,实时辨识得到新的系统参数;并且,相比于传统的SCOA方法,本文提出的SCOA+SSA方法能将辨识精度提高5.44%,但付出的代价是增加了2.9%的耗时。
中图分类号:
- TP273
| 1 | Zhao J H, Gong X, Hu Y F, et al. An ammonia coverage ratio observing and tracking controller: stability analysis and simulation evaluation[J]. Sci China Inf Sci, 2019, 62: 062201. |
| 2 | Zhang H, Chen P E, Wang J M, et al. Integrated study of inland-vessel diesel engine two-cell SCR systems with dynamic references[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(3): 1195-1206. |
| 3 | Zhao J H, Hu Y F, Gong X, et al. Modelling and control of urea-SCR systems through the triple-step non-linear method in consideration of time-varying parameters and reference dynamics[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement Control, 2018, 40(1): 287-302. |
| 4 | Zhao J H, Zhou S T, Hu Y F, et al. Open-source dataset for control-oriented modelling in diesel engines[J]. Sci China Inf Sci, 2019, 62(7): 077201. |
| 5 | Chen P E, Wang J M. Coordinated active thermal management and selective catalytic reduction control for simultaneous fuel economy improvement and emissions reduction during low-temperature operations[J]. Dyn Syst Meas Control, 2015, 13(7): 634-641. |
| 6 | Zhao J H, Hu Y F, Gao B Z. Sequential optimization of eco-driving taking into account fuel economy and emissions[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 4(99): 1-13. |
| 7 | Ma Y, Wang J M. Integrated power management and aftertreatment system control for hybrid electric vehicles with road grade preview[J]. IEEE Trans Veh Technol, 2017, 66: 10935-10945. |
| 8 | Luo X. Parameter identification of the photovoltaic cell model with a hybrid Jaya-NM algorithm[J]. International Journal for Light Electron Optics, 2018, 171(1): 200-203. |
| 9 | Gao F C, Han L X. Implementing the Nelder-Mead simplex algorithm with adaptive parameters[J]. Computational Optimization and Applications, 2010, 51(1): 259-277. |
| 10 | Liu Y, Heidari A, Ye X, et al. Boosting slime mould algorithm for parameter identification of photovoltaic models[J]. Energy, 2021(5): 121-128. |
| 11 | Tang Z Z, Gu Q F, Ni W, et al. Parameter identification of ship integrative load model based on improved chaos optimization algorithm[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2017, 12(1): 56-63. |
| 12 | Yuan X F, Zhang T, Dai X S, et al. Master-slave model-based parallel chaos optimization algorithm for parameter identification problems[J]. 2016, 83(3): 1727-1741. |
| 13 | 李冬琴. 加速混沌优化算法的改进及其在船型论证中的应用[J].江苏科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 24(4): 5-11. |
| Li Dong-qin. Improvement of stepped-up chaos optimization algorithm and its application to ship demonstration[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 24(4): 5-11. | |
| 14 | Zhang G H, Xing K Y, Zhang G Y, et al. Memetic algorithm with meta-Lamarckian learning and simplex search for distributed flexible assembly permutation flowshop scheduling problem[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 96115-96128. |
| 15 | Lu Y T, Zhou Y Q, Wu X L. A hybrid lightning search algorithm-simplex method for global optimization[J]. Discrete Dynamics in Nature Society, 2017(2017): 1-23. |
| 16 | Kong X S, Zheng D B. A knowledge-informed simplex search method based on historical quasi-gradient estimations and its application on quality control of medium voltage insulators[J]. Processes, 2021, 9(5): 770-779. |
| 17 | Chen H, Li W, Yang X. A whale optimization algorithm with chaos mechanism based on quasi-opposition for global optimization problems[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 158(113): 6-12. |
| 18 | Musanna F, Dangwal D, Kumar S. Novel image encryption algorithm using fractional chaos and cellular neural network[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence Humanized Computing, 2021(6): 1-22. |
| 19 | 孙耀, 胡云峰, 周杰敏, 等. 基于分层控制器的SCR系统滚动时域优化控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(1): 61-71. |
| Sun Yao, Hu Yun-feng, Zhou Jie-min, et al. Moving horizon optimization control of SCR system based on hierarchical controller[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(1): 61-71. | |
| 20 | 赵靖华, 胡云峰, 高炳到, 等. 基于尿素选择催化还原系统的氨覆盖率非线性降维观测器设计[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 49(2): 583-590. |
| Zhao Jing-hua, Hu Yun-feng, Gao Bing-zhao, et al. Design of nonlinear reduced-order observer for ammonia coverage based on urea-SCR systems[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 49(2): 583-590. |
| [1] | 王守瑞,靳伍银,芮执元,张霞. 基于快速非奇异终端滑模的三维天车负载摆动控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3508-3517. |
| [2] | 孙耀,胡云峰,周杰敏,程欢,曲婷,赵靖华,陈虹. 基于分层控制器的SCR系统滚动时域优化控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 61-71. |
| [3] | 高金武,贾志桓,王向阳,邢浩. 基于PSO-LSTM的质子交换膜燃料电池退化趋势预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2192-2202. |
| [4] | 高金武,王义琳,刘华洋,王艺达. 基于滑模观测器的质子交换膜燃料电池阴极进气系统解耦控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2156-2167. |
| [5] | 李昂,杨泓渊,雷小萌,宋凯文,千承辉. 基于等效连杆模型的六足机器人行进姿态闭环控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1696-1708. |
| [6] | 朱航,于瀚博,梁佳辉,李宏泽. 基于电场模型的无人机搜寻改进算法及仿真分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 3029-3038. |
| [7] | 鲜斌,张诗婧,韩晓薇,蔡佳明,王岭. 基于强化学习的无人机吊挂负载系统轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2259-2267. |
| [8] | 许芳,张君明,胡云峰,曲婷,曲逸,刘奇芳. 智能车辆路径跟踪横纵向耦合实时预测控制器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2287-2294. |
| [9] | 韩光信,赵聚乐,胡云峰. 控制输入受限的板球系统滚动线性二次型调节器控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1982-1989. |
| [10] | 于树友,常欢,孟凌宇,郭洋,曲婷. 基于扰动观测器的轮式移动机器人滚动时域路径跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1097-1105. |
| [11] | 吴爱国,韩俊庆,董娜. 基于极局部模型的机械臂自适应滑模控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1905-1912. |
| [12] | 王伟,赵健廷,胡宽荣,郭永仓. 基于快速非奇异终端滑模的机械臂轨迹跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 464-471. |
| [13] | 刘富,安毅,董博,李元春. 基于ADP的可重构机械臂能耗保代价分散最优控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 342-350. |
| [14] | 曲兴田,王学旭,孙慧超,张昆,闫龙威,王宏一. 熔融沉积成型技术3D打印机加热系统的模糊自适应PID控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 77-83. |
| [15] | 马常友, 高海波, 丁亮, 于海涛, 邢宏军, 邓宗全. 机器人末端执行器自更换机构设计及对接策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2027-2037. |
|
||