吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1273-1280.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210020
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于曲线压缩和极限梯度提升算法的锂离子电池健康状态估计
刘兴涛1,2( ),刘晓剑1,武骥1,2(
),刘晓剑1,武骥1,2( ),何耀3,刘新天3
),何耀3,刘新天3
- 1.合肥工业大学 汽车与交通工程学院,合肥 230009
2.合肥工业大学 安徽省智慧交通车路协同工程研究中心,合肥 230009
3.合肥工业大学 汽车工程技术研究院,合肥 230009
State of health estimation method for lithium⁃ion battery based on curve compression and extreme gradient boosting
Xing-tao LIU1,2( ),Xiao-jian LIU1,Ji WU1,2(
),Xiao-jian LIU1,Ji WU1,2( ),Yao HE3,Xin-tian LIU3
),Yao HE3,Xin-tian LIU3
- 1.School of Automotive and Transportation Engineering,Hefei University of Technology,Hefei 230009,China
2.Engineering Research Center for Intelligent Transportation and Cooperative Vehicle-Infrastructure of Anhui Province,Hefei University of Technology,Hefei 230009,China
3.Automotive Research Institute,Hefei University of Technology,Hefei 230009,China
摘要:
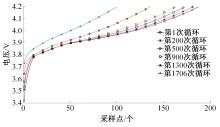
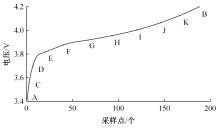
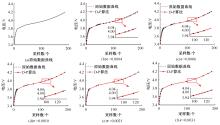
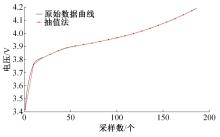
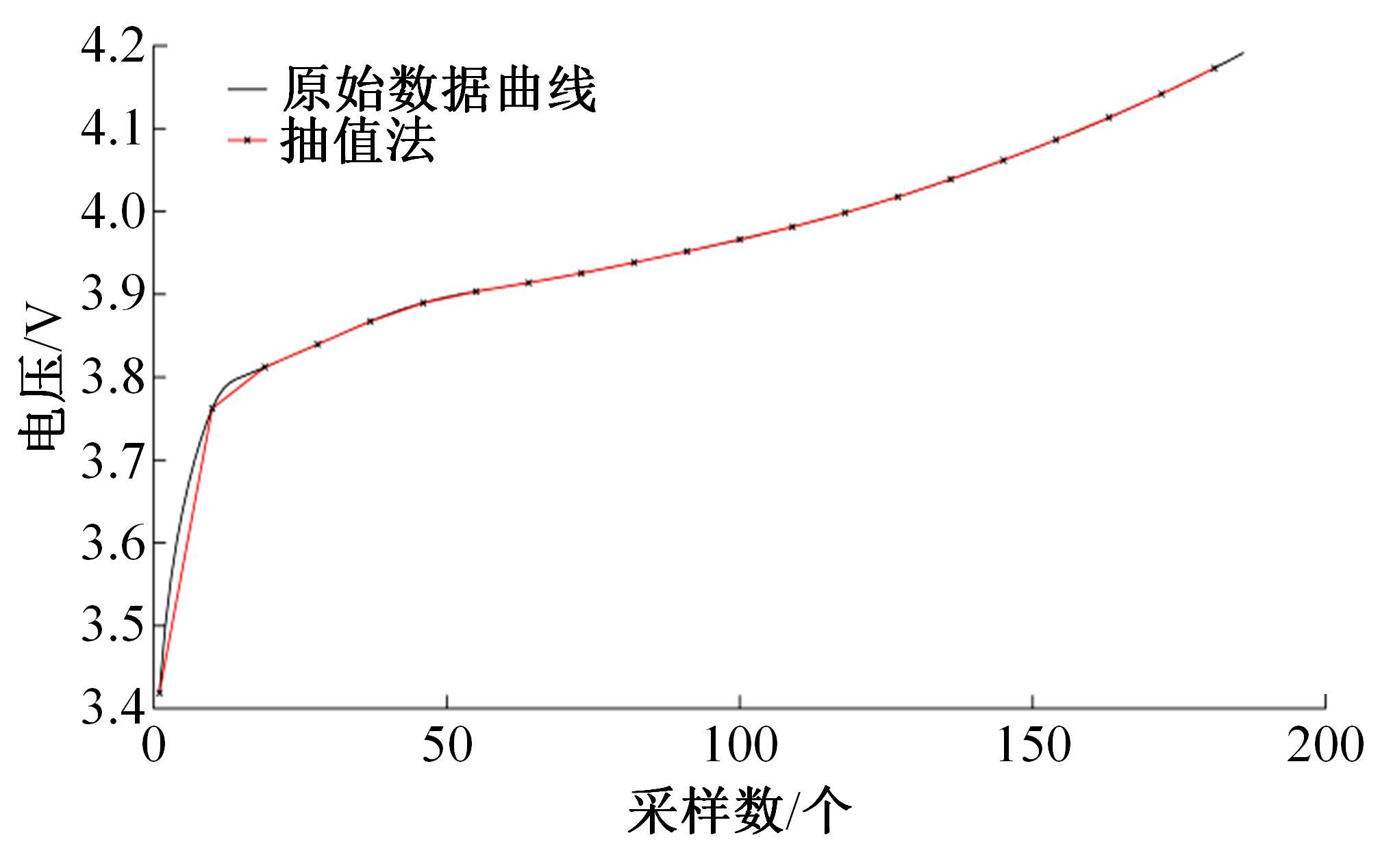
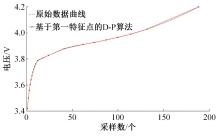
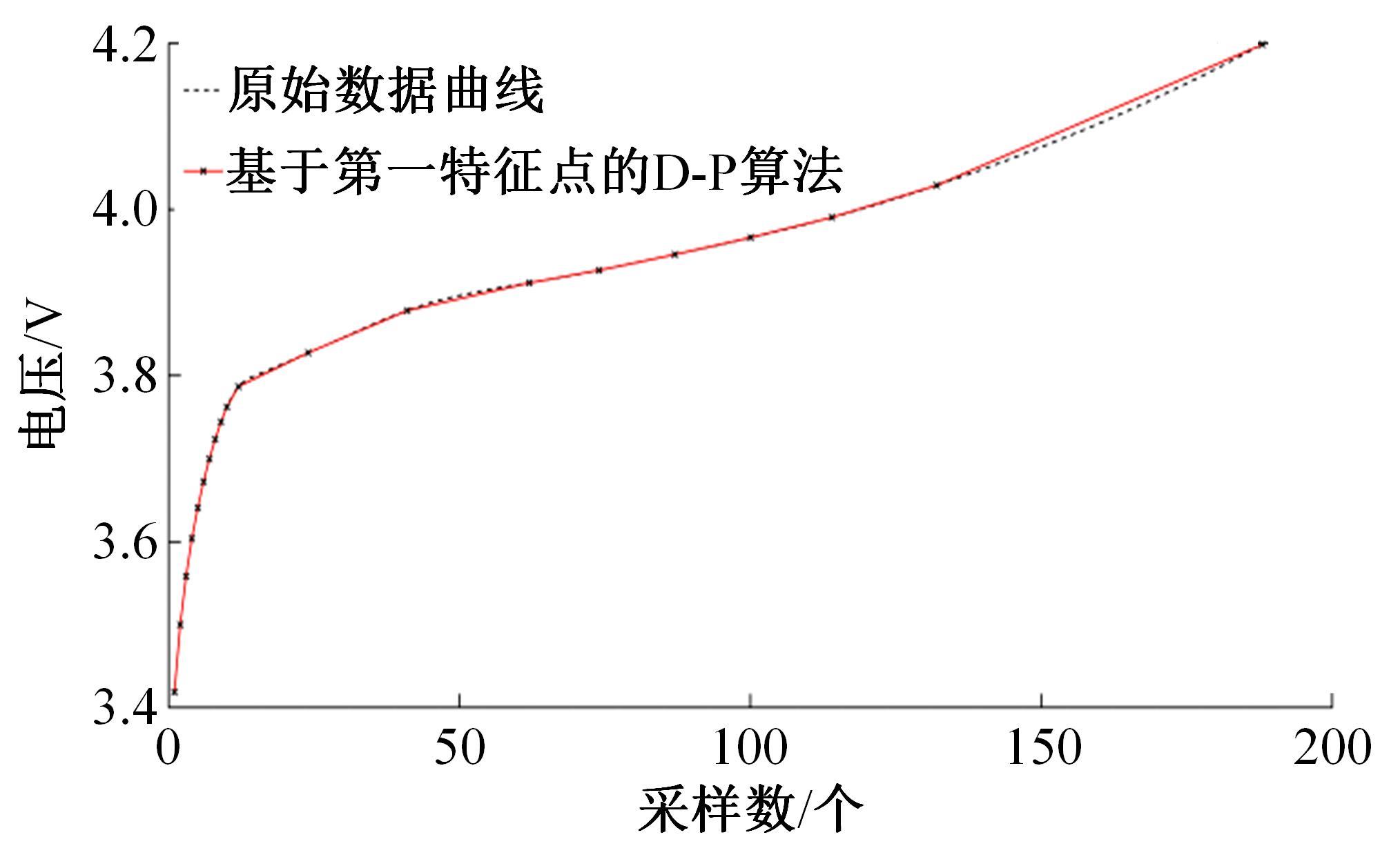
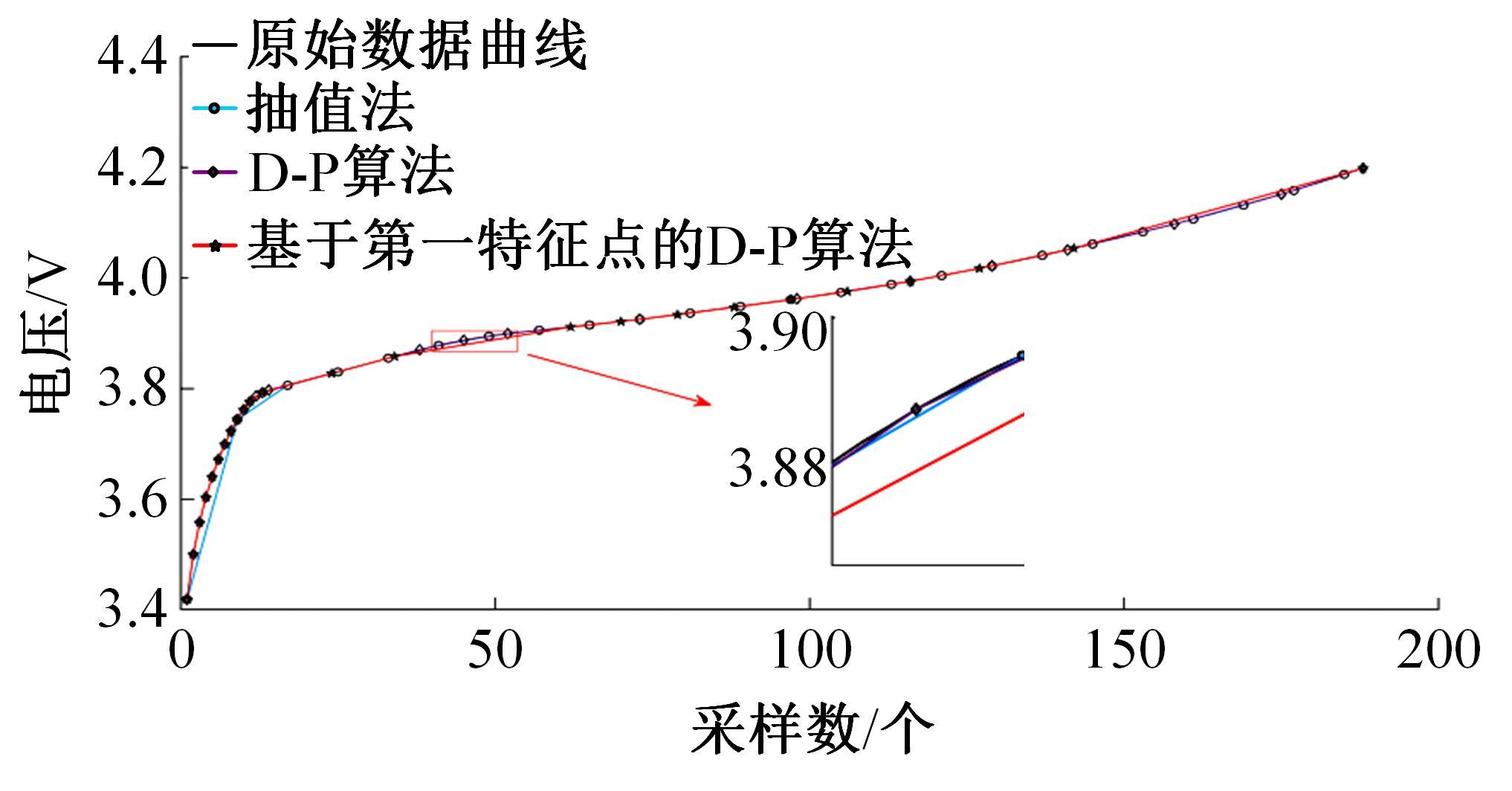
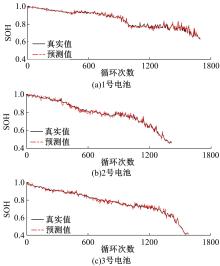
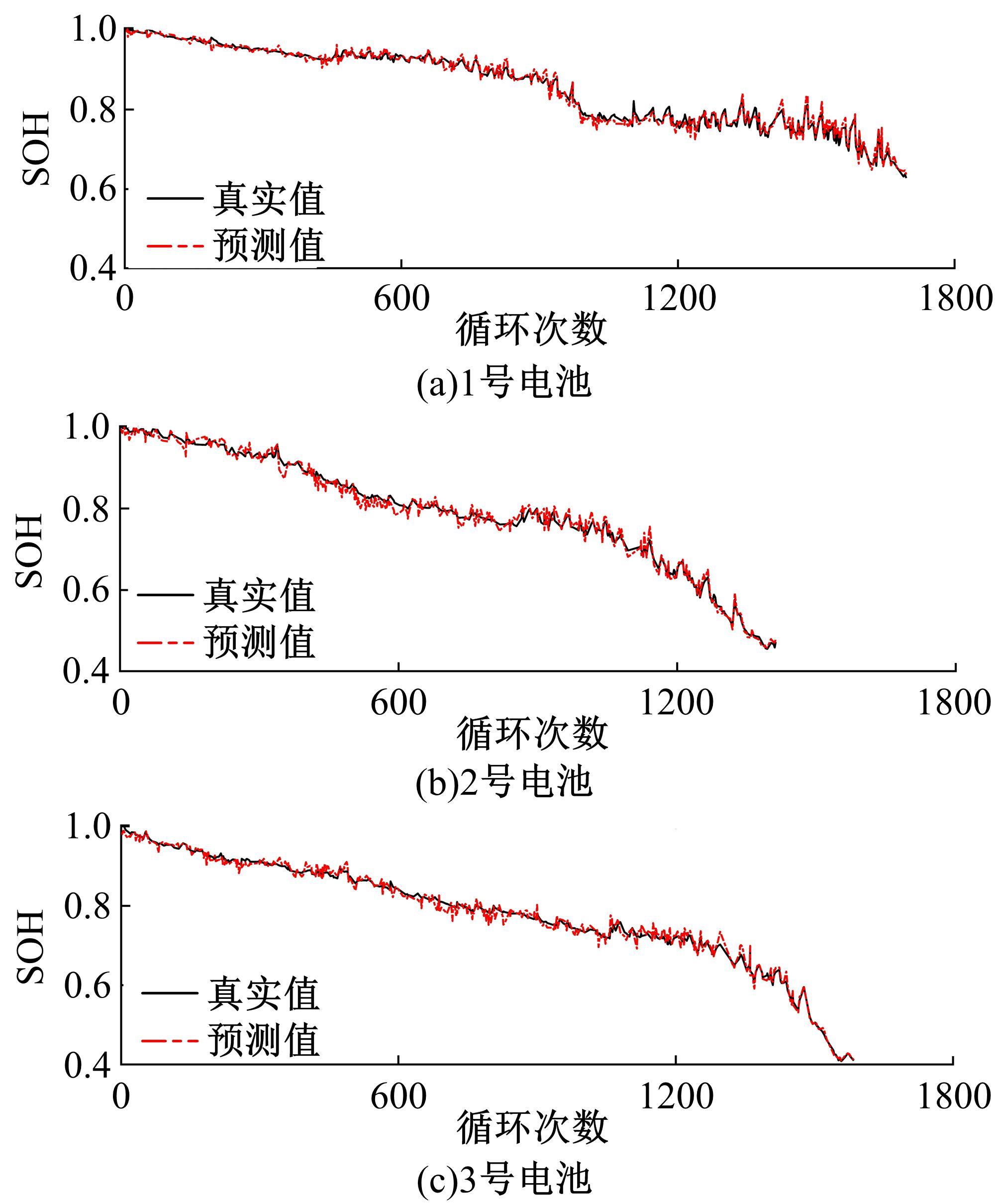
