吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (5): 1677-1686.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190410
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
动态公交专用道的设置及其仿真分析评价
- 1.吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
2.吉林大学 大数据和网络管理中心 130022
Setting of dynamic bus lane and its simulation analysis and evaluation
Xian-min SONG1( ),Ming-ye ZHANG1,Zhen-jian LI2(
),Ming-ye ZHANG1,Zhen-jian LI2( ),Xin WANG1,Ya-nan ZHANG1
),Xin WANG1,Ya-nan ZHANG1
- 1.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Big Data and Network Management Center,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
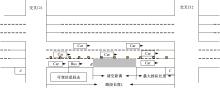
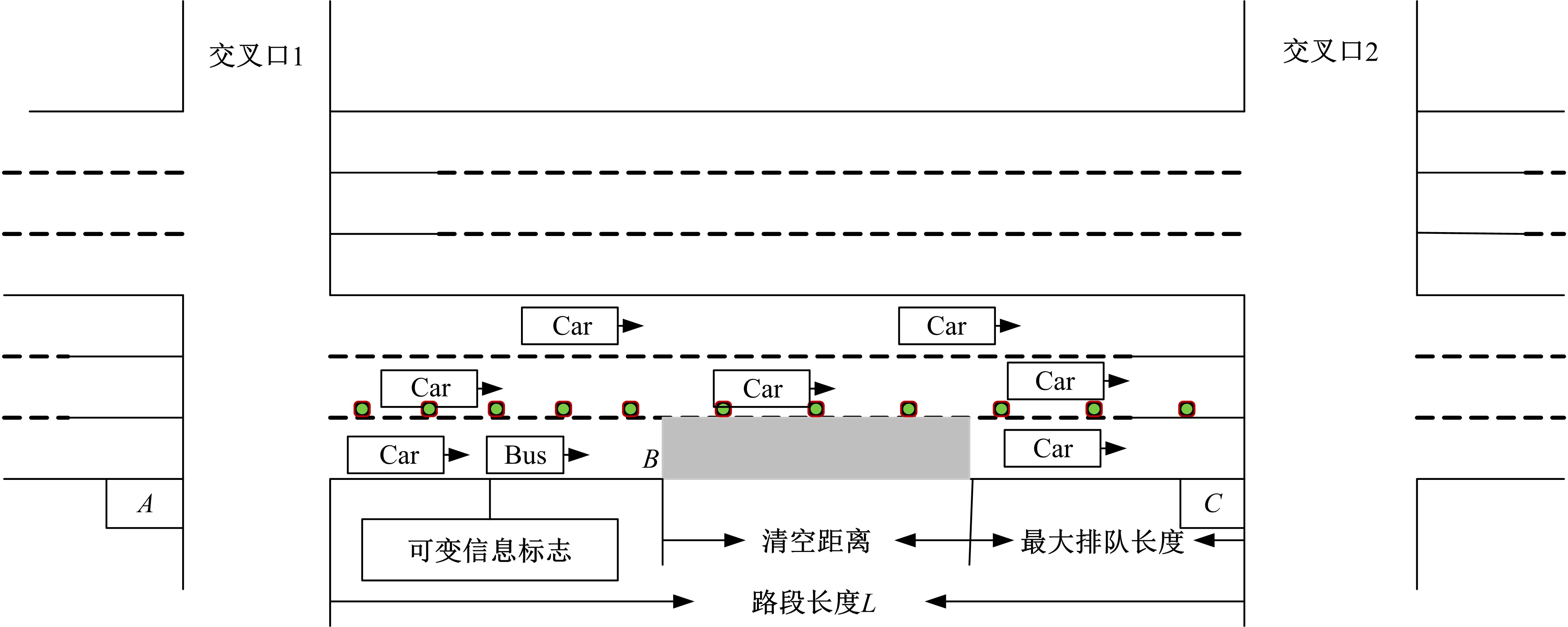
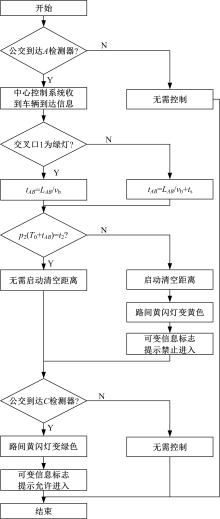
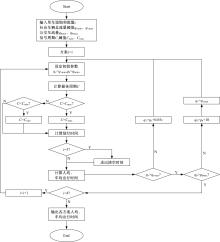
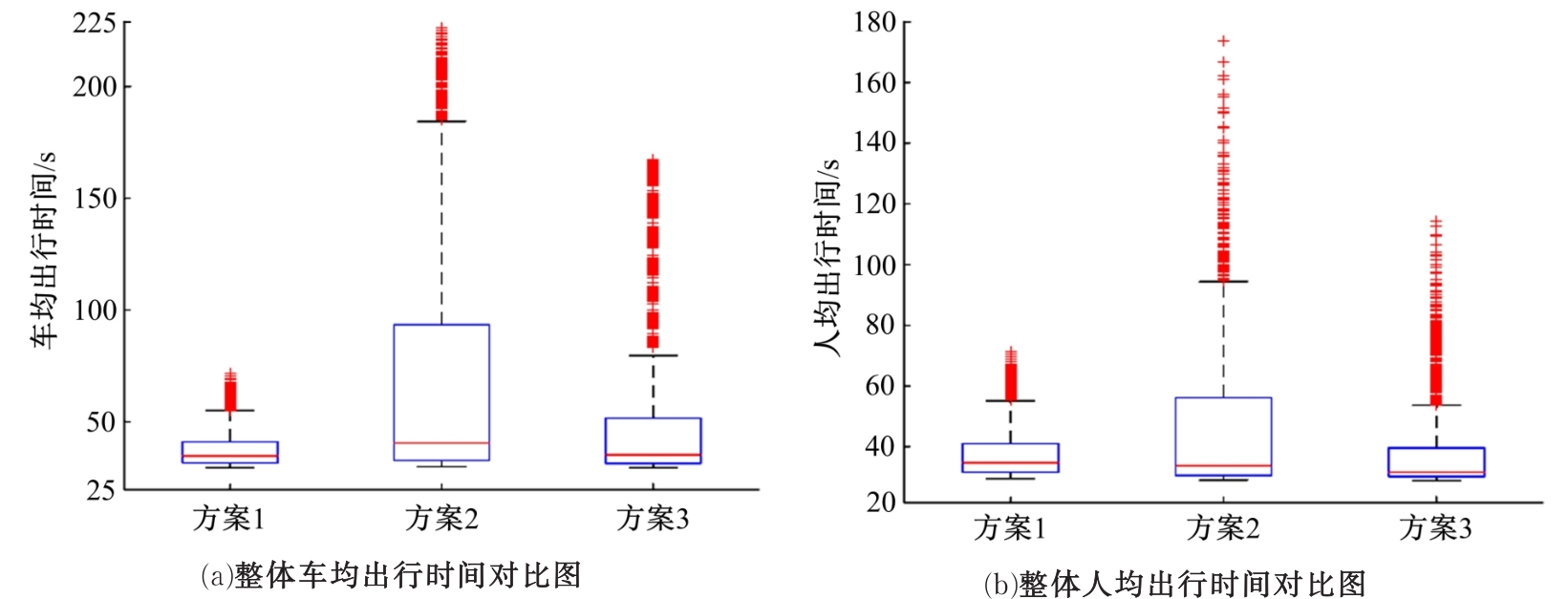
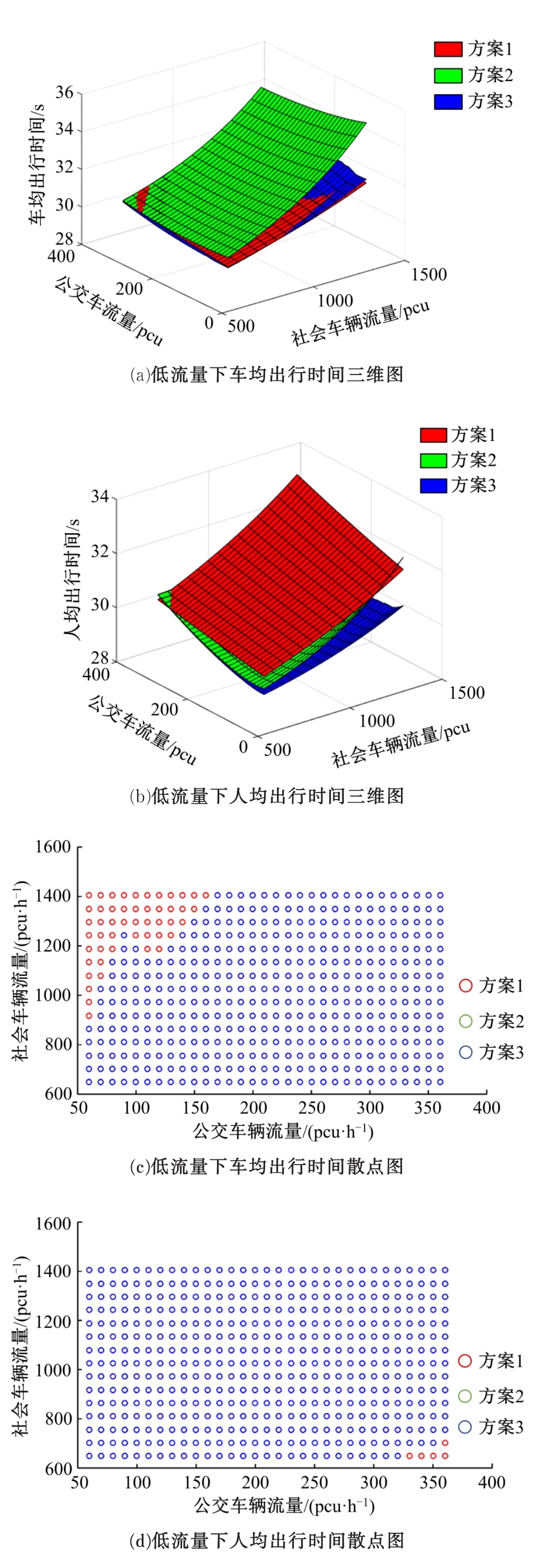
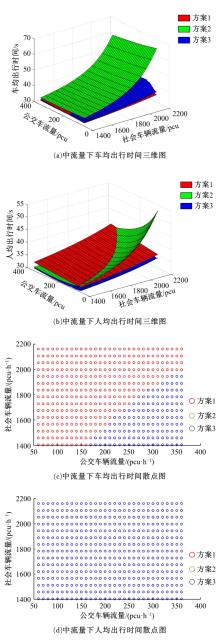
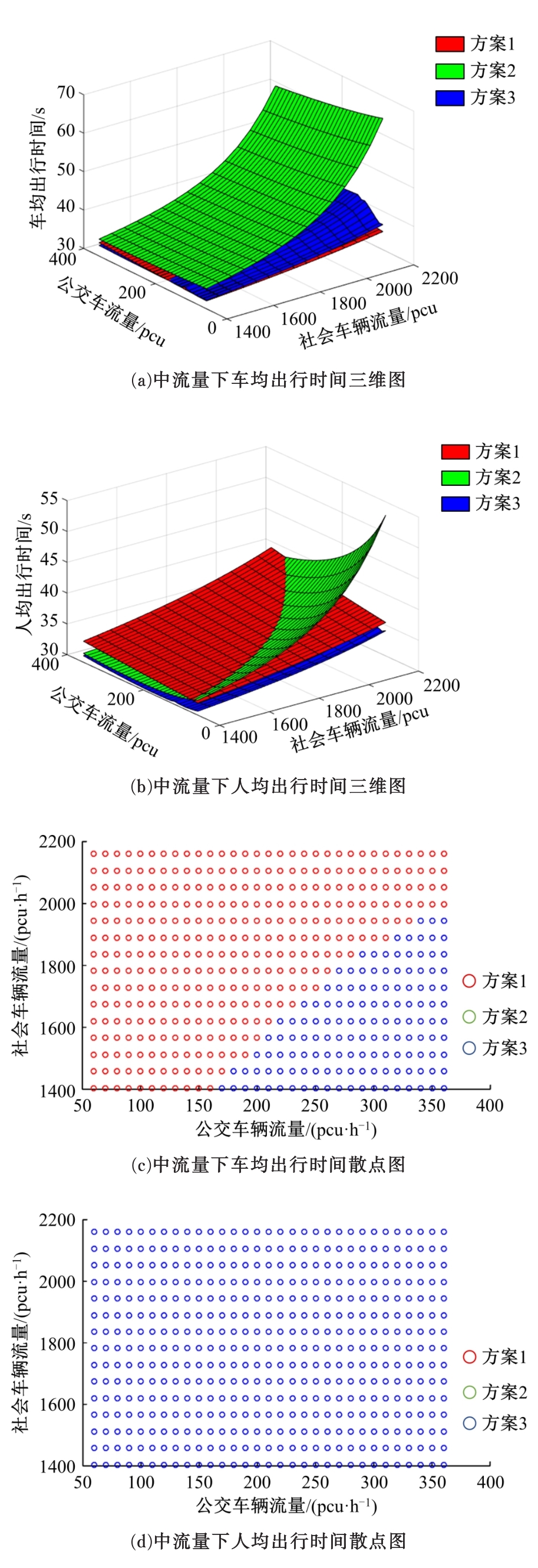
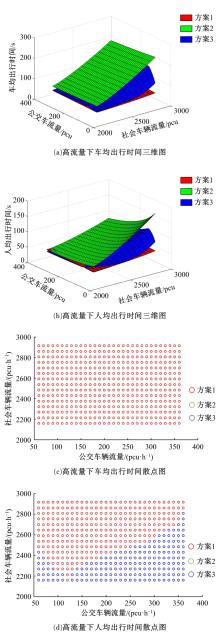
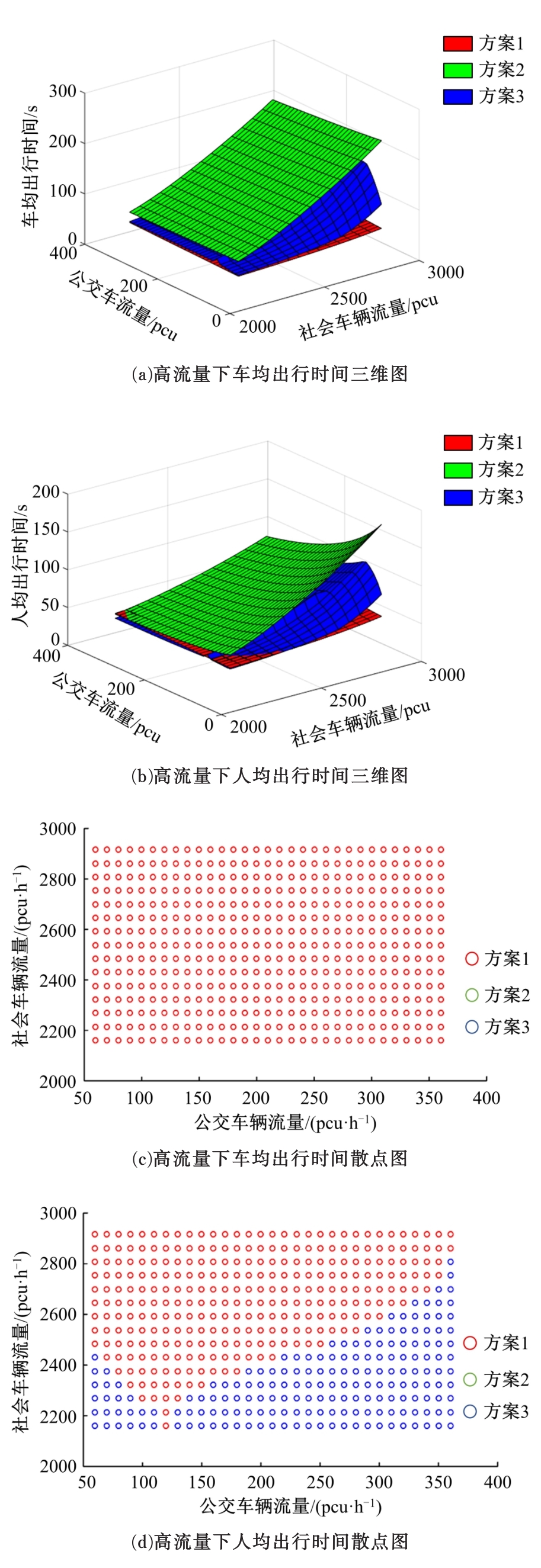
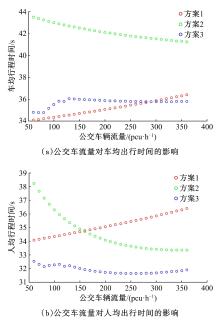
