吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1583-1592.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200506
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
骨架式车身多材料及梁截面形状和尺寸优化
- 1.同济大学 汽车学院,上海 201804
2.武汉理工大学 现代汽车零部件技术湖北省重点实验室,武汉 430070
3.武汉理工大学 汽车零部件技术湖北省协同创新中心,武汉 430070
Optimization of multi⁃material and beam cross⁃sectional shape and dimension of skeleton⁃type body
Chao MA1( ),Yun-kai GAO1(
),Yun-kai GAO1( ),Zhe LIU1,Yue-xing DUAN1,Lin-li TIAN2,3
),Zhe LIU1,Yue-xing DUAN1,Lin-li TIAN2,3
- 1.School of Automotive Studies,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.Hubei Key Laboratory of Advanced Technology for Automotive Components,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430070,China
3.Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center for Automotive Components Technology,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430070,China
摘要:
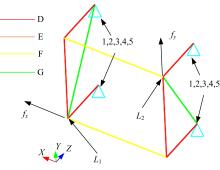
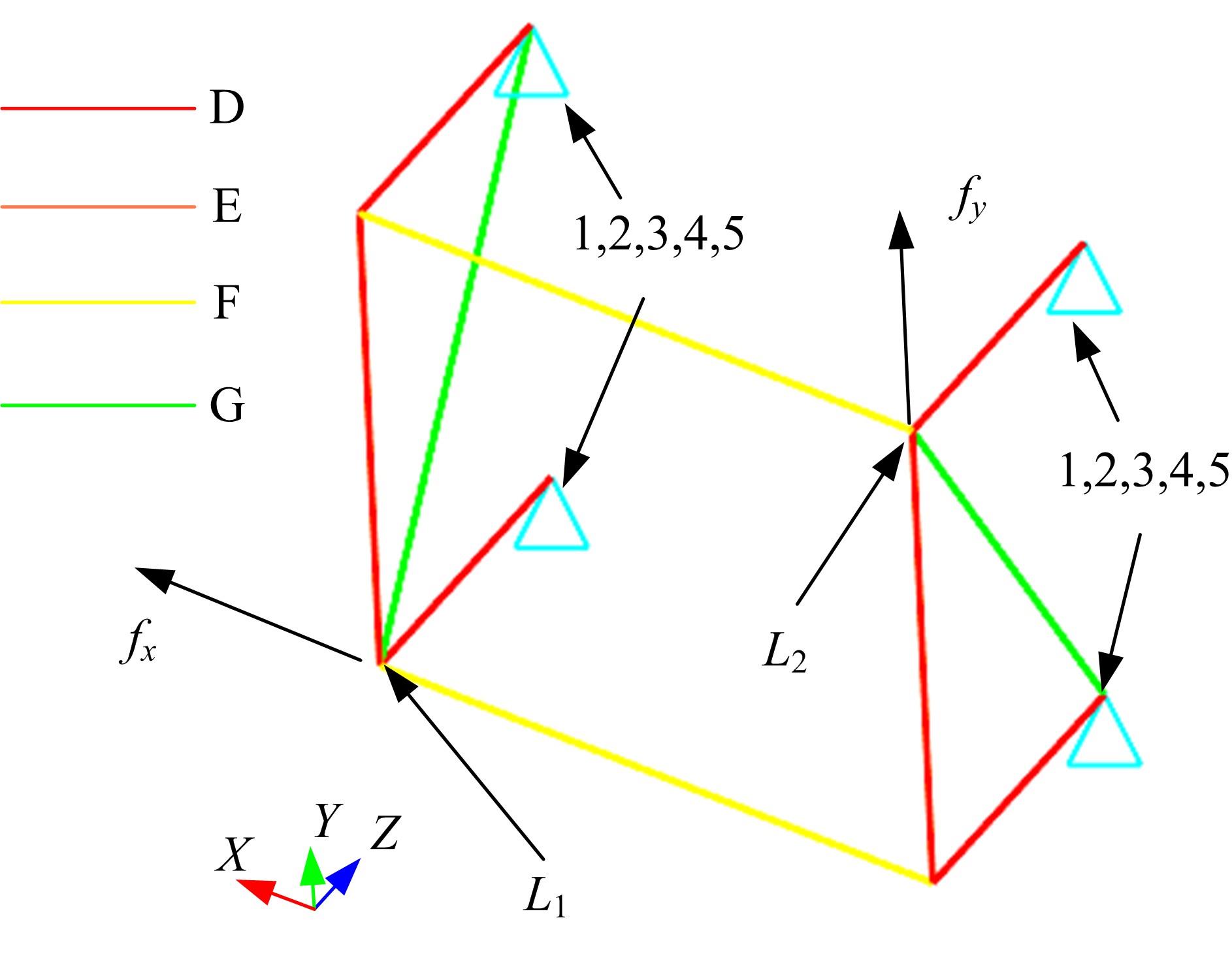
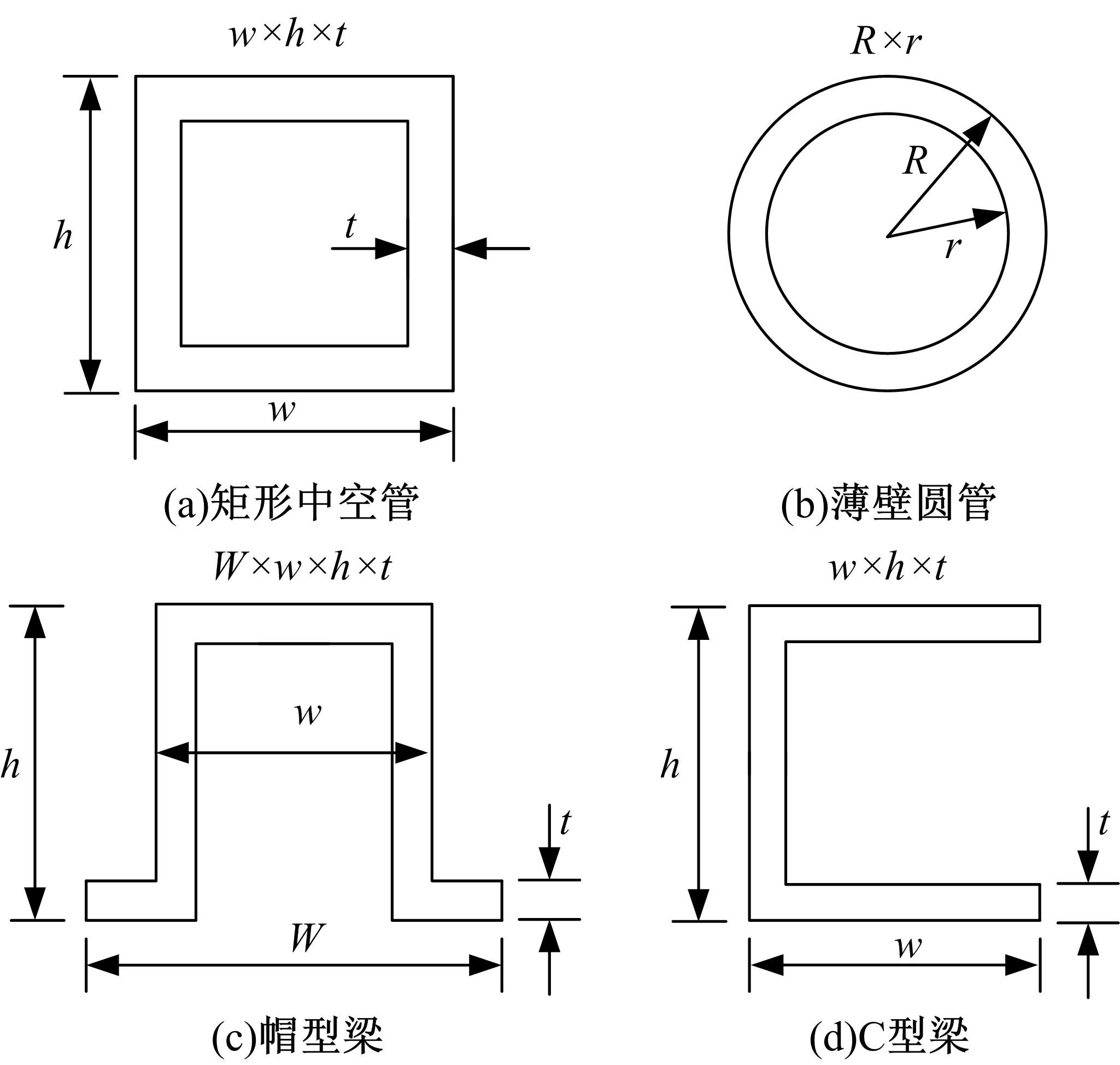
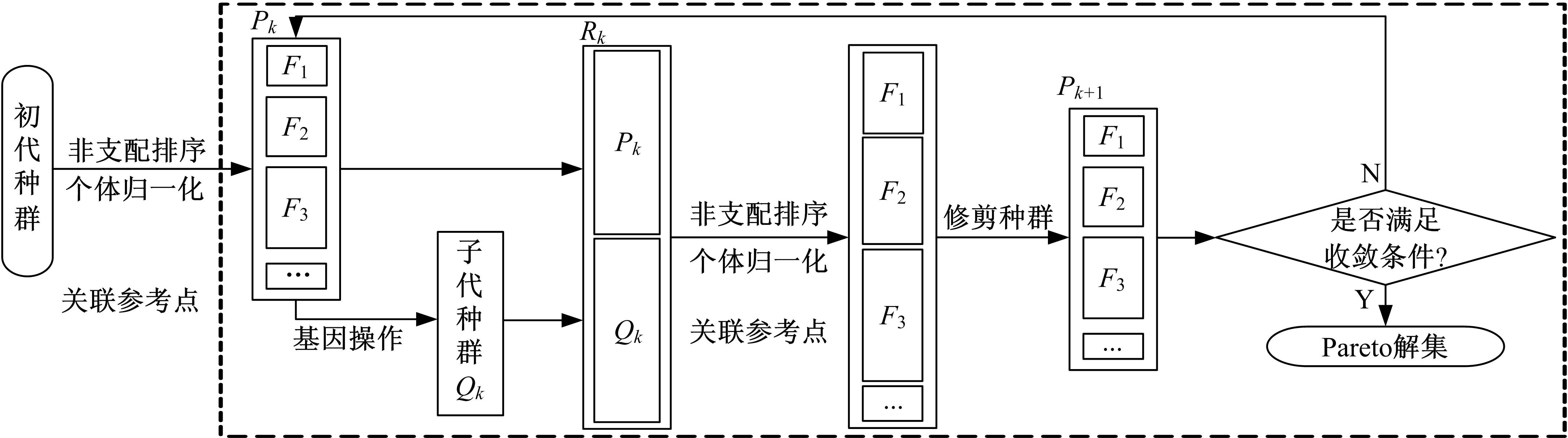
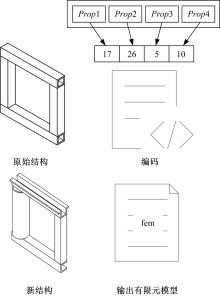
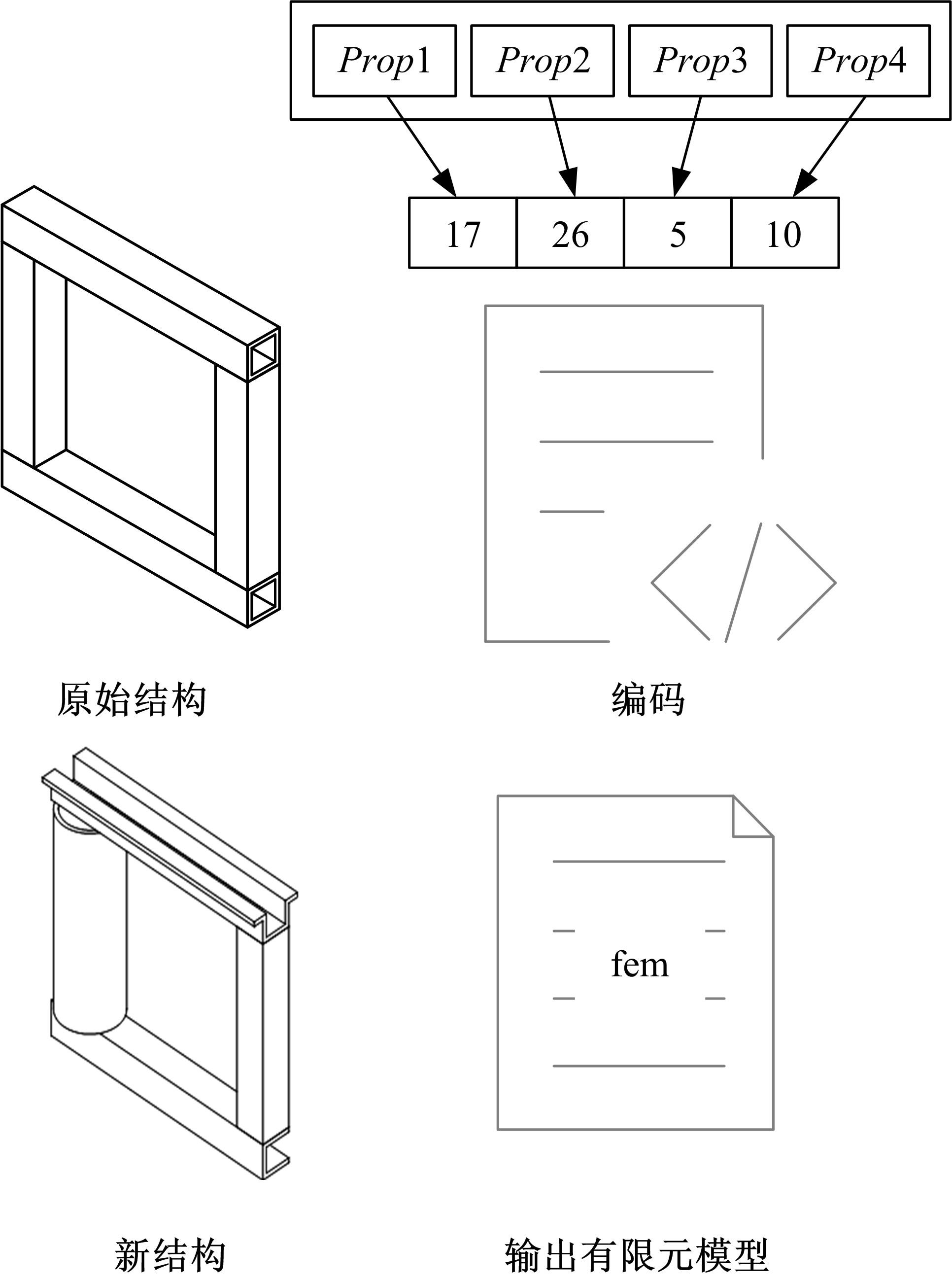
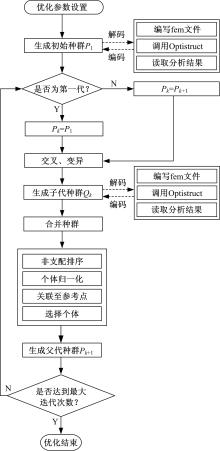
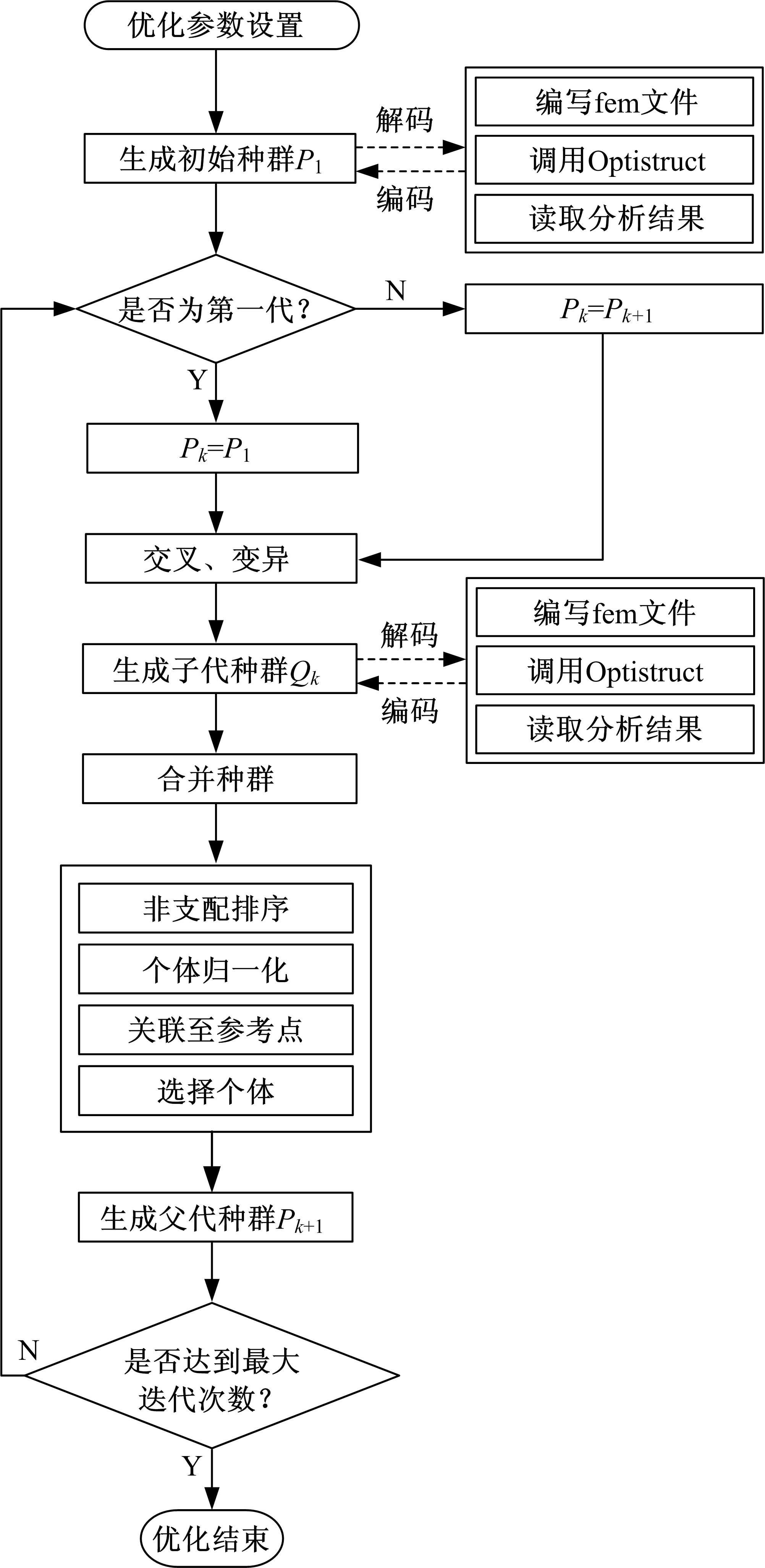
