吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 1465-1473.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230274
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于谱变换和高阶稀疏Hodrick⁃Prescott分解的茶叶品种鲁棒判别方法
- 1.浙江工贸职业技术学院 人工智能学院,浙江 温州 325002
2.温州大学 计算机与人工智能学院,浙江 温州 325002
3.安徽农业大学 茶树生物学与资源利用国家重点实验室,安徽 合肥 230036
4.南京林业大学 信息科学技术学院,南京 210037
Robust discrimination method for tea varieties based on spectral transformation and high⁃order Sparsity⁃aided Hodrick⁃Prescott decomposition
Xiu-zhi ZHAO1,2( ),Jing-ming NING3,De-hong XIE4(
),Jing-ming NING3,De-hong XIE4( )
)
- 1.College of Artificial Intelligence,Zhejiang Industry & Trade Vocational College,Wenzhou 325002,China
2.School of Computer and Artificial Intelligence,Wenzhou University,Wenzhou 325002,China
3.State Key Laboratory of Tea Plant Biology and Utilization,Anhui Agricultural University,Hefei 230036,China
4.College of Information Science and Technology,Nanjing Forestry University,Nanjing 210037,China
摘要:
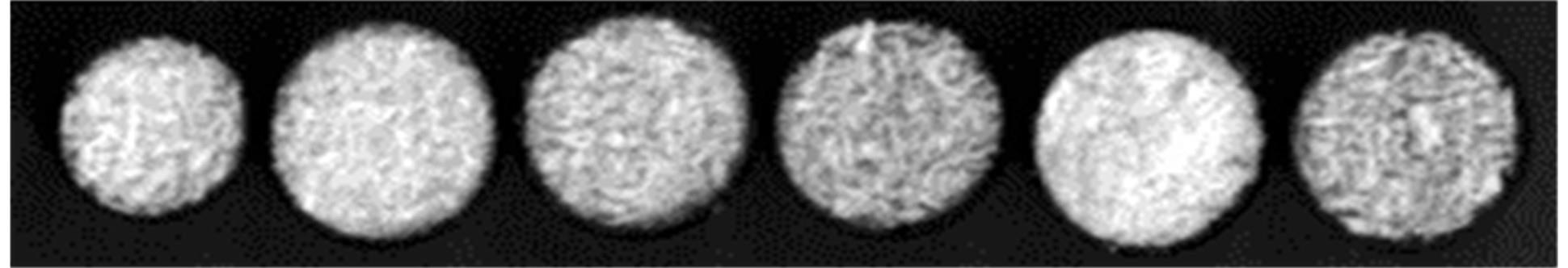
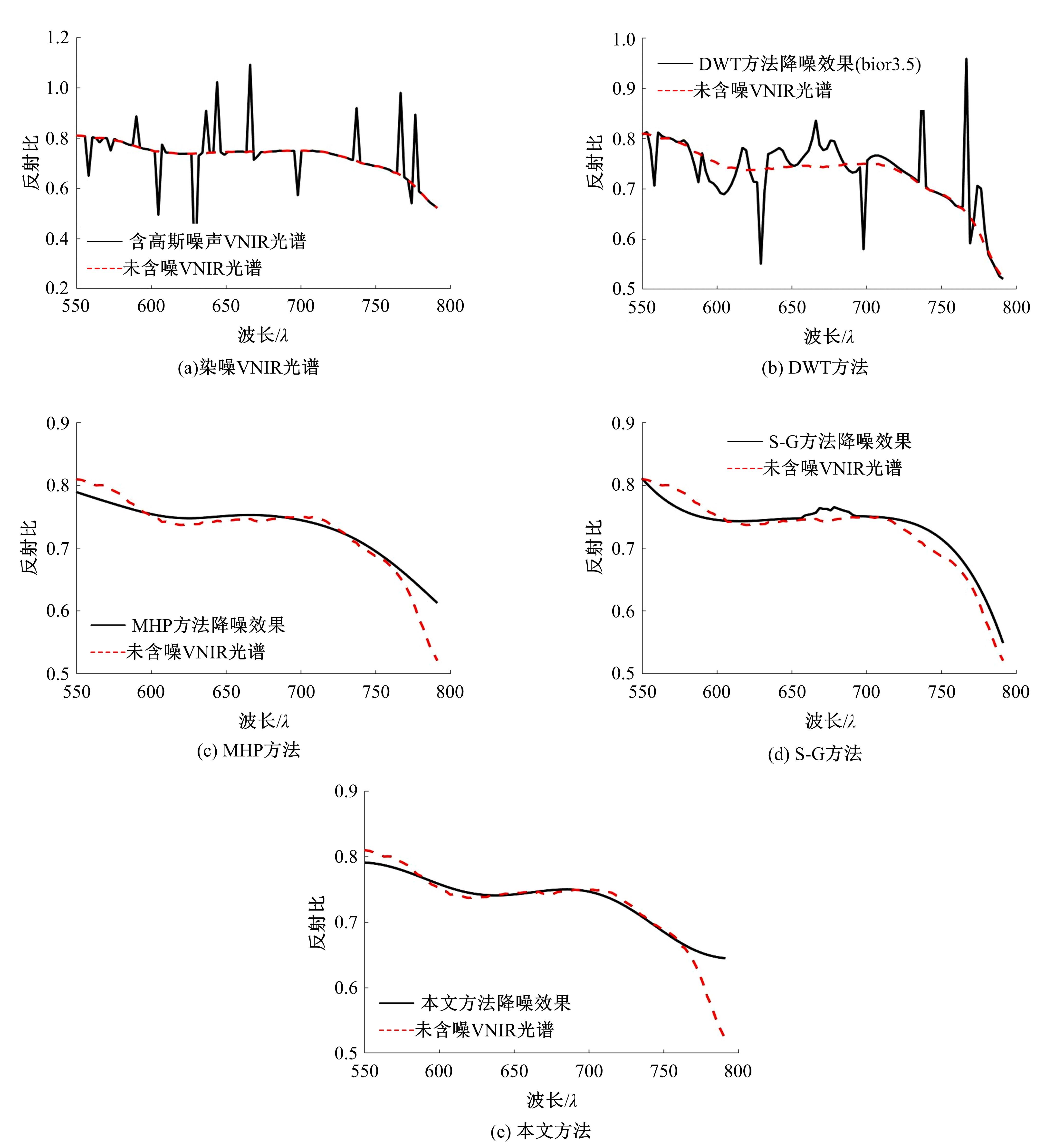
为了提高可见-近红外光谱定性分析的精度,需对光谱进行降噪预处理。针对降噪易产生额外小谱峰、恶化定性分析准确度的问题,提出一种基于谱变换和高阶稀疏Hodrick-Prescott分解的降噪方法。在该方法的优化方程中,假设可见-近红外光谱由低通的基本波形光谱、带通的特征波形光谱及噪声组成,以含噪光谱与基本波形光谱、带通的特征波形光谱之间残差L2范数为残差项,保证估计值逼近真实值;依据特征波形光谱的稀疏性,以其二阶差分的L1范数为正则化项,约束估计特征波形光谱,从而分解出茶叶中重要的特征吸收峰。该方法同时利用滤波器的谱变换技术获得低通和带通零相位滤波器矩阵,协助分解基本波形光谱和特征波形光谱,并利用L-曲线方法获取优化方程中的最佳正则化参数。本实验以6种茶叶的可见-近红外光谱为基础实验数据。在实验中,以信噪比、均方根差和茶叶品种定性分析分类模型的准确性为衡量指标,与小波分解法、改进的Hodrick-Prescott法和Savitzky-Golay法进行了比较。实验结果显示:对含高斯噪声合成光谱数据和含高斯-脉冲混合噪声合成光谱数据,该方法信噪比最高;对于合成和真实两个数据集,分类模型准确率均高于上述3种方法预处理后的结果,且远高于含噪数据下的分类结果。因此,该方法在可见-近红外光谱降噪方面具有优势,能应用于基于可见-近红外光谱的茶叶品种定性检测的预处理。
中图分类号:
- O657.3
| 1 | Ren G, Liu Y, Ning J, et al. Assessing black tea quality based on visible-near infrared spectra and kernel-based methods[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 2021, 98: 103810. |
| 2 | Liu Y, Peng Q W, Yu J C, et al. Identification of tea based on CARS-SWR variable optimization of visible/near-infrared spectrum[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2020, 100(1): 371-375. |
| 3 | Liu T, Liu H, Li Y F, et al. Flexible FTIR spectral imaging enhancement for industrial robot infrared vision sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(1): 544-554. |
| 4 | Xie B, Xiong Z, Wang Z, et al. Gamma spectrum denoising method based on improved wavelet threshold[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2020, 52(8): 1771-1776. |
| 5 | Xi Y, Li Y, Duan Z, et al. A novel pre-processing algorithm based on the wavelet transform for raman spectrum[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2018, 72(12): 1752-1763. |