提出了一种新型动态公交专用道,不仅确保了公交优先策略,且可显著提升道路资源时空利用率,降低了社会车辆与公交车辆对道路资源的需求冲突。分析了公交车到达时刻的差异性,基于交叉口车辆排队的消散过程,提出了动态车道清空距离确定方法及车道控制流程;结合HCM2010车辆延误公式和路阻函数,建立了不同道路条件下车均和人均出行时间模型,通过数值模拟仿真对未设置公交专用道、常规公交专用道和动态公交专用道3种车道组织方案的运行效益进行对比分析。实验结果表明:在三车道道路条件下,当社会车辆流量小于2268 pcu/h时,设置动态公交专用道的时间效益更好,为公交车道的优化提供了理论支持。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | 王涛, 陈峻. 基于时间效益的城市公交专用道设置流量条件[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2014, 46(4): 115-121. |
| Wang Tao, Chen Jun. Traffic volume conditions of setting bus lane on urban roadway based on time utility[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014, 46(4): 115-121. | |
| 2 | 黄艳君, 陈学武, 张卫华. 公交专用道设置前后路段交通流模型的比较[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2003, 20(4): 68-70. |
| Huang Yan-jun, Chen Xue-wu, Zhang Wei-hua. Comparison of traffic flow on the road with or without bus lane[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Urban Science Edition), 2003, 20(4): 68-70. | |
| 3 | Basso L J, Guevana C A, Gschwender A, et al. Congestion pricing, transit subsidies and dedicated bus lanes: efficient and practical solutions to congestion[J]. Transport Policy, 2011, 18(5): 676-684. |
| 4 | Li S G, Ju Y F. Evaluation of bus-exclusive lanes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2009, 10(2): 236-245. |
