吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 947-953.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230614
数据不平衡的MobileViT网络交通事故严重程度预测模型
- 南京林业大学 汽车与交通工程学院,南京 210037
Model for predicting severity of accidents based on MobileViT network considering imbalanced data
- College of Automobile and Traffic Engineering,Nanjing Forestry University,Nanjing 210037,China
摘要:
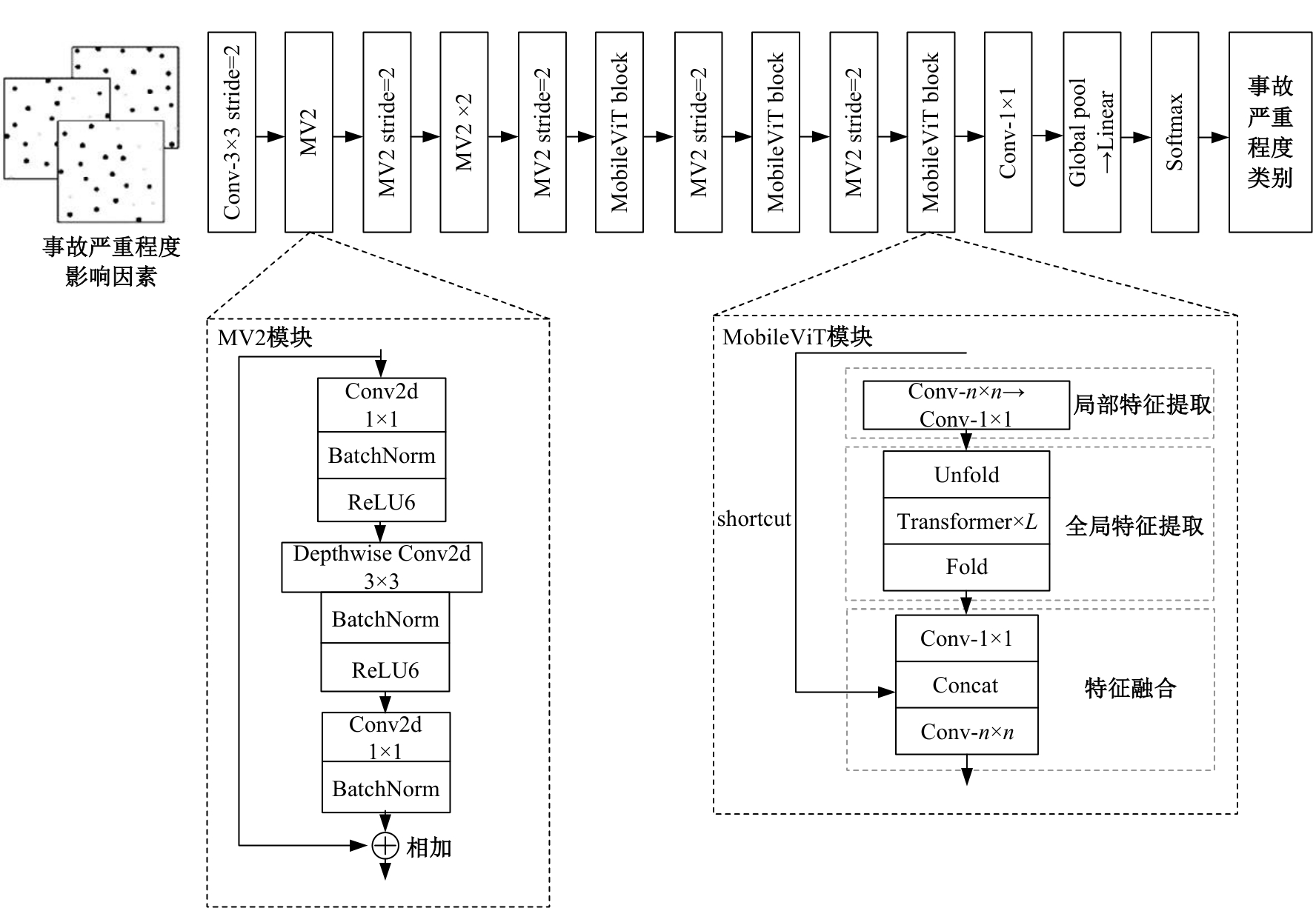
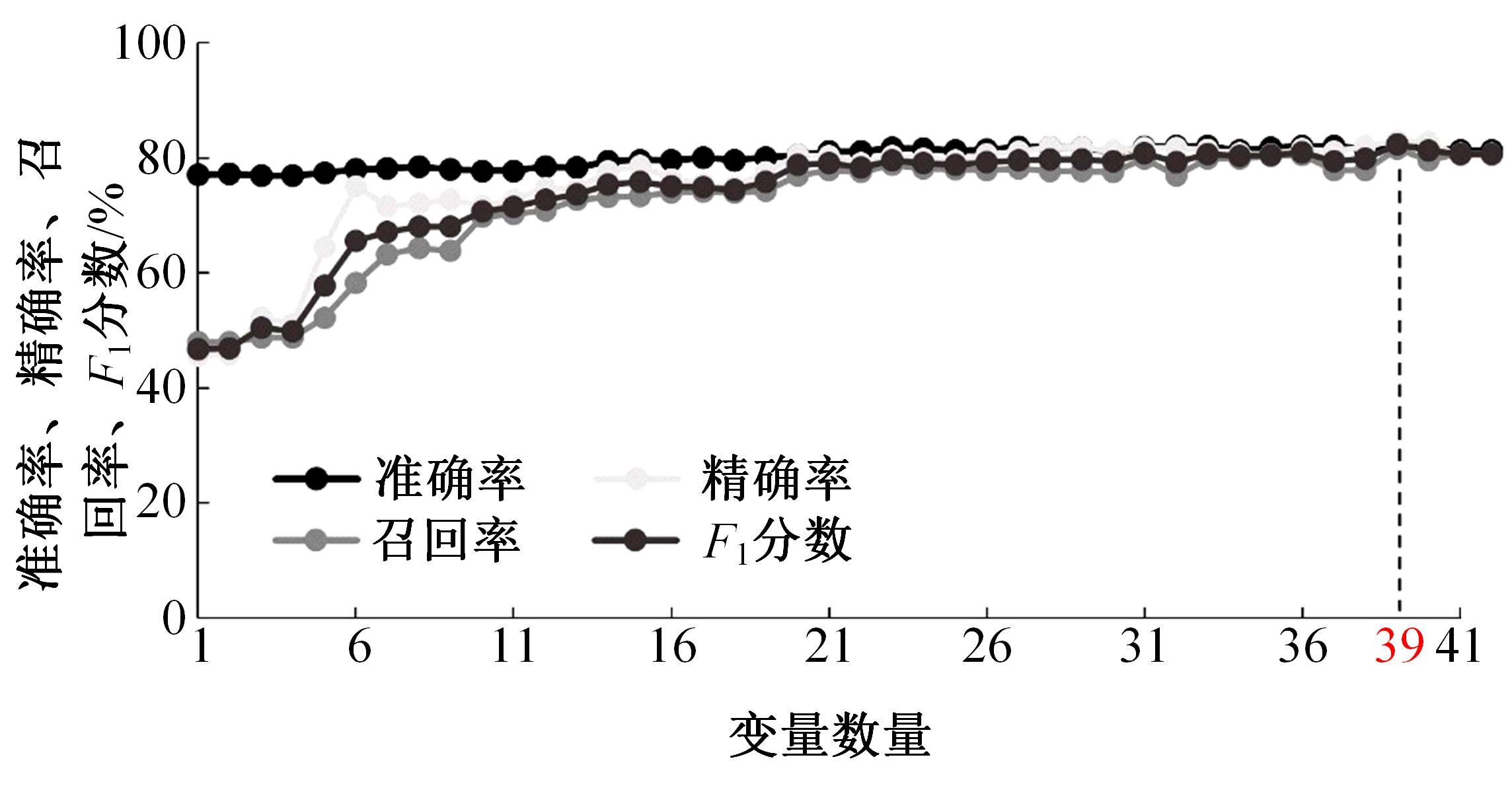
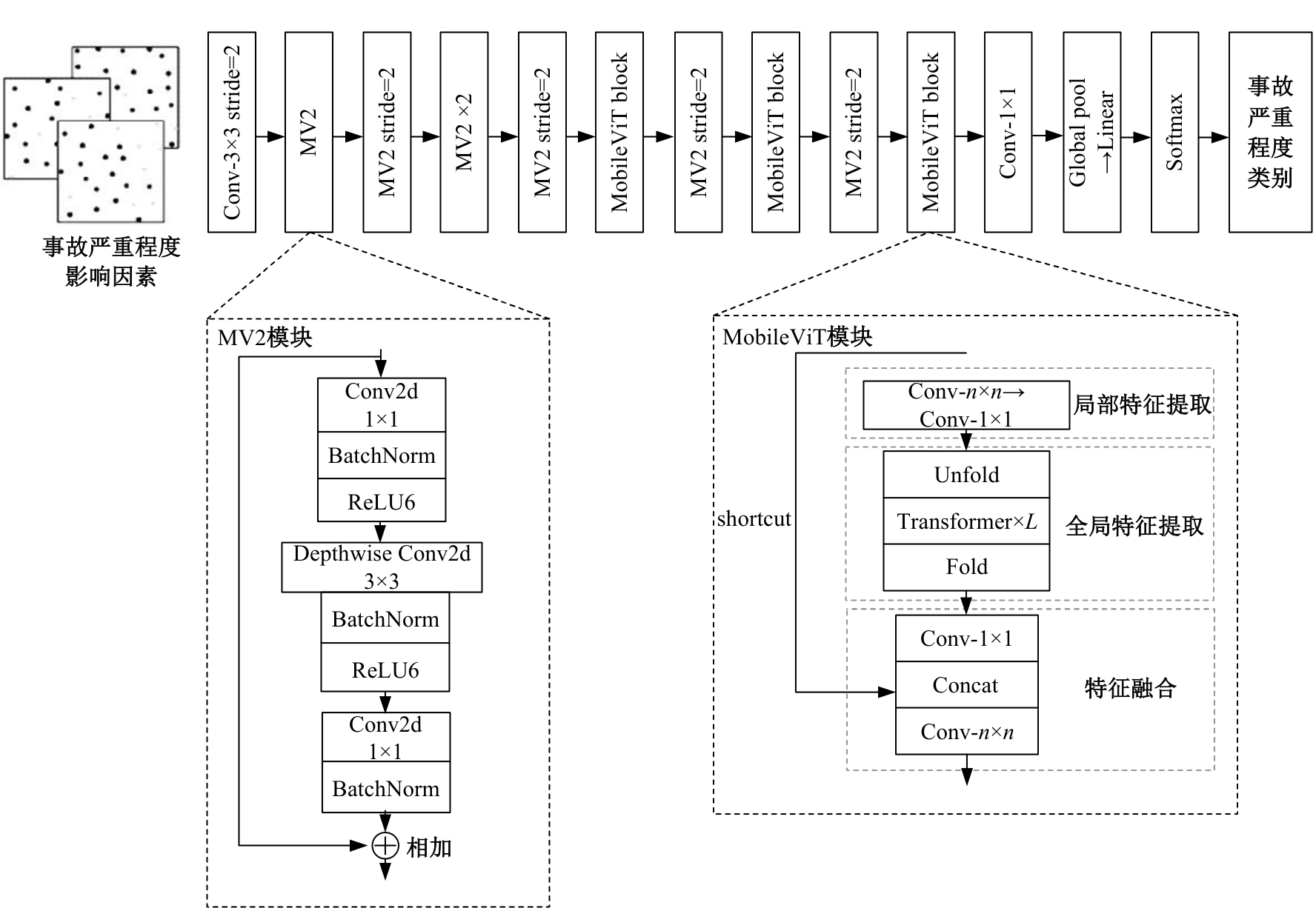
为解决数据不平衡引起的事故严重程度预测精度低的问题,提出了一种基于深度学习技术的交通事故严重程度预测模型。使用机器学习算法确定影响事故严重程度的关键变量,将数值型事故变量转换成图像数据应用于融合卷积神经网络和自注意力机制的MobileViT网络,针对数据量占比小的轻伤和重伤事故,采用焦点损失函数自适应调整轻伤和重伤事故的损失贡献,使模型更关注不平衡数据,利用精确率、召回率和F1分数评估模型预测性能。结果表明:本文模型在总体预测性能指标上达到0.81以上,优于其他基线模型,召回率和F1分数至少提高了4%和2.5%;在轻伤事故的召回率和F1分数上,MobileViT模型比WGAN-GP-XGBoost和ResNet18模型提高了25.9%和4.5%以上,重伤事故的预测性能最好,精确率、召回率和F1分数相比于另外两种模型分别提高了8.9%、4.2%和6.7%以上;使用焦点损失函数改进的MobileViT模型在预测不平衡数据上,效果高于其他数据平衡方法。
中图分类号:
- U491.31
| 1 | 潘义勇, 吴静婷, 缪炫烨. 老年驾驶员事故严重程度影响因素时间不稳定性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2024, 54(10): 2819-2826. |
| Pan Yi-yong, Wu Jing-ting, Miao Xuan-ye. Temporal instability analysis of factors affecting accident severity of elderly drivers[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2024, 54(10): 2819-2826. | |
| 2 | 戢晓峰, 乔新. 建成环境对行人交通事故严重程度的非线性影响[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2023, 23(1): 314-323. |
