吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 1682-1691.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230820
基于改进密集网络和小波分解的自监督单目深度估计
- 1.中国矿业大学 信息与控制工程学院,江苏 徐州 221116
2.中国矿业大学 计算机科学与技术学院,江苏 徐州 221116
Self-supervised monocular depth estimation based on improved densenet and wavelet decomposition
De-qiang CHENG1( ),Wei-chen WANG1,Cheng-gong HAN1,Chen LYU1,Qi-qi KOU2(
),Wei-chen WANG1,Cheng-gong HAN1,Chen LYU1,Qi-qi KOU2( )
)
- 1.School of Information and Control Engineering,China University of Mining and Technology,Xuzhou 221116,China
2.School of Computer Science and Technology,China University of Mining and Technology,Xuzhou,221116 China
摘要:
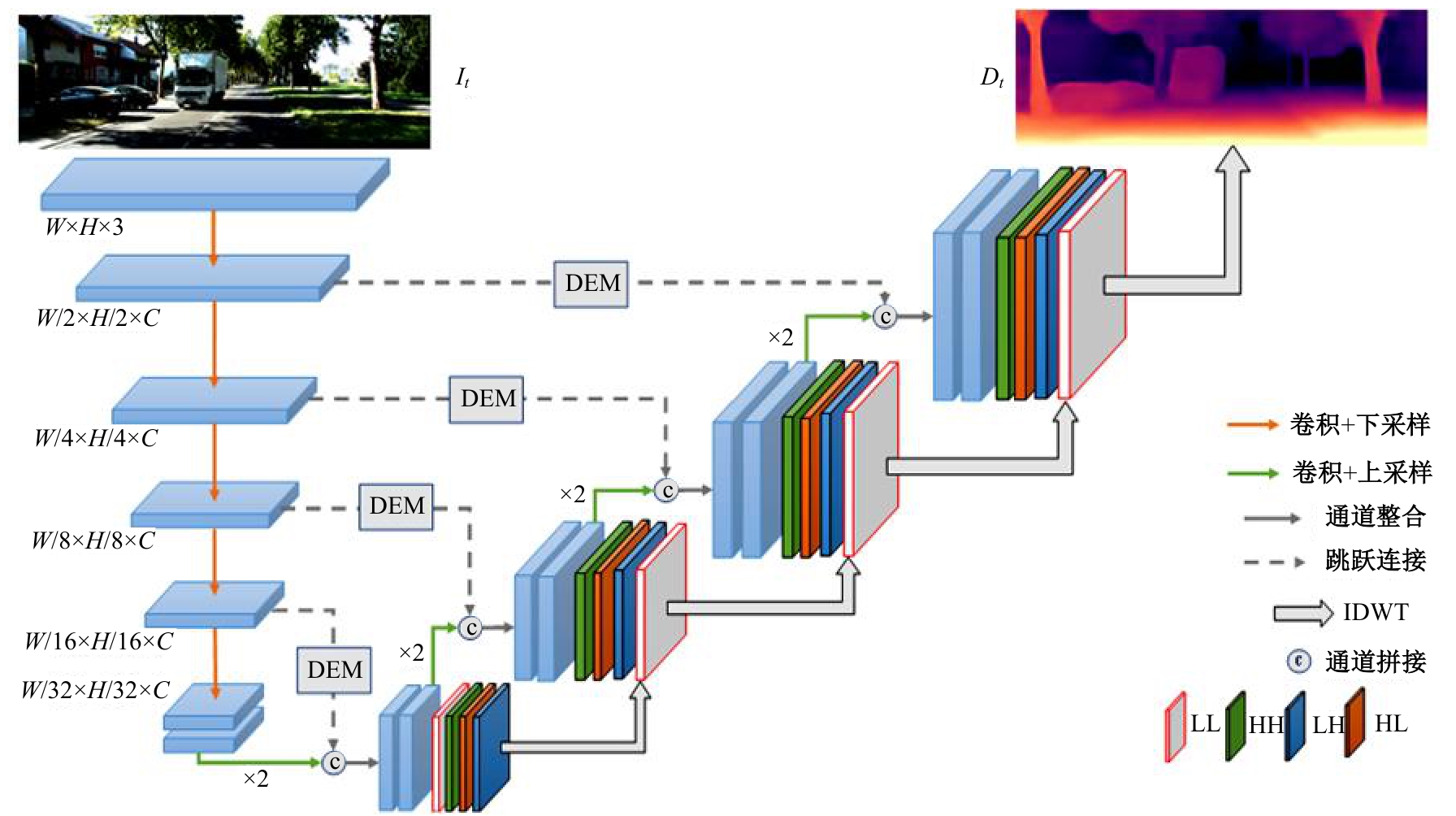
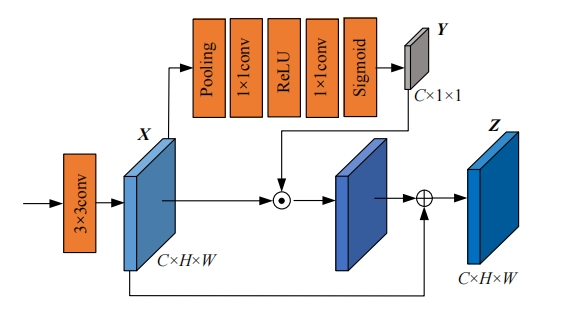
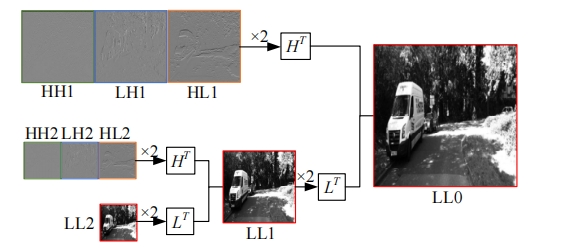
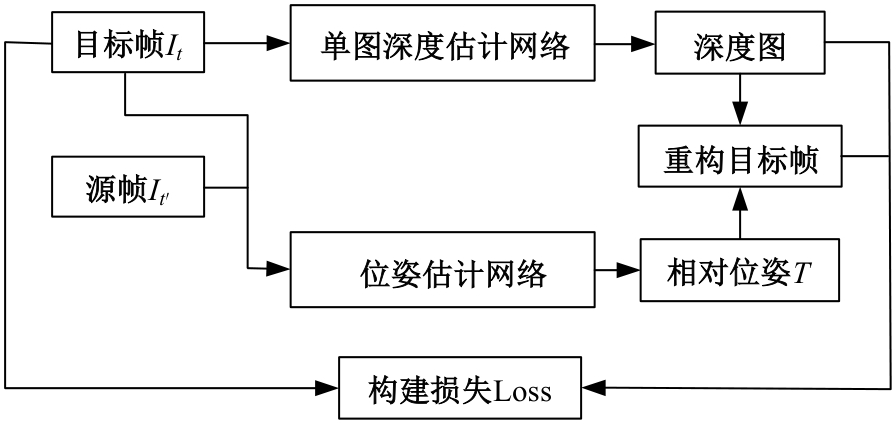
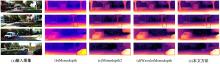
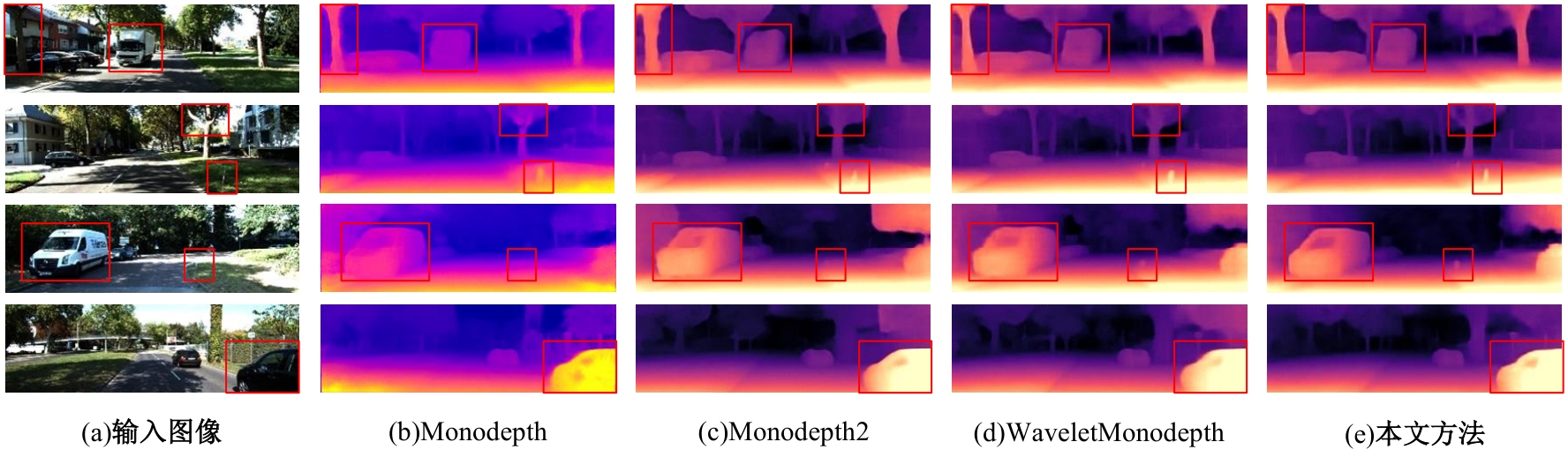
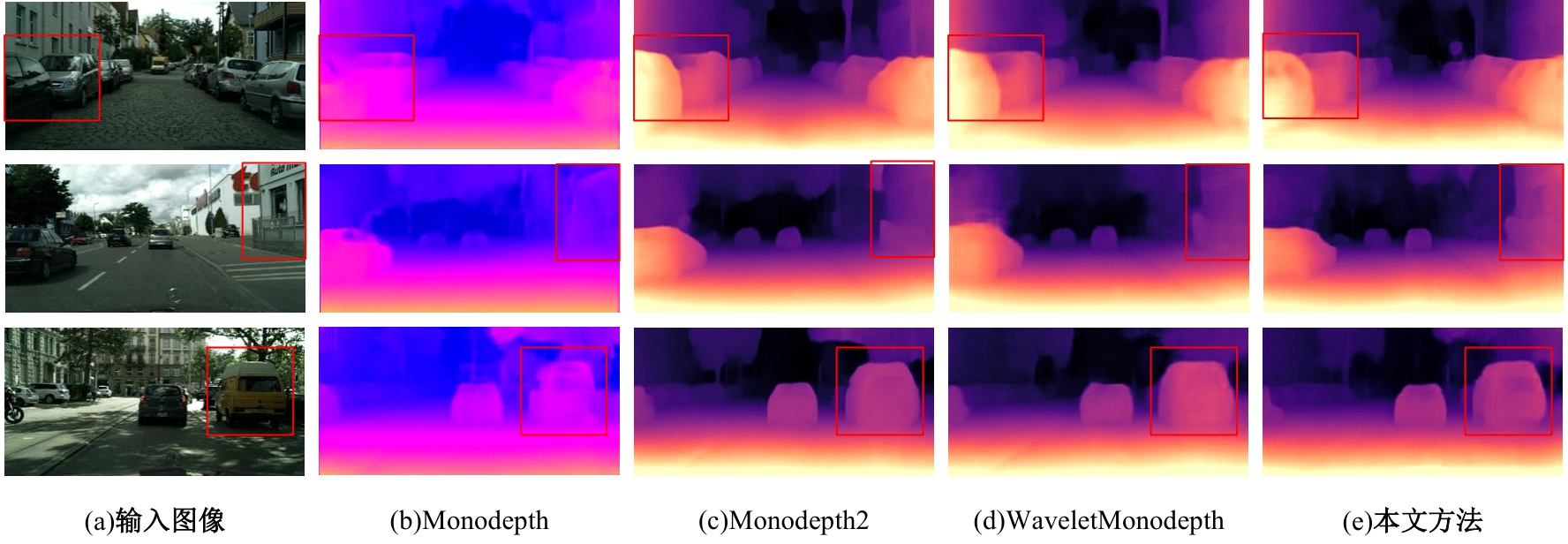
针对传统自监督单目深度估计模型对浅层特征的提取和融合不充分,容易导致小物体漏检、物体边缘模糊等问题,本文提出了一种基于改进密集网络和小波分解的自监督单目深度估计模型。该模型沿用了U-Net结构,其中,编码器采用改进的密集网络,提高了编码器的特征提取和融合能力;跳跃连接中加入细节增强模块,对编码器输出的多尺度特征进一步细化整合;解码器引入小波分解,迫使解码器更加关注高频信息,实现对图像边缘的精细化处理。实验结果表明,本文提出的深度估计模型对小物体特征的捕捉能力更强,生成的深度图边缘更清晰准确。
中图分类号:
- TP391.41
| [1] | 王新竹, 李骏, 李红建, 等. 基于三维激光雷达和深度图像的自动驾驶汽车障碍物检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报 (工学版), 2016, 46(2): 360-365. |
| Wang Xin-zhu, Li Jun, Li Hong-jian, et al. Obstacle detection based on 3D laser scanner and range image for intelligent vehicle[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(2): 360-365. | |
| [2] | 张宇翔, 任爽. 定位技术在虚拟现实中的应用综述[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(1): 308-318. |
