吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (8): 2275-2281.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230249
基于改进粒子群算法的新能源汽车充电站选址方法
- 1.武汉科技大学 信息科学与工程学院,武汉 430081
2.武汉理工大学 智能交通系统研究中心,武汉 430063
New energy vehicle charging station location method based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm
Liang-li ZHANG1( ),Xiao-feng MA2
),Xiao-feng MA2
- 1.School of Information Science and Engineering,Wuhan University of Science and Technology,Wuhan 430081,China
2.Intelligent Transportation Systems Research Center,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430063,China
摘要:
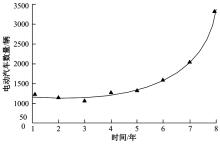
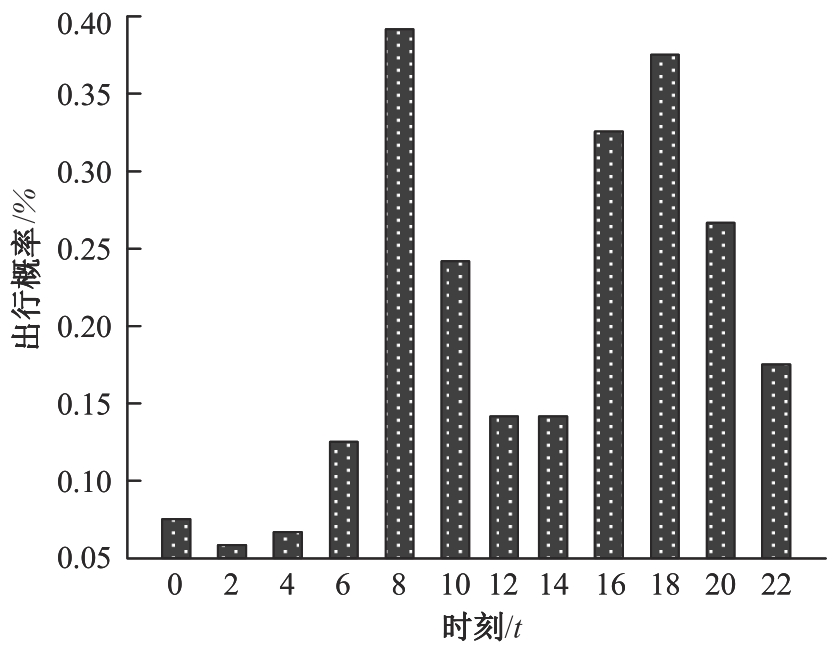
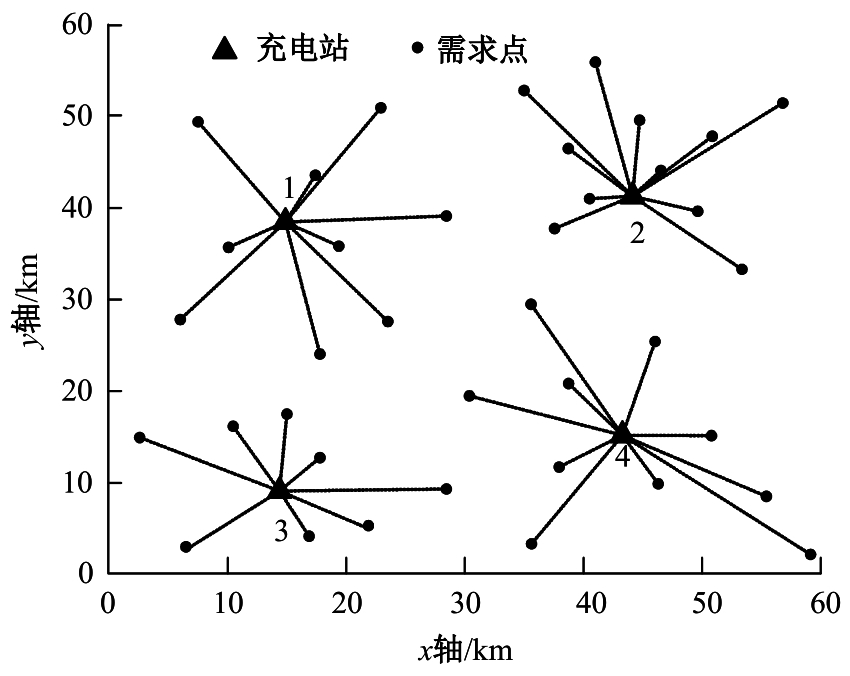
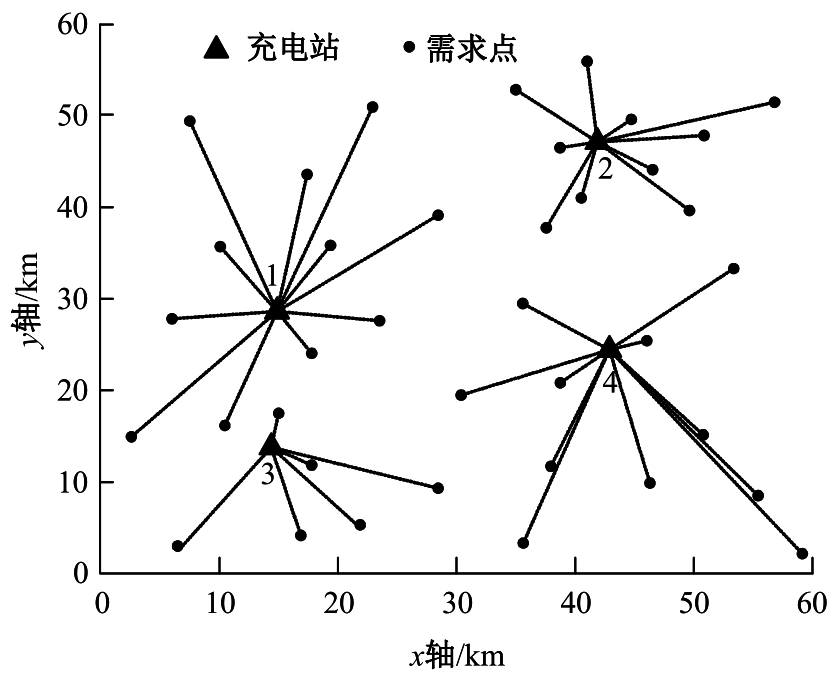
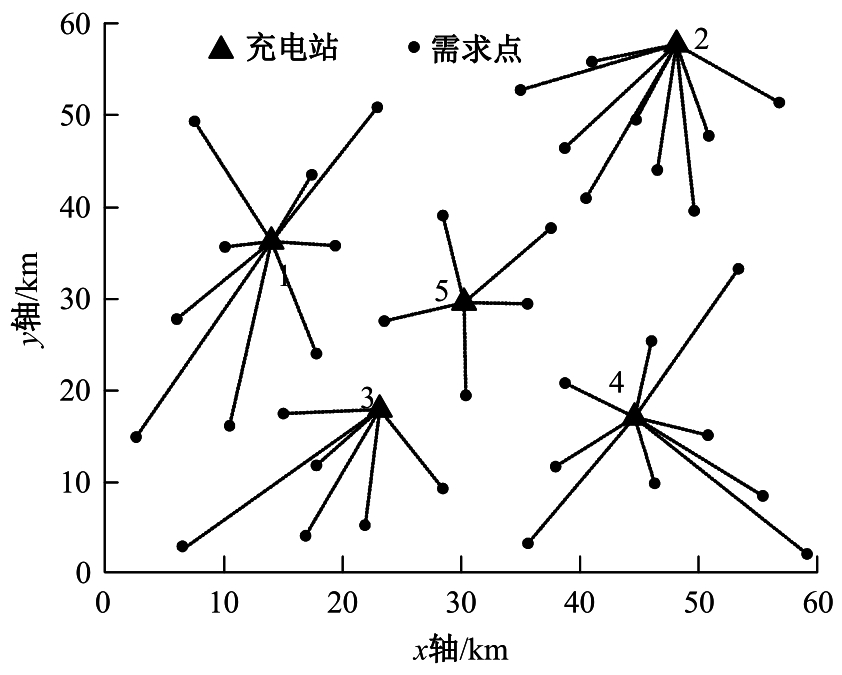
为提高汽车充电站布局的合理性,减少资源浪费,提出基于改进粒子群算法的新能源汽车充电站选址方法。预测电动汽车未来分布情况,将用户出行特征、交通密度、服务半径等因素作为选址的参考依据;以需求点到充电站间的距离最短为目标函数,设置相关约束条件,建立选址模型;探究经典粒子群算法的实现过程,获取粒子速度与位置更新公式;针对方法容易陷入局部最优问题,使用遗传算法对其加以改进;利用改进后的算法求解目标函数,设置初始参数和判定条件,增加粒子交叉、变异等操作,提高粒子群质量,当满足迭代次数要求时,输出个体最优位置,即充电站选址的最优方案。实验结果表明:本文方法所选的位置符合目标函数要求,令充电需求均衡,避免了资源浪费。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | 吴雨, 王育飞, 张宇, 等.基于改进免疫克隆选择算法的电动汽车充电站选址定容方法[J]. 电力系统自动化,2021, 45(7): 95-103. |
| Wu Yu, Wang Yu-fei, Zhang Yu, et al. Siting and sizing method of electric vehicle charging station based on improved immune clonal selection algorithm[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021,45(7): 95-103. | |
| 2 | 张艺涵, 徐菁, 李秋燕, 等. 基于密度峰值聚类的电动汽车充电站选址定容方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(5): 132-139. |
| Zhang Yi-han, Xu Jing, Li Qiu-yan, et al. An electric vehicle charging station siting and sizing method based on a density peaks clustering algorithm[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49 (5): 132-139. | |
| 3 | 冯春, 陈木泉, 蒋雪. 随机充电需求下城市电动汽车充电站选址优化[J]. 计算机仿真, 2022, 39(11): 193-198, 442. |
| Feng Chun, Chen Mu-quan, Jiang Xue. Location optimization of urban electric vehicle charging station under random charging demand[J]. Computer Simulation, 2022,39 (11): 193-198, 442. | |
