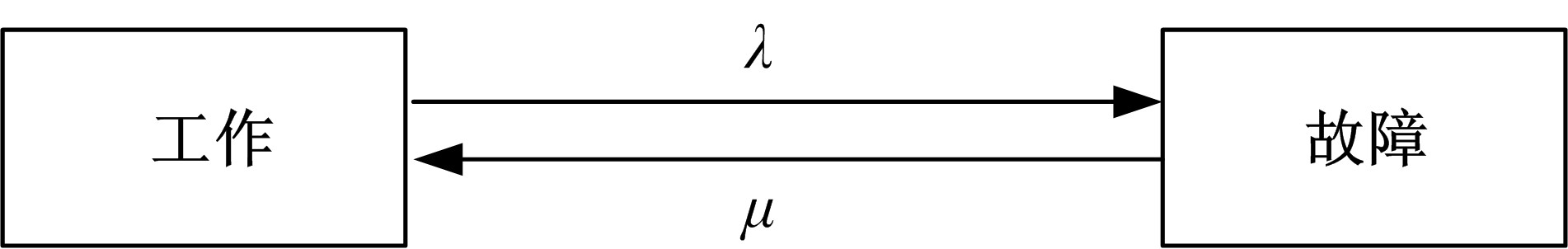吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 697-703.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20191122
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于马尔可夫过程的风电系统可靠性分析
- 1.长春师范大学 数学学院,长春 130032
2.吉林大学 数学学院,长春 130012
Reliability analysis of wind power generation system based on Markov process
Zhi-xin ZHAO1,2( ),Hui TANG1,Ren-yun LIU1(
),Hui TANG1,Ren-yun LIU1( )
)
- 1.School of Mathematics,Changchun Normal University,Changchun 130032,China
2.School of Mathematics,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
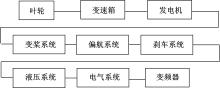
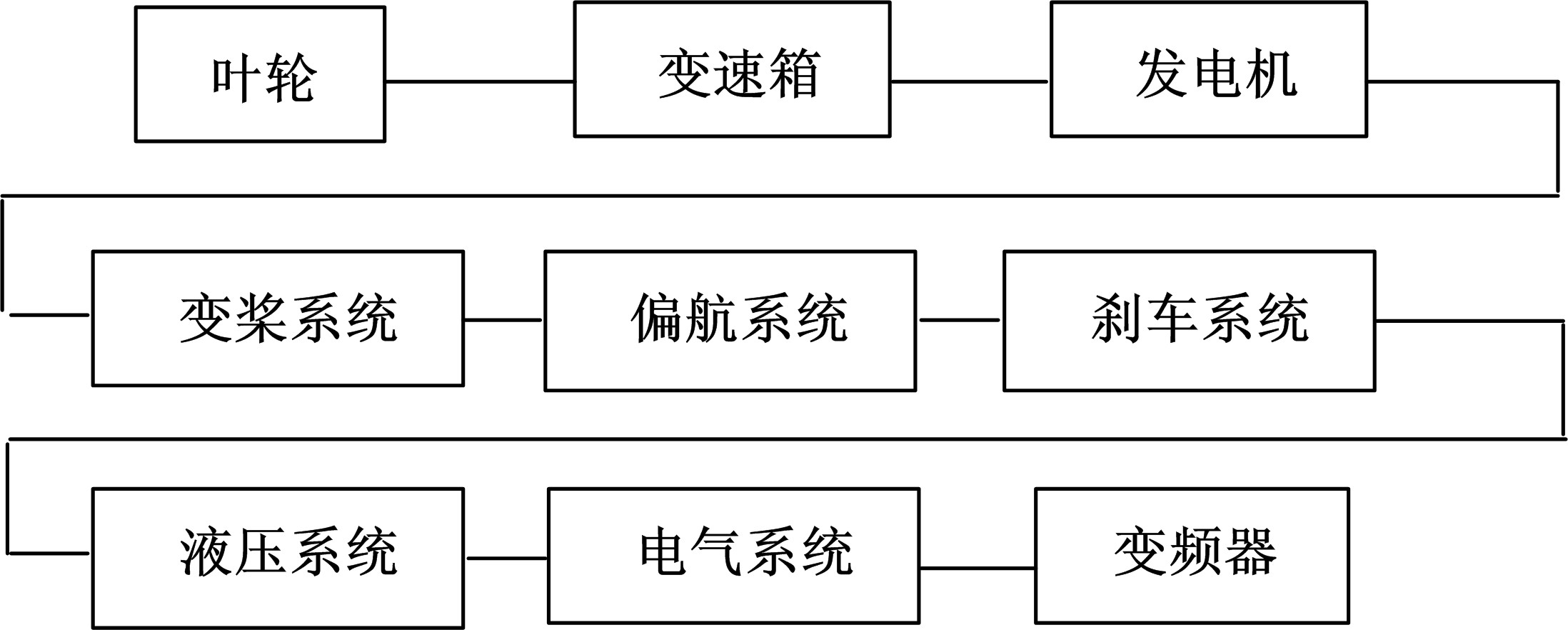
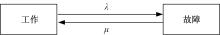
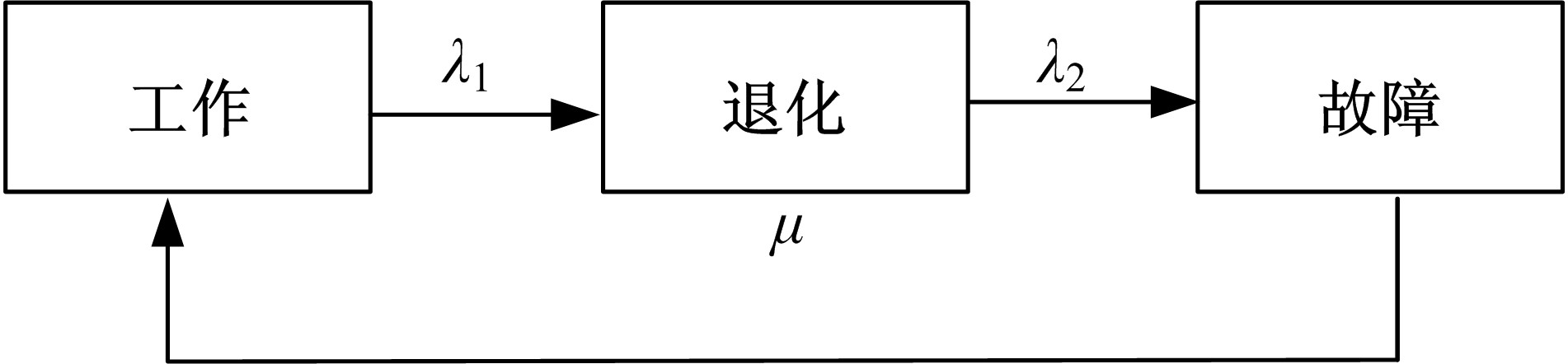
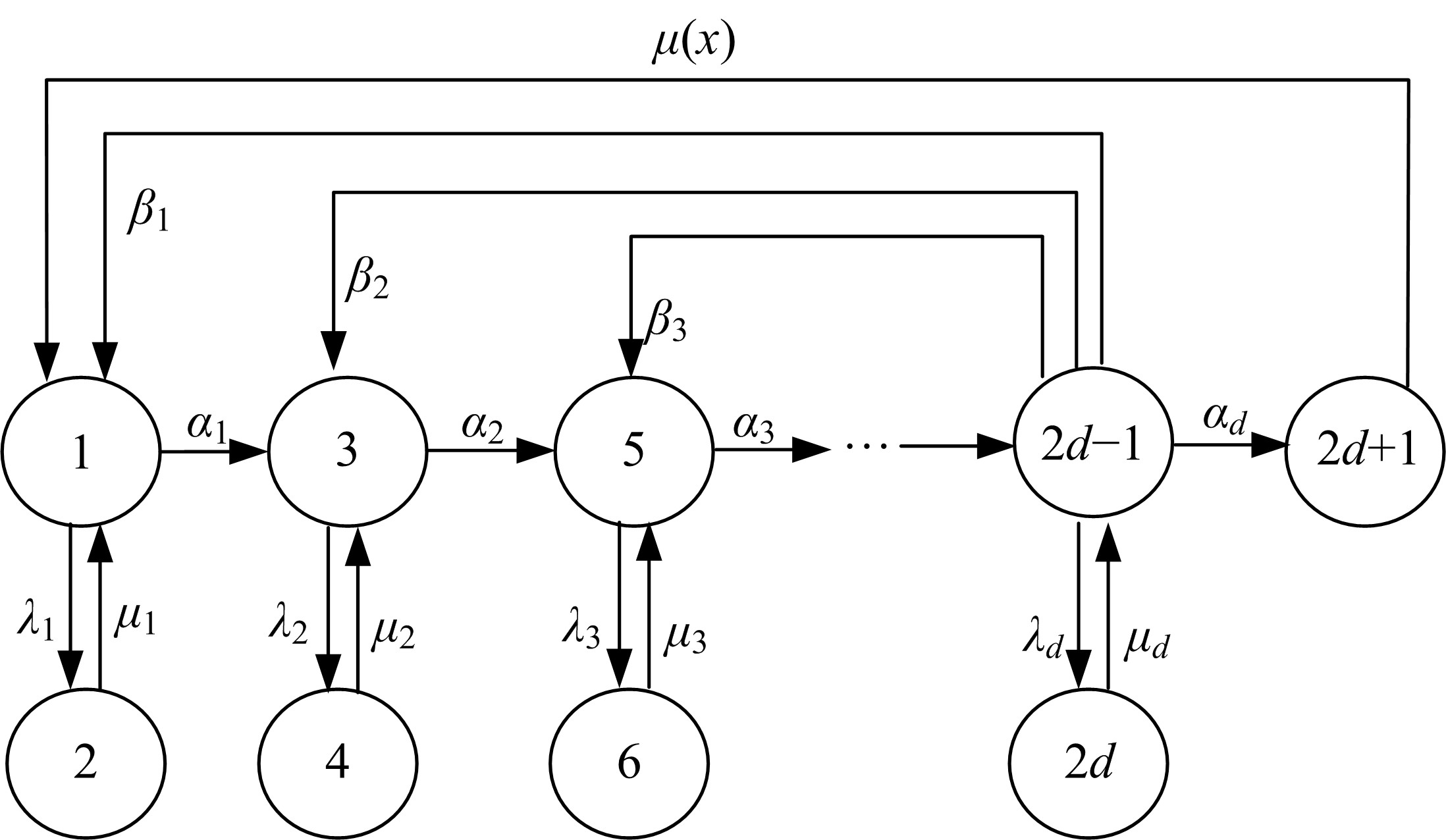
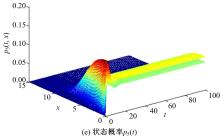
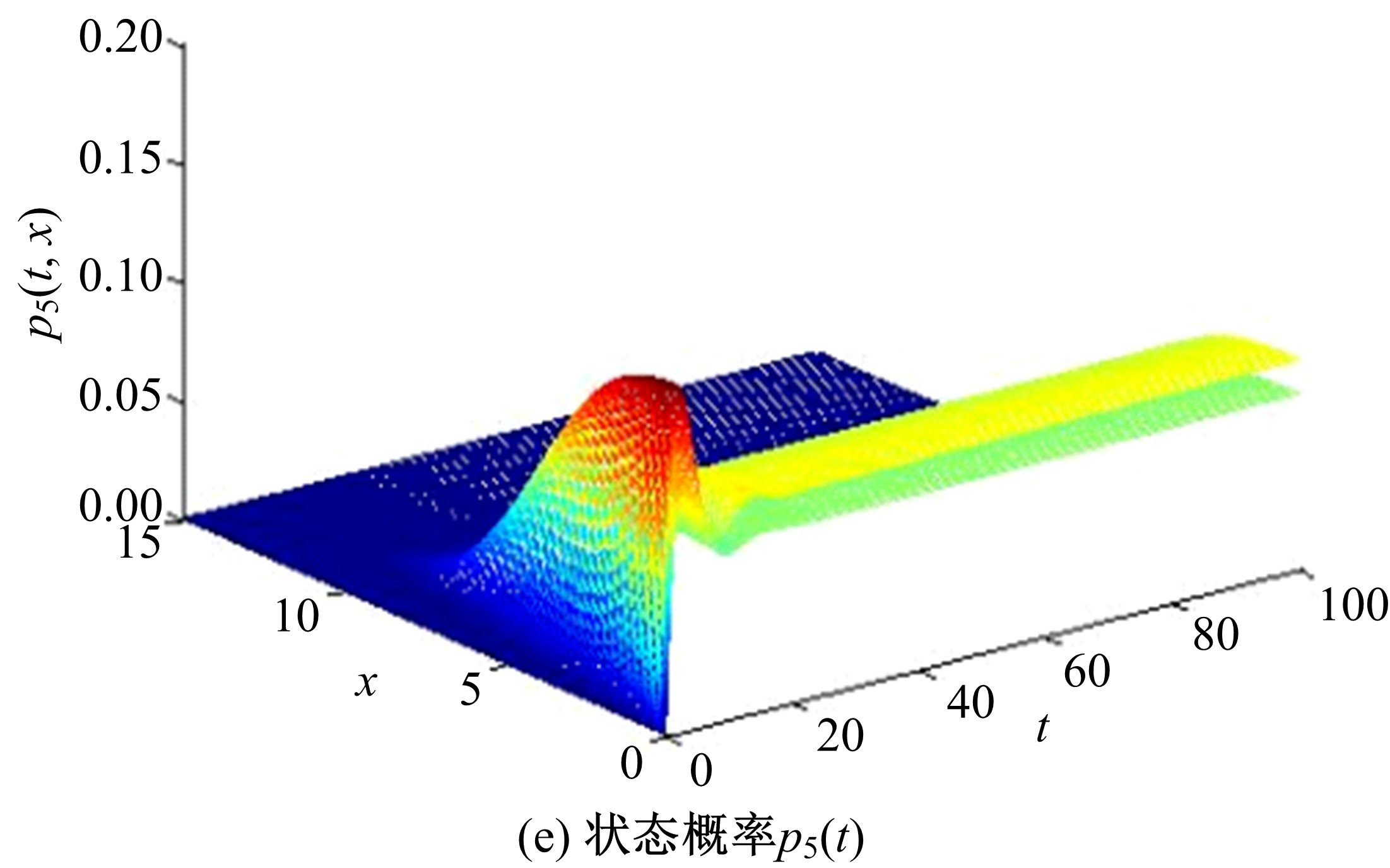
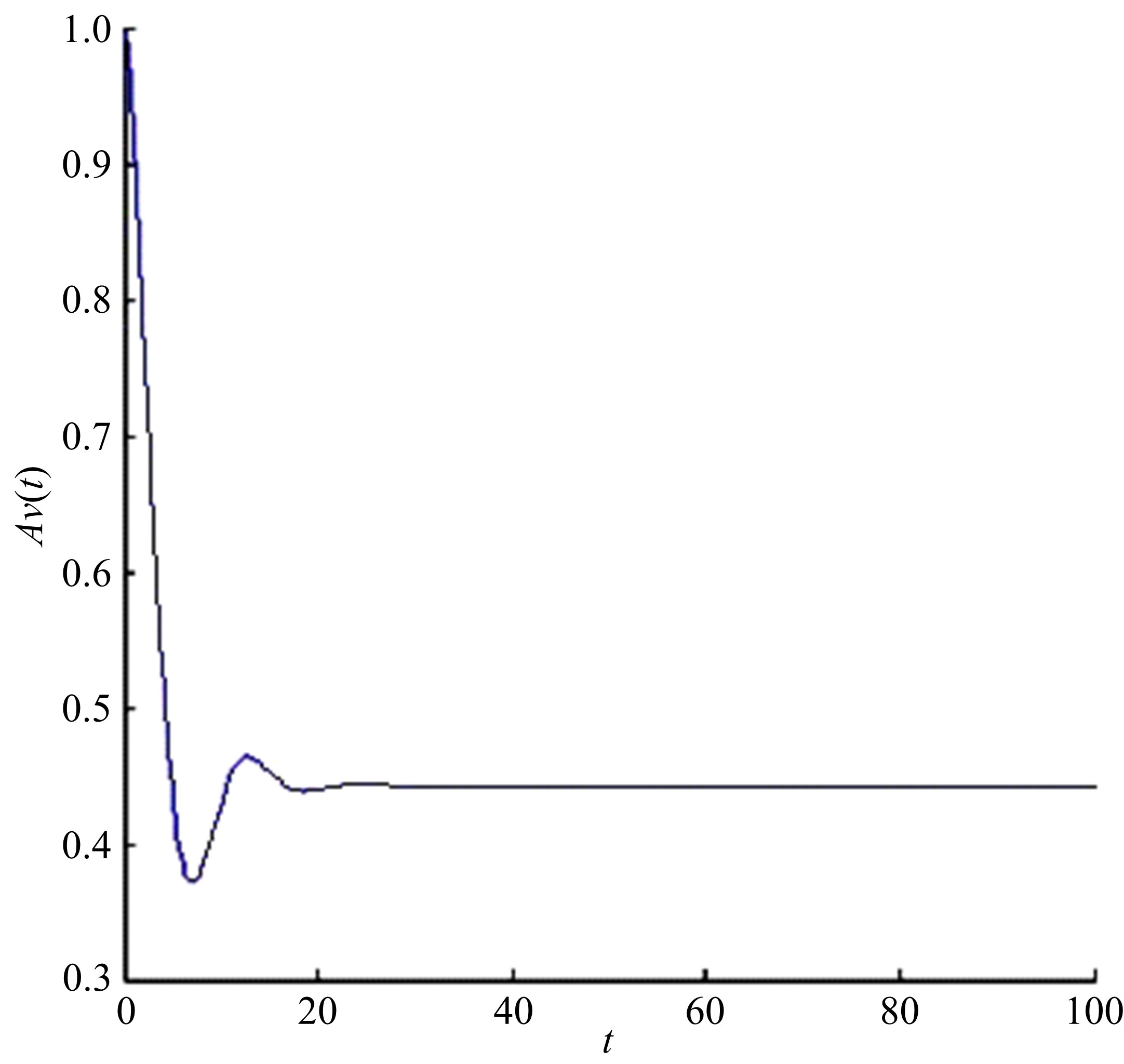
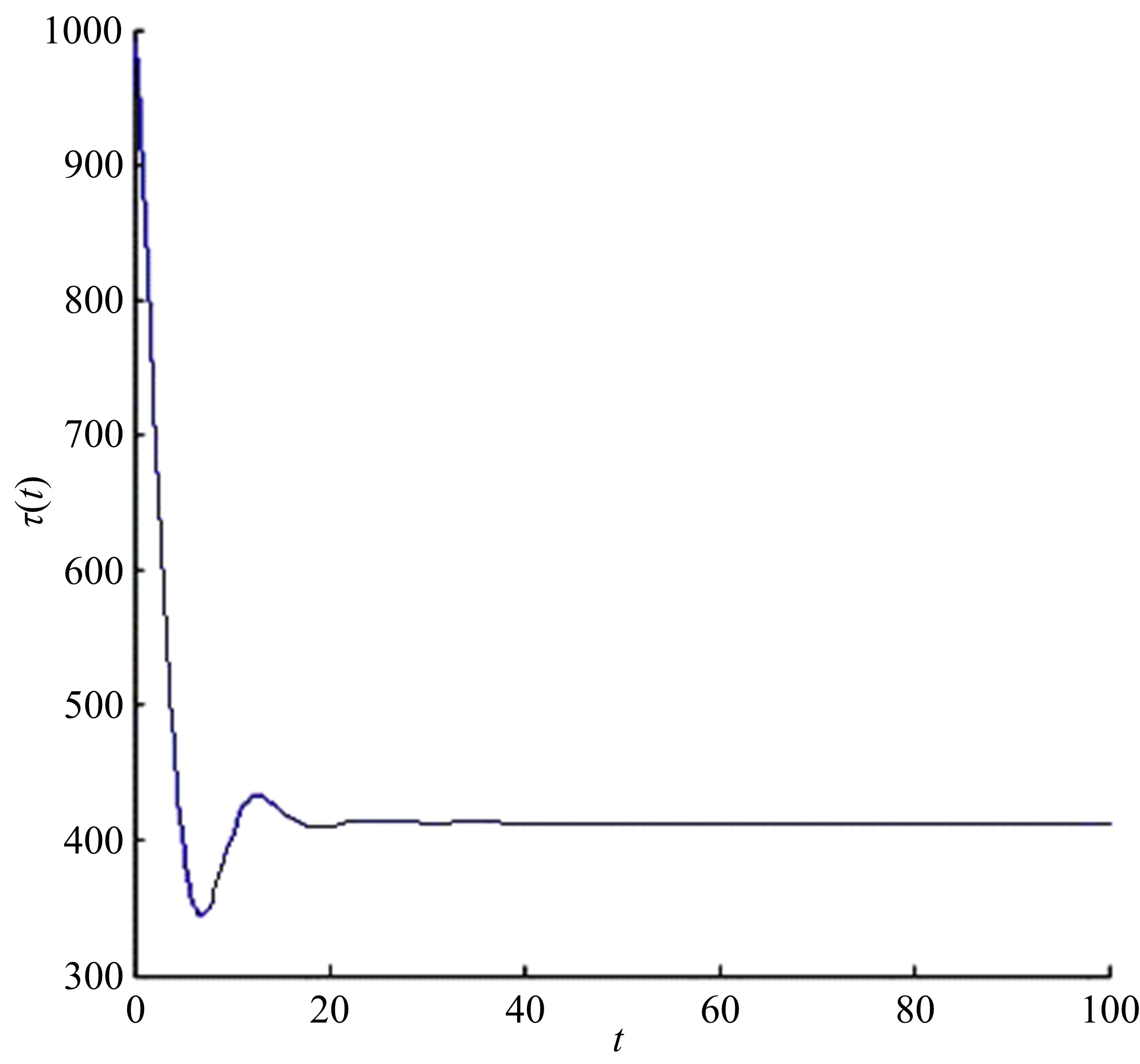
