吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1264-1272.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210068
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
Hybird III假人模型与CHUBM人体生物力学模型的正碰损伤对比
- 1.华南理工大学 机械与汽车工程学院,广州 510640
2.华南理工大学 广东省汽车工程重点实验室,广州 510640
Comparison of injuries in front impact between Hybird III dummy model and CHUBM human biomechanical model
Xiong LI1,2( ),Feng-chong LAN1,2,Ji-qing CHEN1,2(
),Feng-chong LAN1,2,Ji-qing CHEN1,2( ),Fang TONG1,2
),Fang TONG1,2
- 1.School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,China
2.Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Automotive Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,China
摘要:
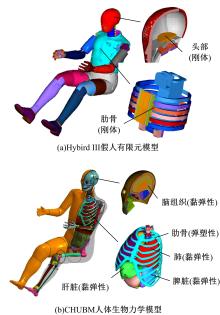
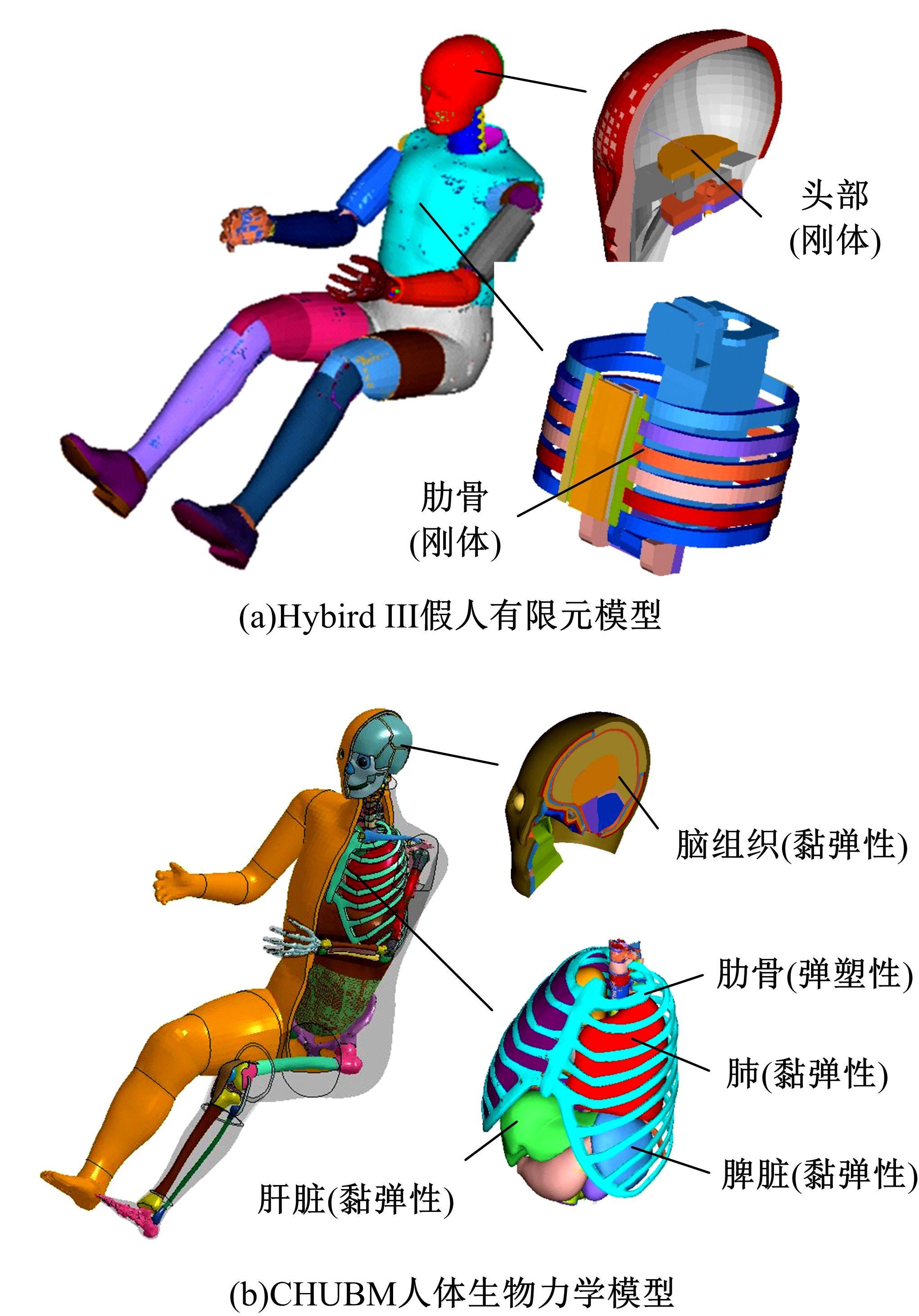
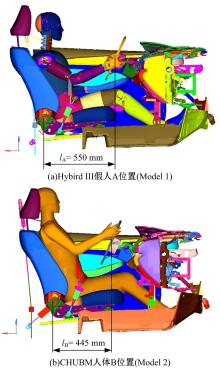
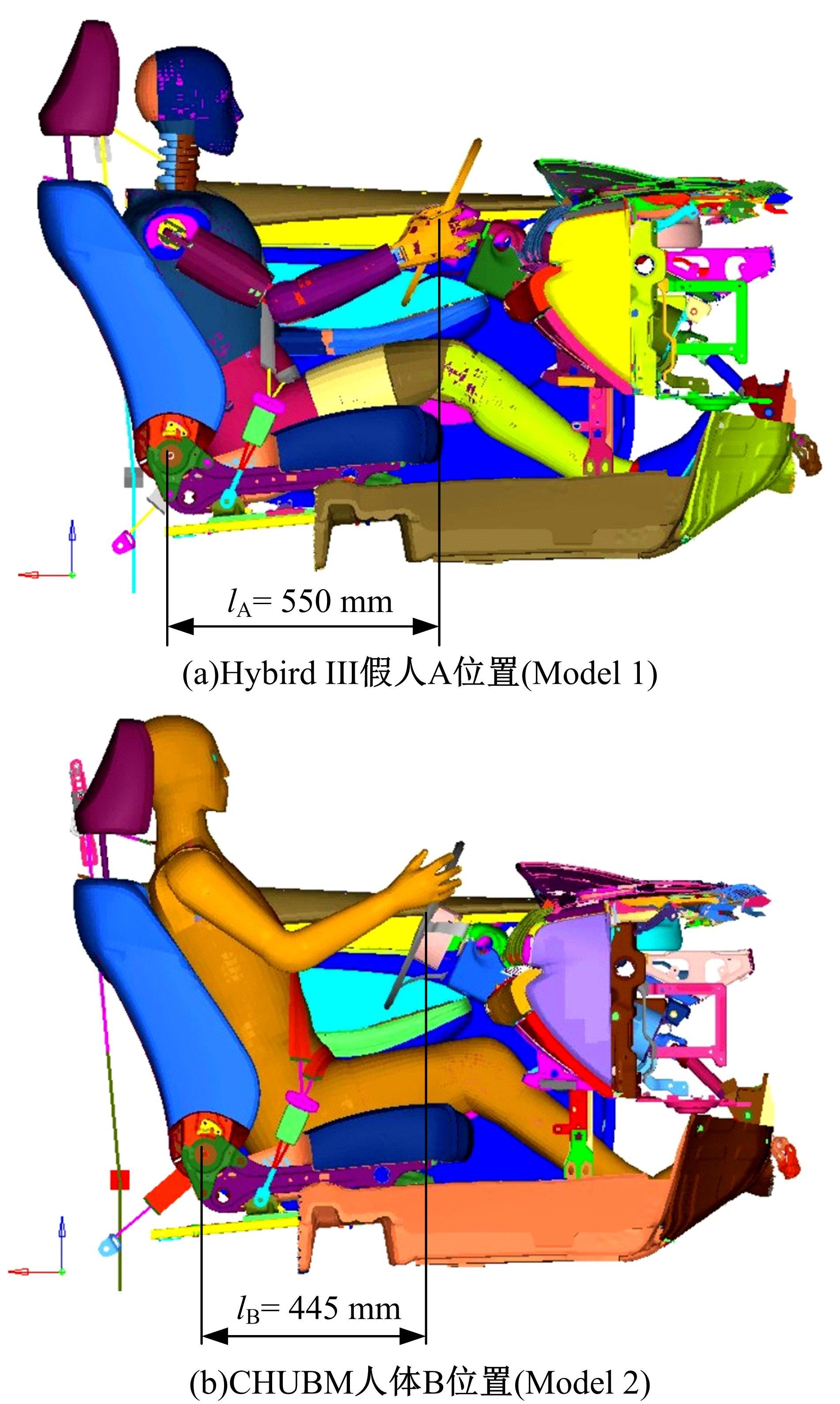
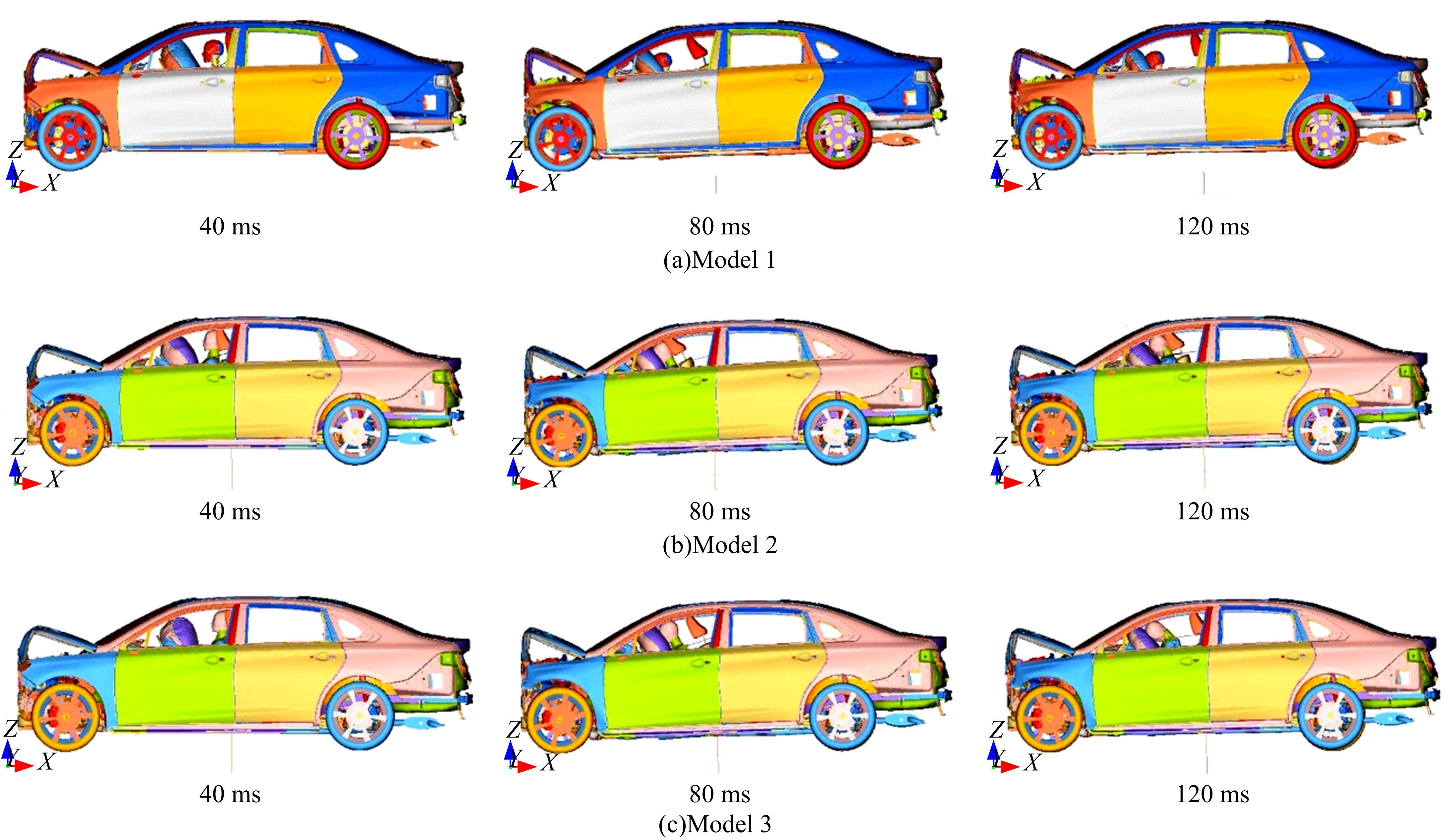
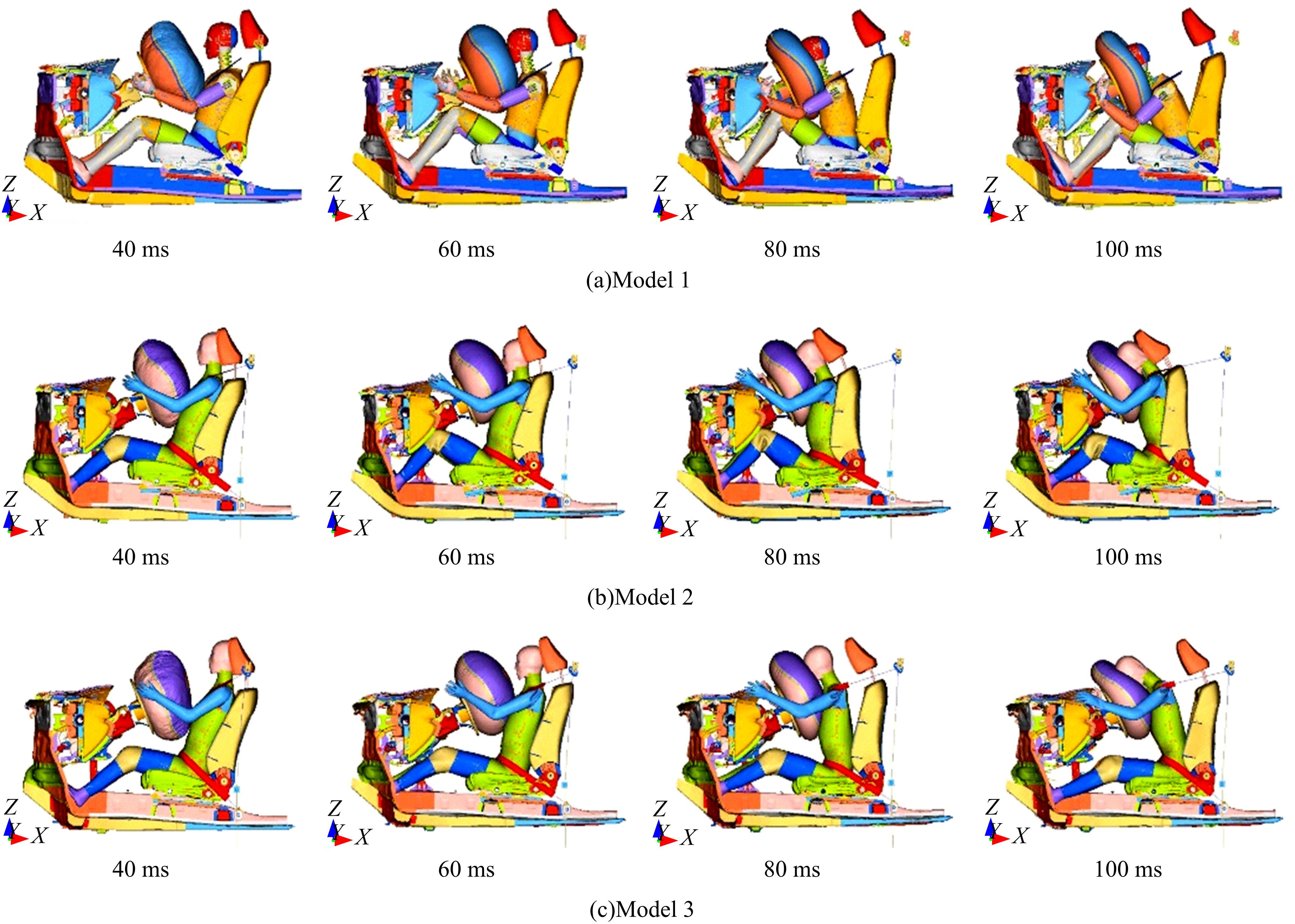
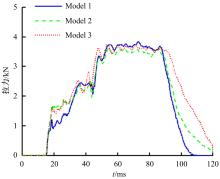
