吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 874-882.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220611
基于分层卷积自编码器的钝体湍流流场降阶分析
夏超1,2( ),王梦佳1,2,朱剑月3(
),王梦佳1,2,朱剑月3( ),杨志刚1,2,4
),杨志刚1,2,4
- 1.同济大学 汽车学院,上海 201804
2.同济大学 上海地面交通工具风洞中心,上海 201804
3.同济大学?铁道与城市轨道交通研究院,上海 201804
4.北京民用飞机技术研究中心,北京 102211
Reduced-order modelling of a bluff body turbulent wake flow field using hierarchical convolutional neural network autoencoder
Chao XIA1,2( ),Meng-jia WANG1,2,Jian-yue Zhu3(
),Meng-jia WANG1,2,Jian-yue Zhu3( ),Zhi-gang YANG1,2,4
),Zhi-gang YANG1,2,4
- 1.School of Automotive Studies,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.Shanghai Automotive Wind Tunnel Center,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
3.Institute of Rail Transit,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
4.Beijing Aeronautical Science & Technology Research Institute,Beijing 102211,China
摘要:
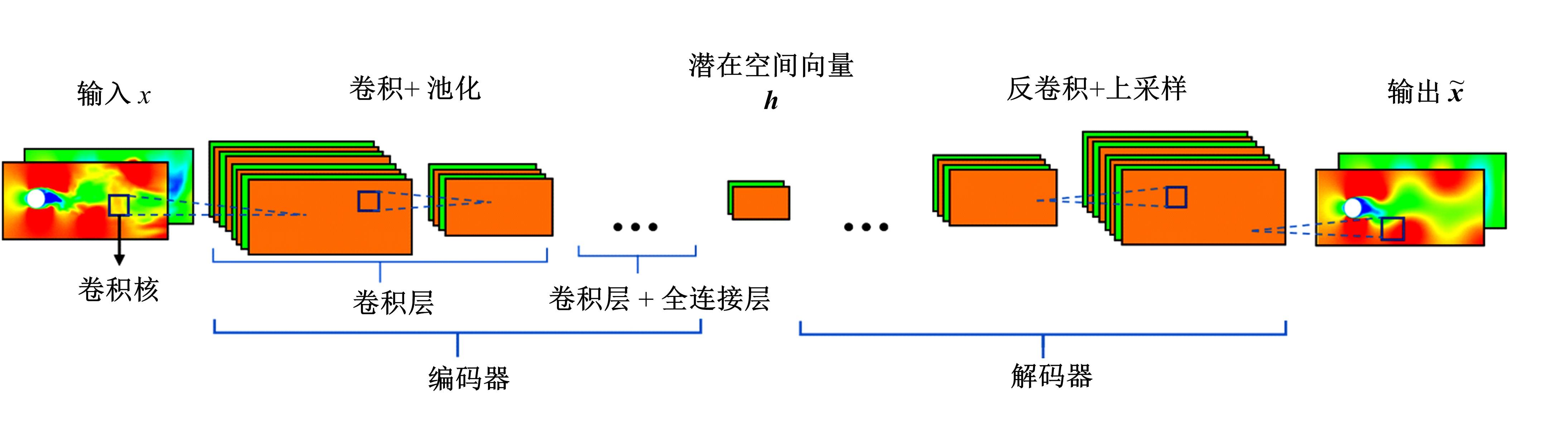
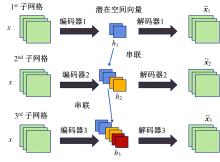
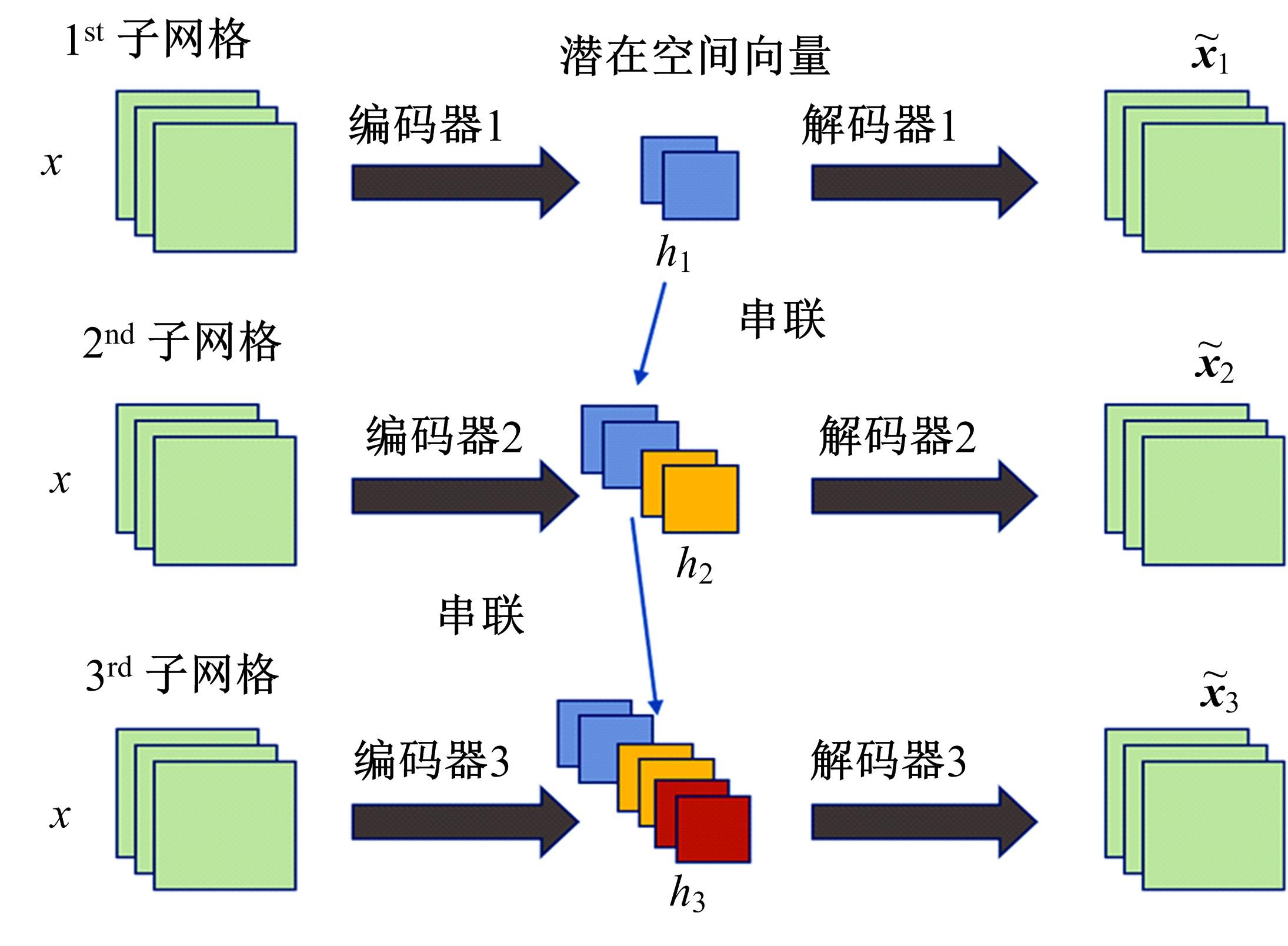
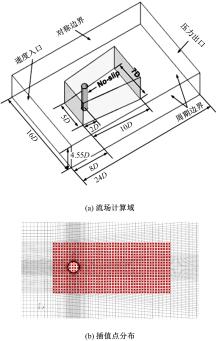
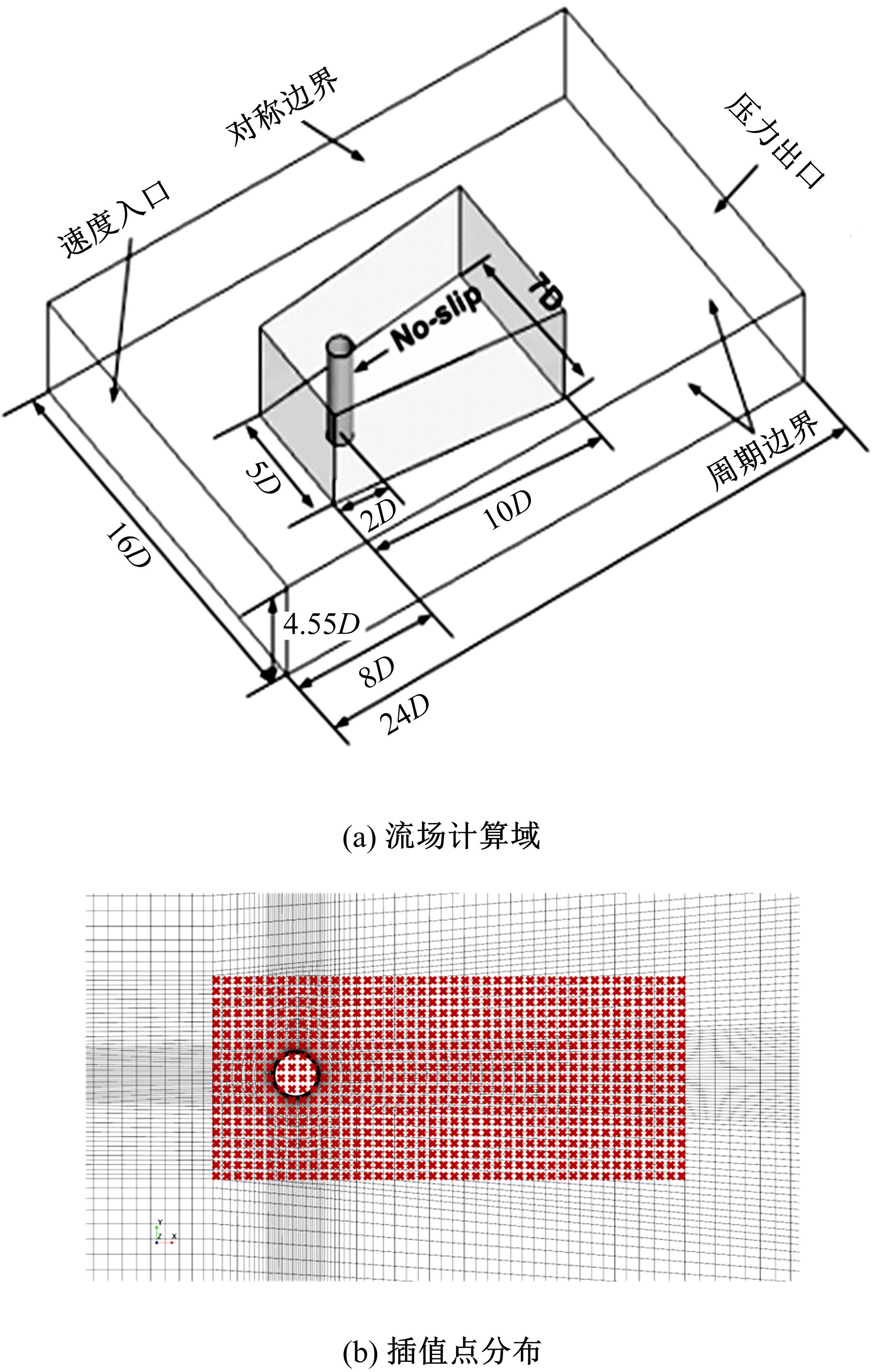
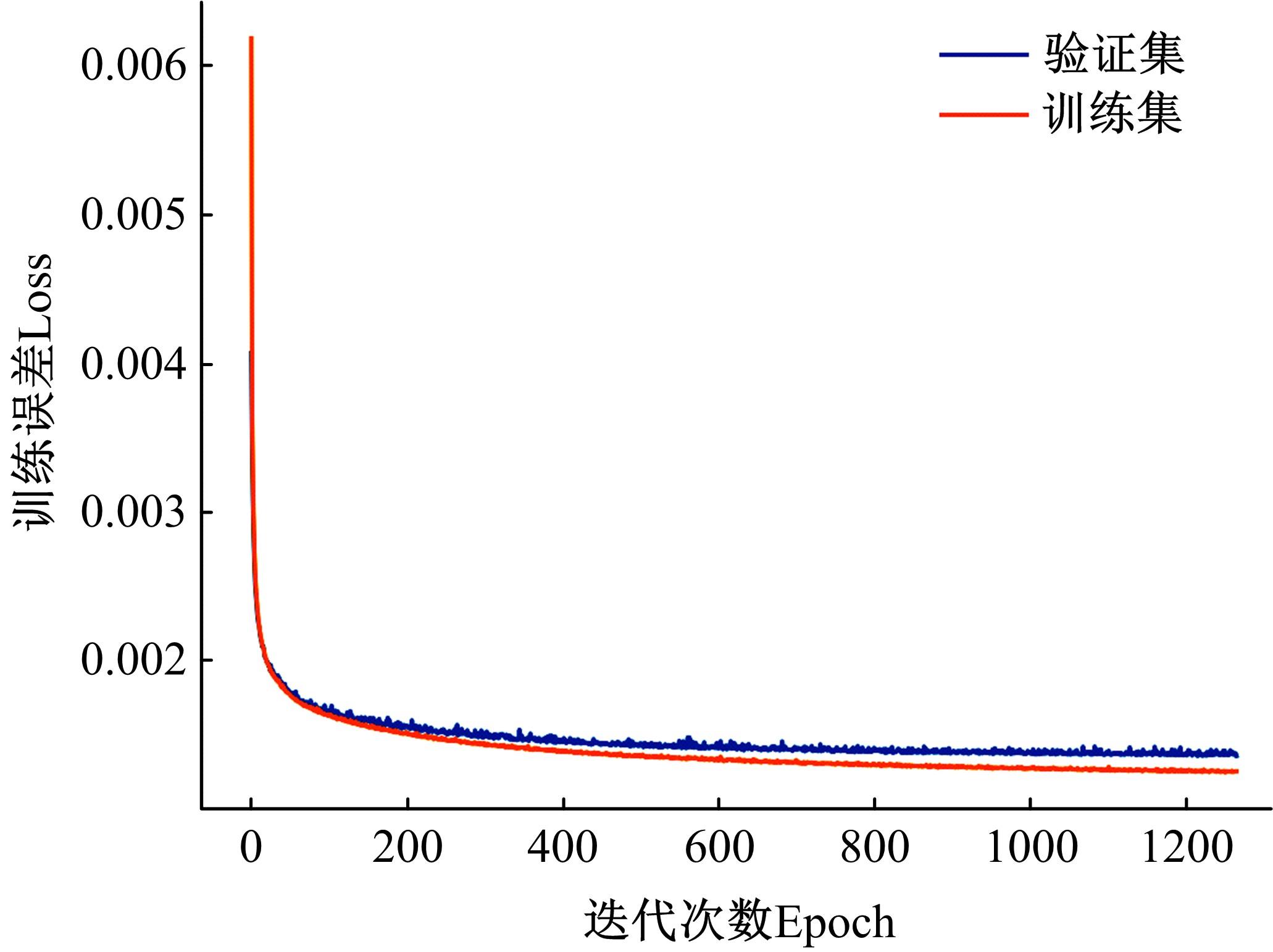
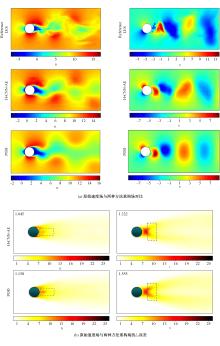
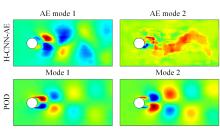
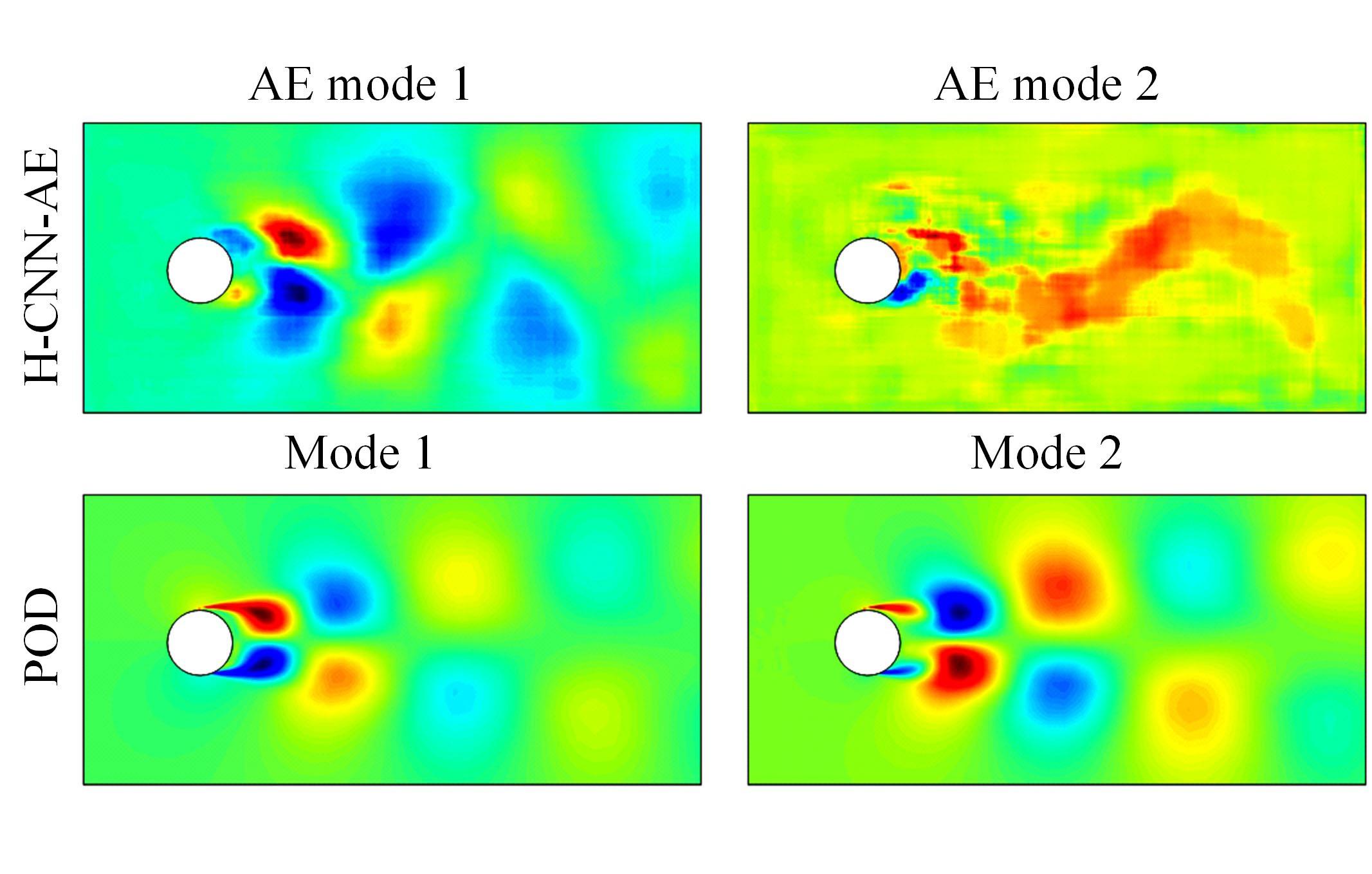
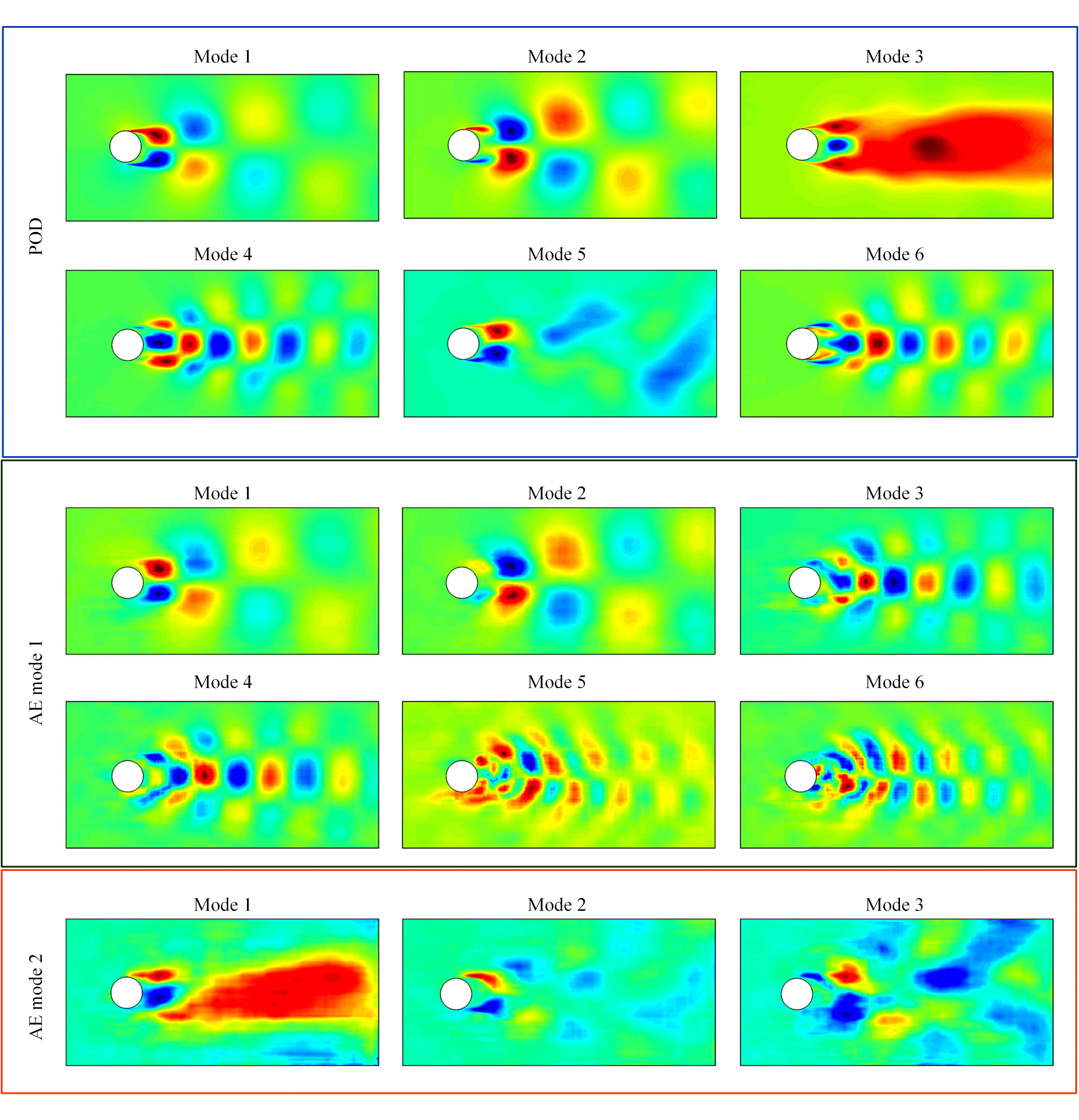
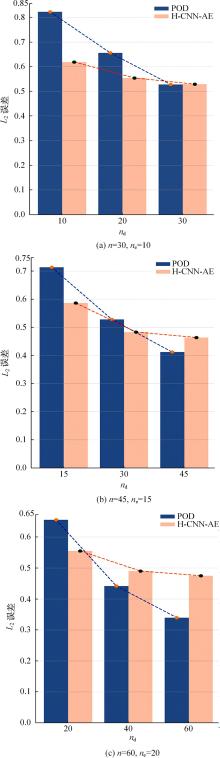
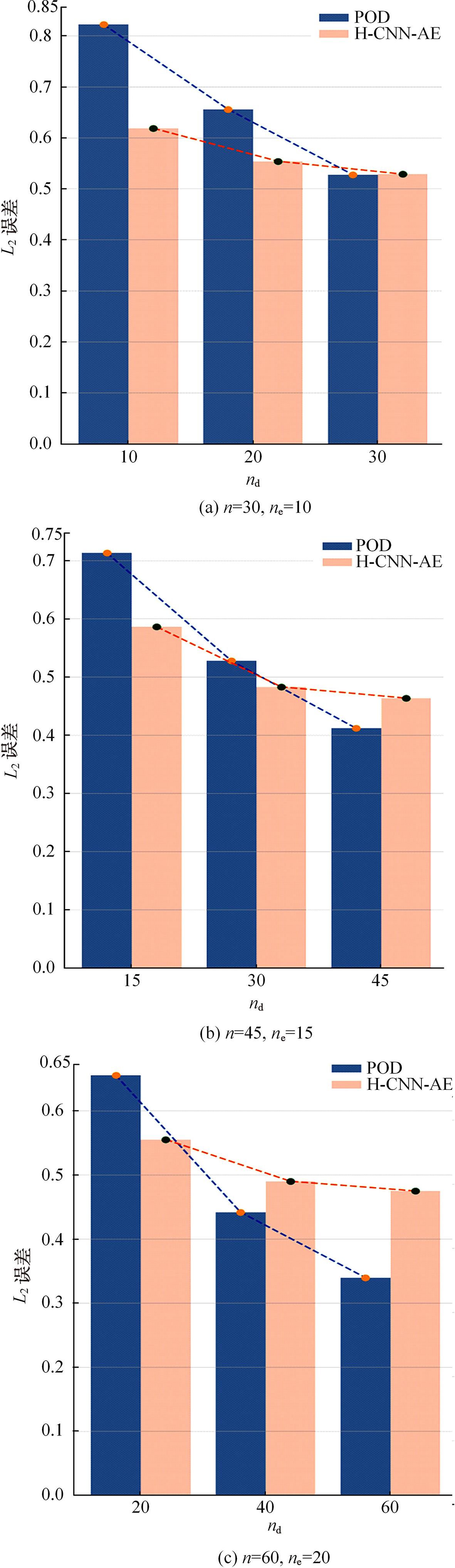
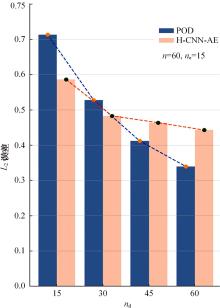
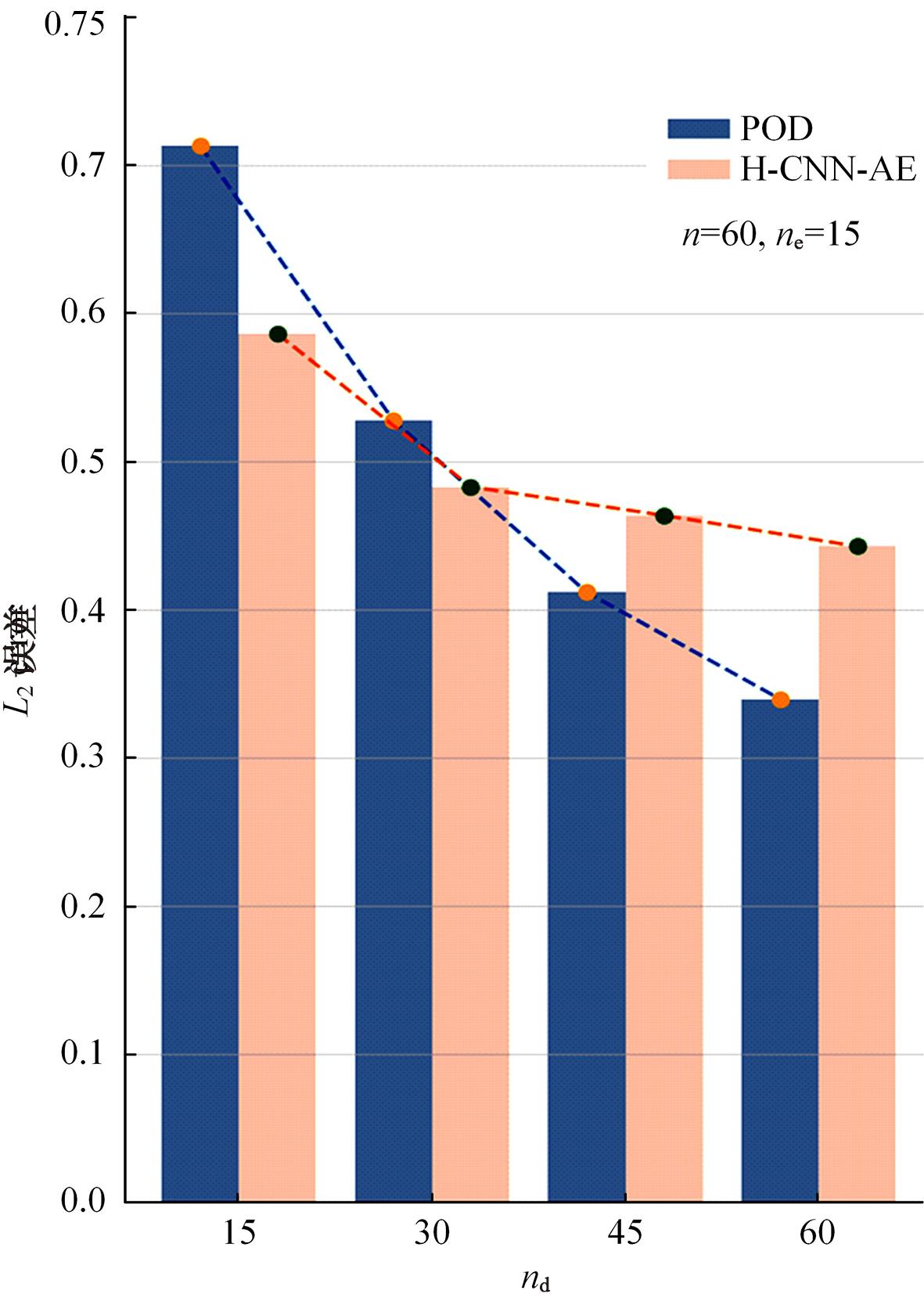
本文采用了一种非线性的分层卷积自编码器,类比于本征正交分解的方法,可以对提取到的低维特征进行能量排序,同时又能在一定范围内达到更高的降阶性能。文中以雷诺数为20 000的三维圆柱钝体湍流尾迹流动为例,分析分层卷积自编码器对该流场的降阶能力,并与本征正交分解的结果作对比。同时,在此基础上延伸出组合模态的概念,并增加每一组低维潜在向量数,观察重构流场与原始流场的均方误差变化。结果表明,在分层层数及每层潜在空间向量数较少时,非线性的分层卷积自编码器相对于本征正交分解的方法对流场有更强的还原能力,但是其优势会随着层数和潜在向量数的增加而减弱。
中图分类号:
- U462
