吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1375-1385.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210062
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
多孔沥青混合料的动态模量及其预估模型
- 1.重庆交通大学 土木工程学院,重庆 400074
2.广西交通投资集团有限公司,南宁 530022
Dynamic modulus of porous asphalt concrete and its prediction model
Zhao-yi HE1( ),Jin-feng LI1,Wen ZHOU2,Zhi-tao GUAN1
),Jin-feng LI1,Wen ZHOU2,Zhi-tao GUAN1
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
2.Guangxi Communications Investment Group Corporation Ltd. ,Nanning 530022,China
摘要:
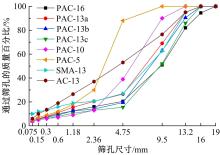
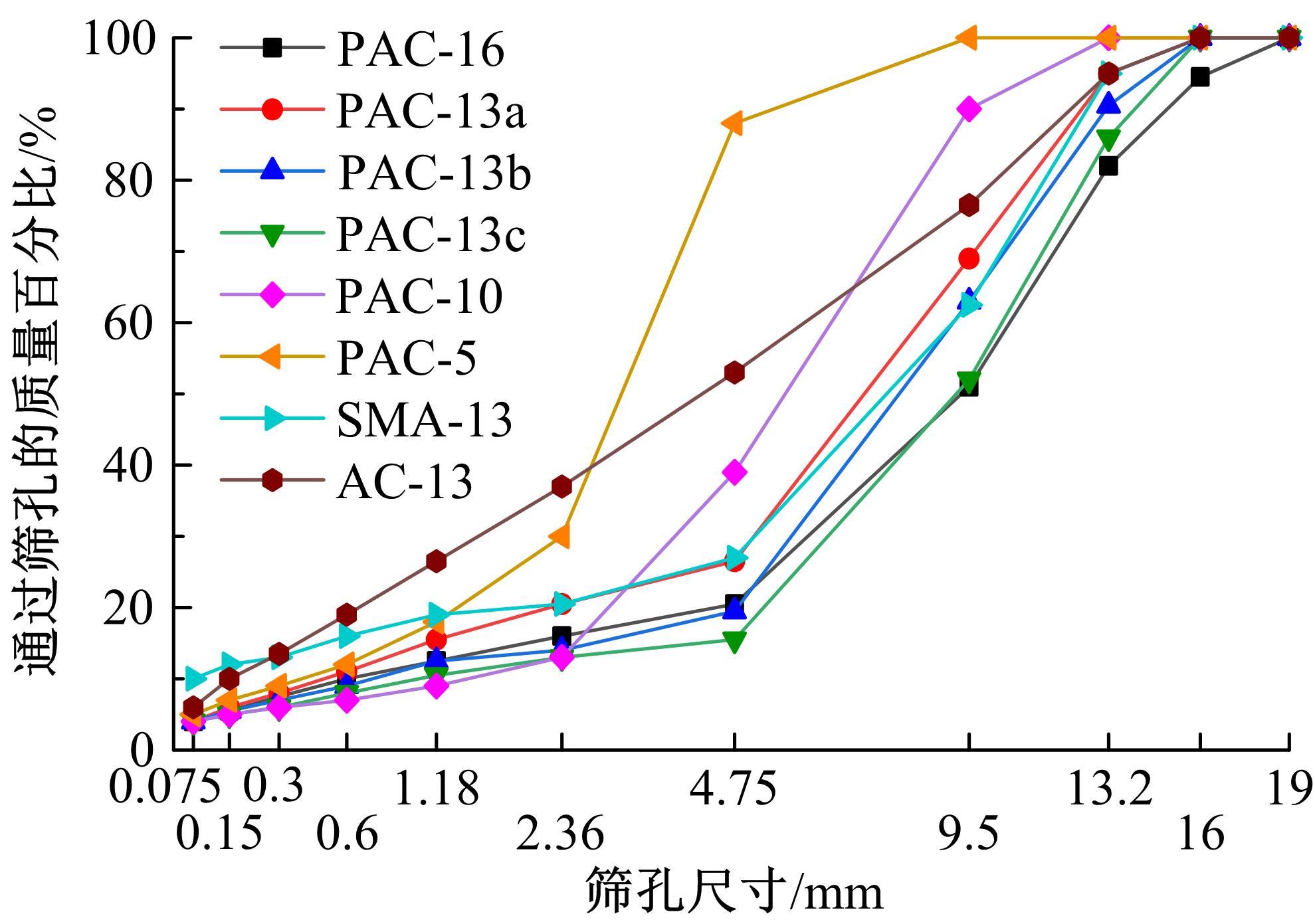
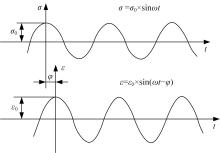
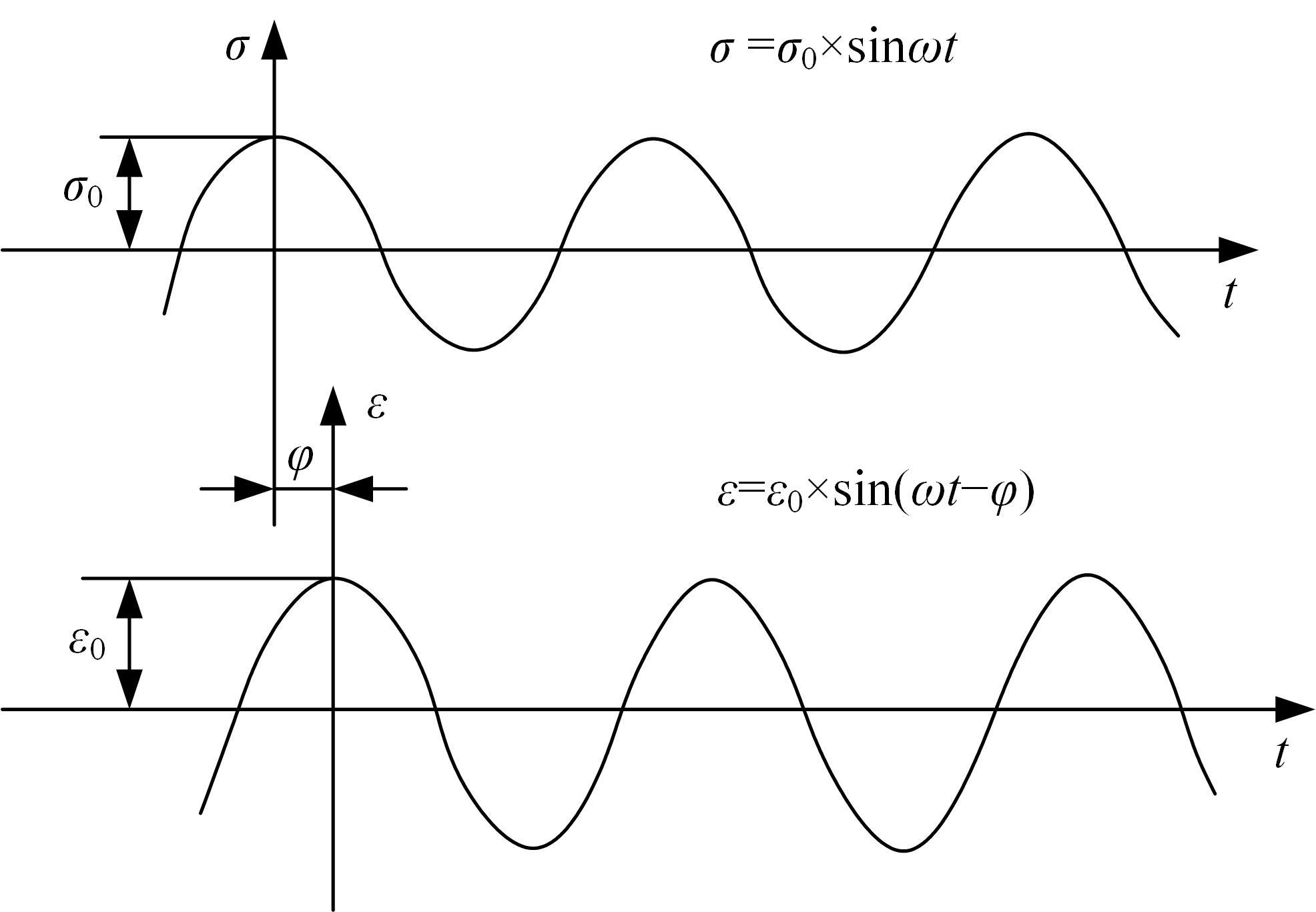
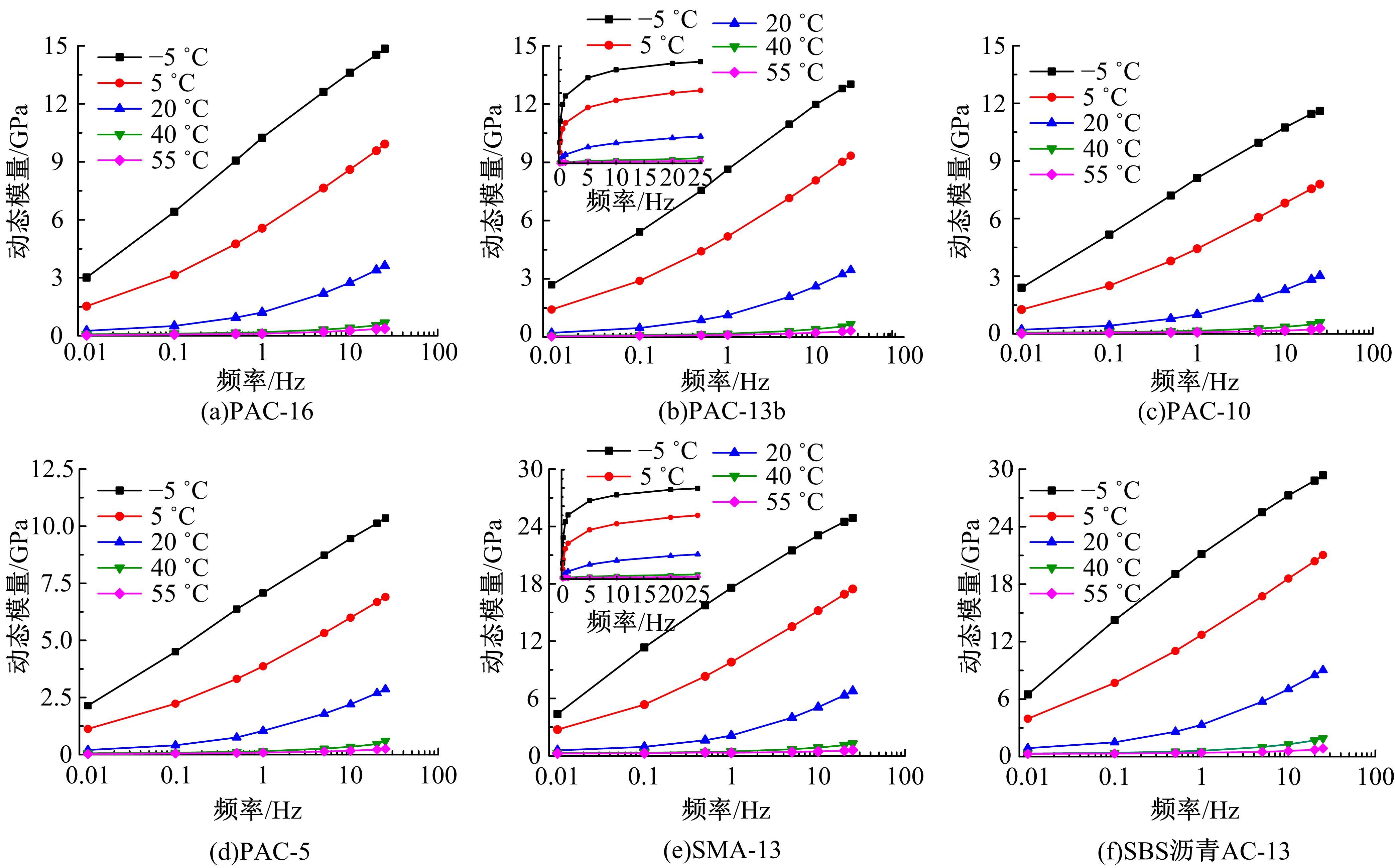
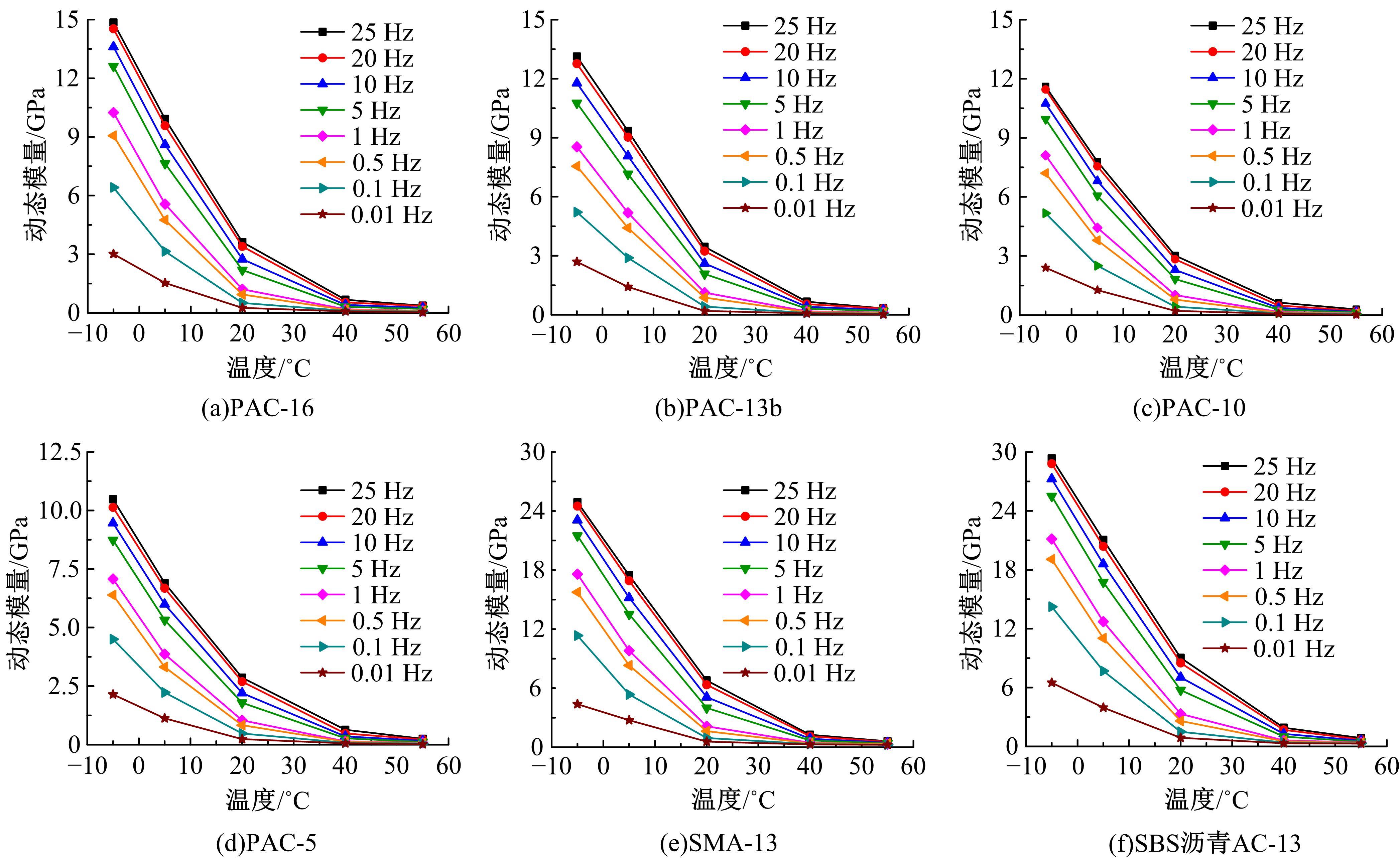
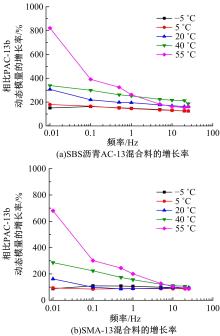
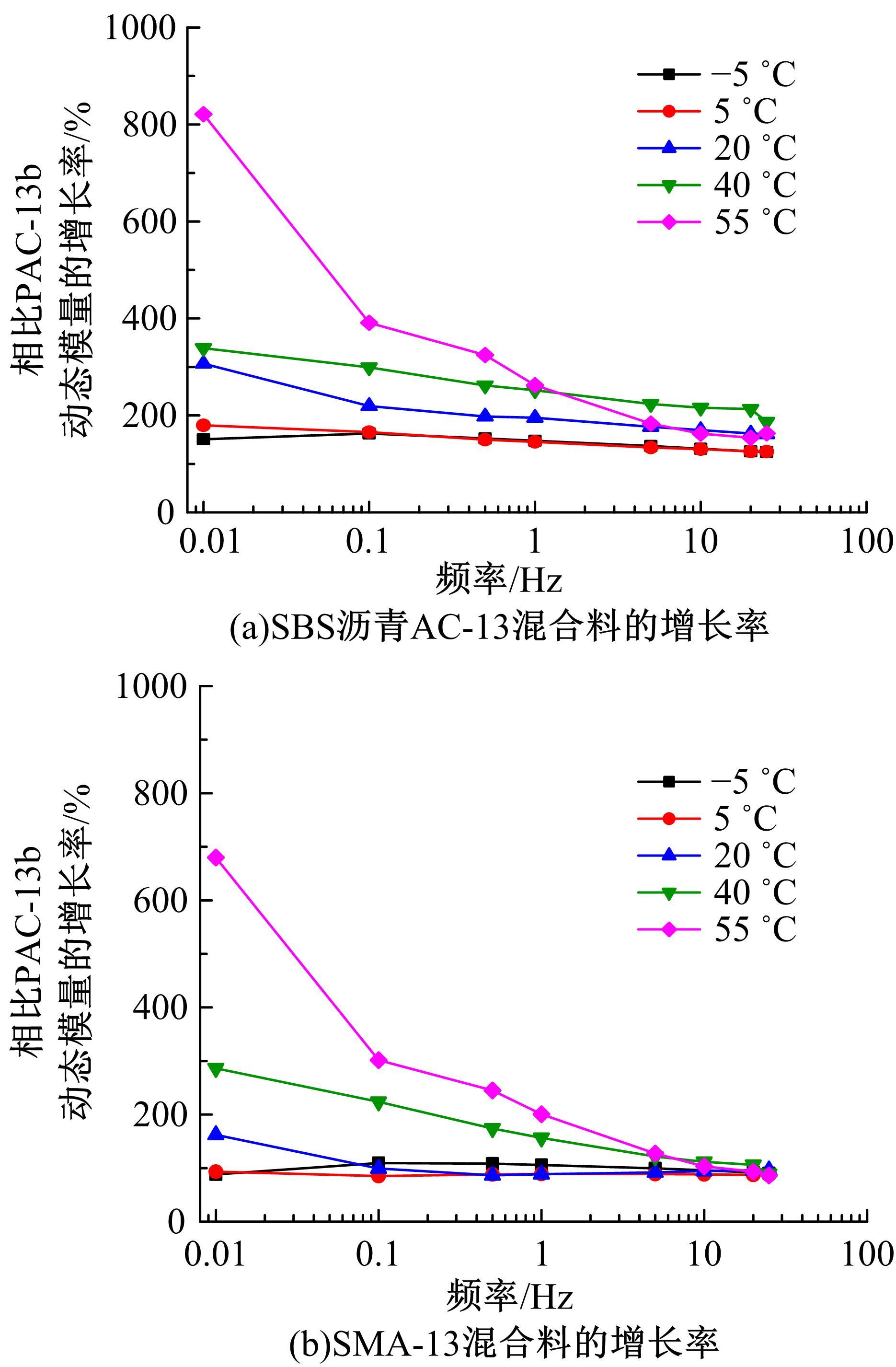
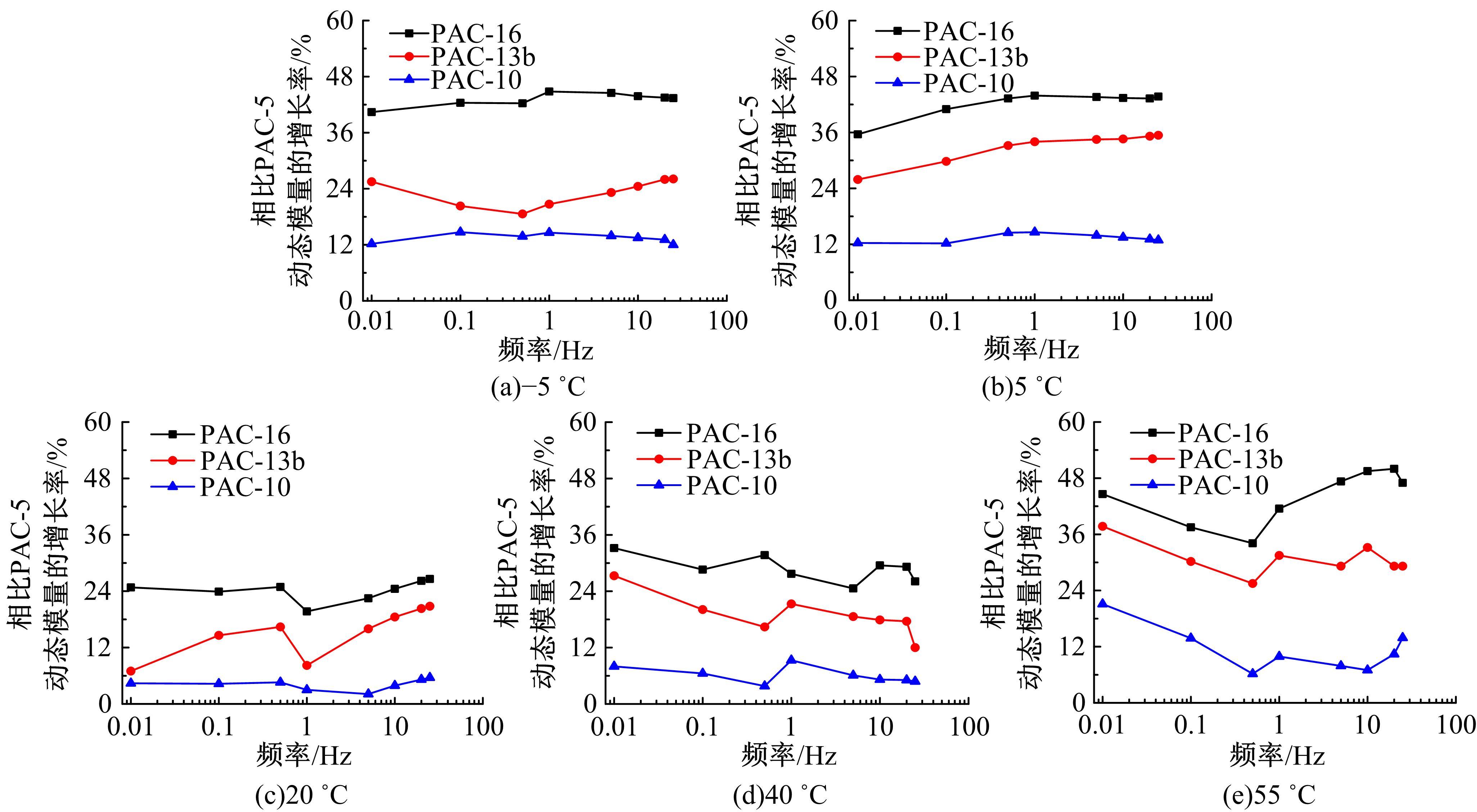
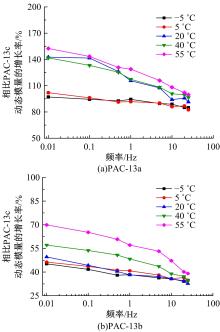
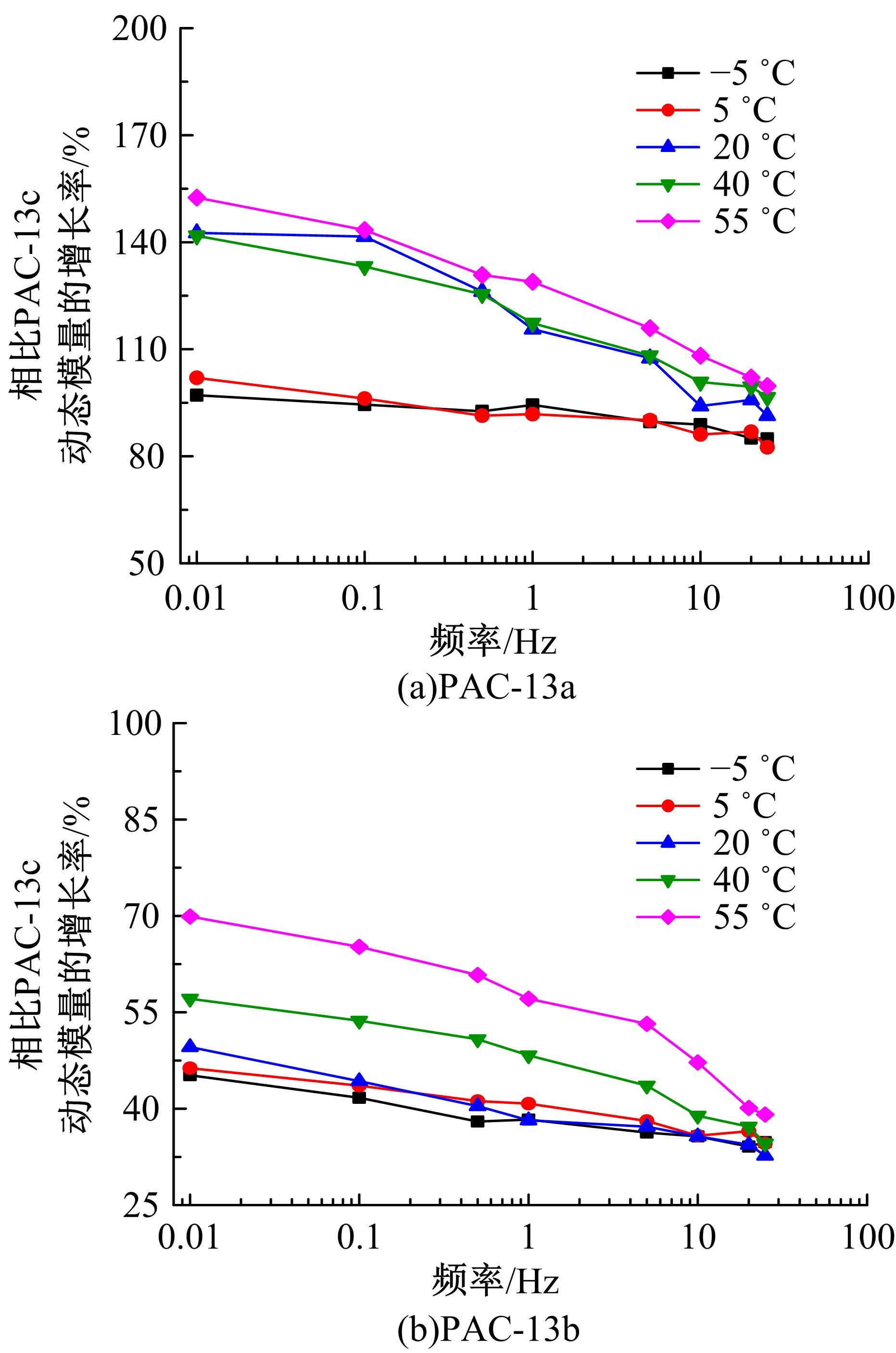
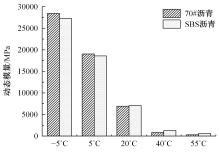
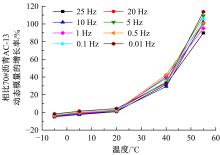
