吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 2321-2331.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211083
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
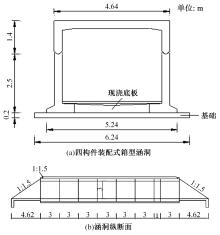
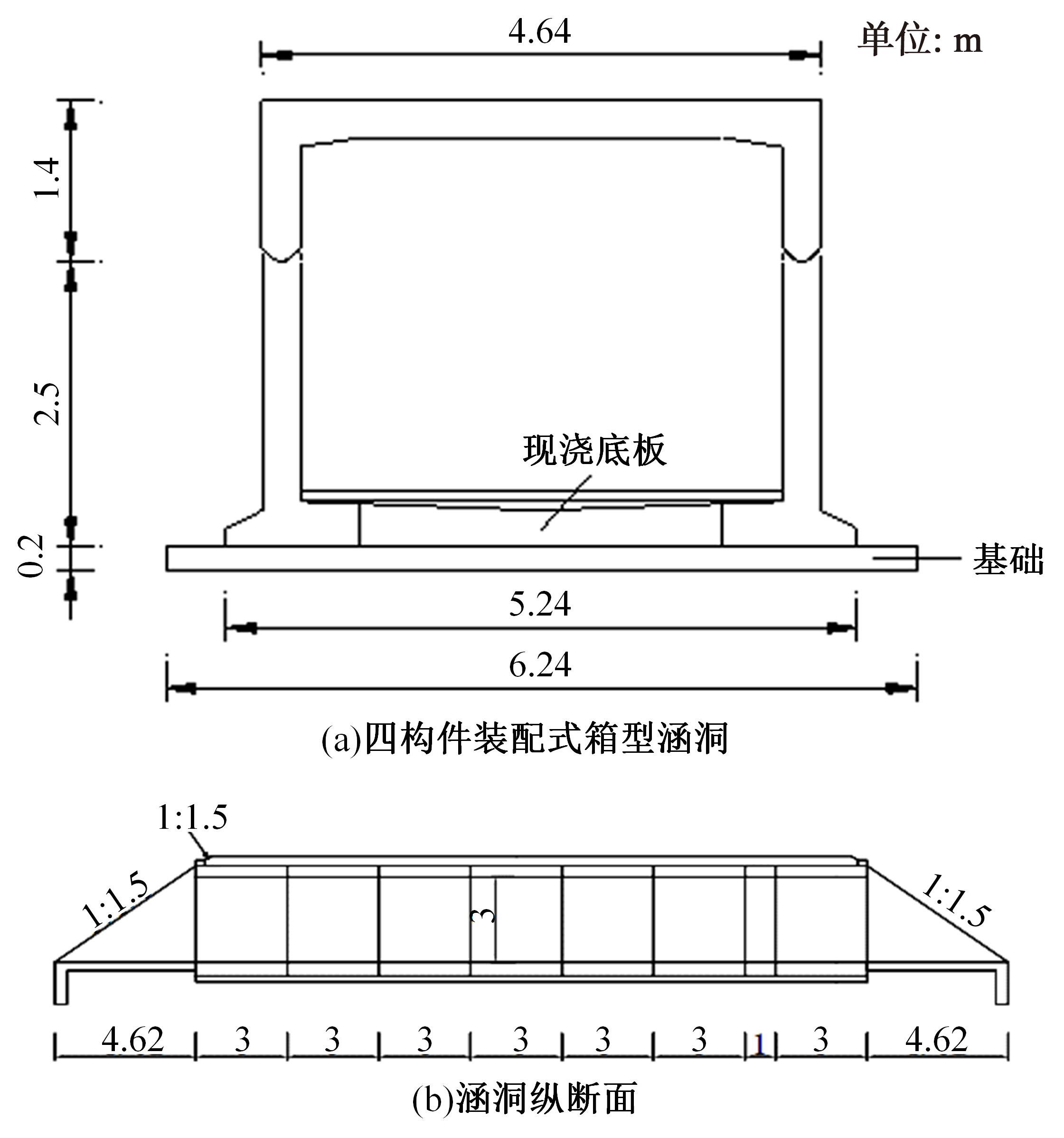
基于现场监测技术的装配式箱涵温度场及冻胀分析
- 吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
Temperature field and frost heaving analysis of prefabricated box culvert based on field monitoring
Ya-feng GONG( ),Shu-zheng WU,Hai-peng BI(
),Shu-zheng WU,Hai-peng BI( ),Guo-jin TAN
),Guo-jin TAN
- College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
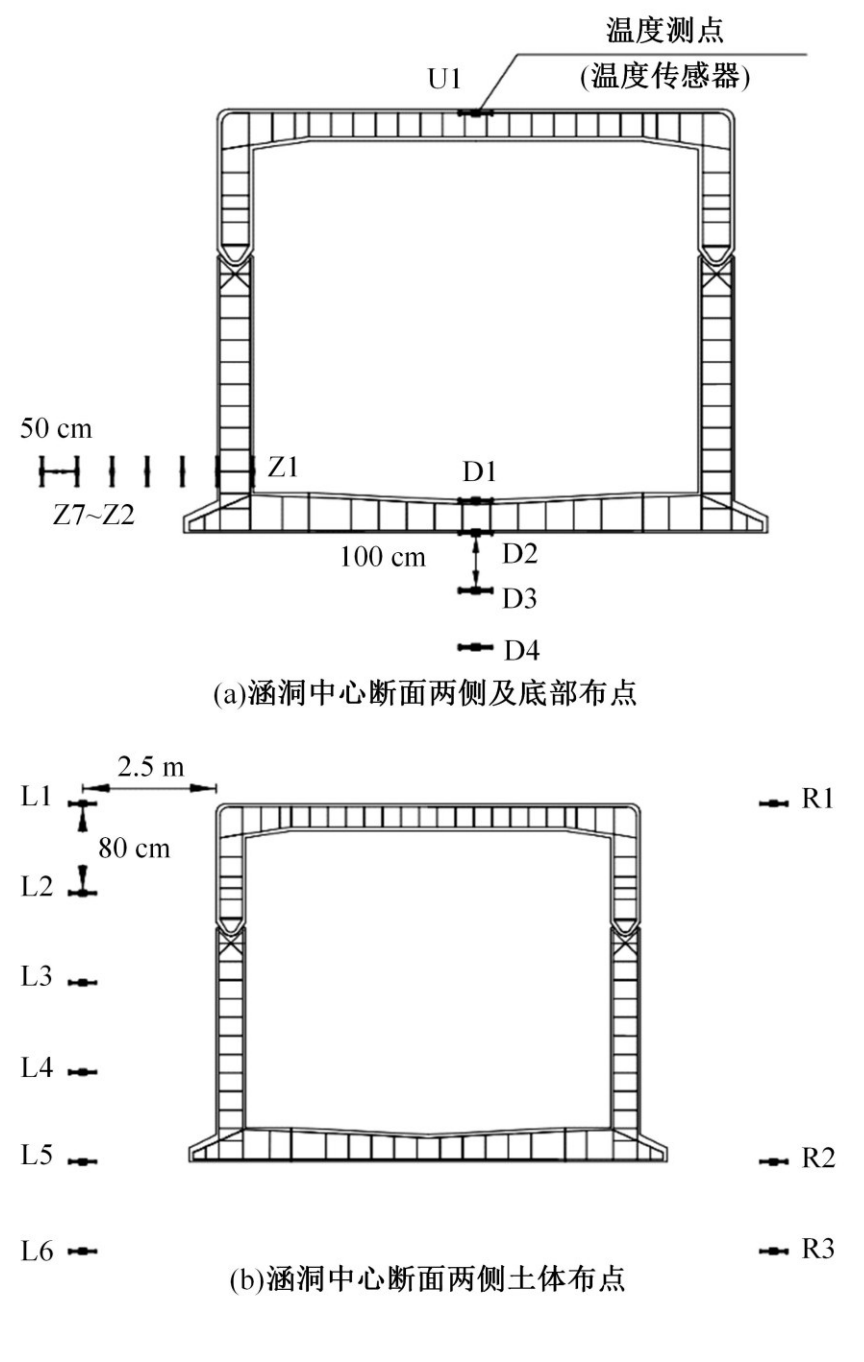
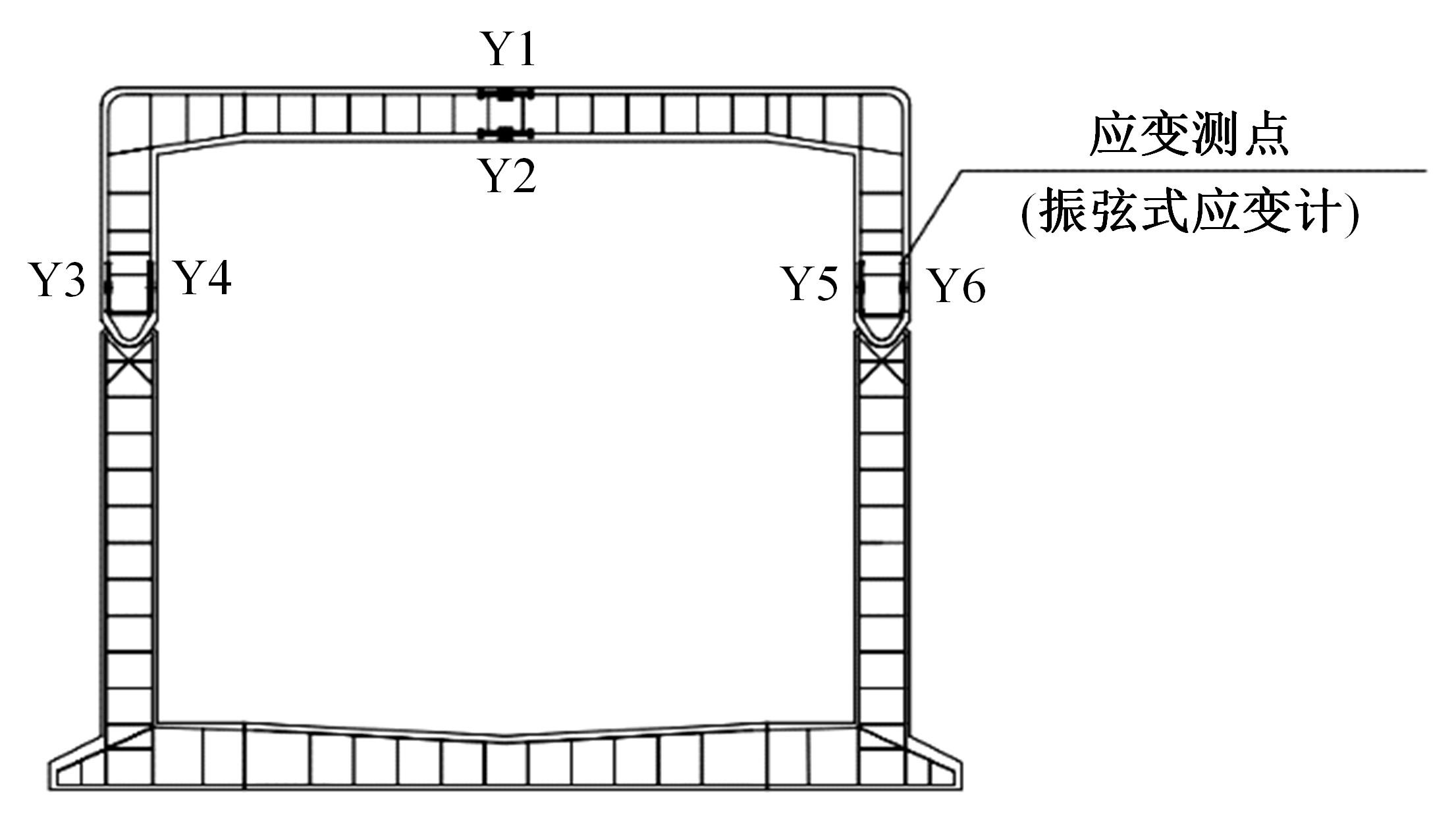
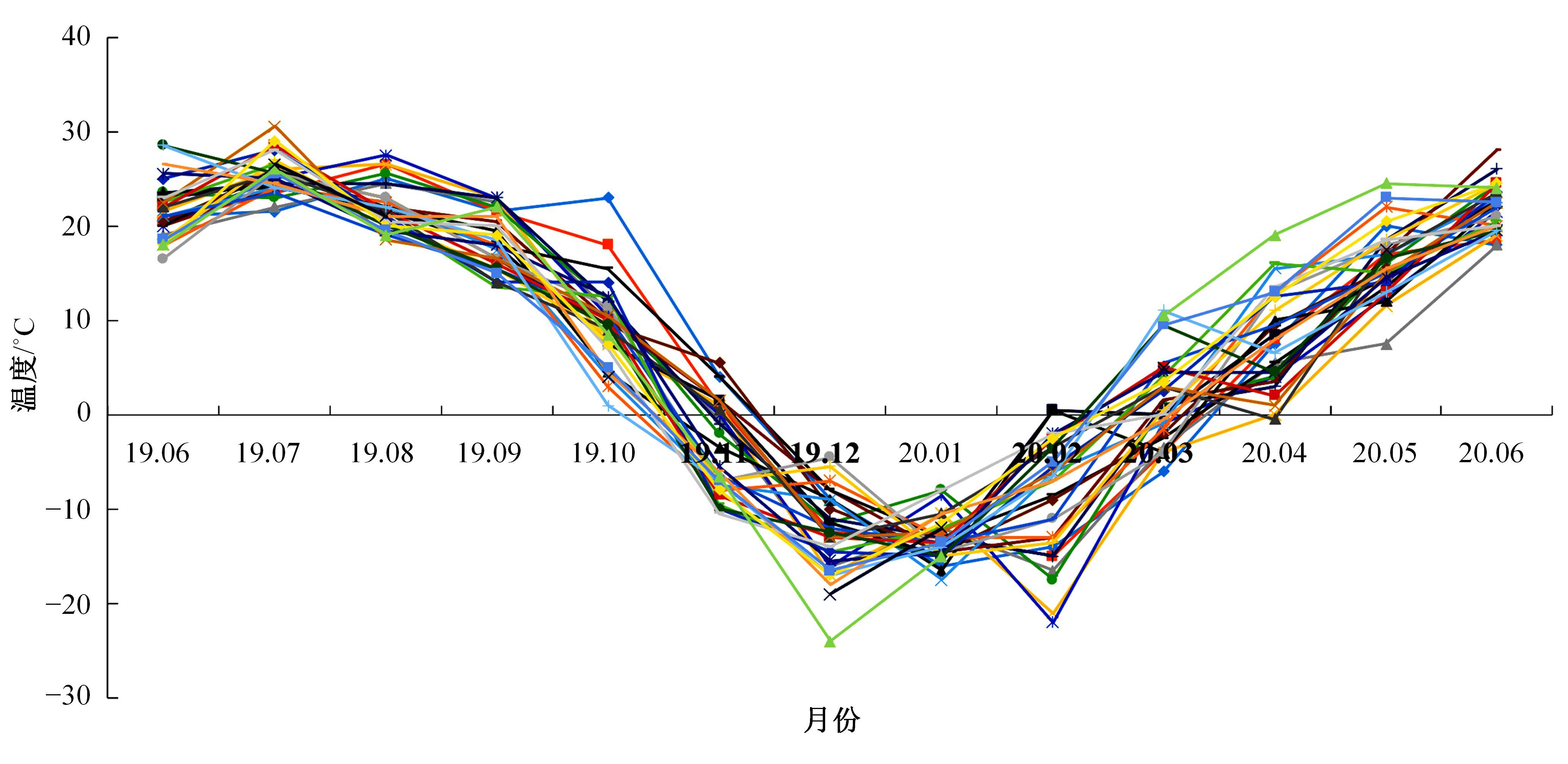
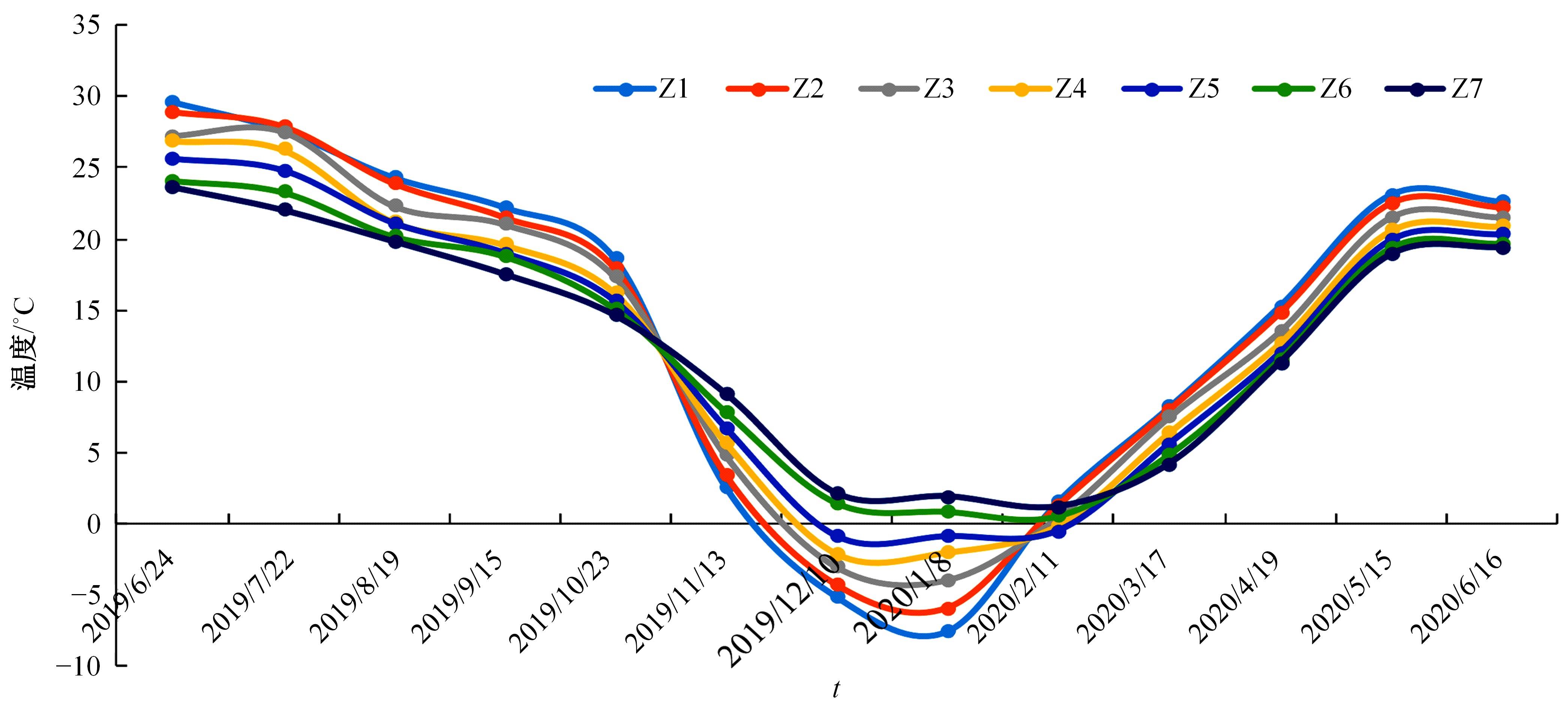
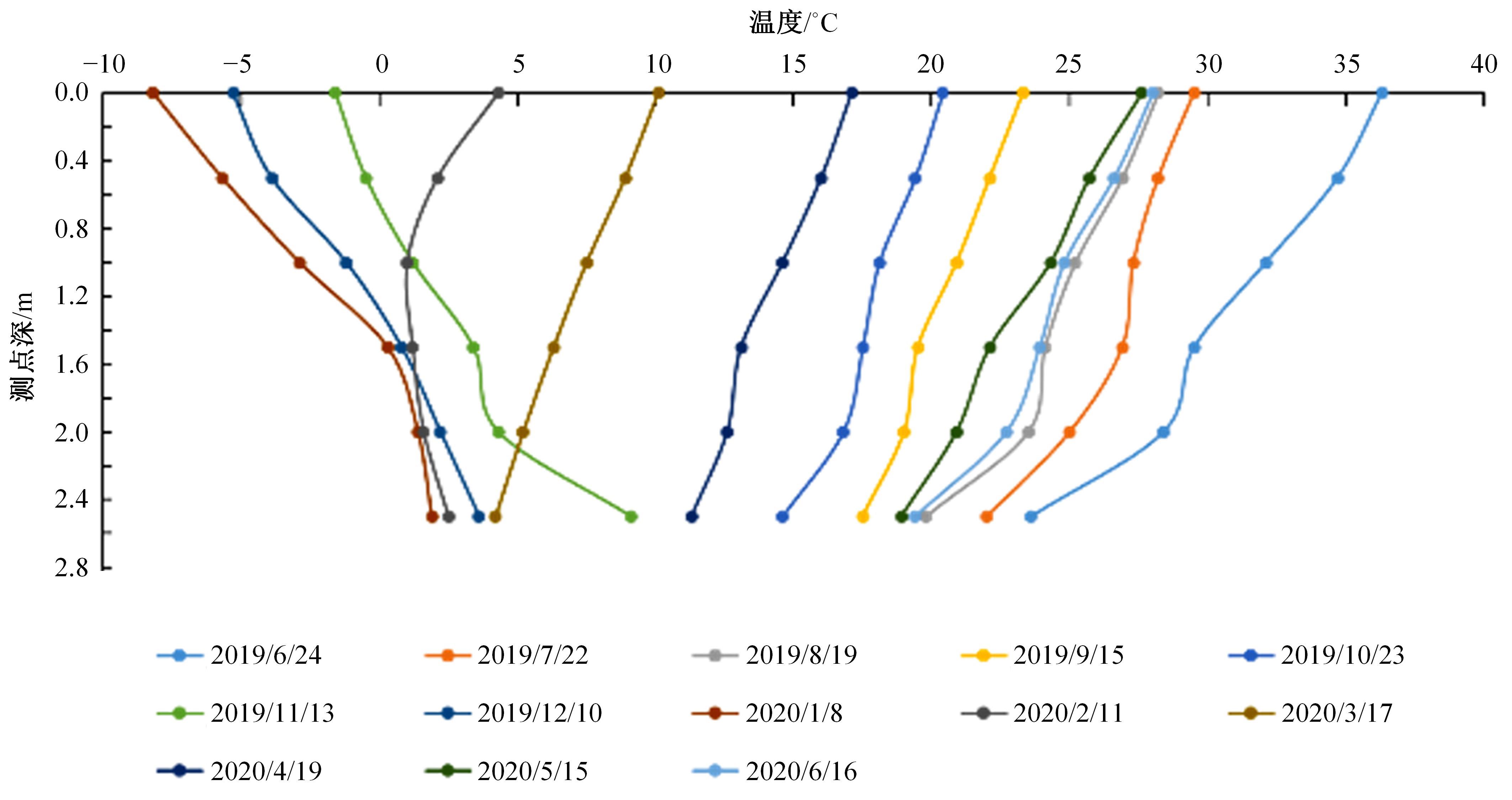
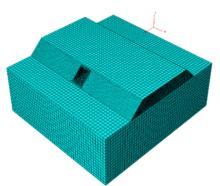
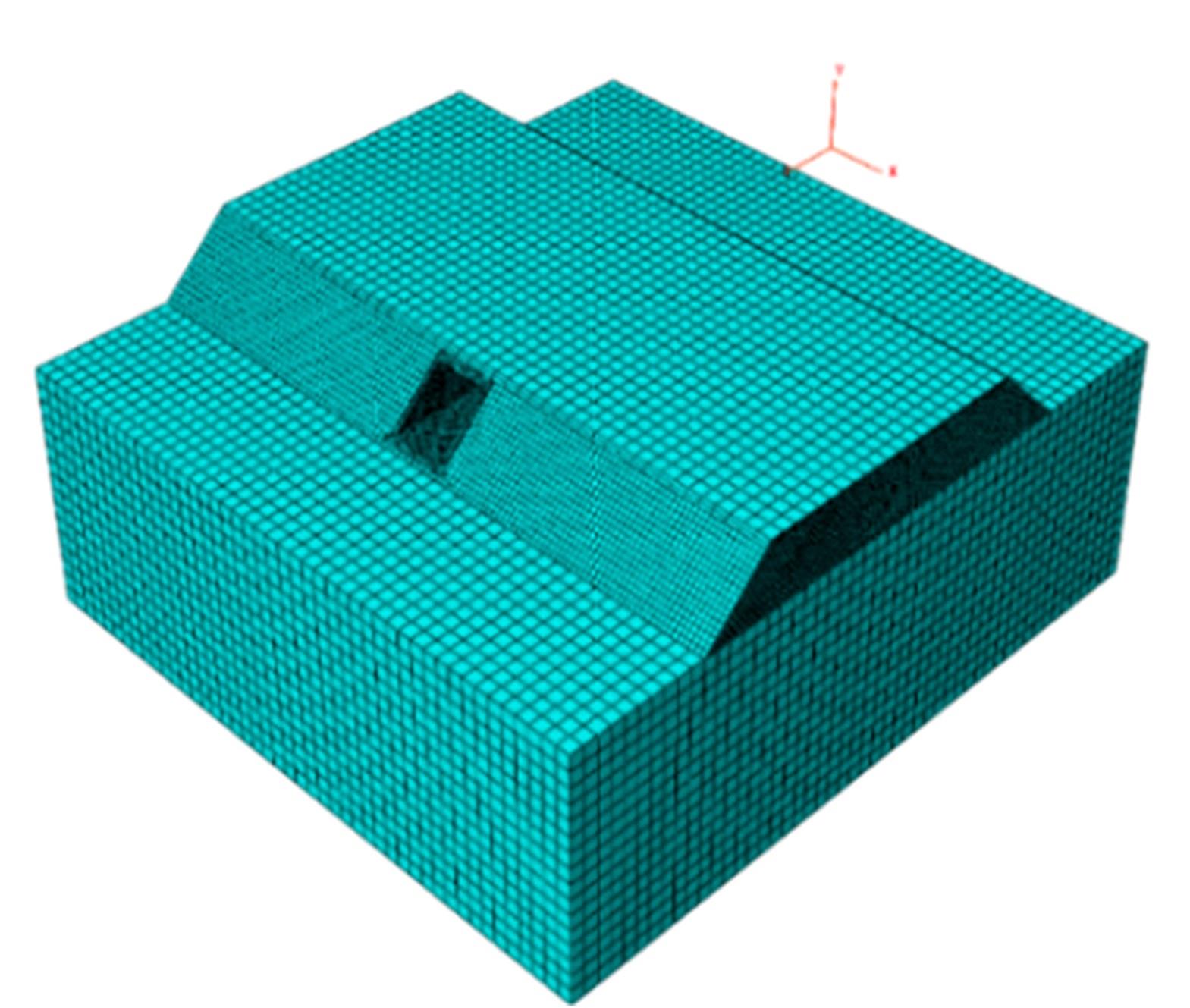
