吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 501-510.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200037
• 材料科学与工程 • 上一篇
光斑直径对激光冲击强化铝合金腐蚀性能的影响
- 1.江苏大学 机械工程学院,江苏 镇江 212013
2.江苏大学 工程技术研究院,江苏 镇江 212013
Effect of spot diameteron corrosion resistance of aluminum alloy subjected to laser shock peening
Kai-yu LUO1,2( ),Jun-cheng CHEN1,Chang-yu WANG1,Jin-zhong LU1
),Jun-cheng CHEN1,Chang-yu WANG1,Jin-zhong LU1
- 1.School of Mechanical Engineering,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China
2.College of Engineering Technology,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China
摘要:
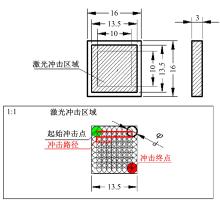
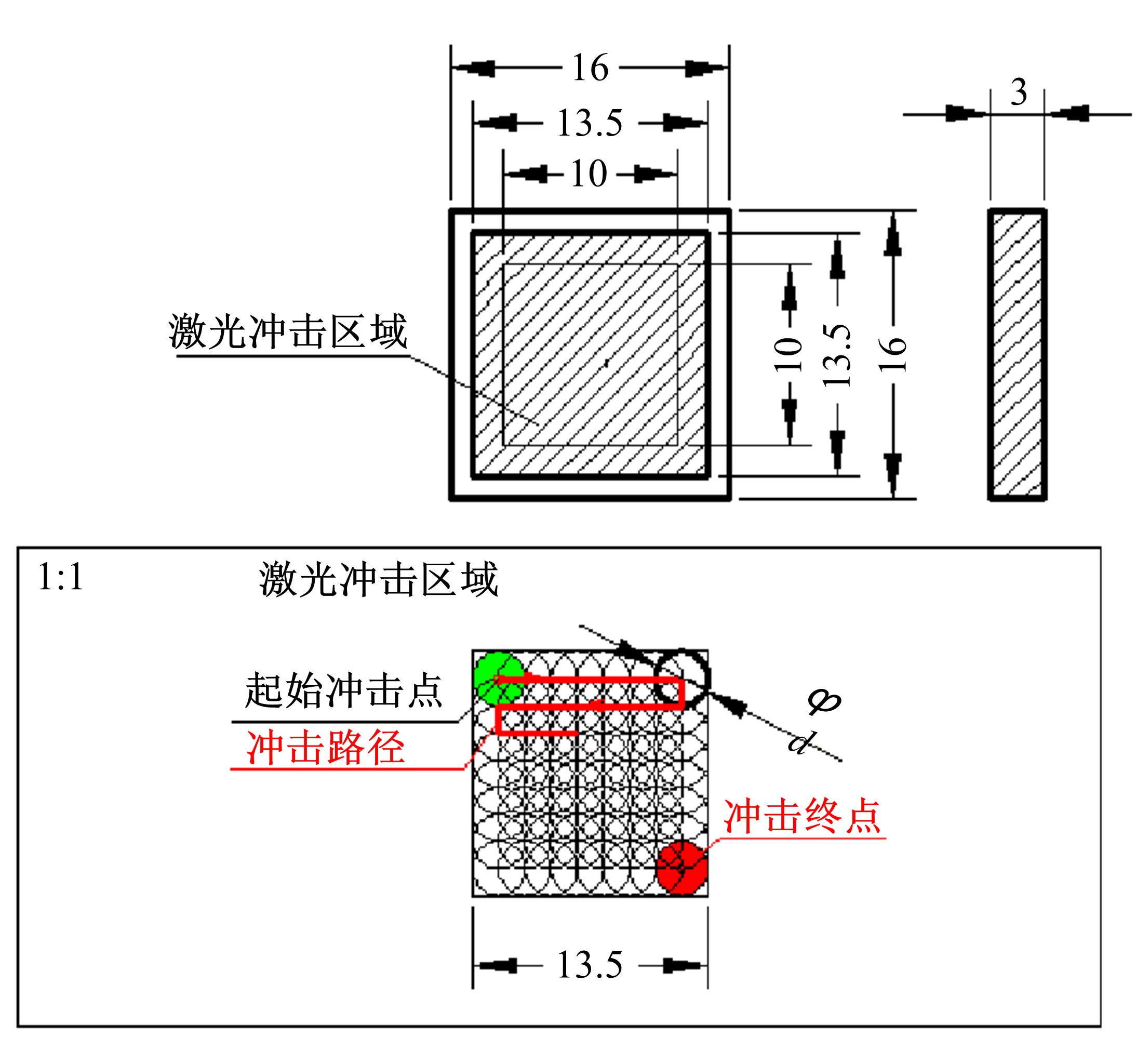
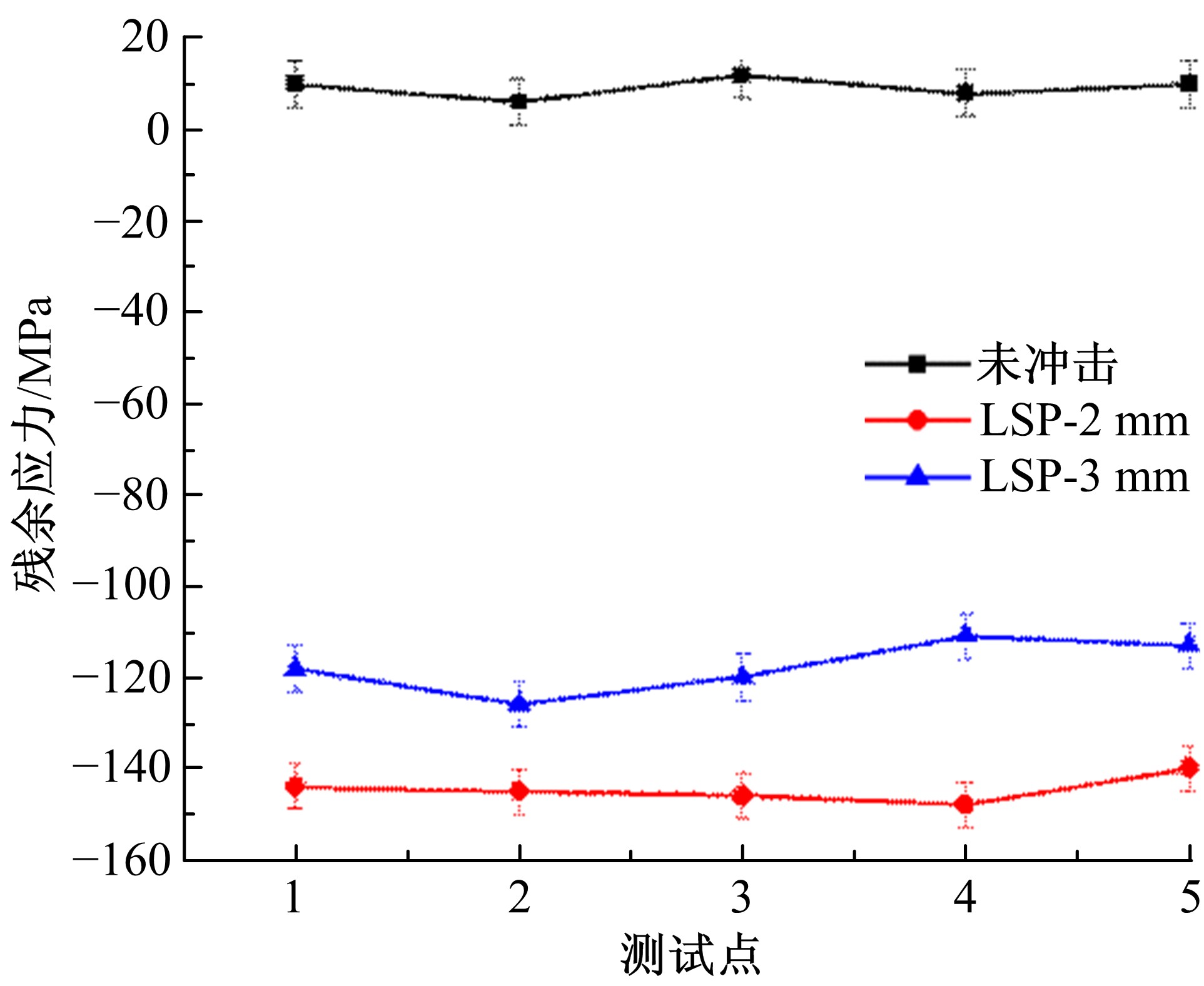
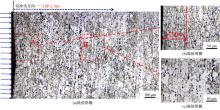
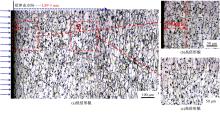
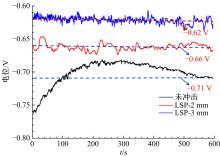
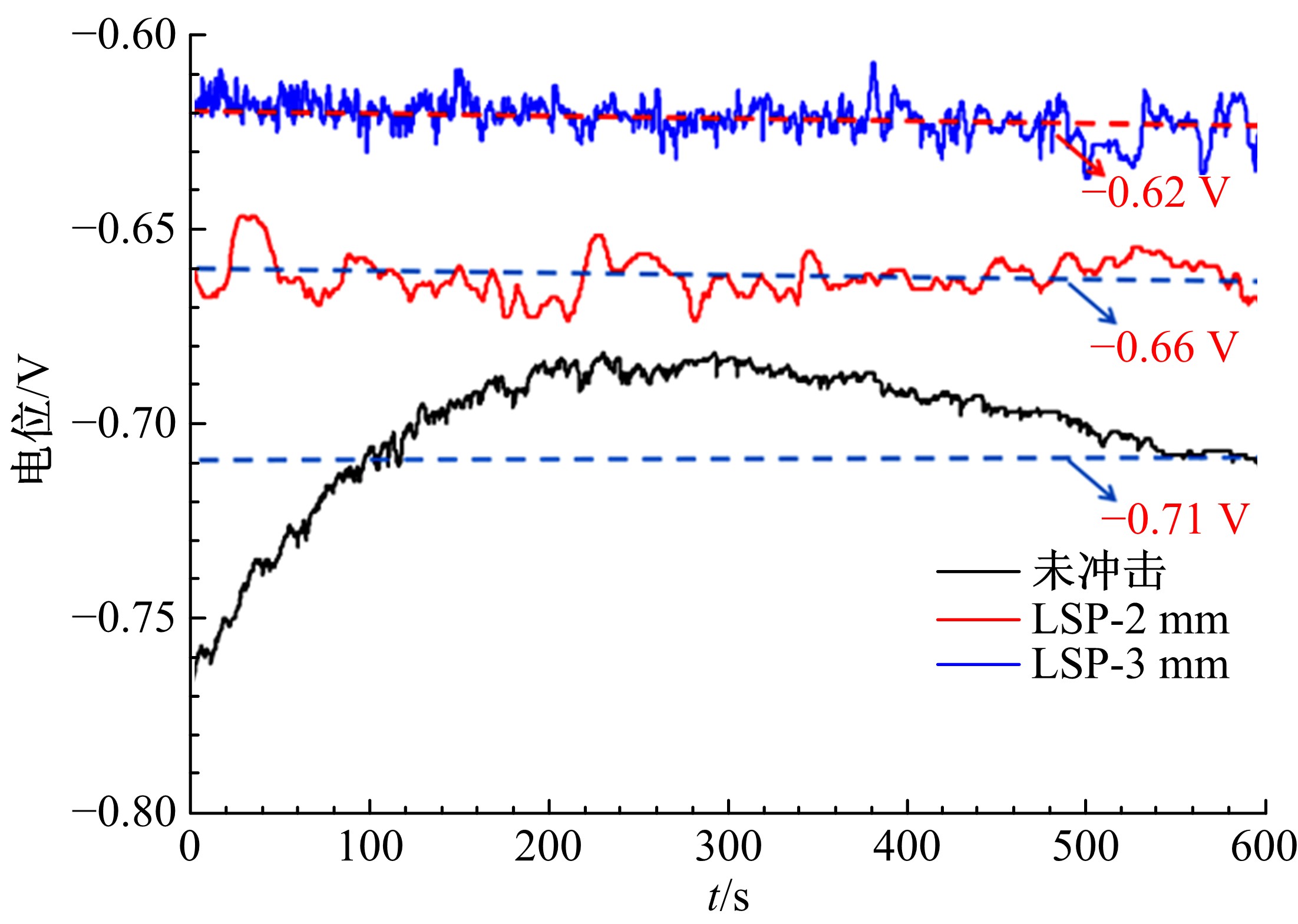
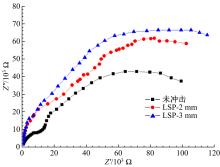
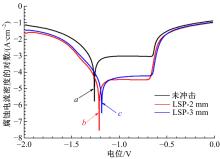
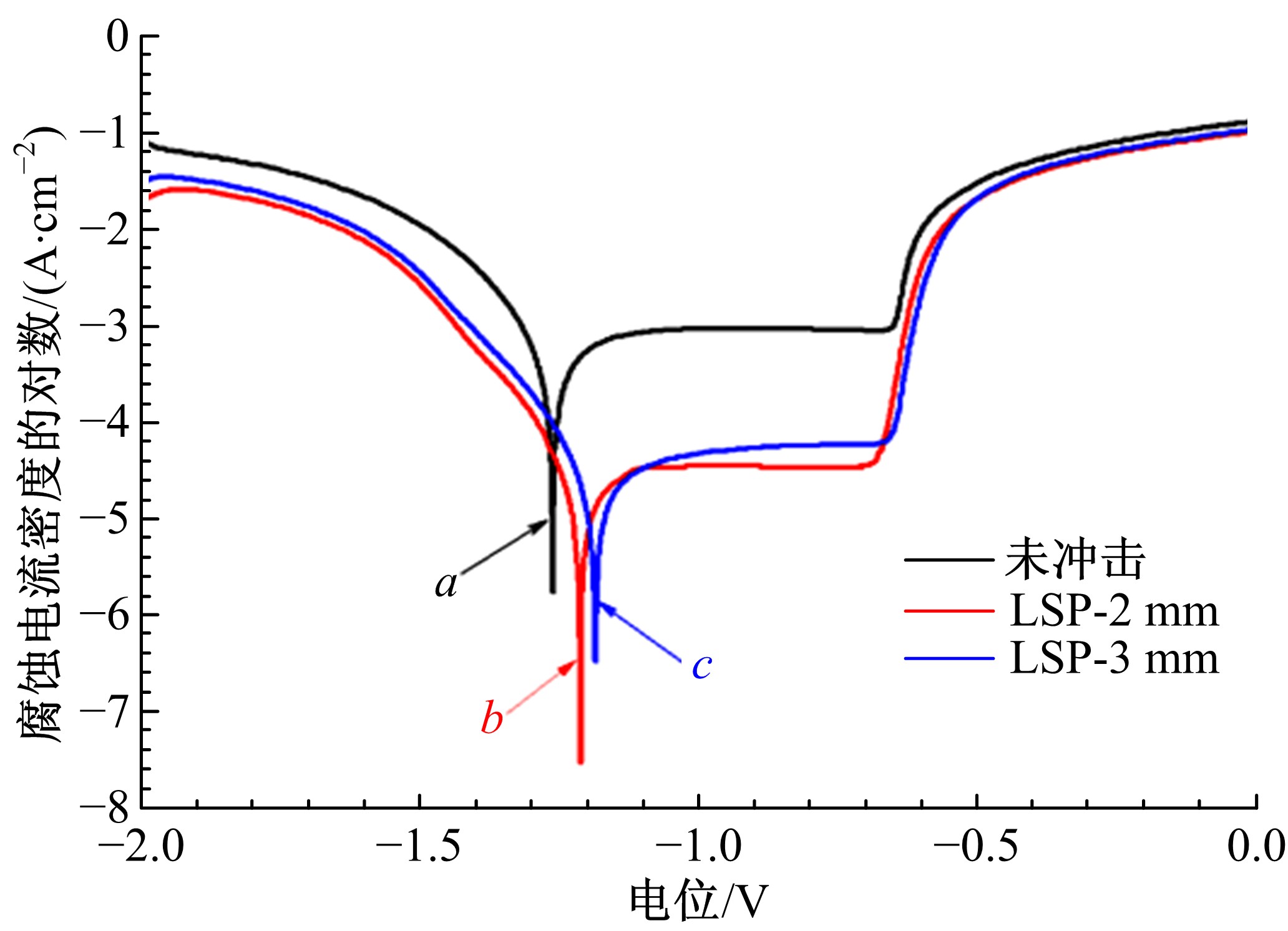
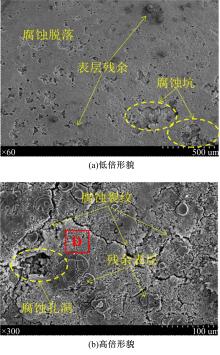