| 1 | Muralidhar S D, Podvin B, Mathelin L, et al. Spatio-temporal proper orthogonal decomposition of turbulent channel flow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019(864): 614-639. |
| 2 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012(25): 1097-1105. |
| 3 | Hinton G, Deng L, Yu D, et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: The shared views of four research groups[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2012, 29(6): 82-97. |
| 4 | Karpathy A, Toderici G, Shetty S, et al. Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Columbus,USA,2014: 1725-1732. |
| 5 | Silver D, Schrittwieser J, Simonyan K, et al. Mastering the game of go without human knowledge[J]. Nature, 2017, 550(7676): 354-359. |
| 6 | 叶舒然, 张珍, 王一伟,等. 基于卷积神经网络的深度学习流场特征识别及应用进展[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(4):185-199. |
| Ye Shu-ran, Zhang Zhen, Wang Yi-wei, et al. Progress in deep convolutional neural network based flow field recognition and its applications[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(4):185-199. | |
| 7 | Kutz J N. Deep learning in fluid dynamics[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2017(814):1-4. |
| 8 | Ling J, Kurzawski A, Templeton J. Reynolds averaged turbulence modelling using deep neural networks with embedded invariance[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2016(807):155-166. |
| 9 | Lecun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. |
| 10 | Hinton G E, Salakhutdinov R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504-507. |
| 11 | Kai F, Fukagata K, Taira K. Super-resolution reconstruction of turbulent flows with machine learning[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019( 870):106-120. |