| Ji Xiao-feng, Qiao Xin. Nonlinear influence of built environment on pedestrian traffic accident severity[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2023, 23(1): 314-323. | |
| 3 | Zheng M, Li T, Zhu R, et al. Traffic accident´s severity prediction: a deep-learning approach-based CNN network[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 39897-39910. |
| 4 | 吕璞, 柏强, 陈琳. 融合深度反残差与注意力机制的山区高速公路事故严重程度预测模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(6): 205-213. |
| Lv Pu, Bai Qiang, Chen Lin. A model for predicting the severity of accidents on mountainous expressways based on deep inverted residuals and attention mechanisms[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(6): 205-213. | |
| 5 | Wang S, Zhang J, Li J, et al. Traffic accident risk prediction via multi-view multi-task spatio-temporal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2023, 35(12): 12323-12336. |
| 6 | Tian Z, Zhang S. Deep learning method for traffic accident prediction security[J]. Soft Computing, 2022, 26(11): 5363-5375. |
| 7 | Mehta S, Rastegari M. Mobilevit: light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer[J/OL].[2023-06-07]. |
| 8 | Rahim M A, Hassan H M. A deep learning based traffic crash severity prediction framework[J].Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2021,154: No. 106090. |
| 9 | Khan M N, Ahmed M M. A novel deep learning approach to predict crash severity in adverse weather on rural mountainous freeway[J]. Journal of Transportation Safety & Security, 2023, 15(8): 795-825. |
| 10 | 刘文文. 基于深度学习的摩托车事故严重程度预测研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学交通运输学院, 2022. |
| Liu Wen-wen. Research on motorcycle accident severity prediction based on deep learning[D]. Chongqing: College of Traffic & Transportation, Chongqing Jiaotong University 2022. | |
| 11 | Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980-2988. |
| 12 | Sharma A, Vans E, Shigemizu D, et al. DeepInsight: a methodology to transform a non-image data to an image for convolution neural network architecture[J]. Scientific reports, 2019, 9(1): No. 11399. |
| 13 | 马永杰, 程时升, 马芸婷, 等. 卷积神经网络及其在智能交通系统中的应用综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2021, 21(4): 48-71. |
| Ma Yong-jie, Cheng Shi-sheng, Ma Yun-ting, et al. Review of convolutional neural network and its application in intelligent transportation system[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2021, 21(4): 48-71. | |
| 14 | Yan H, Ma X, Pu Z. Learning dynamic and hierarchical traffic spatiotemporal features with transformer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 23(11): 22386-22399. |
| 15 | Li Y, Yang Z, Xing L, et al. Crash injury severity prediction considering data imbalance: a wasserstein generative adversarial network with gradient penalty approach[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2023, 192: No.107271. |