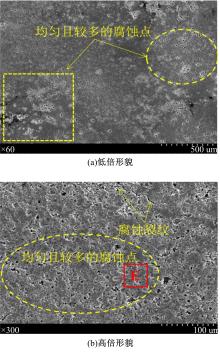
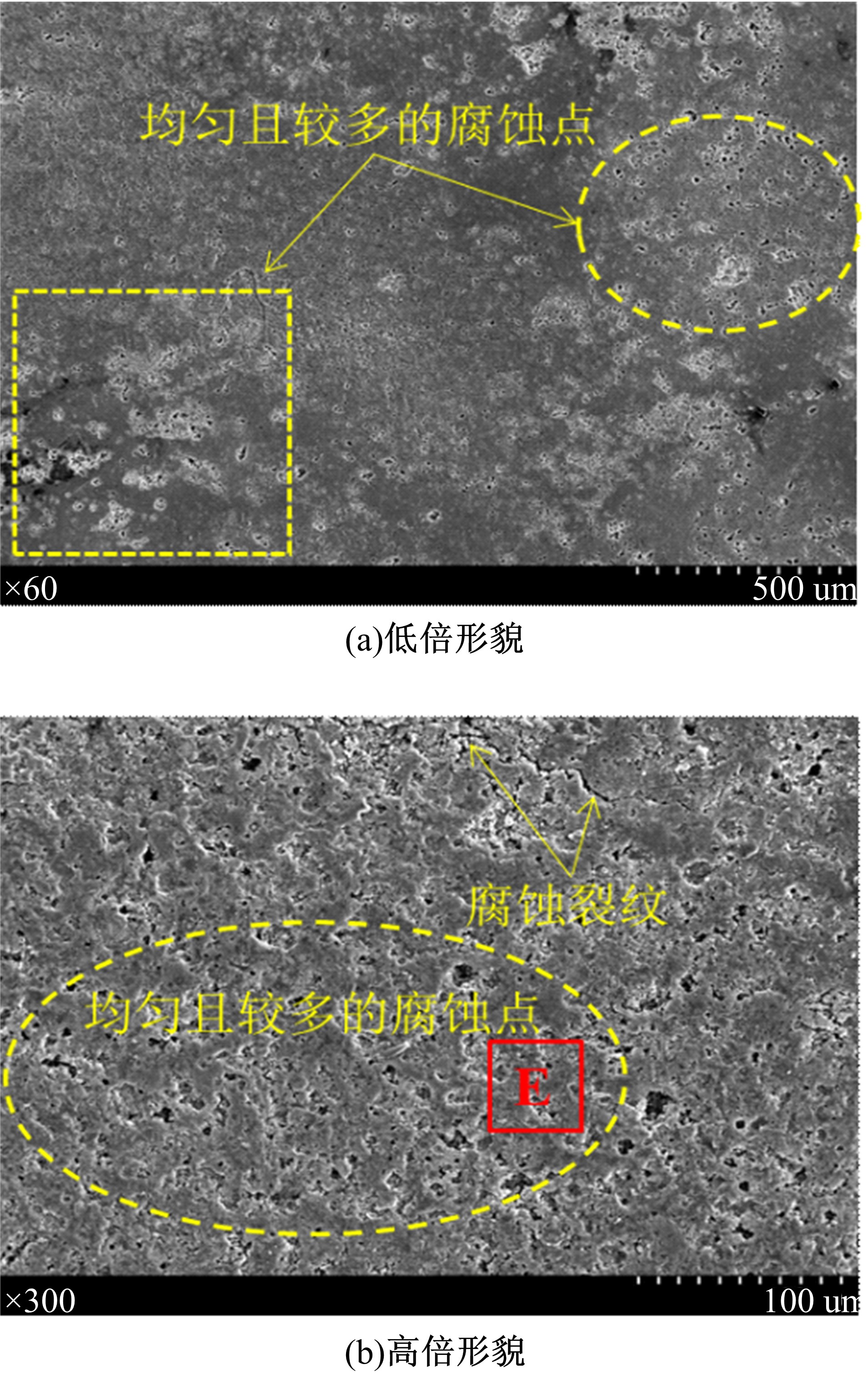
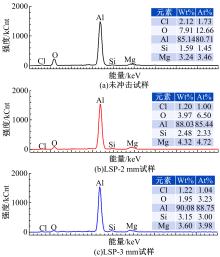
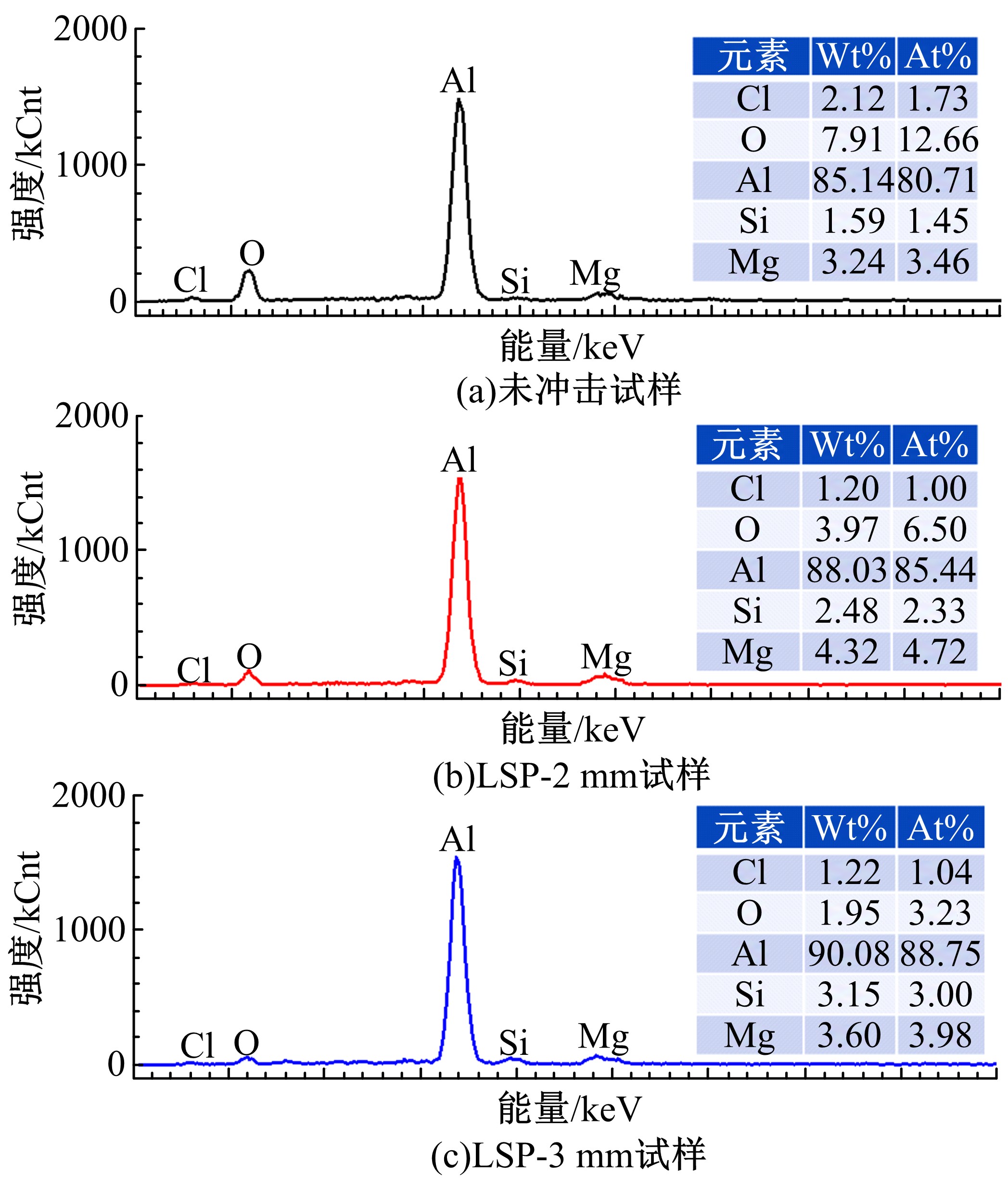
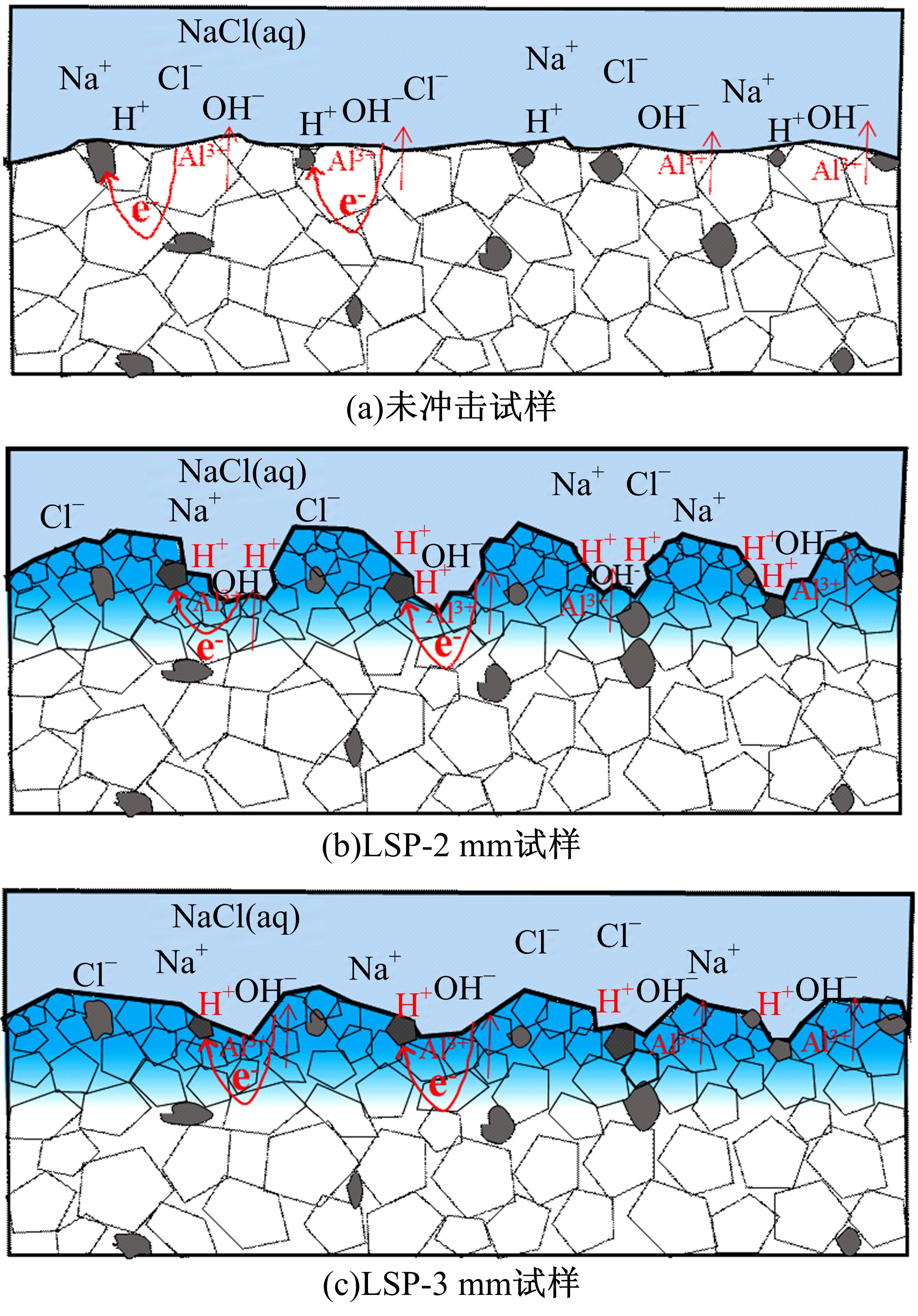
为研究不同光斑直径对激光冲击强化6061-T6铝合金电化学腐蚀性能的影响,测量了表面粗糙度和残余应力,进行了截面金相和电化学腐蚀实验。结果表明:激光冲击强化使材料的表层晶粒细化、表面粗糙度增大且产生残余压应力。未冲击试样、2 mm和3 mm光斑直径激光冲击试样的腐蚀电流密度分别为:154.5 μA/cm2、14.70 μA/cm2和11.17 μA/cm2,激光冲击强化有效地提高了材料的耐腐蚀性能。2 mm光斑直径激光冲击试样相比于3 mm光斑直径激光冲击试样拥有较差的表面形貌,其耐腐蚀性能较差。
中图分类号:
- TN249
| 1 | Salimianrizi A, Foroozmehr E, Badrossamay M, et al. Effect of laser shock peening on surface properties and residual stress of Al6061-T6[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2016, 77: 112-117. |
| 2 | 缪宏, 左敦稳, 王珉, 等.喷丸强化对NAK80钢表面完整性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(5): 1290-1294. |
| Miao Hong, Zuo Dun-wen, Wang Min, et al. Effect of shot peening on surface integrity of NAK80 steel[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(5): 1290-1294. | |