| 12 | 叶舒然, 张珍, 宋旭东,等. 自动编码器在流场降阶中的应用[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2019, 37(3):498-504. |
| Ye Shu-ran, Zhang Zhen, Song Xu-dong, et al. Applications of autoencoder in reduced-order modeling of flow field[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2019, 37(3):498-504. | |
| 13 | Omata N, Shirayama S. A novel method of low-dimensional representation for temporal behavior of flow fields using deep autoencoder[J]. AIP Advances, 2019, 9(1):No.015006. |
| 14 | Murata T, Kai F, Fukagata K. Nonlinear mode decomposition with convolutional neural networks for fluid dynamics[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2020, 882: No.A13. |
| 15 | Kai F, Hasegawa K, Nakamura T, et al. Model order reduction with neural networks: application to laminar and turbulent flows[J].SN Computer Science, 2021, 2(6):No.467. |
| 16 | Kai F, Nakamura T, Fukagata K. Convolutional neural network based hierarchical autoencoder for nonlinear mode decomposition of fluid field data[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2020, 32(9):No.95110. |
| 17 | 杜祥波, 陈少强, 侯靖尧,等. 基于卷积神经网络的钝体尾迹识别研究[J]. 力学学报, 2022,54(1):59-67. |
| Du Xiang-bo, Chen shao-qiang, Hou jing-yao, et al. Wake recognition of a blunt body based on convolutional neural network[J]. Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2022,54(1):59-67. | |
| 18 | Le Q, Ngiam J, Chen Z, al et, Tiled convolutional neural networks [J]. Adv Neural Inf Proc Syst,2010,23:1279-1287. |
| 19 | Saegusa R, Sakano H, Hashimoto S. Nonlinear principal component analysis to preserve the order of principal components[J]. Neurocomputing, 2004,61:57-70. |
| 20 | Chu S J, Xia C, Wang H F, et al. Three-dimensional spectral proper orthogonal decomposition analyses of the turbulent flow around a seal-vibrissa-shaped cylinder[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2021, 33(2):No.25106. |