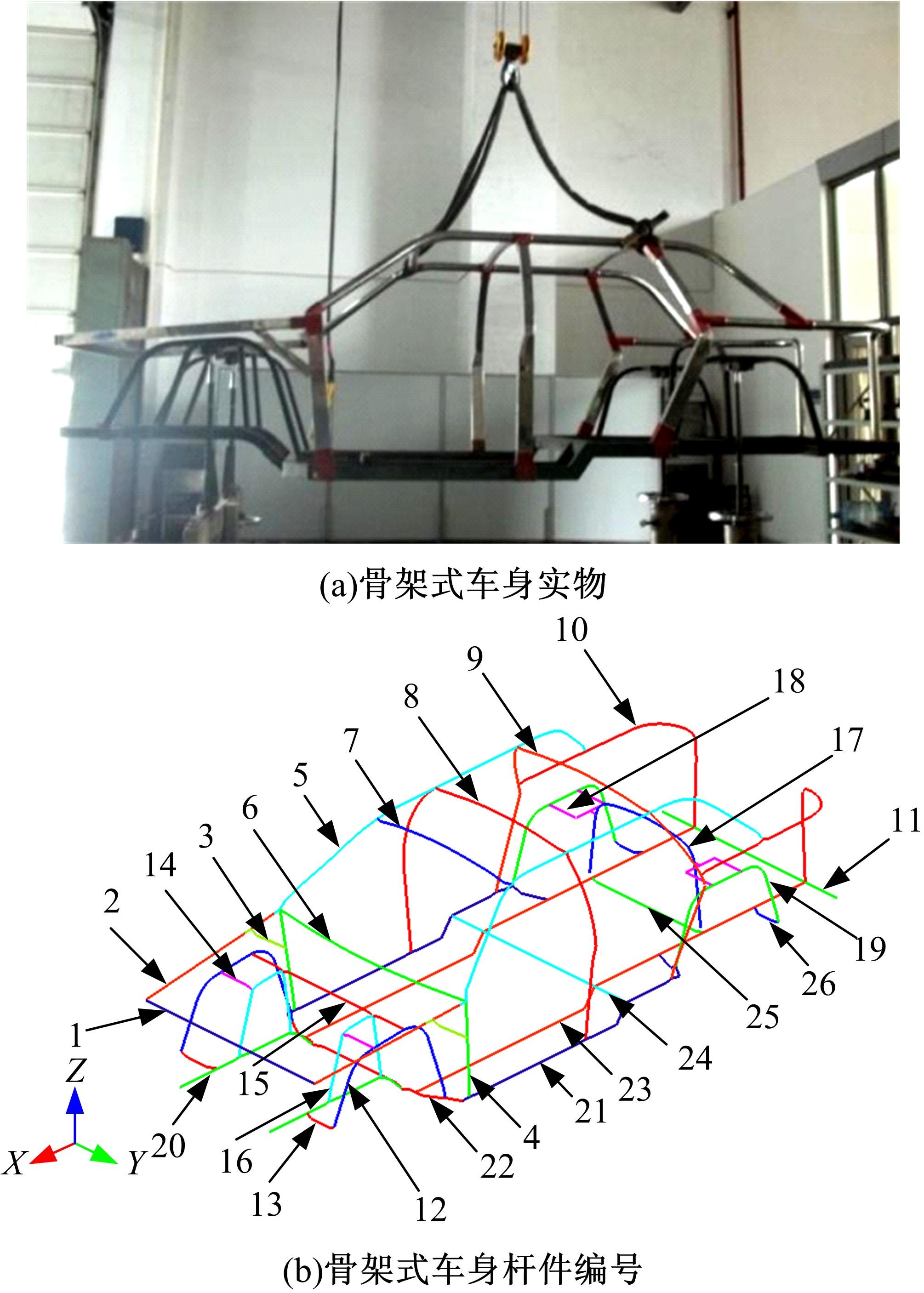
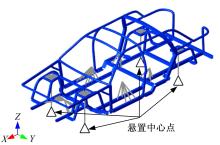
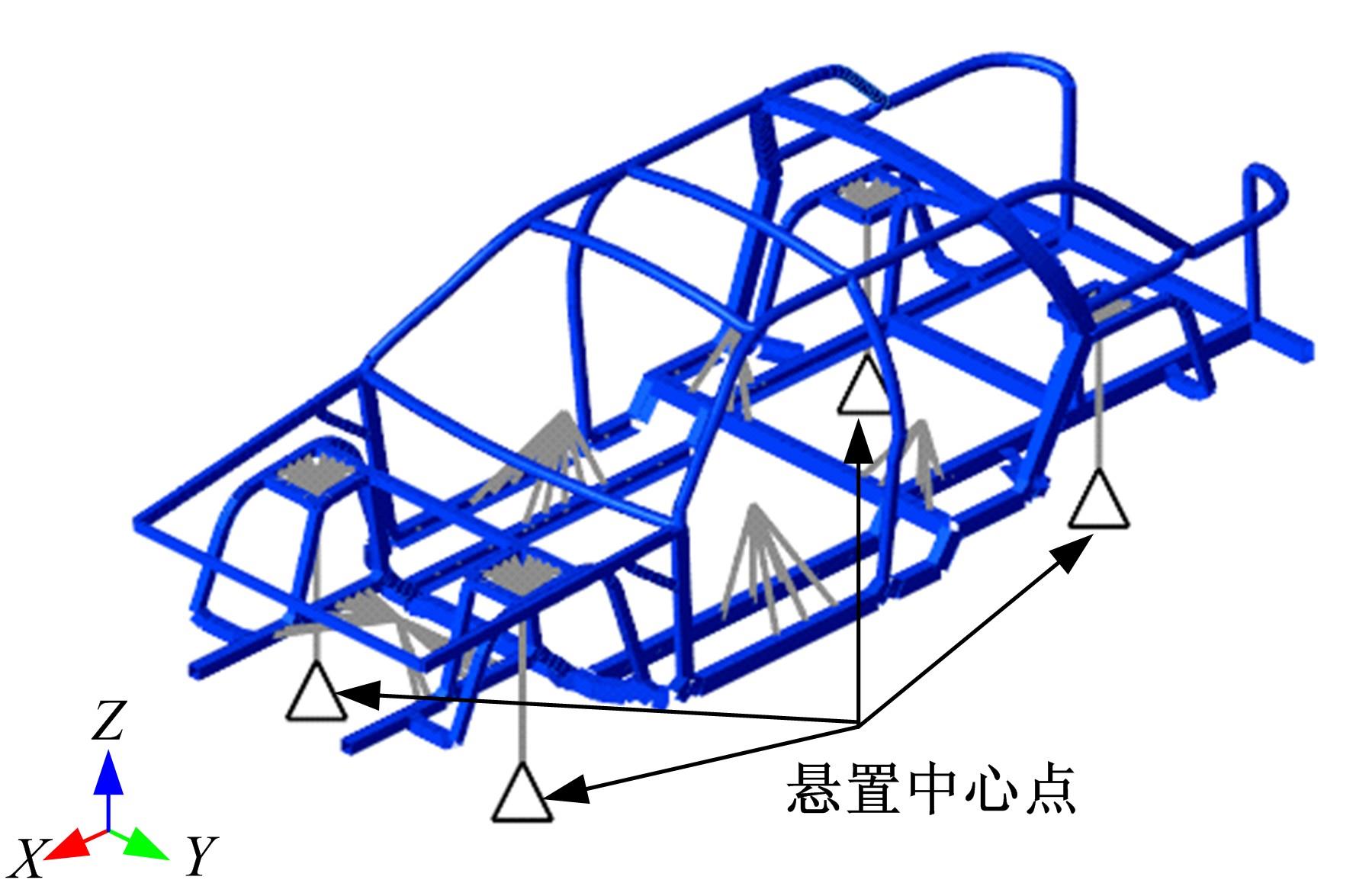
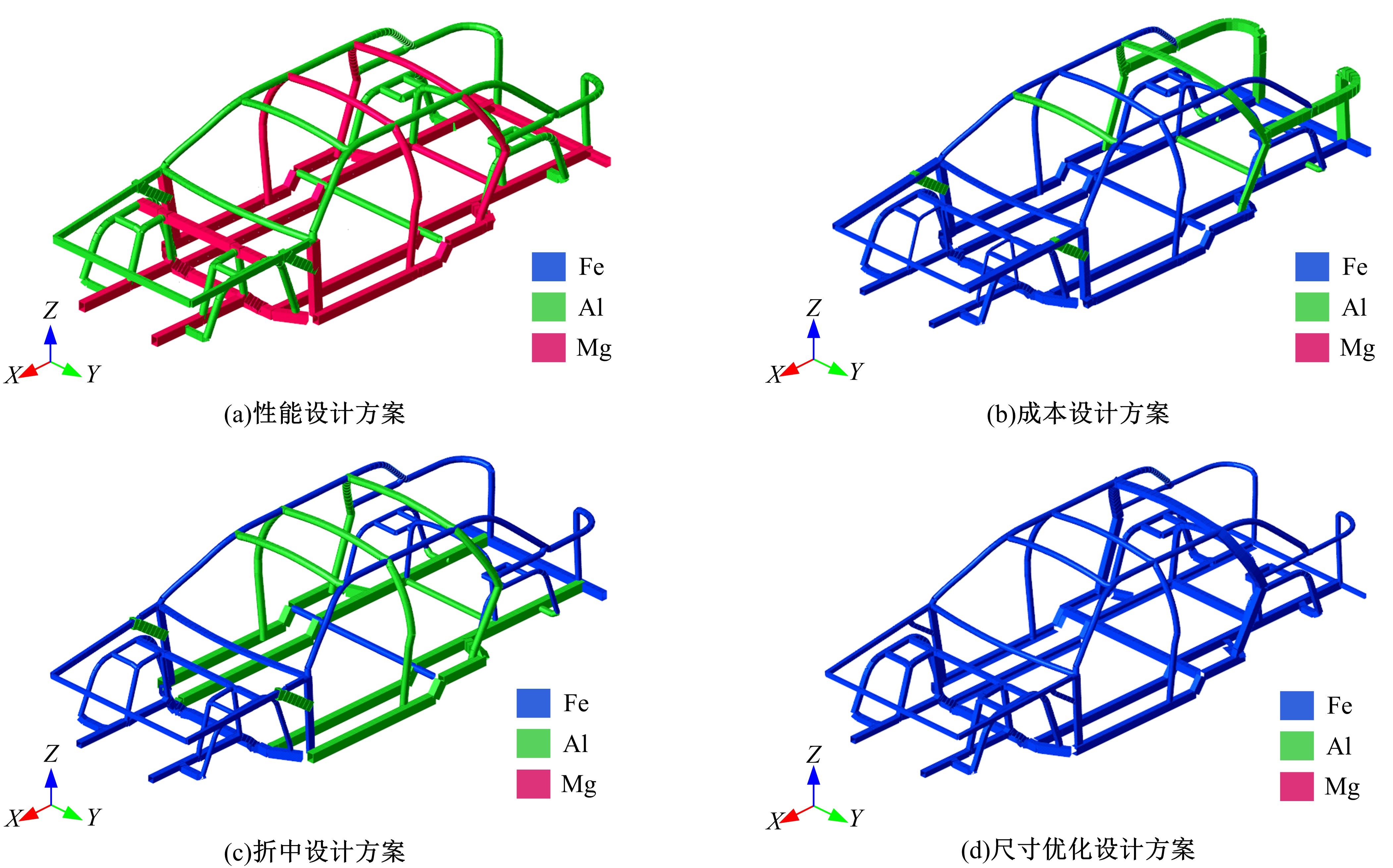
针对骨架式车身提出一种以材料类型、梁的截面形状和尺寸为离散设计变量的结构优化方法。基于某概念骨架式车身,以其总质量、制造成本、多种载荷工况下指定点的位移和结构中的最大轴向应力均最小,而以第一阶固有频率最大为目标函数,进行多目标优化。使用改进的第三代非支配排序遗传算法求解该多目标优化问题,并且综合考虑了轻量化设计、制造成本及结构性能因素,最终筛选出合理的设计方案。优化结果表明:相较于单一的离散尺寸优化,本文提出的考虑多种类型设计变量的结构优化方法,使轻量化设计效果更加优异。
中图分类号:
- U463
| 1 | 侯文彬, 张红哲, 徐金亭,等. 基于概念设计的客车车身结构设计与优化系统[J]. 湖南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 40(10): 58-63. |
| Hou Wen-bin, Zhang Hong-zhe, Xu Jin-ting, et al. System of design and optimization system for bus body structure based on concept design[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences), 2013, 40(10): 58-63. | |
| 2 | Gui C, Bai J, Zuo W. Simplified crashworthiness method of automotive frame for conceptual design[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2018, 131(10): 324-335. |
| 3 | 赵永宏, 李永成, 陈东, 等. 基于改进图分解法的多材料车身结构优化设计方法[J]. 汽车工程, 2020, 42(4): 560-566. |
| Zhao Yong-hong, Li Yong-cheng, Chen Dong, et al. Optimization design method of multi-material car body structure based on modified graphic decomposition[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2020, 42(4): 560-566. | |