| 3 | Sun Q Q, Han Q Y, Xu R, et al. Localized corrosion behaviour of AA7150 after ultrasonic shot peening:Corrosion depth vs. impact energy[J]. Corrosion Science,2018, 130: 218-230. |
| 4 | 汪志太, 林鑫, 曹永青, 等.外部冷却条件对激光熔凝Ni-Sn合金反常共晶形成的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(12): 91-96. |
| Wang Zhi-tai, Lin Xin, Cao Yong-qing, et al. External cooling condition effects on formation of anomalous eutectic in Ni-Sn alloy by laser remelting[J]. Chinese J Lasers, 2014, 41(12): 91-96. | |
| 5 | 罗开玉, 邢月华, 柴卿锋, 等. 激光冲击强化对2Cr13不锈钢腐蚀疲劳性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(3): 850-858. |
| Luo Kai⁃yu, Xing Yue⁃hua, Chai Qing⁃feng, et al. Effect of laser shock peening on corrosion fatigue behaviour of 2Cr13 stainless steel[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 850-858. | |
| 6 | 吴边, 王声波, 郭大浩, 等. 激光冲击铝合金改性处理研究[J]. 光学学报, 2005, 25(10): 1352-1356. |
| Wu Bian, Wang Sheng-bo, Guo Da-hao, et al. Research of material modification induced by laser s hock processing on aluminum alloy[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2005, 25(10):1352-1356. | |