| Zhang Yu-xiang, Ren Shuang. Overview of the application of location technology in virtual reality[J]. Computer Science, 2021,48 (1): 308-318. | |
| [3] | 史晓刚, 薛正辉, 李会会, 等. 增强现实显示技术综述[J]. 中国光学, 2021, 14(5): 1146-1161. |
| Shi Xiao-gang, Xue Zheng-hui, Li Hui-hui, et al. Overview of augmented reality display technology [J]. China Optics, 2021, 14 (5): 1146-1161. | |
| [4] | Eigen D, Fergus R. Predicting depth, surface normals and semantic labels with a common multi-scale convolutional architecture[C]∥2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 2015: 2650-2658. |
| [5] | Fu H, Gong M, Wang C, et al. Deep ordinal regression network for monocular depth estimation[C]∥ 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 2002-2011. |
| [6] | Garg R, Vijay K B G, Carneiro G, et al. Unsupervised CNN for single view depth estimation: geomery to the rescue[C]∥European Conference Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 740-756. |
| [7] | Zhou T H, Brown M, Snavely N, et al. Unsupervised learning of depth and ego-motion from video[C]∥2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Hawaii, USA, 2017: 1851-1858. |
| [8] | Clément G, Oisin M A, Michael F, et al. Digging into self-supervised monocular depth estimation[C]∥ 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 3828-3838. |
| [9] | Ashutosh S, Sun M, Andrew Y N. Make3D:learning 3D scene structure from a single still image[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2008, 31(5): 824-840. |
| [10] | Eigen D, Puhrsch C, Fergus R. Depth map prediction from a single image using a multi-scale deep network[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 2366-2374. |
| [11] | Zachary T, Jia D. Deepv2D: video to depth with differentiable structure from motion[C]∥International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) 2020, Addis Ababa, Ethiopian, 2020: 181204605. |