为了精确地估计锂离子电池的健康状态(SOH),提出了一种基于道格拉斯-普克算法和极限梯度提升(XGBoost)算法的方法。首先对每组电压数据进行预处理,利用道格拉斯-普克算法对每次循环的恒流充电电压曲线进行矢量压缩;在此数据的基础上,运用XGBoost算法建立锂离子电池退化过程模型并估计SOH。对比实验结果表明,所提方法可有效压缩电池电压曲线、降低网络训练数据维度,同时具有较高的预测精度和较快的运行速度,可实现锂离子电池SOH的快速准确估计。
中图分类号:
- TM91
| 1 | Wu Ji, Wang Yu-jie, Zhang Xu, et al. A novel state of health estimation method of Li-ion battery using group method of data handling[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 327: 457-464. |
| 2 | 刘新天, 刘兴涛, 何耀, 等. 基于Vmin-EKF的动力锂电池组SOC估计[J]. 控制与决策, 2010, 25(3): 445-448. |
| Liu Xin-tian, Liu Xing-tao, He Yao, et al. Based-Vmin-EKF SOC estimation for power Li-ion battery pack[J]. Control and Decision, 2010, 25(3): 445-448. | |
| 3 | Tian Hui-xin, Qin Peng-liang, Li Kun, et al. A review of the state of health for lithium-ion batteries: research status and suggestions[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 261: No. 120813. |
| 4 | 刘新天, 李涵琪, 魏增福, 等. 基于Drift-Ah积分法的CKF估算锂电池SOC[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34(3): 535-541. |
| Liu Xin-tian, Li Han-qi, Wei Zeng-fu, et al. CKF estimation Li-ion battery SOC based on Drift-Ah integral method[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34(3): 535-541. | |
| 5 | 陈猛, 乌江, 焦朝勇, 等. 锂离子电池健康状态多因子在线估计方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2020, 54(1): 169-175. |