本文讨论了具有多种维修策略的多状态可修退化风电系统。根据风电系统运行环境和原理,利用马尔可夫过程和可靠性理论建立了风电系统的可靠性模型,该风电系统随时间变化可退化成多个离散状态,且系统在功能完好和完全故障之间的多个中间状态相互转化;然后,将该系统转化为一个抽象柯西问题,探讨了该可修退化系统各状态概率的存在唯一性;最后,在能效等级确定的条件下,对该退化系统各状态概率和可用度等指标进行了模拟。研究发现,通过马尔可夫过程可以描述可修退化风电系统,同时利用该模型可以有效地对系统相关可靠性指标进行定量分析。
中图分类号:
- TB112
| 1 | 李俊峰. 2012中国风电发展报告[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2012. |
| 2 | 王志新. 海上风力发电技术[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2012. |
| 3 | 李飞龙, 林勇刚, 李伟, 等. 风能静液压传动控制技术[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2014, 44(6): 1664-1668. |
| Li Fei-long, Lin Yong-gang, Li Wei, et al. Energy hydraulic transmission system of wind turbine[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(6): 1664-1668. | |
| 4 | 马文星, 刘彬, 刘春宝, 等. 风力发电液力调速系统及其控制[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2013, 43(5): 1276-1283. |
| Ma Wen-xing, Liu Bin, Liu Chun-bao, et al. Hydrodynamic speed adjusting system and its control of wind turbine[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2013, 43(5): 1276-1283. | |