| 16 | Niyogisubizo J, Liao L, Zou F, et al. Predicting traffic crash severity using hybrid of balanced bagging classification and light gradient boosting machine[J]. Intelligent Data Analysis, 2023, 27(1): 79-101. |
| 17 | Cicek E, Akin M, Uysal F, et al. Comparison of traffic accident injury severity prediction models with explainable machine learning[J]. Transportation Letters, 2023, 15(9): 1043-1054. |
| 18 | Zhang Y, Li H, Ren G. Analyzing the injury severity in single-bicycle crashes: an application of the ordered forest with some practical guidance[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2023, 189: No. 107126. |
| 19 | Mohammadpour S I, Khedmati M, Zada M J H. Classification of truck-involved crash severity: dealing with missing, imbalanced, and high dimensional safety data[J]. PLoS one, 2023, 18(3): No.e0281901. |
| 20 | Silagyi II D V, Liu D. Prediction of severity of aviation landing accidents using support vector machine models[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2023, 187: No. 107043. |
| [1] | 陈永恒,杨家伟,孙经宇. 借道左转交叉口的网联左转车辆最佳轨迹控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 614-622. |
| [2] | 陈发城,鲁光泉,林庆峰,张浩东,马社强,刘德志,宋会军. 有条件自动驾驶下驾驶人接管行为综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 419-433. |