| Chen Meng, Wu Jiang, Jiao Chao-yong, et al. Multi-factor online estimation method for health status of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2020, 54(1): 169-175. | |
| 6 | 颜湘武, 邓浩然, 郭琪, 等. 基于自适应无迹卡尔曼滤波的动力电池健康状态检测及梯次利用研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34(18): 3937-3948. |
| Yan Xiang-wu, Deng Hao-ran, Guo Qi, et al. Study on the state of health detection of power batteries based on adaptive unscented Kalman filters and the battery echelon utilization[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34(18): 3937-3948. | |
| 7 | Sankarasubramanian S, Krishnamurthy B. A capacity fade model for lithium-ion batteries including diffusion and kinetics[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 70: 248-254. |
| 8 | You G W, Park S, Oh D. Real-time state-of-health estimation for electric vehicle batteries: a data-driven approach[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 176: 92-103. |
| 9 | Li Y, Zou C F, Berecibar M, et al. Random forest regression for online capacity estimation of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 232(9): 197-210. |
| 10 | Deng Yuan-wang, Ying He-jie, Jia-qiang E, et al. Feature parameter extraction and intelligent estimation of the state-of-health of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy, 2019, 176: 91-102. |
| 11 | 潘海鸿, 吕治强, 付兵, 等. 采用极限学习机实现锂离子电池健康状态在线估算[J]. 汽车工程, 2017, 39(12):1375-1381, 1396. |