| 5 | 吴娇蓉, 王宇沁, 魏明, 等. 路侧公交专用道设置长度对公交线路运行可靠性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版,2017, 47(1): 82-91. |
| Wu Jiao-rong, Wang Yu-qin, Wei Ming, et al. Impact of length of road-side bus lane on bus operational reliability[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(1): 82-91. | |
| 6 | 梁士栋, 赵淑芝, 马明辉, 等. 路段直线式公交站点对公交车延误的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版,2016, 46(6): 1807-1817. |
| Liang Shi-dong, Zhao Shu-zhi, Ma Ming-hui,et al. Impacts of linear bus stop on bus delays[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(6): 1807-1817. | |
| 7 | Viegas J, Lu B. Widening the scope for bus priority with intermittent bus lanes[J]. Transportation Planning & Technology, 2001, 24(2): 87-110. |
| 8 | Viegas J, Lu B. The intermittent bus lane signals setting within an area[J]. Transportation Research Part C Emerging Technologies, 2004, 12(6): 453-469. |
| 9 | Viegas J, Lu B, Vieiar J, et al. Demonstration of the intermittent bus lane in Lisbon[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2006, 39(12): 239-244. |
| 10 | Yang H, Wang W. An innovative dynamic bus lane system and its simulation-based performance investigation[J]. IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 2009(7): 105-110. |
| 11 | 谢秋峰. 设置间歇式公交专用道的路段通行能力研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学交通学院, 2012. |
| Xie Qiu-feng. Research on the capacity of road section with intermittent bus lane[D]. Nanjing: School of Transportation, Southeast University, 2012. | |
| 12 | Wu W, Head L, Yan S, et al. Development and evaluation of bus lanes with intermittent and dynamic priority in connected vehicle environment[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 22(4): 301-310. |
| 13 | Wu D, Deng W, Song Y, et al. Evaluating operational effects of bus lane with intermittent priority under connected vehicle environments[J/OL].[2017-04-19]. |
| [1] | 张大伟,祝海涛. 考虑行人差异性的人群疏散最优决策理论模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 549-556. |
| [2] | 贾洪飞,丁心茹,杨丽丽. 城市潮汐车道优化设计的双层规划模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 535-542. |
| [3] | 尹超英,邵春福,王晓全,熊志华. 考虑空间异质性的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 543-548. |
| [4] | 宗长富,文龙,何磊. 基于欧几里得聚类算法的三维激光雷达障碍物检测技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 107-113. |