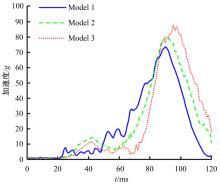
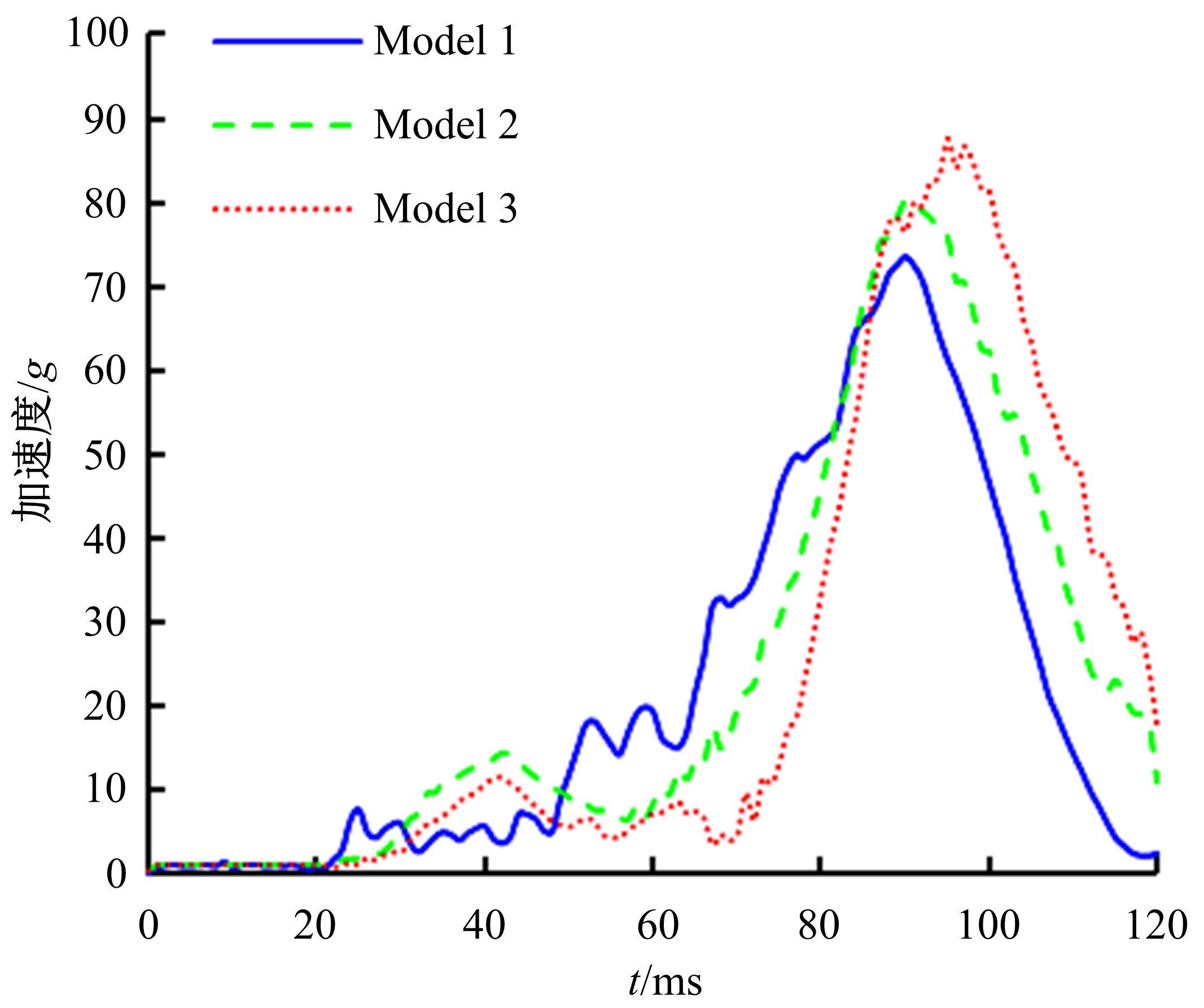
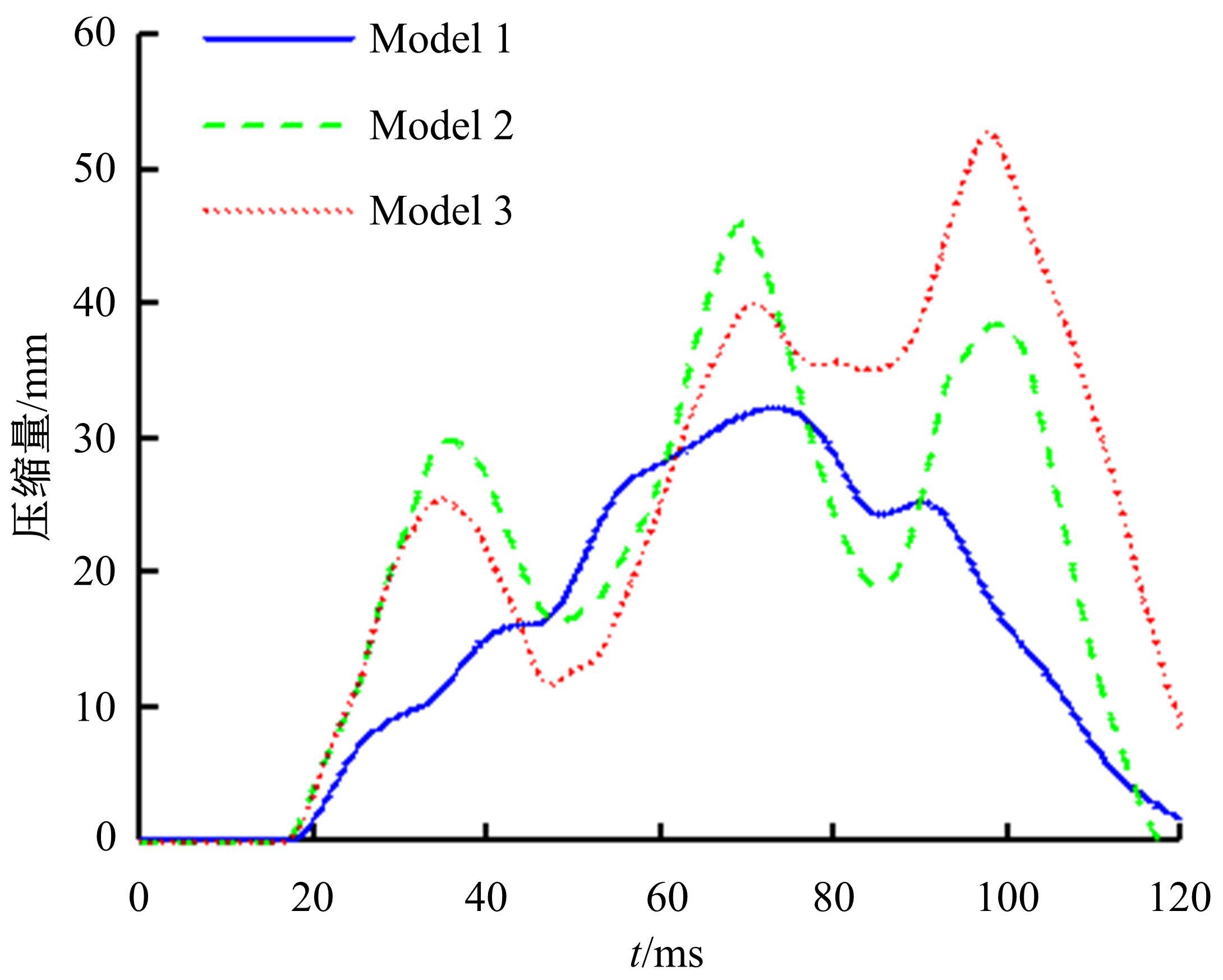
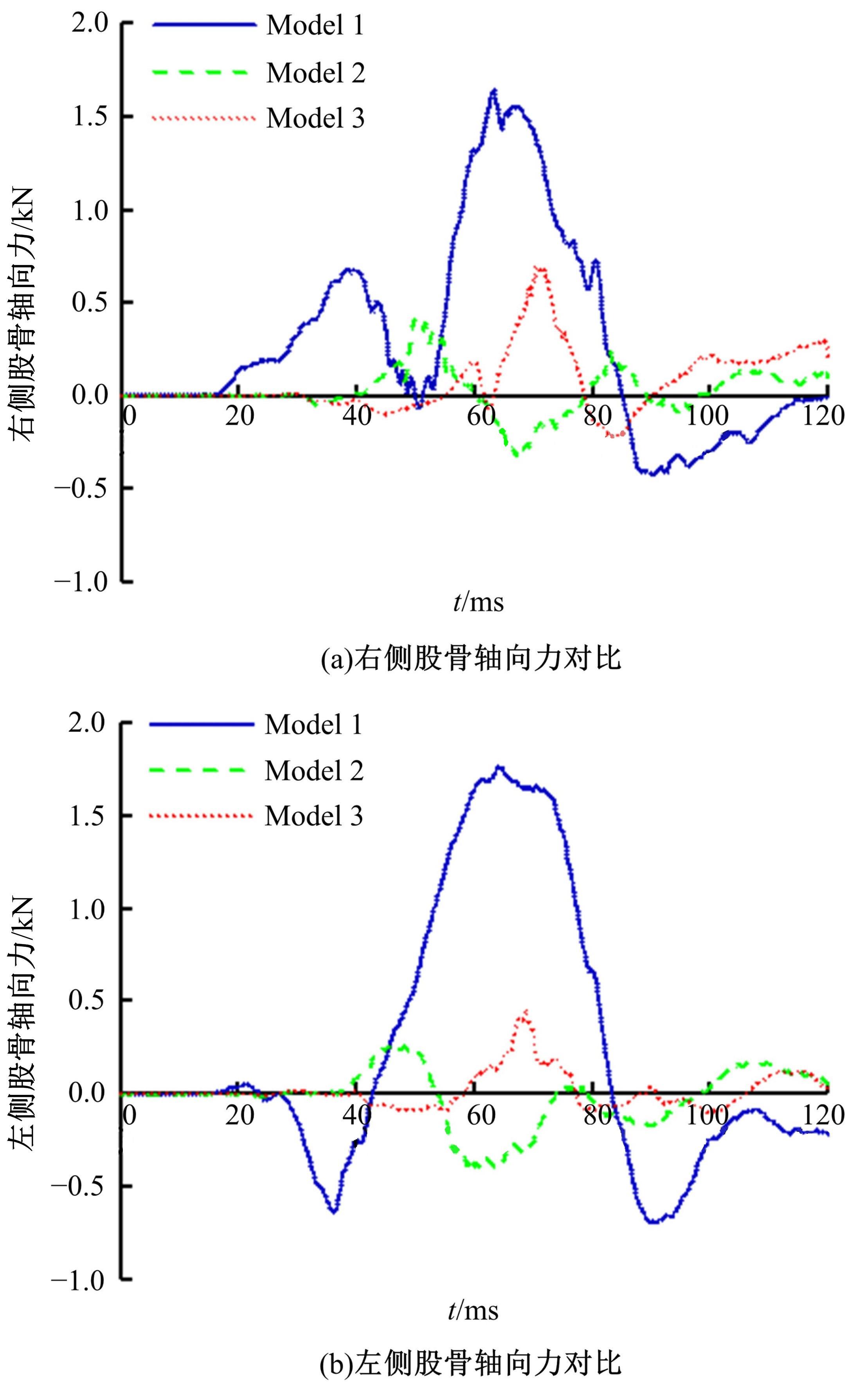
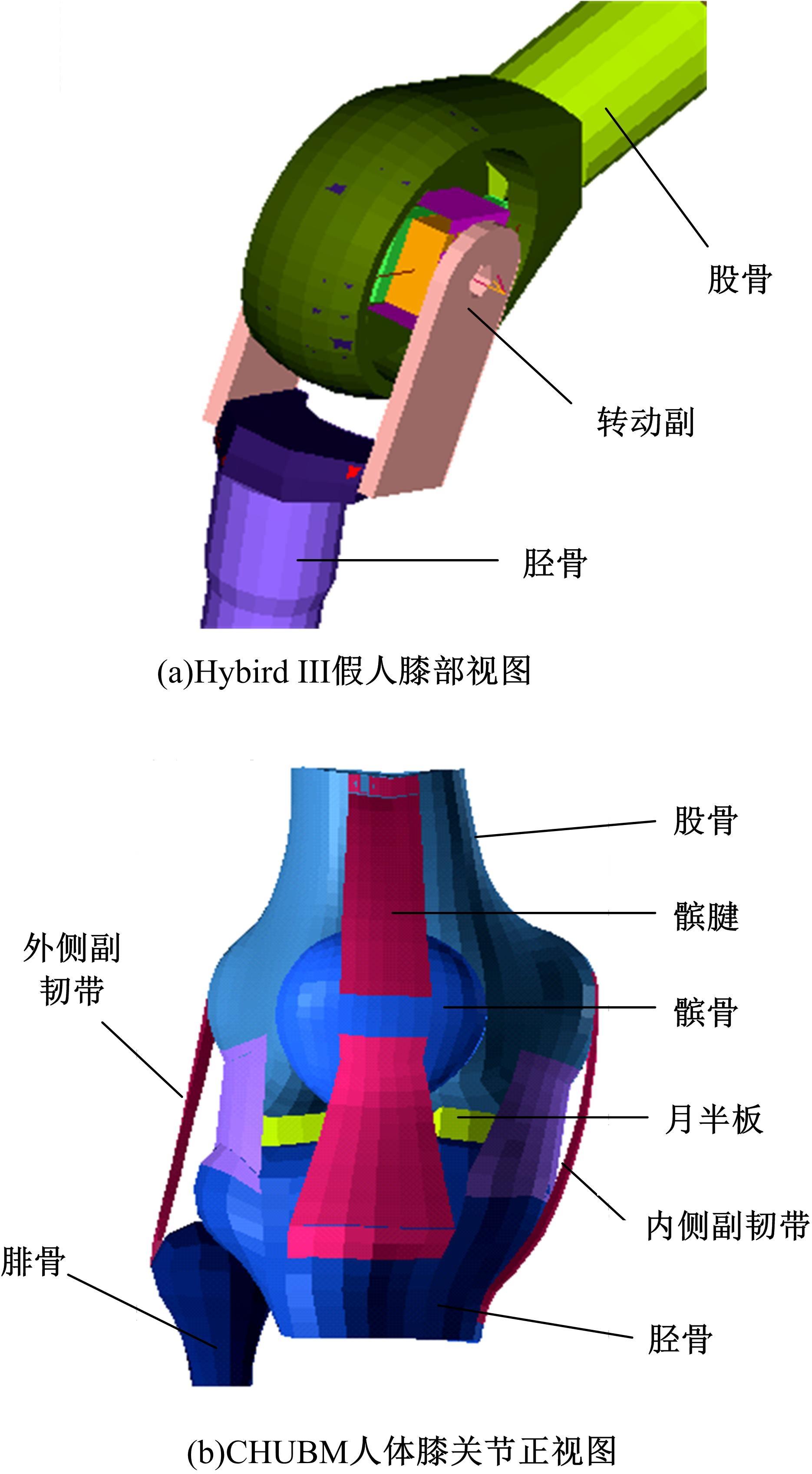
首先,采用Hybird III假人和CHUBM人体模型搭建了50 km/h速度下正面100%刚性壁障虚拟碰撞仿真平台。然后,建立了Hybird III假人座椅在A位置与CHUBM人体座椅分别在A和B位置的整车碰撞有限元模型,并对3种情况下驾驶员的头部、胸部及大腿损伤进行了对比分析。结果显示:座椅A位置的Hybird III假人和座椅B位置的CHUBM人体动态响应具有较好的一致性,不同座椅位置下的CHUBM人体的头部、胸部损伤均比Hybird III假人的高;CHUBM人体在座椅A位置的损伤比B位置的要高,同时肋骨发生了骨折现象。研究结果表明:CHUBM人体模型具有更加真实的人体解剖和仿生逼真度,对汽车约束系统的安全性评价要求更高,可为汽车安全性设计提供相应参考。
中图分类号:
- U461.91
| 1 | Zhu F, Dong L, Jin X, et al. Testing and modeling the responses of hybrid III crash-dummy lower extremity under high-speed vertical loading[J]. Stapp Car Crash Journal, 2015, 59: 521-536. |
| 2 | Fildes B, Fitzharris M, Gabler H C, et al. Chest and abdominal injuries to occupants in far side crashes[C]∥Proceedings of the 20th International Technical Conference on Enhanced Safety of Vehicles, Washington, DC, USA, 2007:1-8. |