| Pan Hai-hong, Lv Zhi-qiang, Fu Bing, et al. Online estimation of lithium-ion battery's state of health using extreme learning machine[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2017, 39(12): 1375-1381, 1396. | |
| 12 | Zhao Lin, Wang Yi-peng, Cheng Jian-hua. A hybrid method for remaining useful life estimation of lithium-ion battery with regeneration phenomena[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(9): No.1890. |
| 13 | Yang Duo, Zhang Xu, Pan Rui, et al. A novel Gaussian process regression model for state-of-health estimation of lithium-ion battery using charging curve[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 384: 387-395. |
| 14 | He W, Williard N, Osterman M, et al. Prognostics of lithium-ion batteries based on Dempster–Shafer theory and the bayesian monte carlo method[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(23): 10314-10321. |
| 15 | Patil A, Patil V, Shin D W, et al. Issue and challenges facing rechargeable thin film lithium batteries[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43(8/9): 1913-1942. |
| 16 | 于靖, 陈刚, 张笑, 等. 面向自然岸线抽稀的改进道格拉斯-普克算法[J]. 测绘科学, 2015, 40(4): 23-27, 33. |
| Yu Jing, Chen Gang, Zhang Xiao, et al. An improved Douglas-Puck algorithm oriented to natural shoreline simplification[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2015, 40(4): 23-27, 33. | |