| 7 | 周建忠, 刘会霞, 冯爱新, 等. 激光冲击波技术用材料加工的研究进展[J]. 应用激光, 2005, 25(1): 27-31, 44. |
| Zhou Jian-zhong, Liu Hui-xia, Feng Ai-xin, et al. Advances on the application of laser induced shock wave in metal processing[J]. Applied Laser, 2005, 25(1): 27-31, 44. | |
| 8 | 张青来, 王荣, 张冰昕, 等. 激光冲击强化对AZ31镁合金力学性能和组织结构的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2015, 42(3): 39-45. |
| Zhang Qing-lai, Wang Rong, Zhang Bing-xin, et al. Effect of laser shock processing on mechanical properties and microstructures of AZ31 magnesium alloy[J]. Chinese J Lasers, 2015, 42(3): 39-45. | |
| 9 | 汪诚, 赖志林, 何卫锋, 等. 激光冲击次数对1Cr11Ni2W2MoV不锈钢高周疲劳性能的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(1): 46-51. |
| Wang Cheng, Lai Zhi-lin, He Wei-feng, et al. Effect of multi-impact on high cycle fatigue properties of 1Cr11Ni2W2MoV stainless steel subject to laser shock processing[J]. Chinese J Lasers, 2014, 41(1): 46-51. | |
| 10 | 王江涛, 张永康, 陈菊芳, 等. 激光冲击对7075铝合金等离子弧焊接头电化学腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2015, 42(12): 106-115. |