| [12] | Benjamin U, Zhou H Z, Jonas U, et al. Demon: depth and motion network for learning monocular stereo[C]∥2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Hawaii, USA, 2017: 5038-5047. |
| [13] | Clément G, Oisin M A, Gabriel J B. Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency[C]∥2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Hawaii, USA, 2017: 270-279. |
| [14] | Bian J W, Li Z C, Wang N, et al. Unsupervised scale-consistent depth and ego-motion learning from monocular video[C]∥33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 1-12. |
| [15] | Han C, Cheng D, Kou Q, et al. Self-supervised monocular depth estimation with multi-scale structure similarity loss[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 31: 3251-3266. |
| [16] | Xiang J, Wang Y, An L,et al. Visual attention-based self-supervised absolute depth estimation using geometric priors in autonomous driving[J/OL].(2022-10-06)[2023-06-13].. |
| [17] | Suri Z K. Pose constraints for consistent self-supervised monocular depth and ego-motion[J/OL].(2023-04-18)[2023-06-13].. |
| [18] | Houssem B, Adrian V, Andrew C. STDepthFormer: predicting spatio-temporal depth from video with a self-supervised transformer model[C]∥Detroit, USA, 2023: No.230301196. |
| [19] | Matteo P, Filippo A, Fabio T, et al. Towards real-time unsupervised monocular depth estimation on CPU[C]∥2018 IEEE/RSJ international Conference Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 2018: 5848-5854. |
| [20] | Diana W, Ma F C, Yang T J, et al. FastDepth: fast monocular depth estimation on embedded systems[C]∥2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, Canada, 2019: 6101-6108. |