| 17 | Zhao Liang-bin, Shi Guo-you. A method for simplifying ship trajectory based on improved Douglas–Peucker algorithm[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 166: 37-46. |
| 18 | Jiang Fu, Yang Jia-jun, Cheng Yi-jun, et al. An aging-aware SOC estimation method for lithium-ion batteries using XGBoost algorithm[C]∥2019 IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 1-8. |
| 19 | Yang Jin-shan, Zhao Chen-yue, Yu Hao-tong, et al. Use GBDT to predict the stock market[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2020, 174: 161-171. |
| 20 | 米学军, 盛广铭, 张婧, 等. GIS中面积偏差控制下的矢量数据压缩算法[J]. 地理科学, 2012, 32(10): 1236-1240. |
| Mi Xue-jun, Sheng Guang-ming, Zhang Jing, et al. A new algorithm of vector date compression based on the tolerance of area error in GIS [J]. Geographical Sciences, 2012, 32(10): 1236-1240. | |
| 21 | 王笑天, 吕海洋. 基于第一特征点的道格拉斯-普克压缩算法[J]. 软件导刊, 2016, 15(11): 68-70. |
| Wang Xiao-tian, Lv Hai-yang. Douglas-Puck compression algorithm based on the first feature point[J]. Software Guide, 2016, 15(11): 68-70. |
| [1] | 华琛,牛润新,余彪. 地面车辆机动性评估方法与应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1229-1244. |
| [2] | 李雄,兰凤崇,陈吉清,童芳. Hybird III假人模型与CHUBM人体生物力学模型的正碰损伤对比[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1264-1272. |
| [3] | 张英朝,李昀航,郭子瑜,王国华,张喆,苏畅. 长头重型卡车气动减阻优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 745-753. |
