吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2018, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6): 1694-1702.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20170894
不确定条件下危险品配送路线多准则优化
- 兰州交通大学 交通运输学院,兰州 730070
Multi-criteria optimization for hazardous materials distribution routes under uncertain conditions
DAI Cun-jie( ),LI Yin-zhen(
),LI Yin-zhen( ),MA Chang-xi,CHAI Huo,MU Hai-bo
),MA Chang-xi,CHAI Huo,MU Hai-bo
- School of Traffic and Transportation,Lanzhou Jiaotong University, Lanzhou 730070,China
摘要:
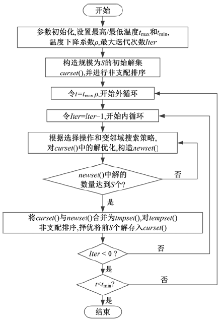
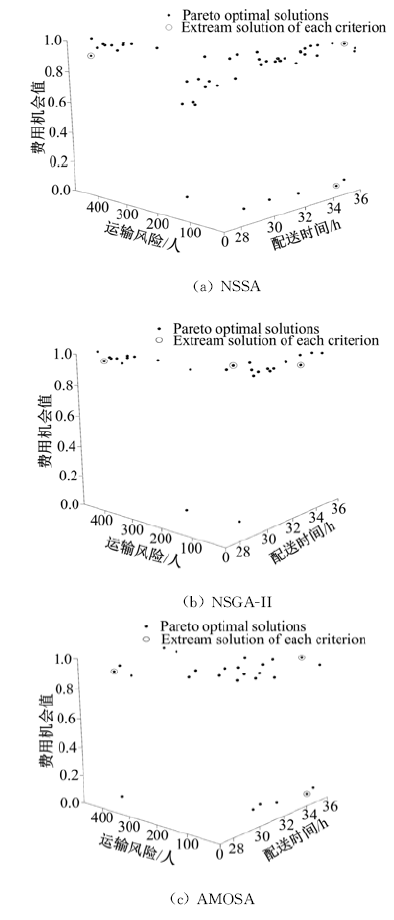
针对非满载的危险品配送车辆路线优化问题,考虑危险品数量对运输风险的影响,利用分段线性逼近方法对配送过程中的潜在风险动态评估。根据运输企业的不同优化准则以及配送路线的不确定性属性,基于可信性理论和期望值方法,建立了有容量约束的危险品配送路线多准则优化模型。设计了改进的模拟退火算法对模型求解,并利用快速非支配排序方法和动态拥挤距离计算方法提高求解效率,改善Pareto解在解空间内分布的均匀性,结合解的编码方式设计变邻域搜索策略提高算法的局部和全局搜索能力。采用不同算例验证了模型的合理性和算法的有效性,研究结果可为危险品运输企业在多种不确定条件下的配送路线选择提供决策支持。
中图分类号:
- U116.2
| [1] |
Pradhananga R, Taniguchi E, Yamada T , et al. Environmental analysis of Pareto optimal routes in hazardous material transportation[J]. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2014,125(1):506-517.
doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.01.1492 |
| [2] |
Bula G A, Prodhon C, Gonzalez F A , et al. Variable neighborhood search to solve the vehicle routing problem for hazardous materials transportation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017,324(PtB):472-480.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.11.015 |
| [3] |
Tarantilis C, Kiranoudis C T . Using the vehicle routing problem for the transportation of hazardous materials[J]. Operational Research, 2001,1(1):67-78.
doi: 10.1007/BF02936400 |
| [4] |
Androutsopoulos K N, Zografos K G . Solving the bicriterion routing and scheduling problem for hazardous materials distribution[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2010,18(5):713-726.
doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2009.12.002 |
| [5] |
Androutsopoulos K N, Zografos K G . A bi-objective time-dependent vehicle routing and scheduling problem for hazardous materials distribution[J]. Euro Journal on Transportation & Logistics, 2012,1(1/2):157-183.
doi: 10.1007/s13676-012-0004-y |
| [6] |
Zografos K G, Androutsopoulos K N . A heuristic algorithm for solving hazardous materials distribution problems[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2004,152(2):507-519.