| 3 | Ma Z W, Jing L L, Wang J L, et al. Biomechanical analysis of occupant's brain response and injury in vehicle interior second impact utilizing a refined head finite element model[J]. Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology, 2017, 17(1): No. 1740018. |
| 4 | Mroz K, Bostrom O, Pipkorn B, et al. Comparison of hybrid III and human body models in evaluating thoracic response for various seat belt and airbag loading conditions[C]∥Proceedings of the International IRCOBI Conference on the Biomechanics of Injury, Hanover, Germany, 2010: 265-279. |
| 5 | Arun M W J, Umale S, Humm J R, et al. Evaluation of kinematics and injuries to restrained occupants in far-side crashes using full-scale vehicle and human body models[J]. Traffic Injury Prevention, 2016, 17(Sup.1): 116-123. |
| 6 | Ye X, Gaewsky J P, Miller L E, et al. Numerical investigation of driver lower extremity injuries in finite element frontal crash reconstruction[J]. Traffic Injury Prevention, 2018, 19(Sup.1):21-28. |
| 7 | Golman A J, Danelson K A, Miller L E, et al. Injury prediction in a side impact crash using human body model simulation[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2014, 64: 1-8. |
| 8 | 阮世捷, 胡习之, 曲杰. 汽车安全与人体损伤生物力学的有限元模拟研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 35(6): 1-7. |
| Ruan Shi-jie, Hu Xi-zhi, Qu Jie. Finite element simulation research of automotive safety and injury biomechanics of human body[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2007, 35(6): 1-7. | |
| 9 | Mueller B C, Sherwood C P, Arbelaez R A, et al. Comparison of Hybrid III and THOR dummies in paired small overlap tests[J]. Stapp Car Crash Journal, 2011, 55: 379-409. |
| 10 | 中国汽车技术研究中心. C-NCAP管理规则[EB/OL]. [2020-12-21]. |
| 11 | 陈吉清, 杜天亚, 兰凤崇. 钝性碰撞中人体肝脏生物力学响应数值分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2018, 48(2): 398-406. |
| Chen Ji-qing, Du Tian-ya, Lan Feng-chong. Numerical analysis of human liver biomechanical response to blunt impacts[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(2): 398-406. | |