| [5] | 隋振,姜源. 基于MIMO类脑情感学习回路的横-纵向综合控制驾驶员模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 140-146. |
| [6] | 常玉林,袁才鸿,孙超,张鹏. 基于改进元胞传输模型的城市路网实际阻抗计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 132-139. |
| [7] | 谷远利, 张源, 芮小平, 陆文琦, 李萌, 王硕. 基于免疫算法优化LSSVM的短时交通流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857. |
| [8] | 别一鸣,姜凯,汤茹茹,王琳虹,熊昕宇. 考虑方案过渡影响的单点交通控制时段划分方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1844-1851. |
| [9] | 程国柱, 冯思鹤, 冯天军. 占用车行道的路内停车泊位设置条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1858-1864. |
| [10] | 梁泉,翁剑成,周伟,荣建. 基于关联规则的公共交通通勤稳定性人群辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1484-1491. |
| [11] | 龙海波,杨家其,赵学彧. 基于转运延误风险的多方式协同货运载运工具配置优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1492-1499. |
| [12] | 别一鸣,汤茹茹,王运豪,文斌,冯天军,王琳虹. 信号交叉口进口车道饱和流率估计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1459-1464. |
| [13] | 吴文静,陈润超,贾洪飞,罗清玉,孙迪. 车路协同环境下路段掉头区域车辆协同控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1100-1106. |
| [14] | 江亮,贺宜. 电动两轮车风险驾驶行为及事故影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1107-1113. |
| [15] | 曲昭伟,潘昭天,陈永恒,陶鹏飞,孙迪. 基于最优速度模型的改进安全距离跟驰模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1092-1099. |
|
||