| 4 | 田枫, 陈淮莉. 考虑用户选择偏好的电动汽车充电站规划研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(15): 294-301. |
| Tian Feng, Chen Huai-li. Research on planning of electric vehicle charging station considering user choice preference [J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2022,58 (15): 294-301. | |
| 5 | 孙秉珍, 杨佳楠, 白军成, 等. 充电中断情景下电动汽车充电站两阶段多目标区间选址优化决策[J]. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(4): 1005-1014. |
| Sun Bing-zhen, Yang Jia-nan, Bai Jun-cheng, et al. A two-stage multi-objective interval location optimization decision of electric vehicle charging station under charging interruption scenario[J]. Control and Decision, 2022,37 (4): 1005-1014. | |
| 6 | 肖白, 高峰. 含不同容量充电桩的电动汽车充电站选址定容优化方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2022, 42(10): 157-166. |
| Xiao Bai, Gao Feng. Optimization method of electric vehicle charging stations'site selection and capacity determination considering charging piles with different capacities[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2022,42(10): 157-166. | |
| 7 | 严干贵, 刘华南, 韩凝晖, 等. 计及电动汽车时空分布状态的充电站选址定容优化方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41(18): 6271-6284. |
| Yan Gan-gui, Liu Hua-nan, Han Ning-hui, et al. An optimization method for location and capacity determination of charging stations considering spatial and temporal distribution of electric vehicles[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021,41(18): 6271-6284. | |
| 8 | 武渊, 叶宁.城市路网中电动汽车充电站双层多目标选址定容模型[J]. 山西大学学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 44(4): 695-704. |
| Wu Yuan, Ye Ning. Double-layer multi-objective location and capacity model for electric vehicle charging stations in urban road networks [J]. Journal of Shanxi University(Natural Science Edition), 2021,44 (4): 695-704. | |
| 9 | 魏路,高磊,李晋宏,等. 基于密度峰值聚类的交通控制子区划分方法 [J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2023,53(1):124-131. |
| Wei Lu, Gao Lei, Li Jin-hong, et al. Traffic sub⁃area division method based on density peak clustering [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2023,53(1): 124-131. | |