| 12 | 兰凤崇, 黄伟, 陈吉清, 等. 行人下肢高精度数值模型与损伤参数研究[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 43(10): 42-51. |
| Lan Feng-chong, Huang Wei, Chen Ji-qing, et al. Development and injury parameters research of a FE model of lower limb with high precision for adult pedestrians[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences), 2016, 43(10): 42-51. | |
| 13 | 蔡志华, 兰凤崇, 陈吉清, 等. 基于汽车碰撞损伤的人体胸部有限元模型构建与验证[J]. 医用生物力学, 2013, 28(1): 36-43. |
| Cai Zhi-hua, Lan Feng-chong, Chen Ji-qing, et al. Development and validation for finite element model of human thorax based on automotive impact injuries[J]. Journal of Medical Biomechanics, 2013, 28(1): 36-43. | |
| 14 | 陈吉清, 吴凯, 兰凤崇, 等. 中国成年男性全颈椎生物力学建模与验证[J]. 汽车工程, 2016, 38(11): 1305-1311, 1318. |
| Chen Ji-qing, Wu Kai, Lan Feng-chong, et al. Biomechanics modeling and validation for all cervical vertebrae of chinese adult male[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2016, 38(11): 1305-1311, 1318. | |
| 15 | Ma Z W, Chen J Q, Lan F C. Biomechanical response and injury effects on occupant's thorax-abdomen under seat belt loading[J]. International Journal of Vehicle Safety, 2015, 8(1): 1-21. |
| 16 | Du T Y, Chen J Q, Lan F C, et al. Thoracic response of the Chinese human body model in 50th percentile male size (CHUBM-M50) in blunt impacts-investigation in speed, direction and location[J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2019, 24(1): 71-85. |
| 17 | 张学荣, 刘学军, 陈晓东, 等. 正面碰撞安全带约束系统开发与试验验证[J]. 汽车工程, 2007, 29(12): 1055-1058. |
| Zhang Xue-rong, Liu Xue-jun, Chen Xiao-dong, et al. Development and test validation of safety belt restraint system for frontal impact[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2007, 29(12): 1055-1058. | |
| 18 | 韩勇, 杨济匡, 水野幸治, 等. 车辆碰撞速度对行人致命损伤风险的影响研究[J]. 汽车工程学报, 2011, 1(4): 399-406. |
| Han Yong, Yang Ji-kuang, Mizuno Koji, et al. Effects of vehicle impact velocity on pedestrian fatal injury risk[J]. Chinese Journal of Automotive Engineering, 2011, 1(4): 399-406. | |