doi: 10.1016/S0377-2217(03)00041-9 |
| [7] |
Zografos K G, Androutsopoulos K N . A decision support system for integrated hazardous materials routing and emergency response decisions[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2008,16(6):684-703.
doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2008.01.004 |
| [8] |
Pradhananga R, Taniguchi E, Yamada T . Ant colony system based routing and scheduling for hazardous material transportation[J]. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2010,2(3):6097-6108.
doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.04.022 |
| [9] |
Pradhananga R, Taniguchi E, Yamada T , et al. Bi-objective decision support system for routing and scheduling of hazardous materials[J]. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 2014,48(2):135-148.
doi: 10.1016/j.seps.2014.02.003 |
| [10] | 吕品 . 基于改进VRP模型的危险品配送路径优化及其求解研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2011,7(11):87-91. |
| Lyu Pin . Research on route optimization and algorithm of hazardous materials distribution based on improved VRP model[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2011,7(11):87-91. | |
| [11] | 于晓桦, 刘凯峥, 刘浩学 , 等. 基于遗传算法的固定起讫点危险品配送路线优化[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2013,43(12):44-50. |
| Yu Xiao-hua, Liu Kai-zheng, Liu Hao-xue , et al. Route optimization for dangerous material distribution with fixed origin and destination site based on improved genetic algorithm[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2013,43(12):44-50. | |
| [12] |
李双琳, 马祖军, 邹坤 . 危险品物流中的多目标定位-路径问题[J]. 运筹与管理, 2014,23(3):8-15.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3221.2014.03.002 |
|
Li Shuang-lin, Ma Zu-jun, Zou Kun . Multi-objective location-routing problem for hazardous materials logistics[J]. Operations Research and Management Science, 2014,23(3):8-15.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3221.2014.03.002 |
|
| [13] |
Bula G A, Gonzalez F A, Prodhon C , et al. Mixed integer linear programming model for vehicle routing problem for hazardous materials transportation[J]. IFAC Papersonline, 2016,49(12):538-543.
doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2016.07.691 |
| [14] | 袁文燕, 徐腾飞, 杨丰梅 , 等. 基于新风险度量方式的危险品车辆路径双目标优化模型[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2016,46(14):275-284. |
| Yuan Wen-yan, Xu Teng-fei, Yang Feng-mei , et al. Bi-objective decision model for vehicle routing of hazardous material based on new risk measure[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2016,46(14):275-284. | |
| [15] |
Button N P, Reilly P M . Uncertainty in incident rates for trucks carrying dangerous goods[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2000,32(6):797-804.
doi: 10.1016/S0001-4575(00)00003-8 pmid: 10994607 |
| [16] |
Chang T S, Nozick L K, Turnquist M A . Multiobjective path finding in stochastic dynamic networks, with application to routing hazardous materials shipments[J]. Transportation Science, 2005,39(3):383-399.
doi: 10.1287/trsc.1040.0094 |
| [17] |
Jia H, Zhang L, Lou X , et al. A fuzzy-stochastic constraint programming model for hazmat road transportation considering terrorism attacking[J]. Systems Engineering Procedia, 2011,1:130-136.
doi: 10.1016/j.sepro.2011.08.022 |
| [18] |
Du J, Li X, Yu L , et al. Multi-depot vehicle routing problem for hazardous materials transportation[J]. Information Sciences, 2017,399(C):201-218.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2017.02.011 |
| [19] | 秦军昌, 张金梁, 王刊良 . 危险品运输线路问题的鲁棒优化模型[J]. 统计与决策, 2009(20):25-26. |
| Qin Jun-chang, Zhang Jin-liang, Wang Kan-liang . Robust optimization model of hazardous materials transportation route[J]. Statistics and Decision, 2009,24(20):25-26. | |
| [20] |
Erkut E, Ingolfsson A . Transport risk models for hazardous materials: revisited[J]. Operations Research Letters, 2013,33(1):81-89.
doi: 10.1016/j.orl.2004.02.006 |
| [21] |
Abkowitz M, Cheng P D . Developing a risk/cost framework for routing truck movements of Hazardous materials[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 1988,20(1):39-51.