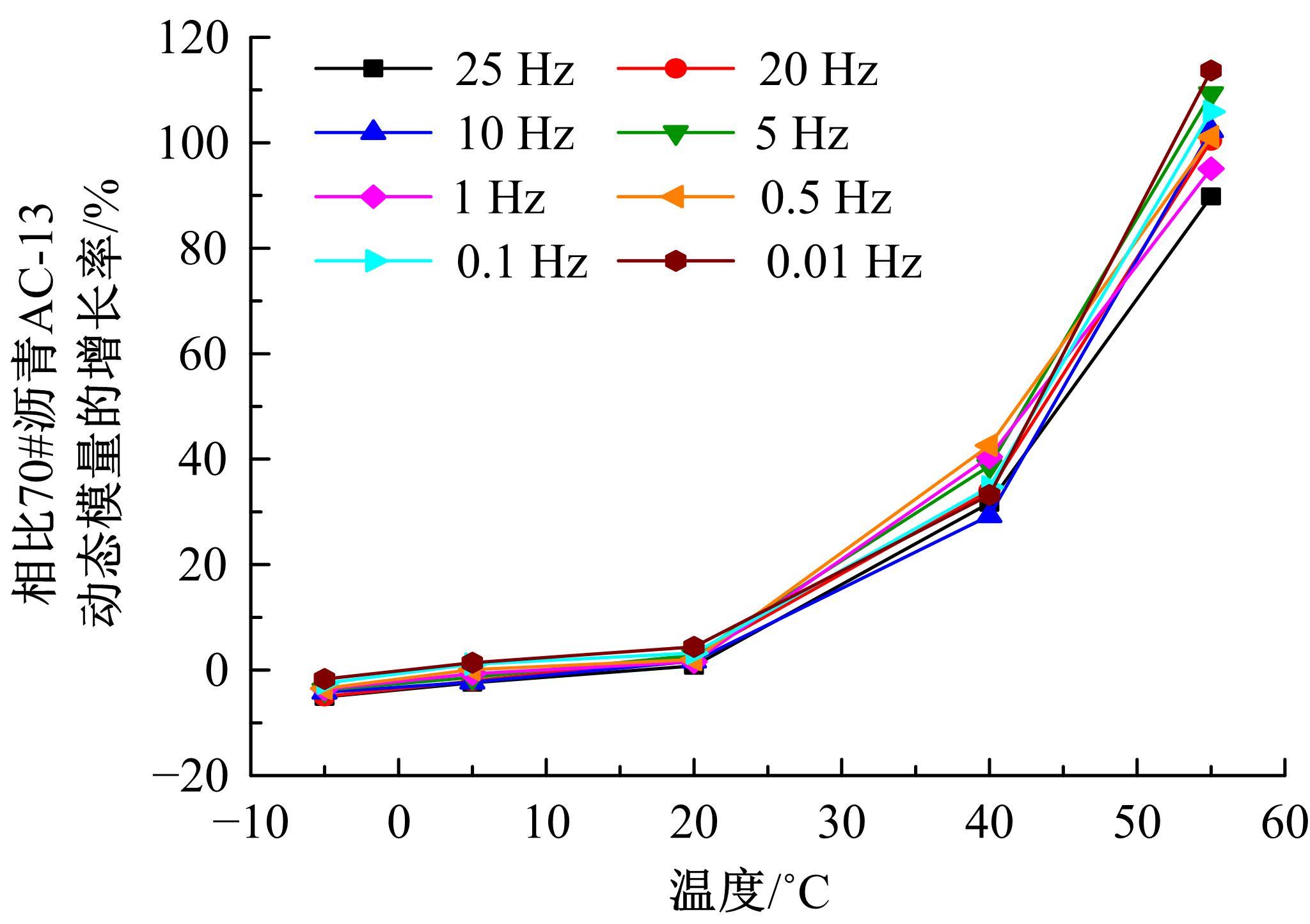
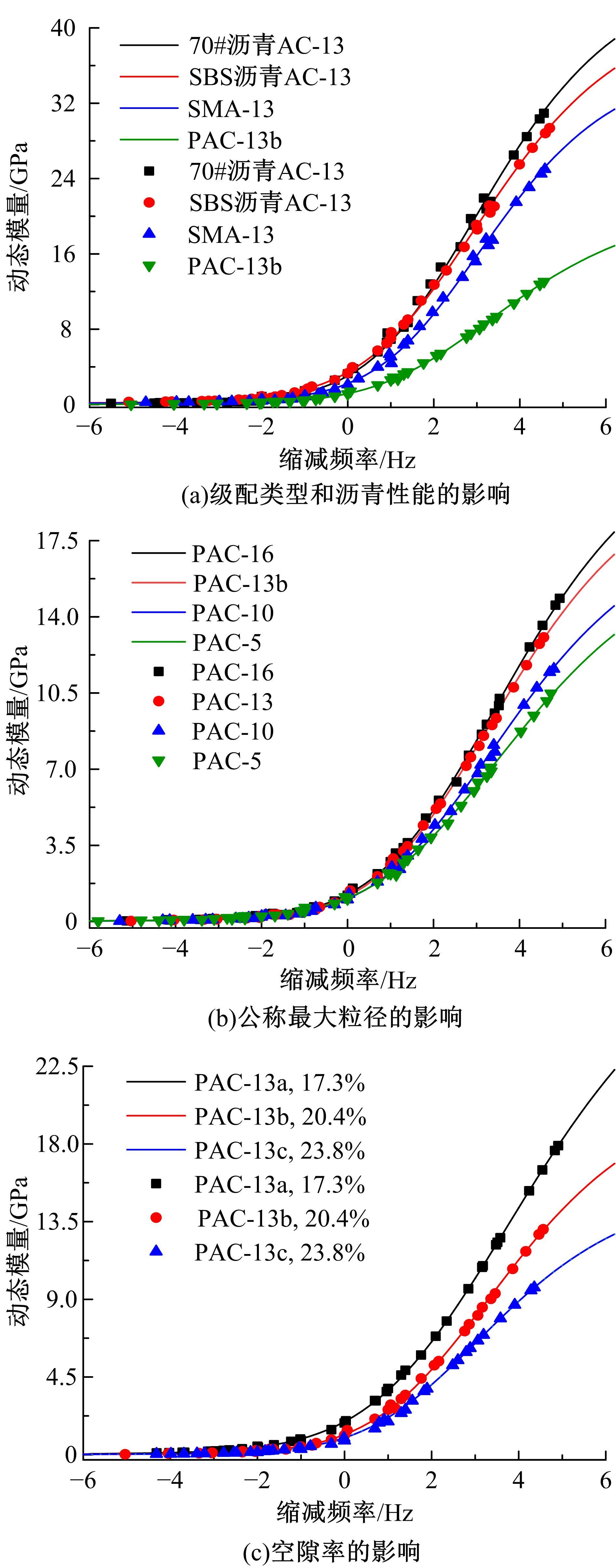
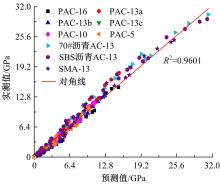
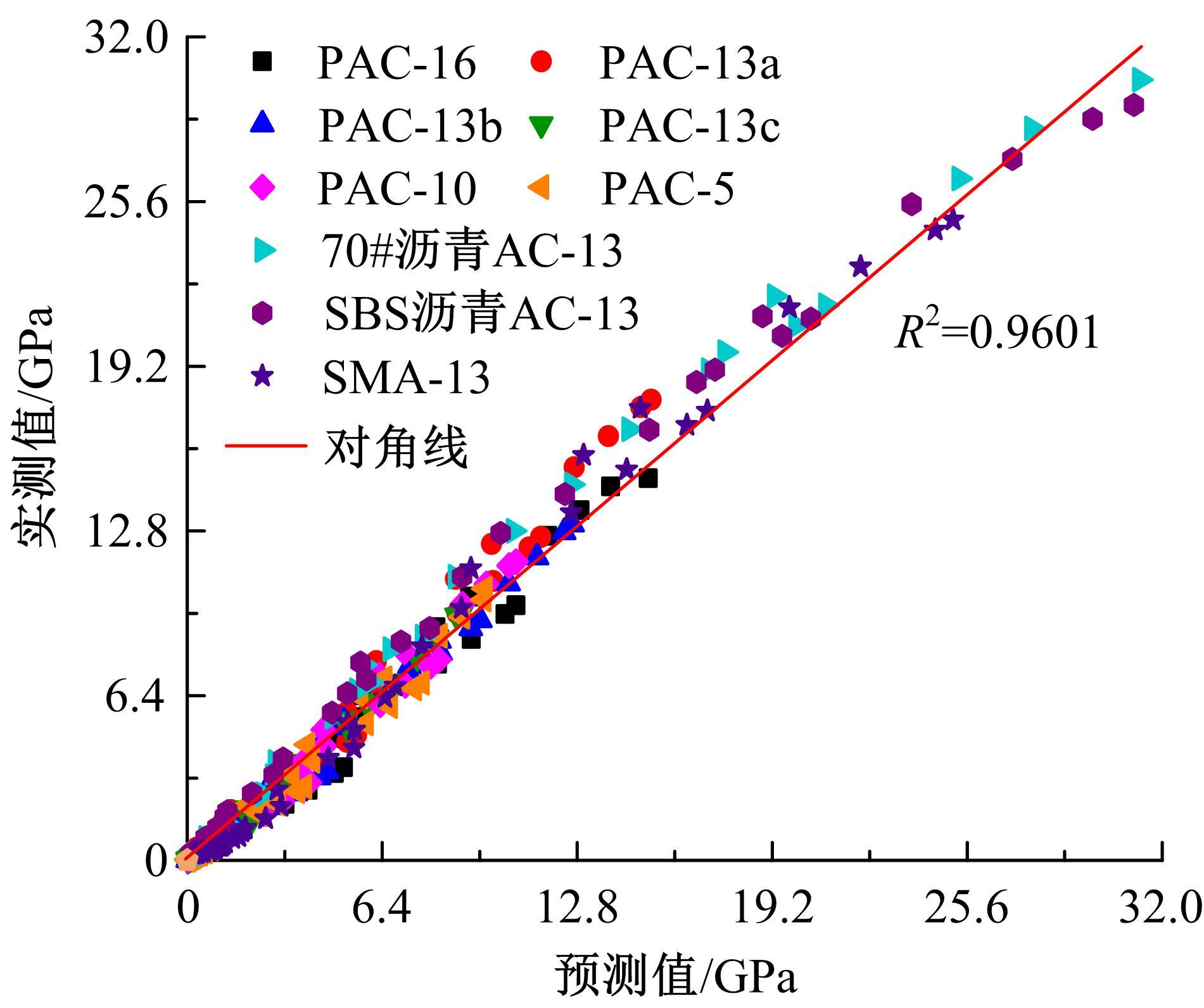
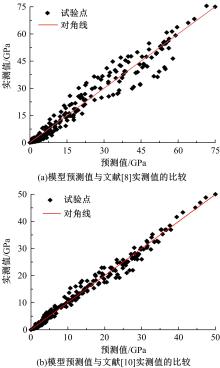
针对连续密级配沥青混合料AC-13、沥青玛蹄脂碎石SMA-13以及6种多孔沥青混合料(PAC-16、PAC-13a、PAC-13b、PAC-13c、PAC-10和PAC-5)开展了不同荷载频率和温度下的动态模量试验。试验结果显示:沥青混合料的动态模量随着加载频率的增大而增大,随着温度的升高而减小,变化幅度均呈逐渐减小趋势;相比空隙率为20.3%的PAC-13b,SBS沥青AC-13和SMA-13混合料的动态模量分别平均增加了196.8%和125.1%;空隙率相近的情况下,多孔沥青混合料的动态模量随着公称最大粒径的增大略有增大;公称最大粒径相同时,空隙率减小了1%,多孔沥青混合料的动态模量平均增加了约15.8%。基于时-温度等效原理,构建了移位因子与温度的关系表达式,利用Sigmoidal模型推导计算了混合料动态模量的主曲线;综合考虑了加载频率、试验温度、沥青黏度、混合料体积特性及集料级配等多个因素的影响,建立了适用于不同级配沥青混合料动态模量的预估模型,预测值与实测结果具有较高吻合度,说明该模型能够应用于沥青路面的结构设计和分析。
中图分类号:
- U414
| 1 | 陈俊, 姚成, 周若愚, 等. 多孔沥青混合料渗水性能的方向差异性及其受空隙结构的影响[J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 48(5): 920-926. |
| Chen Jun, Yao Cheng, Zhou Ruo-yu, et al. Directional differentce of water permeability of porous asphalt mixture and influence of pore structure[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 48(5): 920-926. | |