| 4 | 王震虎, 王万林, 张松波, 等. 基于车身概念模型的白车身主断面尺寸优化[J]. 汽车工程, 2018, 40(8): 904-911. |
| Wang Zhen-hu, Wang Wan-lin, Zhang Song-bo, et al. Size optimization on main cross-sections of body-in-white based on conceptual model for car body[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2018, 40(8): 904-911. | |
| 5 | 那景新, 高剑峰. 基于局部搜索和整体优化的客车杆件截面参数正向设计[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2014, 44(6): 1564-1570. |
| Na Jing-xin, Gao Jian-feng. Top-down design method based on local search and global optimization for cross-sectional size of bus body[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(6): 1564-1570. | |
| 6 | 康元春, 李园, 高永正. 基于DOE方法的客车车身骨架尺寸优化[J]. 重庆交通大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 33(4): 160-163. |
| Kang Yuan-chun, Li Yuan, Gao Yong-zheng. Size optimization of bus body frame based on DOE[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University(Natural Sciences), 2014, 33(4): 160-163. | |
| 7 | 柯俊, 陈志勇, 史文库, 等. 基于振动控制的客车地板模态分析及结构优化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(3): 719-725. |
| Ke Jun, Cheng Zhi-yong, Shi Wen-ku, et al. Modal analysis and structure optimization of bus floor based on floor vibration control[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(3): 719-725. | |