doi: 10.1016/0001-4575(88)90013-9 pmid: 3337764 |
| [22] |
Guo X, Verma M . Choosing vehicle capacity to minimize risk for transporting flammable materials[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2010,23(2):220-225.
doi: 10.1016/j.jlp.2009.07.007 |
| [23] | Liu B . Theory and Practice of Uncertain Programming[M]. Heidelberg:Physica-Verlag, 2002: 41-43. |
| [24] | Li X . Credibilistic Programming: An Introduction to Models and Applications[M]. Heidelberg:Springer-Verlag, 2013: 31-43. |
| [25] |
Hassanzadeh R, Mahdavi I, Mahdavi-Amiri N , et al. A genetic algorithm for solving fuzzy shortest path problems with mixed fuzzy arc lengths[J]. Mathematical & Computer Modelling, 2013,57(1/2):84-99.
doi: 10.1016/j.mcm.2011.03.040 |
| [26] |
王占中, 赵利英, 曹宁博 . 基于多层编码遗传算法的危险品运输调度模型[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2017,47(3):751-755.
doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb201703009 |
|
Wang Zhan-zhong, Zhao Li-ying, Cao Ning-bo . Hazardous material transportation scheduling model based on mutilayer coding genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017,47(3):751-755.
doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb201703009 |
|
| [27] |
Eglese R W . Simulated annealing: A tool for operational research[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 1990,46(3):271-281.
doi: 10.1016/0377-2217(90)90001-R |
| [28] |
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S , et al. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002,6(2):182-197.
doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 |
| [29] |
Uchoa E, Pecin D, Pessoa A , et al. New benchmark instances for the capacitated vehicle routing problem[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2016,257(3):845-858.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2016.08.012 |
| [30] |
Han D H, Kim Y D, Lee J Y . Multiple-criterion shortest path algorithms for global path planning of unmanned combat vehicles[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2014,71(1):57-69.
doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2014.02.013 |
| [1] | 王露,刘玉雯,陈红. 侧风下峡谷桥隧连接段汽车的行驶特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 736-748. |
| [2] | 王芳荣, 郭柏苍, 金立生, 高琳琳, 岳欣羽. 次任务驾驶安全评价指标筛选及其权值计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1710-1715. |
| [3] | 谭立东, 刘丹, 李文军. 基于蝇复眼的交通事故现场全景图像阵列仿生设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1738-1744. |
| [4] | 李显生, 孟祥雨, 郑雪莲, 程竹青, 任圆圆. 非满载罐体内液体冲击动力学特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 737-743. |
| [5] | 王占中, 赵利英, 曹宁博. 基于多层编码遗传算法的危险品运输调度模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 751-755. |
| [6] | 徐进, 陈薇, 周佳, 罗骁, 邵毅明. 汽车转向盘操作与驾驶负荷的相关性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 438-445. |
| [7] | 郭应时, 付锐, 赵凯, 马勇, 袁伟. 驾驶人换道意图实时识别模型评价及测试[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1836-1844. |
| [8] | 孙璐, 徐建, 崔相民. 面板数据模型分析及交通事故预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1771-1778. |
| [9] | 王喆, 杨柏婷, 刘昕, 刘群, 宋现敏. 基于模糊聚类的驾驶决策判别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1414-1419. |
| [10] | 马勇, 石涌泉, 付锐, 郭应时. 驾驶人分心时长对车道偏离影响的实车试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1095-1101. |
| [11] | 李晖晖, 滑立, 杨宁, 刘坤. 基于MSA特征和模拟退火优化的遥感图像多目标关联算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(4): 1353-1359. |
| [12] | 徐建, 孙璐. 解决交通事故数据分析中零值问题的模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(3): 769-775. |
| [13] | 韩啸,刘淑芬,徐天琦. 基于遗传模拟退火算法的改进K-medoids算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 619-623. |
| [14] | 金立生, 王岩, 刘景华, 王亚丽, 郑义. 基于Adaboost算法的日间前方车辆检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(6): 1604-1608. |
| [15] | 金立生,牛清宁,刘景华,秦彦光,吕欢欢. 不同道路线形下驾驶人认知分散状态监测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 642-647. |
|