| 6 | 沈毅, 张敏, 张淼. 基于小波阈值降噪和经验模态分解的高光谱图像分类算法[J]. 宇航学报, 2012, 33(4): 471-477. |
| Shen Yi, Zhang Min, Zhang Miao. Hyperspectral image classification algorithm based on wavelet threshold noise reduction and empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2012, 33(4): 471-477. | |
| 7 | 周风波, 李长庚, 朱红求. 基于提升小波变换的阈值改进去噪算法在紫外可见光谱中的研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2018, 38(2): 506-510. |
| Zhou Feng-bo, Li Chang-geng, Zhu Hong-qiu. Research on improved denoising algorithm in UV-VIS spectrum based on threshold boosted wavelet transform[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(2): 506-510. | |
| 8 | Zheng H M, Dang C L, Gu S M, et al. A quantified self-adaptive filtering method: effective IMFs selection based on CEEMD[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2018, 29(8): 085701. |
| 9 | Huang H, Hu S, Sun Y A. A discrete curvature estimation based low-distortion adaptive savitzky-golay filter for ECG denoising[J]. Sensors(Basel), 2019, 19(7): 1424-1617. |
| 10 | 谢德红, 李俊锋, 刘菂, 等. 基于改进Hodrick-Prescott分解模型的近红外自适应降噪方法[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2020, 40(5): 1650-1655. |
| Xie De-hong, Li Jun-feng, Liu Jing, et al. Near-infrared adaptive noise reduction method based on improved Hodrick-Prescott decomposition model[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(5): 1650-1655. | |
| 11 | Yao Z, Su H, Yao J, et al. Yield-adjusted operation for convolution filter denoising[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 93(49): 16489-16503. |
| 12 | Czarnecki M A. Resolution enhancement in second-derivative spectra[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2015, 69(1): 67-74. |
| 13 | Wu Z, Huang N E. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a noise-assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1-41. |
| 14 | Torres M E, Colominas M A, Schlotthauer G, et al. A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing,Prague, Czech, 2011: 4144-4147. |
| 15 | Ouahilal M, Mohajir M E, Chahhou M, et al. A novel hybrid model based on Hodrick-Prescott filter and support vector regression algorithm for optimizing stock market price prediction[J]. Journal of Big Data, 2017, 4(1): 40357. |
| 16 | Gustafsson F. Determining the initial states in forward-backward filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1996, 44(4): 988-992. |
| 17 | Soares S F C, Gomes A A, Araujo M C U, et al. The successive projections algorithm[J]. Trac Trends in Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 42: 84-98. |