| [21] | Michael R, Michael F, Jamie W, et al. Single image depth prediction with wavelet decomposition[C] ∥ Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Online, 2021: 11089-11098. |
| [22] | Olaf R, Philipp F, Thomas B. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]∥International Conference On Medical Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 2015: 234-241. |
| [23] | Huang G, Liu Z, Maaten L V D, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]∥2017 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Hawaii, USA, 2017: 2261-2269. |
| [24] | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| [25] | Chen X T, Chen X J, Zha Z J. Structure-aware residual pyramid network for monocular depth estimation[C]∥28th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Macau, China, 2019: 694-700. |
| [26] | Geiger A, Lenz P, Stiller C, et al. Vision meets robotics: the kitti dataset[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2013, 32(11): 1231-1237. |
| [27] | Pleiss G, Chen D, Huang G, et al. Memory-efficient implementation of densenets[J/OL].(2017-07-21)[2023-06-13].. |
| [28] | Mehta I, Sakurikar P, Narayanan P J. Structured adversarial training for unsupervised monocular depth estimation[C]∥2018 International Conference on 3D Vision, Verona, Italy, 2018: 314-323. |
| [29] | Matteo P, Fabio T, Stefano M. Learning monocular depth estimation with unsupervised trinocular assumptions[C]∥International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Verona, Italy, 2018: 324-333. |
| [30] | Sudeep P, Rares A, Ambrus G, et al. Superdepth: self-supervised, super-resolved monocular depth estimation[C]∥2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, Canada, 2019: 9250-9256. |