| 2 | Chu L, Fwa T F, Tan K H. Eveluation of wearing course mix designs on sound absorption improvement of porous asphalt pavement[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 141: 402-409. |
| 3 | Zhang Y, Wang L, Zhang W, et al. Modified dynamic modulus test and customised prediction model of asphalt-treated drainage layer material for M-E pavement design[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2016, 17(9): 818-828. |
| 4 | Loulizt A, Al-Qadi I L, Elseifi M. Difference between in situ flexible paavement measure and calculated stresses and strains[J]. Journa of Transportation Engineering, 2006, 132(7): 574-579. |
| 5 | Lee J, Moon S J, Im J, et al. Evaluation of moisture susceptibility of asphalt mixtures using dynamic modulus[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 2017, 45(4): No. 20150136. |
| 6 | Akbarzadeh H, Bayat A, Soleymani H R. Analytical review of the HMA temperature correction factors from laboratory ans falling weight deflectometer tests[J]. International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology, 2012, 5(1): 30-39. |
| 7 | Zhang Y, Luo R, Lytton R L. Characterizing permanent deformation and fracture of asphalt mixture by using compressive dynamic modulus tests[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2012, 24(7): 898-906. |
| 8 | Cho Y H, Park D W, Hwang S D. A predictive equation for dynamic modulus of asphalt mixture used in Korea[J]. Construction and Building Material, 2010, 24(4): 513-519. |
| 9 | Irfan M, Waraich A S, Ahmed S, et al. Characterization of various plant-ptoduced asphalt concrete mixture using dynamic modulus test[J]. Advances in materials Science and Engineering, 2016, 14(2):1-12. |
| 10 | Weldegiorgis M T, Tarefder R A. Prescision study for dynamic modulus testing of asphalt concrete using independent assurance testing[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2015, 27(3):04014133. |
| 11 | Wen Y, Wang Y. Effect of oxidative aging on dynamic modulus of hot-mix asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2019, 31(1): 1-15. |