| 5 | 曲波, 郑阳, 刘大欣. 风电惯性台架模拟惯量的计算[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(): 155-159. |
| Qu Bo, Zheng Yang, Liu Da-xin. Calculation of intertia moment about wind turbine test-bed braking system[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(Sup.1): 155-159. | |
| 6 | Tavner P J, Xiang J, Spinato E. Reliability analysis for wind turbines[J]. Wind Energy, 2007, 10(1): 1-18. |
| 7 | Selwyn T S, Kesavan R. Availability analysis of wind turbines and its sub assemblies with markov analysis at uncertain wind[J]. Advanced Science Letters,2013, 19(8): 2210-2214. |
| 8 | Florin M, Ciprian N. Availability evaluation of wind as a repairable system[C]∥International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment, Romania, 2014: 756-761. |
| 9 | Arabian H H, Oraee H, Tavner P J. Wind turbine productivity considering electrical subassembly reliability[J]. Renewable Energy, 2010, 35(1): 190-197. |
| 10 | 李大字, 冯园园, 刘展, 等. 风力发电机组可靠性建模与维修策略优化[J]. 电网技术, 2011, 35(9): 122-127. |
| Li Da-zi, Feng Yuan-yuan, Liu Zhan, et al. Reliability modeling and maintenance strategy optimization for wind power generation sets[J]. Power System Technology, 2011, 35(9): 122-127. | |
| 11 | 秦洋, 马慧民, 朱田玮, 等. 风力发电系统可靠性建模与优化检修策略[J]. 电力科学与工程, 2015, 31(7): 53-58. |
| Qin Yang, Ma Hui-min, Zhu Tian-wei, et al. Reliability modelling and maintenance strategy optimization for wind power system[J]. Electric Power Science and Engineering, 2015, 31(7): 53-58. | |
| 12 | Byon E, Yu D. Season-dependent condition-based maintenance for a wind turbine using a partially observed Markov decision process[J]. IEEE Transaction on Power System, 2010, 25(4): 1823-1834. |
| 13 | 张晓红, 曾建潮, 石冠男, 等. 基于退化状态空间划分的风电机组视情维修决策[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(9): 1909-1916. |