| 18 | Bogawar P S, Bhoyar K K. An improved multiclass support vector machine classifier using reduced hyper-plane with skewed binary tree[J]. Appled Intellence, 2018, 48(11): 4382-4391. |
| 19 | 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016. |
| 20 | Zhang L Z, Dai H M, Zhang J L, et al. A study on origin traceability of white tea(white peony) based on near-infrared spectroscopy and machine learning algorithms[J]. Foods, 2023, 12(3): 499-523. |
| 21 | He Y C, Jiang H, Chen Q S. High-precision identification of the actual storage periods of edible oil by FT-NIR spectroscopy combined with chemometric methods[J]. Analytical Methods, 2020, 12(29): 3722-3728. |
| 22 | Mishra P, Karami A, Nordon A, et al. Automatic de-noising of close-range hyperspectral images with a wavelength-specific shearlet-based image noise reduction method[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2019, 281: 1034-1044. |
| [1] | 周丰丰,张亦弛. 基于稀疏自编码器的无监督特征工程算法BioSAE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1645-1656. |
| [2] | 王文军,余银峰. 考虑数据稀疏的知识图谱缺失连接自动补全算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1428-1433. |
| [3] | 杜先君,贾亮亮. 基于优化堆叠降噪自编码器的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2827-2838. |
| [4] | 许鸿奎,姜彤彤,李鑫,姜斌祥,王永雷. 结合降噪自编码与极限学习机的LTE上行干扰分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 195-203. |
| [5] | 刘远红,郭攀攀,张彦生,李鑫. 基于黎曼流形的稀疏图保持投影的特征提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2268-2279. |
| [6] | 刘洲洲,张倩昀,马新华,彭寒. 基于优化离散差分进化算法的压缩感知信号重构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2246-2252. |
| [7] | 杨建,夏琦,周海超,王国林. 修正胎体弦轮廓载重子午线轮胎的降噪机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1198-1203. |
| [8] | 陈广秋,陈昱存,李佳悦,刘广文. 基于DNST和卷积稀疏表示的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 996-1010. |
| [9] | 王洪雁,邱贺磊,郑佳,裴炳南. 光照变化下基于低秩稀疏表示的视觉跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 268-277. |
| [10] | 单泽彪,刘小松,史红伟,王春阳,石要武. 动态压缩感知波达方向跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1938-1944. |
| [11] | 李嘉菲, 孙小玉. 基于谱分解的不确定数据聚类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1604-1611. |
| [12] | 刘仲民, 李战明, 李博皓, 胡文瑾. 基于稀疏矩阵的谱聚类图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1308-1313. |
| [13] | 尹明, 战荫伟, 裴海龙. 基于稀疏补算子学习的图像融合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 2052-2058. |
| [14] | 葛长江, 叶辉, 胡兴军, 于征磊. 鸮翼后缘噪声的预测及控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1981-1986. |
| [15] | 莫愁, 陈吉清, 兰凤崇. 逆子结构传递路径分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1751-1756. |
|
||