| [3] | 何永明,冯佳,魏堃,万亚楠. 超高速公路曲线路段车辆制动侧滑影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 591-602. |
| [4] | 吴娇蓉,刘旭东. 不同住房类型空间单元的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 554-565. |
| [5] | 王长帅,徐铖铖,任卫林,彭畅,佟昊. 自动驾驶接管过程中驾驶能力恢复状态对交通流振荡特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 150-161. |
| [6] | 张娜,陈峰,王剑坡,朱亚迪. 基于时空序列相似性的城轨乘客出行模式识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2588-2599. |
| [7] | 周锡浈,宫贺,李敦敦,季彦婕,严杰. 建成环境对路内停车泊位使用率的非线性影响模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2520-2530. |
| [8] | 严利鑫,曾涛,贺宜,郭军华,胡鑫辉. 共驾型智能车辆人机接管行为序列编码与解析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2547-2556. |
| [9] | 曲昭伟,李霖,陈永恒,吴场建. 长区间掉头车辆特性分析及其安全评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2206-2213. |
| [10] | 何永明,权聪,魏堃,冯佳,万亚楠,陈世升. 超高速公路车路协同路侧单元感知融合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1923-1934. |
| [11] | 程国柱,盛林,王浩宇,冯天军. 考虑右转车二次冲突的信号交叉口行人过街安全评价方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1903-1912. |
| [12] | 张明业,杨敏,黎彧,黄世玉,李清韵. 考虑有序充电策略的多车型电动公交调度优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1293-1301. |
| [13] | 秦雅琴,钱正富,谢济铭. 协同换道避障模型和轨迹数据驱动的车辆协同避障策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1311-1322. |
| [14] | 严利鑫,冯进培,郭军华,龚毅轲. 不同险态情景下共驾型智能车辆接管行为特征分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 683-691. |
| [15] | 马潇驰,陆建. 基于基因表达式编程的高架道路事故实时预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 719-726. |
|
||