| 8 | 苏瑞意, 桂良进, 王旭, 等. 燃料电池城市客车结构有限元分析与轻量化设计[J]. 汽车工程, 2008, 30(12): 1099-1102. |
| Su Rui-yi, Gui Liang-jin, Wang Xu, et al. Finite element analysis and light weight design of a fuel cell city bus structure[J].Automotive Engineering, 2008, 30(12): 1099-1102. | |
| 9 | 郑若瑜, 肖守讷, 朱涛, 等. 25T客车车体结构轻量化研究[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2017(11): 157-160. |
| Zheng Ruo-yu, Xiao Shou-ne, Zhu Tao, et al. Contrastive research on lightweight schemes of 25T locomotive body[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2017(11): 157-160. | |
| 10 | 范子杰. 基于多目标遗传算法的大客车骨架结构协同拓扑优化方法研究[C]∥第十二届设计与制造前沿国际会议(ICFDM2016)论文集, 沈阳, 2016: 488. |
| 11 | Cheng M, Prayogo D, Wu Y, et al. A hybrid harmony search algorithm for discrete sizing optimization of truss structure[J]. Automation in Construction, 2016, 69(9): 21-33. |
| 12 | Qin H, Guo Y, Liu Z, et al. Shape optimization of automotive body frame using an improved genetic algorithm optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2018, 121(7): 235-249. |
| 13 | 侯文彬, 王增飞, 张伟, 等. 基于复杂工程约束的车身梁截面优化设计[J]. 机械工程学报, 2014, 50(18): 127-133. |
| Hou Wen-bin, Wang Zeng-fei, Zhang Wei, et al. Optimization design for auto-body beam section based on complex engineering constraints[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(18): 127-133. | |