| 10 | Li C, Zhang L, Ou Z, et al. Robust model of electric vehicle charging station location considering renewable energy and storage equipment[J]. Energy, 2022, (Jan.1 Pt.A): 121713. |
| 11 | Mowry A M, Mallapragada D S. Grid impacts of highway electric vehicle charging and role for mitigation via energy storage[J]. Energy Policy, 2021, 157: 112508. |
| 12 | Akbari-Dibavar A, Tabar V S, Zadeh S G, et al. Two-stage robust energy management of a hybrid charging station integrated with the photovoltaic system[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(24): 12701-12714. |
| 13 | Schmidt M, Zmuda-Trzebiatowski P, Kicinski M, et al. Multiple-criteria-based electric vehicle charging infrastructure design problem[J]. Energies, 2021, 14(11): 61364214. |
| 14 | Anzola J, Aizpuru I, Arruti A. Partial power processing based converter for electric vehicle fast charging stations[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(3): 13320260. |
| 15 | Welzel F, Klinck C F, Pohlmann Y, et al. Grid and user-optimized planning of charging processes of an electric vehicle fleet using a quantitative optimization model[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 290(1):116717. |
| 16 | Xiao Y, Zhang Y, Kaku I, et al. Electric vehicle routing problem: a systematic review and a new comprehensive model with nonlinear energy recharging and consumption[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 151(9): 111567. |
| 17 | 马云清, 马国顺. 演化博弈视角下PPP模式在新能源汽车换电模式中的应用分析[J]. 应用数学进展, 2021, 10(6): 1887-1903. |
| Ma Yun-qing, Ma Guo-shun. Application analysis of PPP mode in new energy vehicle battery exchange mode from the perspective of evolutionary game[J]. Advances in Applied Mathematics, 2021, 10(6):1887-1903. | |
| 18 | 李翠玉, 胡雅梦, 康亚伟, 等. 应用自适应遗传算法的电动汽车充放电协同调度[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(11): 2508-2513. |
| Li Cui-yu, Hu Ya-meng, Kang Ya-wei, et al. Coordination scheduling of electric vehicle charge and discharge using adaptive genetic algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2508-2513. | |