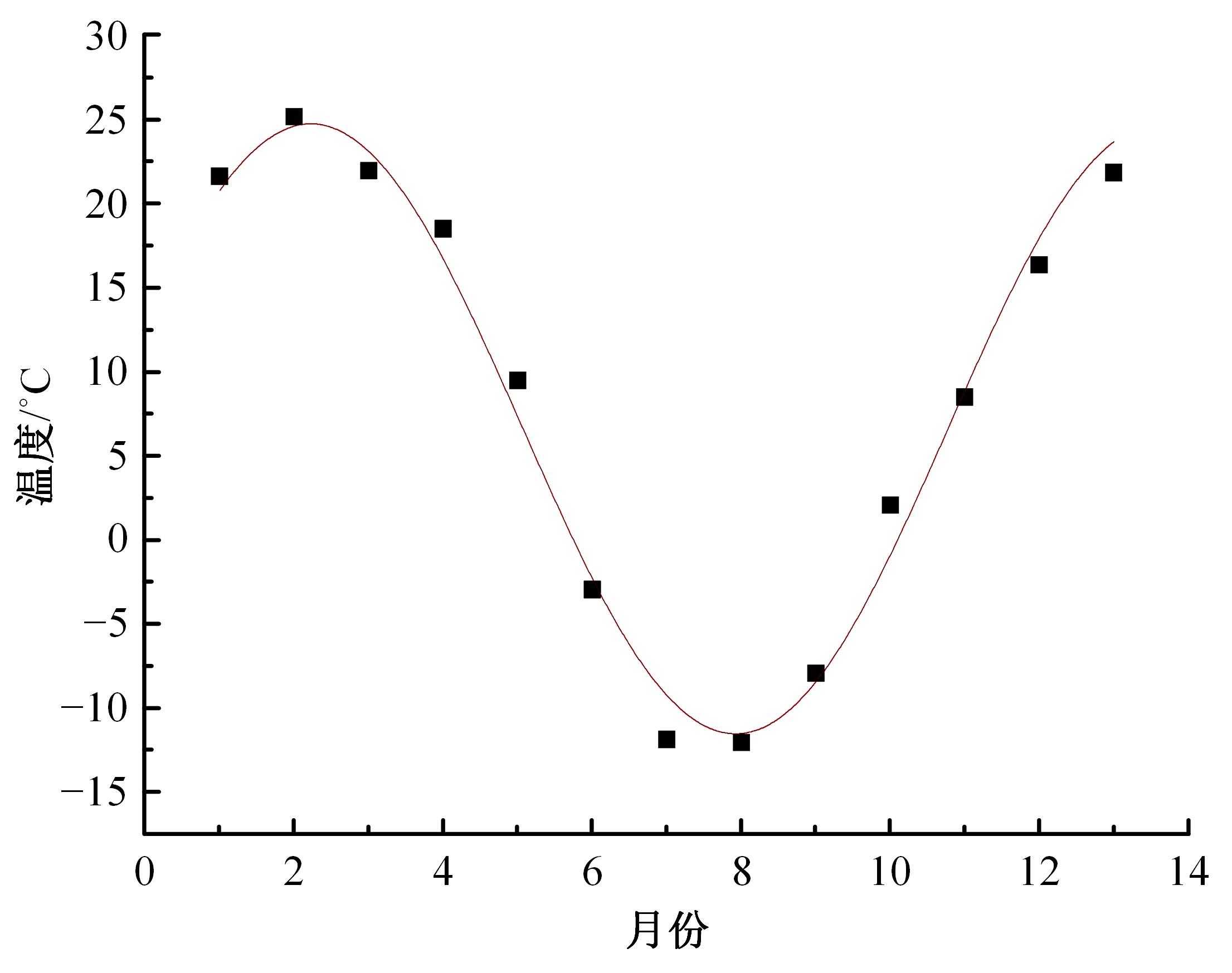
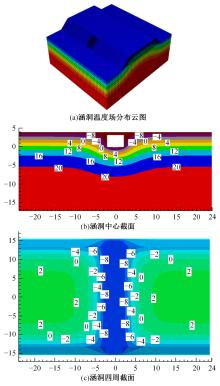
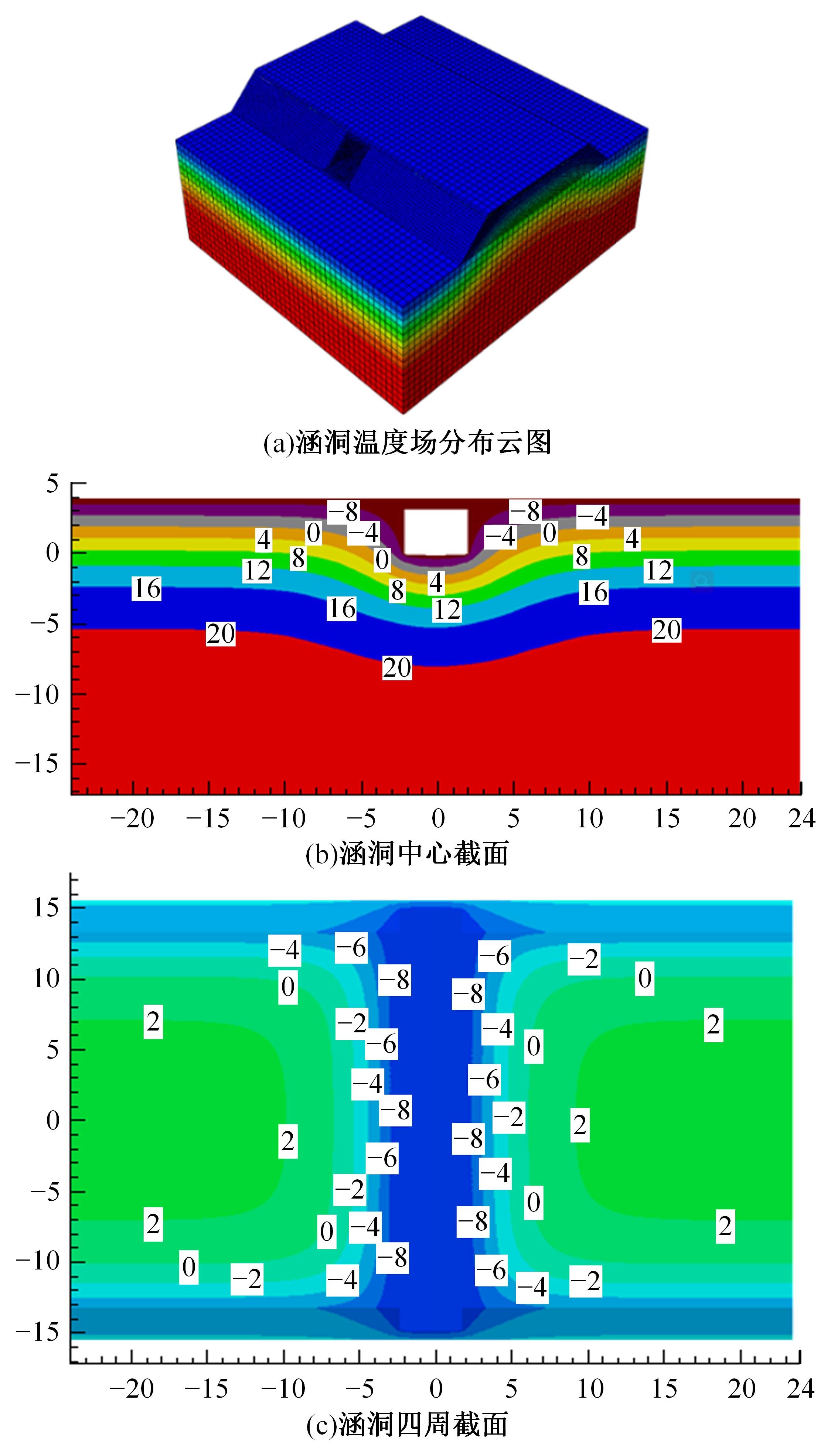
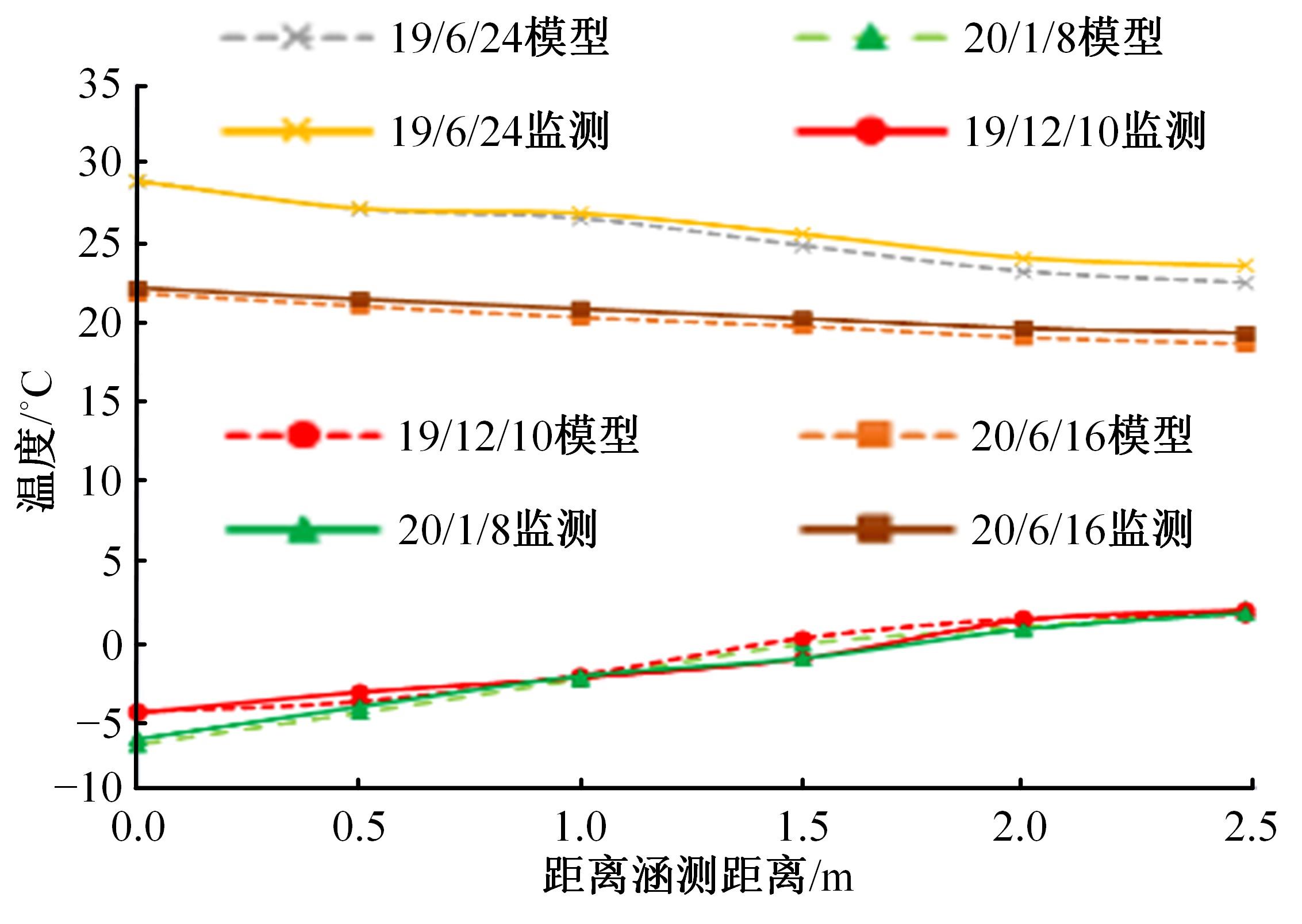
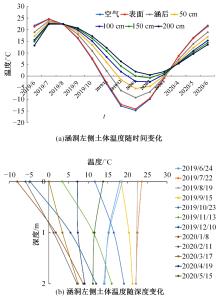
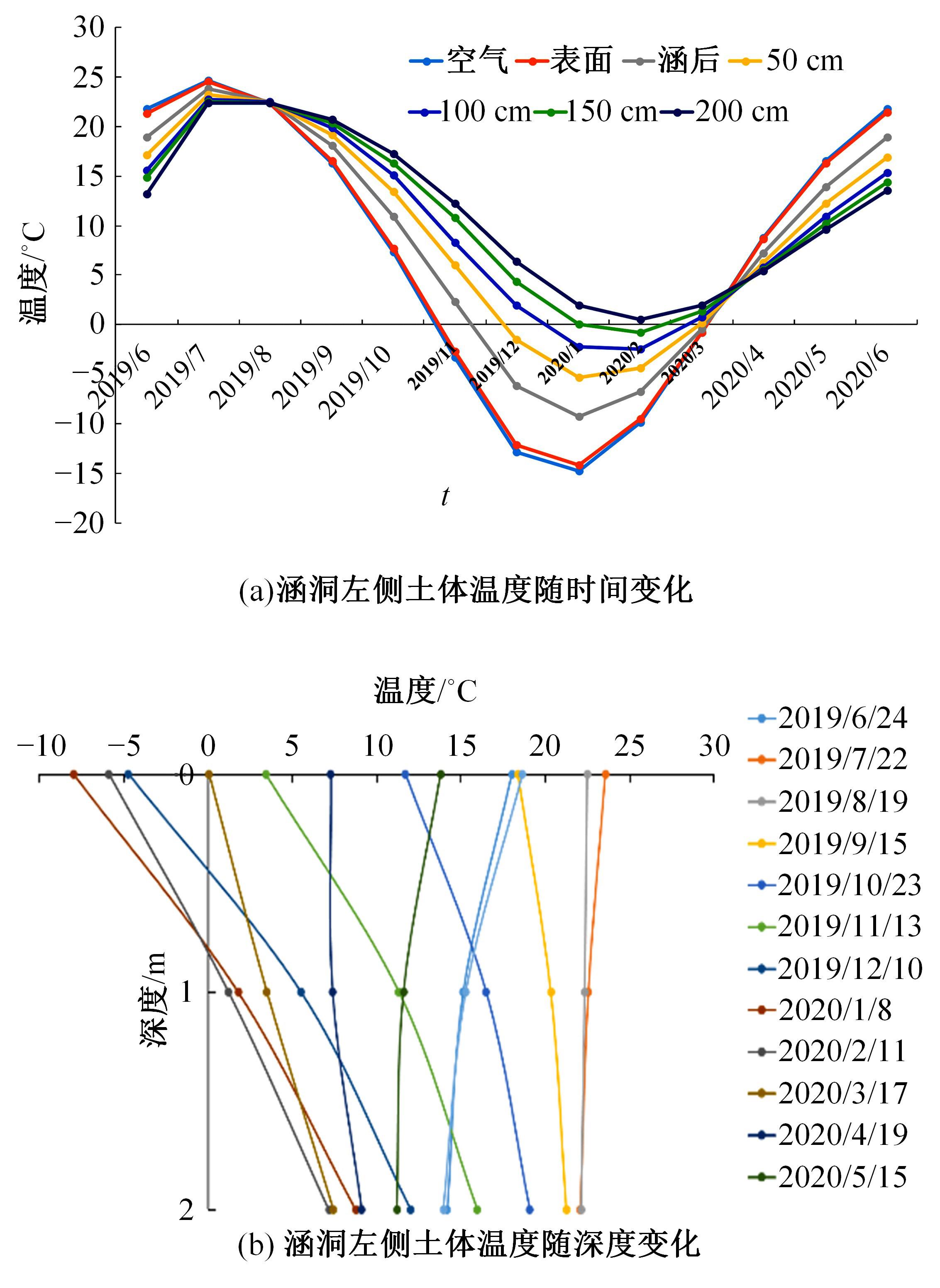
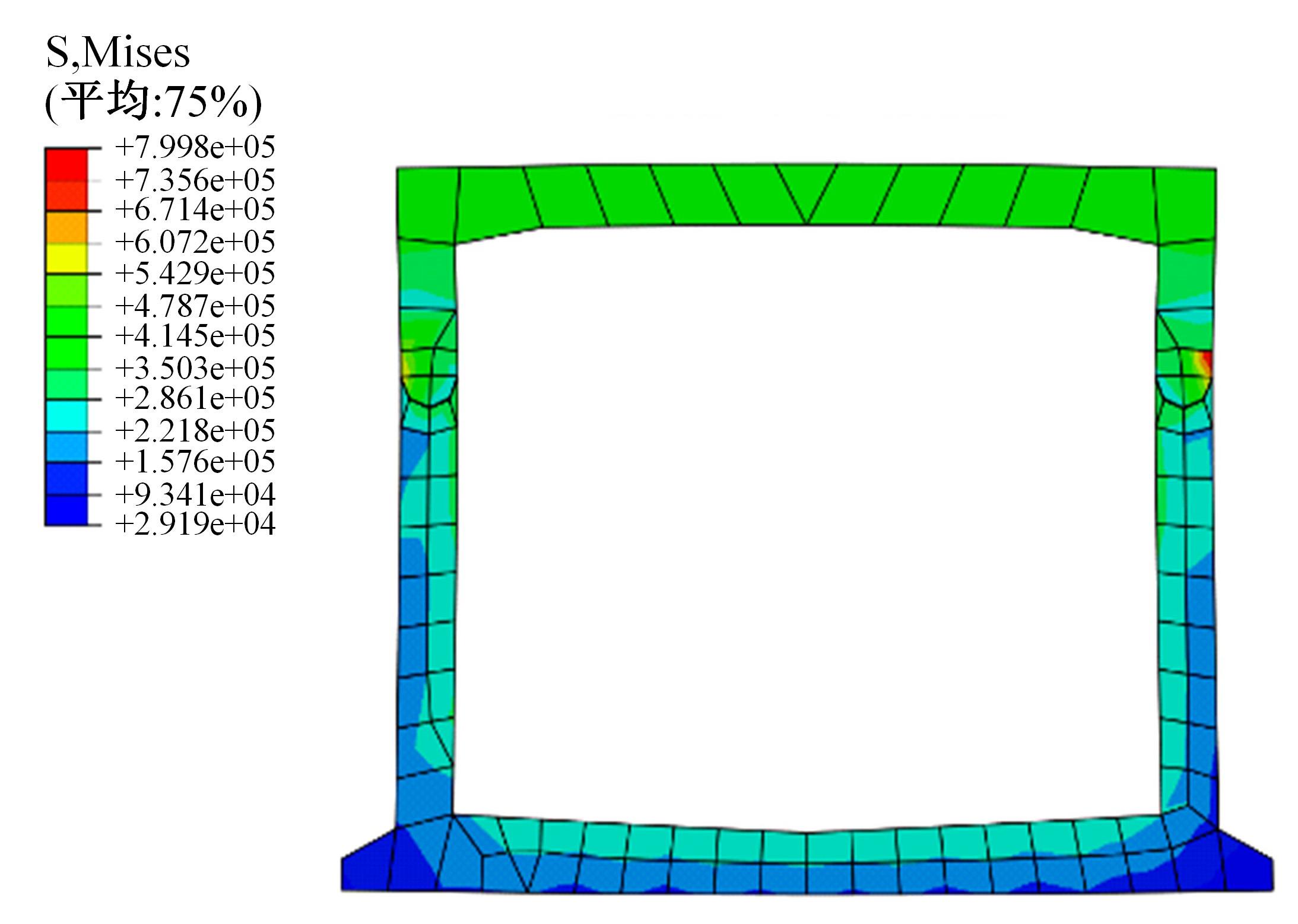
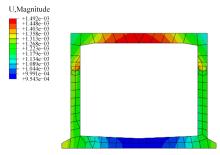
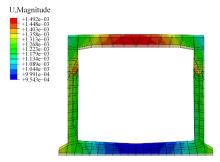
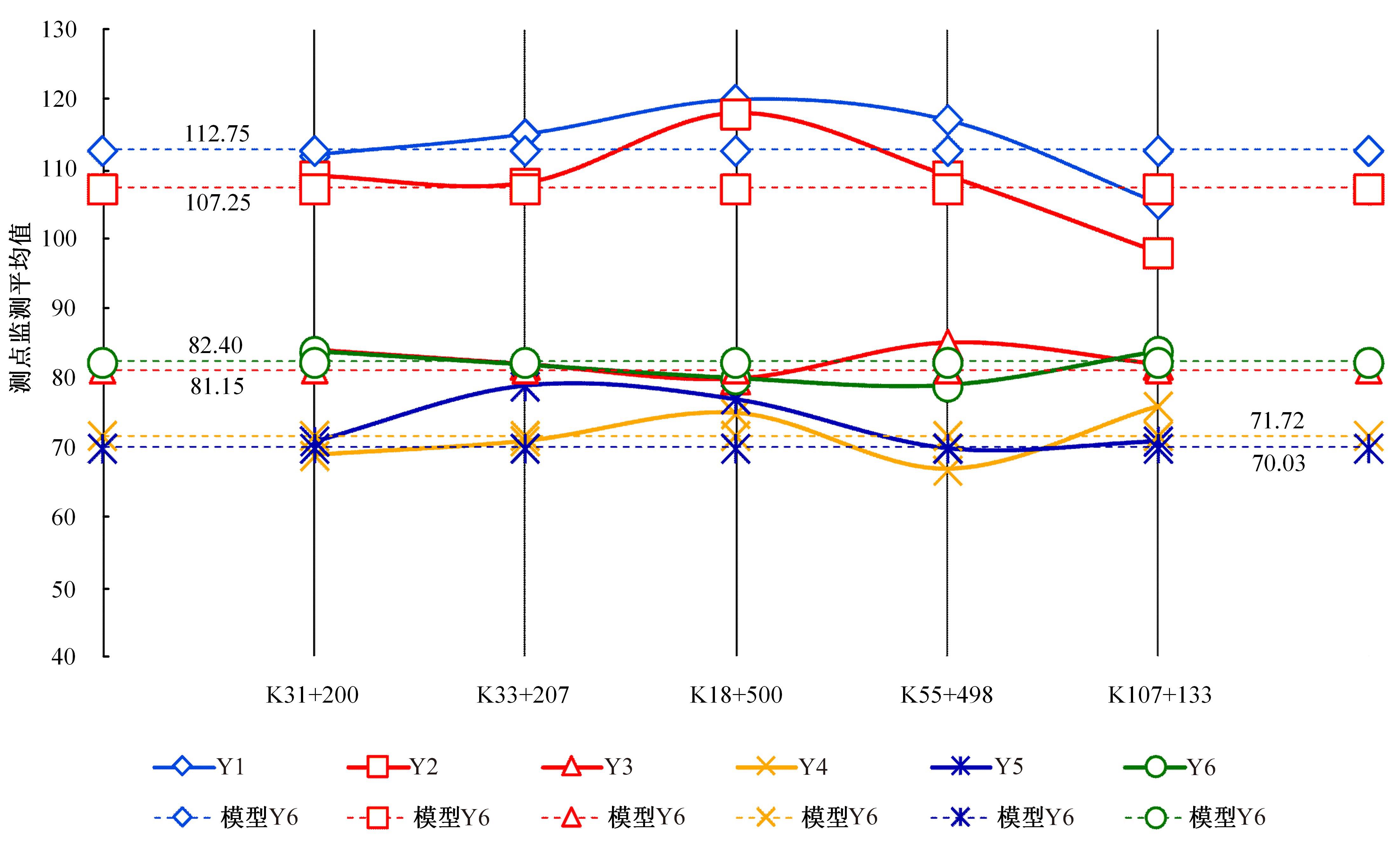
以实际工程为依托,通过获取装配式箱涵周围土体温度及微应变的现场监测技术,在涵周埋设不同数量的温度传感器和振弦应变计,并借助有限元软件分析,探究箱涵周围土体的温度场分布规律及冻胀特性。首先,对箱涵周围土体的温度及微应变进行为期12个月的监控测量;其次,基于焓场求解的非稳态传热理论,通过有限元软件建立相应的数值模型并对比分析监测数据,对装配式箱涵周围土体变化规律进行剖析。研究结果表明:受热辐射和空气对流的共同影响,涵周土体温度呈现出季节性的变化规律;短暂升温形成的棉被效应,导致温度随土体深度呈现先下降后上升的趋势;受冻胀力影响,箱涵应力最大位置在铰接处,隆起位移最大位置在涵顶处。
中图分类号:
- U449.1
| 1 | 张丹,张乃源,李永明,等. 公路预制装配式混凝土箱涵施工技术[J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2020(4): 37-40, 85. |