| 21 | Sirovich L. Turbulence and the dynamics of coherent structures. I. Coherent structures[J]. Quarterly of Applied Mathematics, 1987, 45(3): 561-571. |
| [1] | 杨国俊,齐亚辉,石秀名. 基于数字图像技术的桥梁裂缝检测综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
| [2] | 车翔玖,徐欢,潘明阳,刘全乐. 生物医学命名实体识别的两阶段学习算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2380-2387. |
| [3] | 张振海,季坤,党建武. 基于桥梁裂缝识别模型的桥梁裂缝病害识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1418-1426. |
| [4] | 刘培勇,董洁,谢罗峰,朱杨洋,殷国富. 基于多支路卷积神经网络的磁瓦表面缺陷检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1449-1457. |
| [5] | 朱逢乐,刘益,乔欣,何梦竹,郑增威,孙霖. 基于多尺度级联卷积神经网络的高光谱图像分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3547-3557. |
| [6] | 高海龙,徐一博,侯德藻,王雪松. 基于深度异步残差网络的路网短时交通流预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3458-3464. |
| [7] | 朱冰,李紫薇,李奇. 基于改进SegNet的遥感图像建筑物分割方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 248-254. |
| [8] | 申铉京,张雪峰,王玉,金玉波. 像素级卷积神经网络多聚焦图像融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| [9] | 高明华,杨璨. 基于改进卷积神经网络的交通目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| [10] | 杨怀江,王二帅,隋永新,闫丰,周跃. 简化型残差结构和快速深度残差网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1413-1421. |
| [11] | 王学智,李清亮,李文辉. 融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 675-683. |
| [12] | 李向军,涂洁莹,赵志宾. 基于多尺度融合卷积神经网络的熔解曲线有效性分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 633-639. |
| [13] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [14] | 高文志,王彦军,王欣伟,张攀,李勇,董阳. 基于卷积神经网络的柴油机失火故障实时诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 417-424. |
| [15] | 张龙,徐天鹏,王朝兵,易剑昱,甄灿壮. 基于卷积门控循环网络的齿轮箱故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 368-376. |
|
||