| Zhang Xiao-hong, Zeng Jian-chao, Shi Guan-nan, et al. Optimal decision of condition-based maintenance of wind turbines based on deterioration state-space partition[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(9): 1909-1916. | |
| 14 | 苏春, 周小荃. 基于半马尔科夫决策过程的风力机状态维修优化[J]. 机械工程学报, 2012, 48(2): 44-49. |
| Su Chun, Zhou Xiao-quan. Condition-based maintenance optimization for wind turbines based on Semi-Markov decision process[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(2): 44-49. | |
| 15 | Soro I W, Nourelfath M, Ait-Kadi D. Performance evaluation of multi-state degraded systems with minimal repairs and imperfect preventive maintenance[J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2010, 95(2): 65-69. |
| 16 | 霍娟, 唐贵基, 贾桂红, 等. 并网风电机组寿命分布拟合与维修方案评价[J]. 可再生能源, 2016, 34(5): 712-718. |
| Huo Juan, Tang Gui-ji, Jia Gui-hong, et al. Life distribution fitting and maintenance plan evaluation of grid connected wind turbines[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2016, 34(5): 712-718. | |
| 17 | Rajeevan K, Shouri P V, Nair U. Markov modeling and reliability allocation in wind turbine for availability enhancement[J]. Life Cycle Reliability and Safety Engineering, 2018, 7(3): 147-157. |
| 18 | Geni G, Li X Z, Zhu G T. Functional Analysis Method in Queueing Theorem[M]. UK: Research Information Ltd, 2001. |
| [1] | 张健,吴坤润,杨敏,冉斌. 智能网联环境下交叉口双环自适应控制模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 541-548. |
| [2] | 王殿海,沈辛夷,罗小芹,金盛. 车均延误最小情况下的相位差优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 511-523. |
| [3] | 宋现敏,张明业,李振建,王鑫,张亚南. 动态公交专用道的设置及其仿真分析评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1677-1686. |
| [4] | 贾洪飞,丁心茹,杨丽丽. 城市潮汐车道优化设计的双层规划模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 535-542. |
| [5] | 尹超英,邵春福,王晓全,熊志华. 考虑空间异质性的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 543-548. |
| [6] | 张大伟,祝海涛. 考虑行人差异性的人群疏散最优决策理论模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 549-556. |