| Zhang Dan, Zhang Nai-yuan, Li Yong-ming, et al. Construction technology of highway fabricated concrete box culverts[J]. China Concrete and Cement Product, 2020(4): 37-40, 85. | |
| 2 | Tai B W, Wu Q B, Yue Z R, et al. Ground temperature and deformation characteristics of anti-freeze-thaw embankments in permafrost and seasonal frozen ground regions of China[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2021,189: 103331. |
| 3 | Zhang W H, Pi Y L, Kong W P, et al. Influence of damage degree on the degradation of concrete under freezing-thawing cycles[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020,260: 119903. |
| 4 | 李长江,梁养辉,胡滨,等.季冻区大孔径钢波纹管涵洞温度场分析[J]. 山东交通科技, 2017(6): 28-31. |
| Li Chang-jiang, Liang Yang-hui, Hu Bin, et al. Analysis of temperature field of large- diameter steel corrugated pipe culvert in seasonal frozen areas[J]. Shandong Jiaotong Keji, 2017(6): 28-31. | |
| 5 | 叶朝良,张梓鸿,王月. 深季节冻土区涵洞温度场分布规律测试分析[J]. 铁道标准设计, 2017, 61(8): 16-20, 26. |
| Ye Chao-liang, Zhang Zi-hong, Wang Yue. The test and analysis of temperature field distribution of culvert in deep seasonal frozen region[J]. Railway Standard Design, 2017, 61(8): 16-20, 26. | |
| 6 | 阎菊花,孙学先. 拼装式涵洞施工中高温冻土地基温度场研究[J]. 兰州交通大学学报, 2006(1): 34-36. |
| Yan Ju-hua, Sun Xue-xian. Study of ground temperature field while construction of precast installed culvert in warm permafrost[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2006(1): 34-36. | |
| 7 | 张旭芝,王星华. 高原融区和多年冻土过渡段涵洞地基试验研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2004, 25(4): 69-72. |
| Zhang Xu-zhi, Wang Xing-hua. In-situ experimental study on railway culvert in thaw and permafrost transition regions of tibetan plateau[J]. China Railway Science, 2004, 25(4): 69-72. | |