| 12 | Nobakht M, Sakhaeifar M S. Dynamic modulus and phase angel prediction of laboratory aged asphalt mixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 190: 740-751. |
| 13 | Arefin S, Quasem T, Nazzal M, et al. Accuracy of MEPDG dynamic modulus predictions for short-term and long-term aged asphalt mixtures[J] Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part B: 2019, 145(3): No. 04019025. |
| 14 | 张金喜, 姜凡, 王超, 等. 室内外老化沥青混合料动态模量评价[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2017, 20(6): 937-942. |
| Zhang Jin-xi, Jiang Fan, Wang Chao, et al. Dynamic modulus evaluation of indoor and outdoor aging aspahalt mixture[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2017, 20(6): 937-942. | |
| 15 | Zhao Y, Tang J, Liu H. Construction of triaxial dynamic modulus master curve for aspahtl mixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 37: 21-26. |
| 16 | Nguyen T H, Ahn J, Lee J, et al. Dynamic modulus of porous asphalt and the effect of moisture conditioning[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(8): No.1230. |
| 17 | Ruan L, Luo R, Hu X, et al. Effect of bell-shaped loading and haversine loading on the dynamic modulus and resilient modulus of asphalt mixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 161: 124-131. |
| 18 | Al-Adham K, Baig M G, Wahhab H A A. Prediction of dynamic modulus for elstomer-modified asphalt concrete mixes at desert environment[J]. Arabin Journal for Science and Engineering, 2019, 44: 4141-4149. |
| 19 | 谭忆秋, 傅锡光, 马韶军, 等. 基于无约束共振法沥青混合料动态模量试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2015, 48(12): 116-122. |
| Tan Yi-qiu, Fu Xi-guang, Ma Shao-jun, et al. Experimental study on dynamic modulus of asphalt mixture based on free-free resonant test[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2015, 48(12): 116-122. | |
| 20 | 吴浩, 张久鹏, 王秉刚. 多孔沥青混合料空隙特征与路用性能关系[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2010, 10(1): 1-5. |
| Wu Hao, Zhang Jiu-peng, Wang Bing-gang. Relationship between characteristic of void and road performance of porous asphalt mixture[J], Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2010, 10(1): 1-5. | |
| 21 | 公路沥青路面施工技术规范 [S]. |
| 22 | . 公路工程沥青及沥青混合料试验规程 [S]. |