| [7] | 常玉林,袁才鸿,孙超,张鹏. 基于改进元胞传输模型的城市路网实际阻抗计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 132-139. |
| [8] | 宗长富,文龙,何磊. 基于欧几里得聚类算法的三维激光雷达障碍物检测技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 107-113. |
| [9] | 隋振,姜源. 基于MIMO类脑情感学习回路的横-纵向综合控制驾驶员模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 140-146. |
| [10] | 别一鸣,姜凯,汤茹茹,王琳虹,熊昕宇. 考虑方案过渡影响的单点交通控制时段划分方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1844-1851. |
| [11] | 谷远利, 张源, 芮小平, 陆文琦, 李萌, 王硕. 基于免疫算法优化LSSVM的短时交通流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857. |
| [12] | 程国柱, 冯思鹤, 冯天军. 占用车行道的路内停车泊位设置条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1858-1864. |
| [13] | 龙海波,杨家其,赵学彧. 基于转运延误风险的多方式协同货运载运工具配置优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1492-1499. |
| [14] | 别一鸣,汤茹茹,王运豪,文斌,冯天军,王琳虹. 信号交叉口进口车道饱和流率估计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1459-1464. |
| [15] | 梁泉,翁剑成,周伟,荣建. 基于关联规则的公共交通通勤稳定性人群辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1484-1491. |
|
||