| 8 | Liu H W, Pooneh M, Ahmed S, et al. Thermo-hydro-mechanical modeling of frost heave using the theory of poroelasticity for frost-susceptible soils in double-barrel culvert sites[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2019(20): 100251. |
| 9 |
Liu H, Niu F J, Niu Y H, et al. Study on thermal regime of roadbed-culvert transition section along a high speed railway in seasonally frozen regions[J]. Cold Regions Science & Technology. DOI:10.1016/j.coldregions. 2014.07.008 .
doi: 10.1016/j.coldregions. 2014.07.008 |
| 10 | Périer L, Doré G, Burn C R. The effects of water flow and temperature on thermal regime around a culvert built on permafrost[J]. Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions, 2014, 6(5): 415-422. |
| 11 | Kunitake M, Ogata H, Nakazawa T, et al.Temperature distribution in a concrete box culvert using 3-D FEM[C]∥Proceedings of the 2nd Asian-Pacific Conference on Computational Mechanics, Hong Kong China, 1993: 215-228. |
| 12 | 唐赛. 季冻区钢波纹管寒冬温度场分布与力学性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学土木工程学院, 2016. |
| Tang Sai. Study on temperature field distribution and mechanical properties of steel corrugated pipe culvert in seasonal frozen area[D]. Chongqing: School of Civil Engineering, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2016. | |
| 13 | 宫亚峰,王博,谭国金,等. 吉林省两种典型装配式箱涵受力特性对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(6): 1865-1870. |
| Gong Ya-feng, Wang Bo, Tan Guo-jin, et al. Comparative analysis of mechanical characteristics of two typical fabricated culverts in Jilin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1865-1870. | |
| 14 | 宫亚峰,宋加祥,毕海鹏,等. 装配式箱涵结构缩尺模型静载试验及有限元分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1728-1738. |
| Gong Ya-feng, Song Jia-xiang, Bi Hai-peng, et al. Static test and finite element analysis of scale model of fabricated box culvert[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1728-1738. |