| Wang Jiang-tao, Zhang Yong-kang, Chen Ju-fang, et al. Effect of laser shock processing on electrochemical corrosion behavior of 7075 aluminum alloy plasma arc weldments[J]. Chinese J Lasers, 2015, 42(12): 106-115. | |
| 11 | 邢清蒲, 张凌峰, 李少哲, 等. 激光冲击强化对2A02铝合金电化学腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2013, 25(5): 402-405. |
| Xing Qing-pu, Zhang Ling-feng, Li Shao-zhe, et al. Effect of laser shock processing on electrochemical corrosion behavior of 2A02 Aluminum alloy[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2013, 25(5): 402-405. | |
| 12 | 宁成义, 黄亿辉, 张广义, 等. 激光冲击强化6061铝合金耐磨性能及电化学性能的实验研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(6): 254-259. |
| Ning Cheng-yi, Huang Yi-hui, Zhang Guang-yi, et al. Experimental study of wear resistance and eletrochemical corrosion properties of 6061 aluminum alloy treated by laser shock peening[J].China Academic Journal Electronic Publishing House, 2018, 55(6): 254-259. | |
| 13 | Trdan U, Grum J. Evaluation of corrosion resistance of AA6082-T651 aluminium alloy after laser shock peening by means of cyclic polarisation and EIS methods[J]. Corrosion Science, 2012, 59: 324-333. |
