吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 657-665.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200851
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
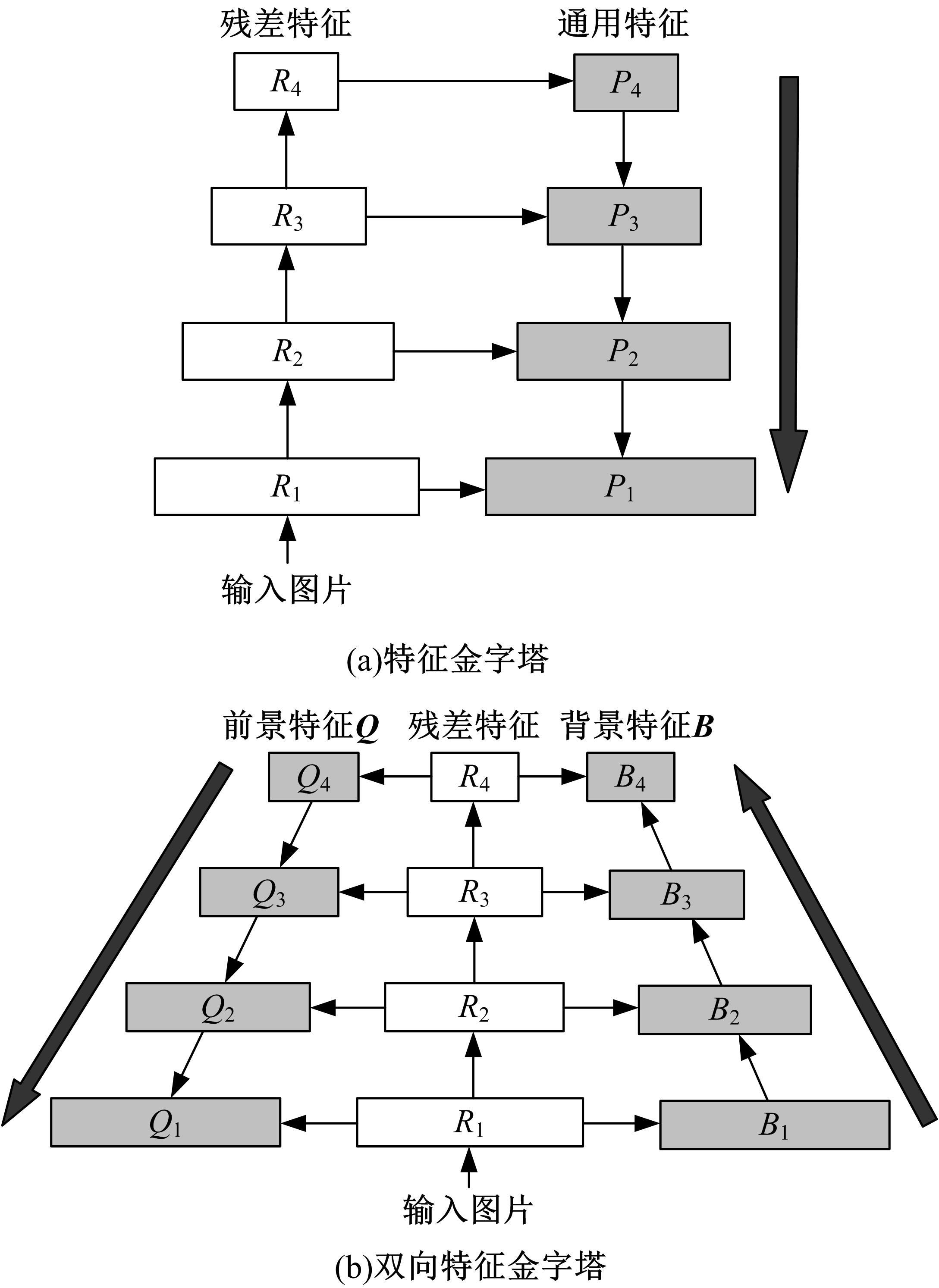
双向特征金字塔全景分割网络
- 大连民族大学 机电工程学院,辽宁 大连 116600
Two⁃way feature pyramid network for panoptic segmentation
Lin MAO( ),Feng-zhi REN,Da-wei YANG(
),Feng-zhi REN,Da-wei YANG( ),Ru-bo ZHANG
),Ru-bo ZHANG
- School of Electromechanical Engineering,Dalian Minzu University,Dalian 116600,China
摘要:
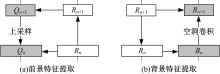
针对传统特征金字塔网络应用于全景分割领域存在的不足,提出了一种双向特征金字塔全景分割网络(T-FPN),解决了特征金字塔单向传递统一特征输出与全景分割双线任务特征需求的矛盾。根据图像前、背景的差异分析,按照前、背景分割任务的不同需求构建了双向传递路径。使用上采样自上而下传递加强前景特征,利用空洞卷积自下而上传播增强背景特征,以双向网络同时提取前景特征和背景特征,营造前、背景分割精度的动态平衡,从而提高全景分割的质量。在MS COCO和Cityscapes数据集上的实验结果表明,本文提出的双向特征金字塔全景分割网络在分割精度上优于现存同类方法,与使用传统特征金字塔提取特征的全景分割算法UPSNet相比,PQ值提高了0.47%。
中图分类号:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Li Y, Chen X, Zhu Z, et al. Attention-guided unified network for panoptic segmentation[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 7019-7028. |
| 2 | Kirillov A, Girshick R, He K, et al. Panoptic feature pyramid networks[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 6392-6401. |
| 3 | Lin T, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 936-944. |
| 4 | Liu H Y, Peng C, Yu C Q, et al. An end-to-end network for panoptic segmentation[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 6165-6174. |
| 5 | Xiong Y W, Liao R J, Zhao H S, et al. UPSNet: a unified panoptic segmentation network[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 8810-8818. |
| 6 | Li J, Raventos A, Bhargava A, et al. Learning to fuse things and stuff[J/OL]. [2020-10-22]. |
| 7 | Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. |
| 8 | 徐谦, 李颖, 王刚. 基于深度学习图像语义分割的机器人环境感知[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(1): 248-260. |
| Xu Qian, Li Ying, Wang Gang. Robotic environment sensing based on semantic segmentation by deep learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(1): 248-260. | |
| 9 | Fan L, Kong H F, Wang W C, et al. Semantic segmentation with global encoding and dilated decoder in street scenes[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 50333-50343. |
| 10 | Ding H H, Jiang X D, Shuai B, et al. Semantic segmentation with context encoding and multi-path decoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 3520-3533. |
| 11 | Yang T J, Collins M D, Zhu Y, et al. DeeperLab: single-shot image parser[J/OL]. [2020-10-23]. |
| 12 | Cheng B, Collins M D, Zhu Y K, et al. Panoptic-DeepLab: a simple, strong, and fast baseline for bottom-up panoptic segmentation[J/OL]. [2020-10-23]. |
| 13 | He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 14 | 张涛, 张乐. 一种基于多尺度特征融合的目标检测算法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(2): 294-300. |
| Zhang Tao, Zhang Le. An object detection algorithm based on multi-scale feature fusion[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(2): 294-300. | |
| 15 | Tian Z, Shen C H, Chen H, et al. FCOS: a simple and strong anchor-free object detector[J/OL]. [2020-10-22]. |