| 23 | AA . Standard test method for determining the dynamic modulus of hot-mix asphalt[S]. |
| 24 | Mirza MW, Witczak M W. Development of a global aging system for shaor and long term aging of asphalt cement[J]. Journal of Associate Asphalt Pavement Technology, 1995, 64: 393-430. |
| 25 | Zhao S, Liu J, Li P, et al. Dynamic modulus characterization of Alaskan asphalt mixtures for mechanistic-empirical pavement design[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2017, 29(11):No. 04017213. |
| [1] | 谷拴成,聂红宾. 极温冻融-荷载作用下碳纤维复合材料修复试件损伤分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2108-2120. |
| [2] | 周靖,黎亚军,赵卫锋,罗宗健,补国斌. 胶合竹板-钢管约束收尘石粉混凝土柱的偏压性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2096-2107. |
| [3] | 张广泰,张路杨,邢国华,曹银龙,易宝. 钢-聚丙烯混杂纤维混凝土剪力墙抗震性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 946-955. |
| [4] | 刘柳,冯卫星. 基于NNBR模型的隧道盾构施工地表沉降实测与计算分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 245-251. |
| [5] | 许卫晓,程扬,杨伟松,鞠佳昌,于德湖. RC框架⁃抗震墙并联结构体系拟静力试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 268-277. |