| 14 | Cui X, Zhang H, Wang S, et al. Design of lightweight multi-material automotive bodies using new material performance indices of thin-walled beams for the material selection with crashworthiness consideration[J].Materials and Design, 2011, 32(2): 815-821. |
| 15 | 兰凤崇, 陈元, 周云郊, 等. 轻质多材料动力电池包箱体选材与优化[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(4): 1227-1234. |
| Lan Feng-chong, Chen Yuan, Zhou Yun-jiao, et al. Multi-material selection and optimization of lightweight battery pack enclosure[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(4): 1227-1234. | |
| 16 | Tejani G G, Savsani V J, Patel V K, et al. Size, shape, and topology optimization of planar and space trusses using mutation-based improved metaheuristics[J]. Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, 2018, 5(2): 198-214. |
| 17 | Hasancebi O, Azad S K. Adaptive dimensional search: a new metaheuristic algorithm for discrete truss sizing optimization[J]. Computers & Structures, 2015, 154(7): 1-16. |
| 18 | Lieu Q X, Do D T T, Lee J. An adaptive hybrid evolutionary firefly algorithm for shape and size optimization of truss structures with frequency constraints[J]. Computers & Structures, 2018, 195(1): 99-112. |
| 19 | Kazemzadeh A S, Hasancebi O, Saka M P. Guided stochastic search technique for discrete sizing optimization of steel trusses: a design-driven heuristic approach[J]. Computers & Structures, 2014, 134(4): 62-74. |
| 20 | Sadollah A, Eskandar H, Bahreininejad A, et al. Water cycle, mine blast and improved mine blast algorithms for discrete sizing optimization of truss structures[J]. Computers & Structures, 2015, 149(3): 1-16. |
| 21 | Silih S, Kravanja S, Premrov M. Shape and discrete sizing optimization of timber trusses by considering of joint flexibility[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2010, 41(2): 286-294. |
| 22 | Lei F, Lv X, Fang G J, et al. Multiobjective discrete optimization using the TOPSIS and entropy method for protection of pedestrian lower extremity[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2020(152): 106349. |
| 23 | 田林雳. 骨架式车身结构及其力流分析方法研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学汽车学院, 2016. |
| Tian Lin-li. Research on framework of frame-type body and its load path analysis[D]. Shanghai: School of Automotive Studies, Tongji University, 2016. | |