| 16 | 汤润发, 宋慧慧, 张开华, 等. 特征注意金字塔调制网络的视频目标分割[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2019, 24(8): 1349-1357. |
| Tang Run-fa, Song Hui-hui, Zhang Kai-hua, et al. Video object segmentation via feature attention pyramid modulating network[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2019, 24(8): 1349-1357. | |
| 17 | Yu F, Koltun V. Multi-Scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[J/OL]. [2020-10-26]. |
| 18 | He K, Gkioxari G, Dollar P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]∥2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980-2988. |
| 19 | 潘晓英, 魏德, 赵逸喆. 基于Mask R-CNN和上下文卷积神经网络的肺结节检测[J/OL]. [2021-06-18]. |
| 20 | Dai Ji-feng, Qi Hao-zhi, Xiong Yu-wen, et al. Deformable convolutional networks[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 764-773. |
| 21 | Lin T Y, Maire M, Belongie S, et al. Microsoft COCO: common objects in context[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 740-755. |
| 22 | Cordts M, Omran M, Ranos S, et al. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Las Vegas, Nevada, USA, 2016: 3213-3223. |
| 23 | 杨丽娟, 李利. 基于双线性插值的内容感知图像缩放算法仿真[J]. 计算机仿真, 2019, 36(12): 244-248. |
| Yang Li-juan, Li Li. Simulation of content-aware image scaling algorithm based on bilinear interpolation[J]. Computer Simulation, 2019, 36(12): 244-248. | |
| 24 | Kirillov A, He K, Girshick R, et al. Panoptic segmentation[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 9396-9405. |
| [1] | 王雪,李占山,吕颖达. 基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| [2] | 欧阳继红,郭泽琪,刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [3] | 康苏明,张叶娥. 基于Hadoop的跨社交网络局部时序链路预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 626-632. |
| [4] | 曲优,李文辉. 基于锚框变换的单阶段旋转目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 162-173. |
| [5] | 赵宏伟,霍东升,王洁,李晓宁. 基于显著性检测的害虫图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2174-2181. |
| [6] | 刘洲洲,张倩昀,马新华,彭寒. 基于优化离散差分进化算法的压缩感知信号重构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2246-2252. |
| [7] | 王生生,陈境宇,卢奕南. 基于联邦学习和区块链的新冠肺炎胸部CT图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2164-2173. |
| [8] | 孙东明,胡亮,邢永恒,王峰. 基于文本融合的物联网触发动作编程模式服务推荐方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2182-2189. |
| [9] | 林俊聪,雷钧,陈萌,郭诗辉,高星,廖明宏. 基于电影视觉特性的动态多目标实时相机规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2154-2163. |
| [10] | 任丽莉,王志军,闫冬梅. 结合黏菌觅食行为的改进多元宇宙算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2190-2197. |
| [11] | 姚引娣,贺军瑾,李杨莉,谢荡远,李英. 自构建改进型鲸鱼优化BP神经网络的ET0模拟计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1798-1807. |
| [12] | 赵宏伟,张子健,李蛟,张媛,胡黄水,臧雪柏. 基于查询树的双向分段防碰撞算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1830-1837. |
| [13] | 马莹莹,陆思园,张晓明,魏文术. 考虑个体风险偏好差异的高速公路出行选择模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1673-1683. |
| [14] | 曹洁,屈雪,李晓旭. 基于滑动特征向量的小样本图像分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| [15] | 孙小雪,钟辉,陈海鹏. 基于决策树分类技术的学生考试成绩统计分析系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1866-1872. |
|
||