| [1] | 章家保,张剑阳,刘赫,李岩. 改进游程编码算法的快速星点提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1467-1473. |
| [2] | 胡刘博,吴建新,刘泉华,张磊. 使用机载分布式阵列对主瓣复合干扰进行分级抑制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 1103-1110. |
| [3] | 王海涛,刘慧卓,张学永,韦健,郭校源,肖俊哲. 基于单目视觉的车辆屏显式封闭驾驶舱前视视野重现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1435-1442. |
| [4] | 苏育挺,景梦瑶,井佩光,刘先燚. 基于光度立体和深度学习的电池缺陷检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(12): 3653-3659. |
| [5] | 窦慧晶,谢东旭,郭威,邢路阳. 基于改进的正交匹配跟踪算法的波达方向估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(12): 3568-3576. |
| [6] | 白琳,刘林军,李轩昂,吴沙,刘汝庆. 基于自监督学习的单目图像深度估计算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1139-1145. |
| [7] | 王春阳,丘文乾,刘雪莲,肖博,施春皓. 基于平面拟合的地面点云精确分割方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 933-940. |
| [8] | 李雪梅,王春阳,刘雪莲,施春浩,李国瑞. 基于超体素双向最近邻距离比的点云配准方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1918-1925. |
| [9] | 赵宏伟,张健荣,朱隽平,李海. 基于对比自监督学习的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1850-1856. |
| [10] | 王震,盖孟,许恒硕. 基于虚拟现实技术的三维场景图像表面重建算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1620-1625. |
| [11] | 李雪梅,王春阳,刘雪莲,谢达. 基于SESTH的线性调频连续波激光雷达信号时延估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 950-958. |
| [12] | 林乐平,卢增通,欧阳宁. 面向非配合场景的人脸重建及识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2941-2946. |
| [13] | 周大可,张超,杨欣. 基于多尺度特征融合及双重注意力机制的自监督三维人脸重建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2428-2437. |
| [14] | 窦慧晶,丁钢,高佳,梁霄. 基于压缩感知理论的宽带信号波达方向估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2237-2245. |
| [15] | 金心宇,谢慕寒,孙斌. 基于半张量积压缩感知的粮情信息采集[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 379-385. |
|