| 14 | Luo K Y, Wang C Y, Sun G F, et al. Investigation and microstructural analyses of massive LSP impacts with coverage area on crack initiation location and tensile properties of AM50 magnesium alloy[J]. Materials Science Engineering A, 2016, 650: 110-118. |
| 15 | Luo K Y, Wang C Y, Cui C Y, et al. Effects of coverage layer on the electrochemical corrosion behaviour of Mg-Al-Mn alloy subjected to massive laser shock peening treatment[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 782: 1058-1075. |
| 16 | Zhao X Y, Chen X, Wang X. Effect of aging processes on corrosion behavior and stress corrosion sensitivity of pre-stretched 7075 aluminum alloy[J]. Material and Corrosion, 2018, 69(7): 850-857. |
| 17 | Torbati-Sarraf H, Stannard T J, Plante E C L, et al. Direct observations of microstructure-resolved corrosion initiation in AA7075-T651 at the nanoscale using vertical scanning interferometry (VSI)[J]. Materials Characterization, 2020, 161: 110166. |
| 18 | Yang Y, Zhou W F, Tong Z P, et al. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of 5083 aluminum alloy subjected to laser shock peening[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2019, 28(10): 1-11. |
| 19 | Lee H S, Kim D S, Jung J S, et al. Influence of peening on the corrosion properties of AISI 304 stainless steel[J]. Corrosion Science, 2009, 51(12): 2826-2830. |
| [1] | 梁继才,廖雁飞,滕菲,梁策,李义. 矩形截面型材三维多点拉弯成形减薄率[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 163-171. |
| [2] | 刘纯国,于晓彤,岳韬,李东来,张明哲. 双曲率筋条壁板铣削回弹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 188-199. |
| [3] | 田银宝,申俊琦,胡绳荪,勾健. EP/EN模数对铝合金VP-CMT焊熔滴过渡及焊道成形的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1663-1668. |
| [4] | 宫文彪,朱芮,郄新哲,崔恒,宫明月. 6082铝合金超厚板搅拌摩擦焊接头组织与性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 512-519. |
| [5] | 刘义伦,王卿,刘驰,李松柏,何军,赵先琼. 蠕变和人工时效对2524铝合金疲劳裂纹扩展性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1636-1643. |
| [6] | 徐戊矫,刘承尚,鲁鑫垚. 喷丸处理后6061铝合金工件表面粗糙度的模拟计算及预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1280-1287. |