| 19 | 张学荣, 黄硕, 许长龙, 等. 侧面碰撞中儿童测试假人与人体模型动态响应差异性研究[J]. 汽车工程学报, 2016, 6(6): 454-459. |
| Zhang Xue-rong, Huang Shuo, Xu Chang-long, et al. Study on dynamic response differences between child dummy and child human model in side impacts[J]. Chinese Journal of Automotive Engineering, 2016, 6(6): 454-459. |
| [1] | 华琛,牛润新,余彪. 地面车辆机动性评估方法与应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1229-1244. |
| [2] | 史文库,张曙光,张友坤,陈志勇,江逸飞,林彬斌. 基于改进海鸥算法的磁流变减振器模型辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 764-772. |
| [3] | 李杰,陈涛,郭文翠,赵旗. 汽车非平稳随机振动空间域虚拟激励法及应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 738-744. |
| [4] | 李伟,宋海生,陆浩宇,史文库,王强,王晓俊. 复合材料板簧迟滞特性线性辨识方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 829-836. |
| [5] | 庄蔚敏,陈沈,吴迪. 碳纤维增强复合材料包裹强化形式对钢管横向冲击性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 819-828. |
| [6] | 张英朝,李昀航,郭子瑜,王国华,张喆,苏畅. 长头重型卡车气动减阻优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 745-753. |