| [4] | 史文库,张曙光,张友坤,陈志勇,江逸飞,林彬斌. 基于改进海鸥算法的磁流变减振器模型辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 764-772. |
| [5] | 李杰,陈涛,郭文翠,赵旗. 汽车非平稳随机振动空间域虚拟激励法及应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 738-744. |
| [6] | 李伟,宋海生,陆浩宇,史文库,王强,王晓俊. 复合材料板簧迟滞特性线性辨识方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 829-836. |
| [7] | 庄蔚敏,陈沈,吴迪. 碳纤维增强复合材料包裹强化形式对钢管横向冲击性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 819-828. |
| [8] | 段亮,宋春元,刘超,魏苇,吕成吉. 基于机器学习的高速列车轴承温度状态识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 53-62. |
| [9] | 庄蔚敏,陈沈,王楠. 温度对车身钢铝胶铆连接结构热应力变化的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 70-78. |
| [10] | 陈剑斌,周宋泽,费峰永,陈永龙,凌国平. 过盈量及滚花方式对装配式凸轮轴压装失效的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1959-1966. |
| [11] | 胡兴军,张靖龙,罗雨霏,辛俐,李胜,胡金蕊,兰巍. 冷却管结构及进气方向对空冷中冷器性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1933-1942. |
| [12] | 罗勇,韦永恒,黄欢,肖人杰,任淋,崔环宇. 驾驶员意图识别的P2.5插混构型双离合器起步控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1575-1582. |
| [13] | 曾小华,宋美洁,宋大凤,王越. 基于车联网信息的公交客车行驶工况数据处理方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1692-1699. |
| [14] | 马超,高云凯,刘哲,段月星,田林雳. 骨架式车身多材料及梁截面形状和尺寸优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1583-1592. |
| [15] | 兰凤崇,李继文,陈吉清. 面向动态场景复合深度学习与并行计算的DG-SLAM算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1437-1446. |
|
||