| 19 | Chen Q, Huang K, Ferguson M R. Capacity expansion strategies for electric vehicle charging networks: model, algorithms, and case study[J]. Naval Research Logistics (NRL), 2022, 69(3): 442-460. |
| 20 | Fescioglu-Unver N, Akta M Y, Kasnakolu C. Feedback controlled resource management model for express service in electric vehicle charging stations[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 311(1): 127629. |
| [1] | 朱瑾,黄琦. 路网资源分配下自动化码头水平运输调度与路径规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2245-2255. |
| [2] | 陈涛,周志刚,雷楠南. 粒子群算法下汽车机械式自动变速系统参数多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1214-1220. |
| [3] | 朱瑾,刘洋. 进口集装箱堆场箱位分配与场桥调度协同优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1347-1354. |
| [4] | 巩亚东,丁明祥,李响,田近民. TC4钛合金材料铣削加工分析及参数优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 917-925. |
| [5] | 张延安,杜岳峰,孟青峰,栗晓宇,刘磊,朱忠祥. 基于改进遗传算法的湿式离合器压力自适应控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 852-864. |
| [6] | 郑长江,胡欢,杜牧青. 考虑枢纽失效的多式联运快递网络结构设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2304-2311. |
| [7] | 李建华,王泽鼎. 考虑路径耗时的城市汽车分布式充电桩选点规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2298-2303. |
| [8] | 田国红,代鹏杰. 基于单亲遗传算法的无人驾驶汽车主动避撞方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2404-2409. |
| [9] | 惠迎新,陈嘉伟. 基于改进遗传算法的挤扩支盘群桩优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2089-2098. |
| [10] | 谭国金,孔庆雯,何昕,张攀,杨润超,朝阳军,杨忠. 基于动力特性和改进粒子群优化算法的桥梁冲刷深度识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1592-1600. |
| [11] | 李艳波,柳柏松,姚博彬,陈俊硕,渠开发,武奇生,曹洁宁. 考虑路网随机特性的高速公路换电站选址[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1364-1371. |
| [12] | 杨红波,史文库,陈志勇,郭年程,赵燕燕. 基于NSGA⁃II的斜齿轮宏观参数多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1007-1018. |
| [13] | 马敏,胡大伟,舒兰,马壮林. 城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| [14] | 张铮,朱齐丹,吕晓龙,樊星. 冗余机械臂运动学逆解的求解优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3379-3387. |
| [15] | 应沛然,曾小清,沈拓,袁腾飞,宋海峰,王奕曾. 基于冗余工序编码的高速列车节能驾驶智能算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3404-3414. |
|