| [7] | 段亮,宋春元,刘超,魏苇,吕成吉. 基于机器学习的高速列车轴承温度状态识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 53-62. |
| [8] | 庄蔚敏,陈沈,王楠. 温度对车身钢铝胶铆连接结构热应力变化的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 70-78. |
| [9] | 陈剑斌,周宋泽,费峰永,陈永龙,凌国平. 过盈量及滚花方式对装配式凸轮轴压装失效的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1959-1966. |
| [10] | 胡兴军,张靖龙,罗雨霏,辛俐,李胜,胡金蕊,兰巍. 冷却管结构及进气方向对空冷中冷器性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1933-1942. |
| [11] | 罗勇,韦永恒,黄欢,肖人杰,任淋,崔环宇. 驾驶员意图识别的P2.5插混构型双离合器起步控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1575-1582. |
| [12] | 曾小华,宋美洁,宋大凤,王越. 基于车联网信息的公交客车行驶工况数据处理方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1692-1699. |
| [13] | 马超,高云凯,刘哲,段月星,田林雳. 骨架式车身多材料及梁截面形状和尺寸优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1583-1592. |
| [14] | 兰凤崇,李继文,陈吉清. 面向动态场景复合深度学习与并行计算的DG-SLAM算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1437-1446. |
| [15] | 杨建,夏琦,周海超,王国林. 修正胎体弦轮廓载重子午线轮胎的降噪机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1198-1203. |
|
||