| 24 | Deb K, Jain H. An evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm using reference-point based non-dominated sorting approach, part I: solving problems with box constraints[J]. Evolutionary Computation, IEEE Transactions on, 2014, 18(4): 577-601. |
| 25 | 高云凯, 马超, 刘哲, 等. 基于NSGA-III的白车身焊装生产平台的离散拓扑优化[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2020, 54(12): 1324-1334. |
| Gao Yun-kai, Ma Chao, Liu Zhe, et al. Discrete topology optimization of body-in-white welding production platform based on NSGA-III[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University,2020, 54(12): 1324-1334. | |
| 26 | 高云凯, 段少东. 基于NSGA-Ⅱ算法的客车底架的离散拓扑优化[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 45(11): 92-97. |
| Gao Yun-kai, Duan Shao-dong. Discrete topology optimization of bus chassis frame based on NSGA-Ⅱ[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2017, 45(11): 92-97. |
| [1] | 罗勇,韦永恒,黄欢,肖人杰,任淋,崔环宇. 驾驶员意图识别的P2.5插混构型双离合器起步控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1575-1582. |
| [2] | 杨建,夏琦,周海超,王国林. 修正胎体弦轮廓载重子午线轮胎的降噪机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1198-1203. |
| [3] | 龙江启,向锦涛,俞平,王骏骋. 适用于非线性主动悬架滑模控制的线性干扰观测器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1230-1240. |
| [4] | 陈鑫,于贵申,张彪,潘凯旋,杨立飞. 搅拌摩擦点焊接头拉伸-剪切行为的等效建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1190-1197. |