| [1] | 惠迎新,陈嘉伟. 基于改进遗传算法的挤扩支盘群桩优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2089-2098. |
| [2] | 宫亚峰,吴树正,毕海鹏,周冬明,谭国金,黄晓明. 玄武岩纤维活性粉末混凝土与钢绞线粘结滑移过程声学特性表征[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1819-1832. |
| [3] | 刘顺,唐小微,栾一晓. 可液化土阻尼系数对地铁结构地震响应的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 159-169. |
| [4] | 卢晓红,乔金辉,周宇,马冲,隋国川,孙卓. 搅拌摩擦焊温度场研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 1-17. |
| [5] | 郭庆林,刘强,吴春利,李黎丽,李懿明,刘富春. 导电沥青及混合料裂缝局部温度场及愈合效果[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1386-1393. |
| [6] | 唐亮,司盼,崔杰,凌贤长,满孝峰. 液化微倾场地群桩地震反应分析拟静力方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 847-855. |
| [7] | 姜屏,周琳,毛天豪,袁俊平,王伟,李娜. 水泥改性废弃泥浆损伤模型及时间效应[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2874-2882. |
| [8] | 惠迎新,孙晓荣,王红雨,高晨. 预制T梁早期水化热温度效应及梁端开裂机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1734-1741. |
| [9] | 宫亚峰,逄蕴泽,王博,谭国金,毕海鹏. 基于吉林省路况的新型预制装配式箱涵结构的力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 917-924. |
| [10] | 张飞,朱玉明,杨尚川,王庶懋. 加筋土挡墙碳排放计算方法与减排性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 631-637. |
| [11] | 宫亚峰,宋加祥,毕海鹏,谭国金,胡国海,林思远. 装配式箱涵结构缩尺模型静载试验及有限元分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1728-1738. |
| [12] | 陶文斌,侯俊领,陈铁林,唐彬. 高预紧力后张法全长锚固支护力学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 631-640. |
| [13] | 高登辉,邢义川,郭敏霞,张爱军,王献涛,马保红. 非饱和重塑黄土⁃混凝土接触面修正双曲线模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 156-164. |
| [14] | 宫亚峰,王博,谭国金,张立敏,吴文丁,毕海鹏. 吉林省两种典型装配式箱涵受力特性对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1865-1870. |
| [15] | 张艳芹,冯雅楠,孔鹏睿,于晓东,孔祥滨. 基于热油携带的静压支承油膜温度场及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1203-1211. |
|
||