| [6] | 单德山,张潇,顾晓宇,李乔. 斜拉索悬链线构形的伸长量解析计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 217-224. |
| [7] | 薛素铎,鲁建,李雄彦,刘人杰. 跳格布置对环形交叉索桁结构静动力性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1687-1697. |
| [8] | 王勃,董元正,董丽欣. 基于短期风速资料的基本风压计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1739-1746. |
| [9] | 李明,王浩然,赵唯坚. 单向带抗剪键叠合板的受力性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 654-667. |
| [10] | 王鹏辉,乔宏霞,冯琼,曹辉,温少勇. 氯氧镁涂层钢筋混凝土两重因素耦合作用下的耐久性模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 191-201. |
| [11] | 李明,王浩然,赵唯坚. 带抗剪键叠合板的力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1509-1520. |
| [12] | 张军,钱诚,郭春燕,钱玉君. 基于多源时空数据的建筑宜居性动态设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1169-1173. |
| [13] | 梁宁慧,缪庆旭,刘新荣,代继飞,钟祖良. 聚丙烯纤维增强混凝土断裂韧度及软化本构曲线确定[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1144-1152. |
| [14] | 张磊,刘保国,储昭飞. 深厚孔隙砂岩含水层疏干排水对盾构斜井的 影响模型试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 788-797. |
| [15] | 李伊,刘黎萍,孙立军. 沥青面层不同深度车辙等效温度预估模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1703-1711. |
|
||