| [5] | 金立生,郭柏苍,王芳荣,石健. 基于改进YOLOv3的车辆前方动态多目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1427-1436. |
| [6] | 兰凤崇,李继文,陈吉清. 面向动态场景复合深度学习与并行计算的DG-SLAM算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1437-1446. |
| [7] | 王波,何洋扬,聂冰冰,许述财,张金换. 底部爆炸条件下车内乘员的腹部损伤[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 792-798. |
| [8] | 庄蔚敏,王鹏跃,高瑞娟,解东旋. 温热成形对AA5754铝合金静态力学性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 847-854. |
| [9] | 宋强,孙丹婷,章伟. 纯电动车机械式自动变速器换挡非线性建模及控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 810-819. |
| [10] | 张家旭,王欣志,赵健,施正堂. 汽车高速换道避让路径规划及离散滑模跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1081-1090. |
| [11] | 袁哲明,袁鸿杰,言雨璇,李钎,刘双清,谭泗桥. 基于深度学习的轻量化田间昆虫识别及分类模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1131-1139. |
| [12] | 何仁,赵晓聪,杨奕彬,王建强. 基于驾驶人风险响应机制的人机共驾模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 799-809. |
| [13] | 宋大凤,杨丽丽,曾小华,王星琦,梁伟智,杨南南. 基于行驶工况合成的混合动力汽车电池寿命优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 781-791. |
| [14] | 陈国迎,姚军,王鹏,夏其坤. 适用于后轮轮毂驱动车辆的稳定性控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 397-405. |
| [15] | 王伟达,武燕杰,史家磊,李亮. 基于驾驶员意图识别的电子液压制动助力系统控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 406-413. |
|
||