| [7] | 鲁金忠,周婉婷,张圣洋,邵亦锴,王长雨,罗开玉. 激光冲击强化层数对6061⁃T6铝合金抗腐蚀性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 842-849. |
| [8] | 李于朋,孙大千,宫文彪. 6082⁃T6铝合金薄板双轴肩搅拌摩擦焊温度场[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 836-841. |
| [9] | 罗开玉,邢月华,柴卿锋,吴世凯,尹叶芳,鲁金忠. 激光冲击强化对2Cr13不锈钢腐蚀 疲劳性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 850-858. |
| [10] | 赵爽,沈继红,张刘,赵晗,陈柯帆. 微细电火花加工表面粗糙度快速高斯评定[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1838-1843. |
| [11] | 胡志清, 颜庭旭, 李洪杰, 吕振华, 廖伟, 刘庚. 深冷处理对铝合金薄板冲剪成形性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1524-1530. |
| [12] | 刘子武, 李剑峰. 叶片材料FV520B再制造熔覆层冲蚀损伤行为及评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 835-844. |
| [13] | 胡志清, 郑会会, 徐亚男, 张春玲, 党停停. 表面微沟槽对Al/CFRP胶结性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 229-235. |
| [14] | 付文智, 刘晓东, 王洪波, 闫德俊, 刘晓莉, 李明哲, 董玉其, 曾振华, 刘桂彬. 关于1561铝合金曲面件的多点成形工艺[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1822-1828. |
| [15] | 陈超, 赵升吨, 崔敏超, 韩晓兰, 范淑琴, 石田徹. AL5052铝合金板平压重塑形连接试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1512-1518. |
|
||