吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 886-892.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200039
基于自动编码机-分类器的视频交通状态自动识别
- 1.重庆交通大学 山地城市交通系统与安全重庆市重点实验室,重庆 400074
2.重庆交通大学 交通运输学院,重庆 400074
Automatic traffic state recognition from videos based on auto⁃encoder and classifiers
Bo PENG1,2( ),Yuan-yuan ZHANG2,Yu-ting WANG2,Ju TANG2,Ji-ming XIE2
),Yuan-yuan ZHANG2,Yu-ting WANG2,Ju TANG2,Ji-ming XIE2
- 1.Chongqing Key Lab of Traffic System & Safety in Mountain Cities,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
2.College of Traffic and Transportation,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
摘要:
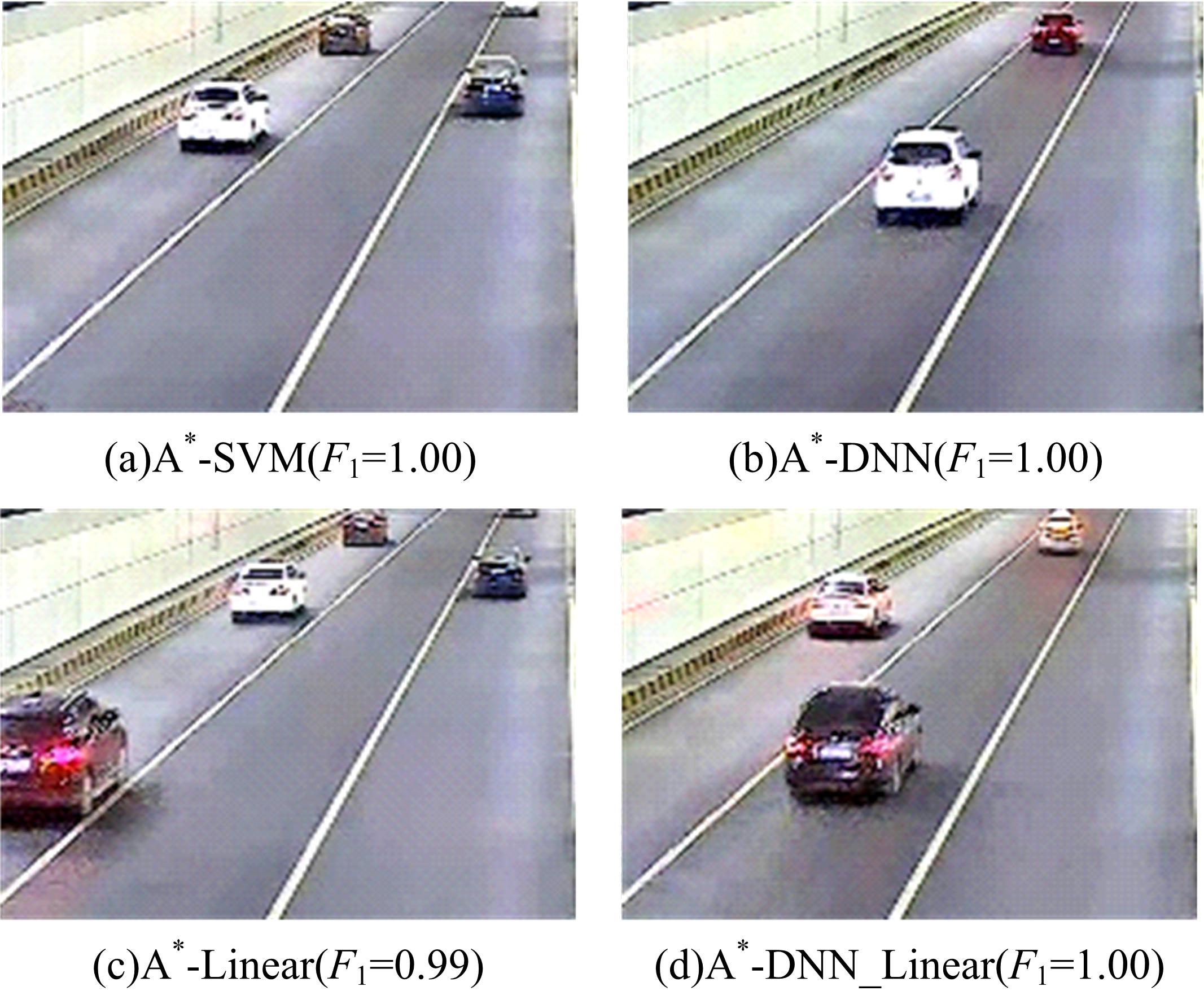
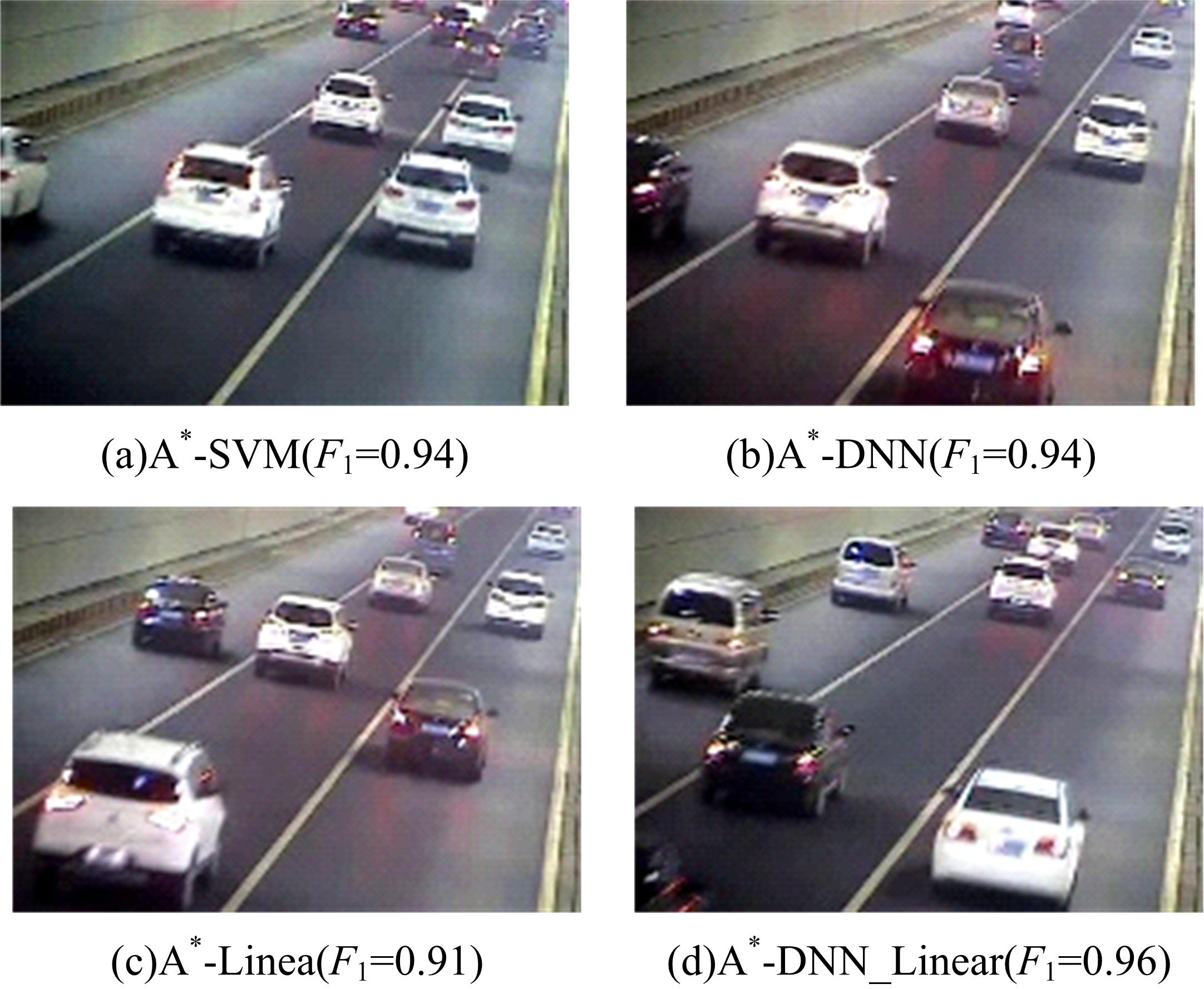
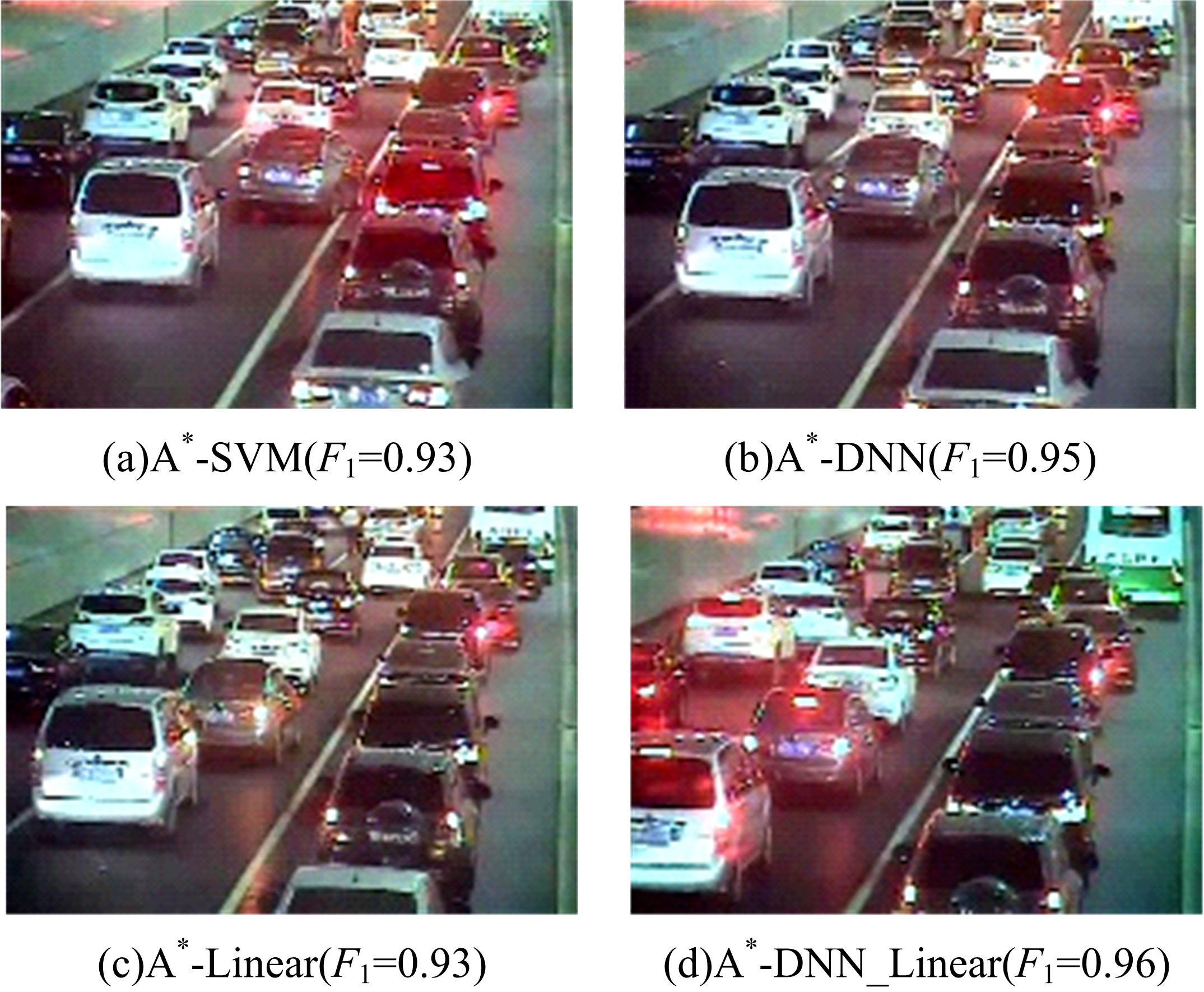
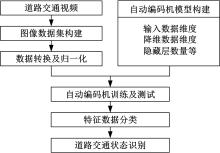
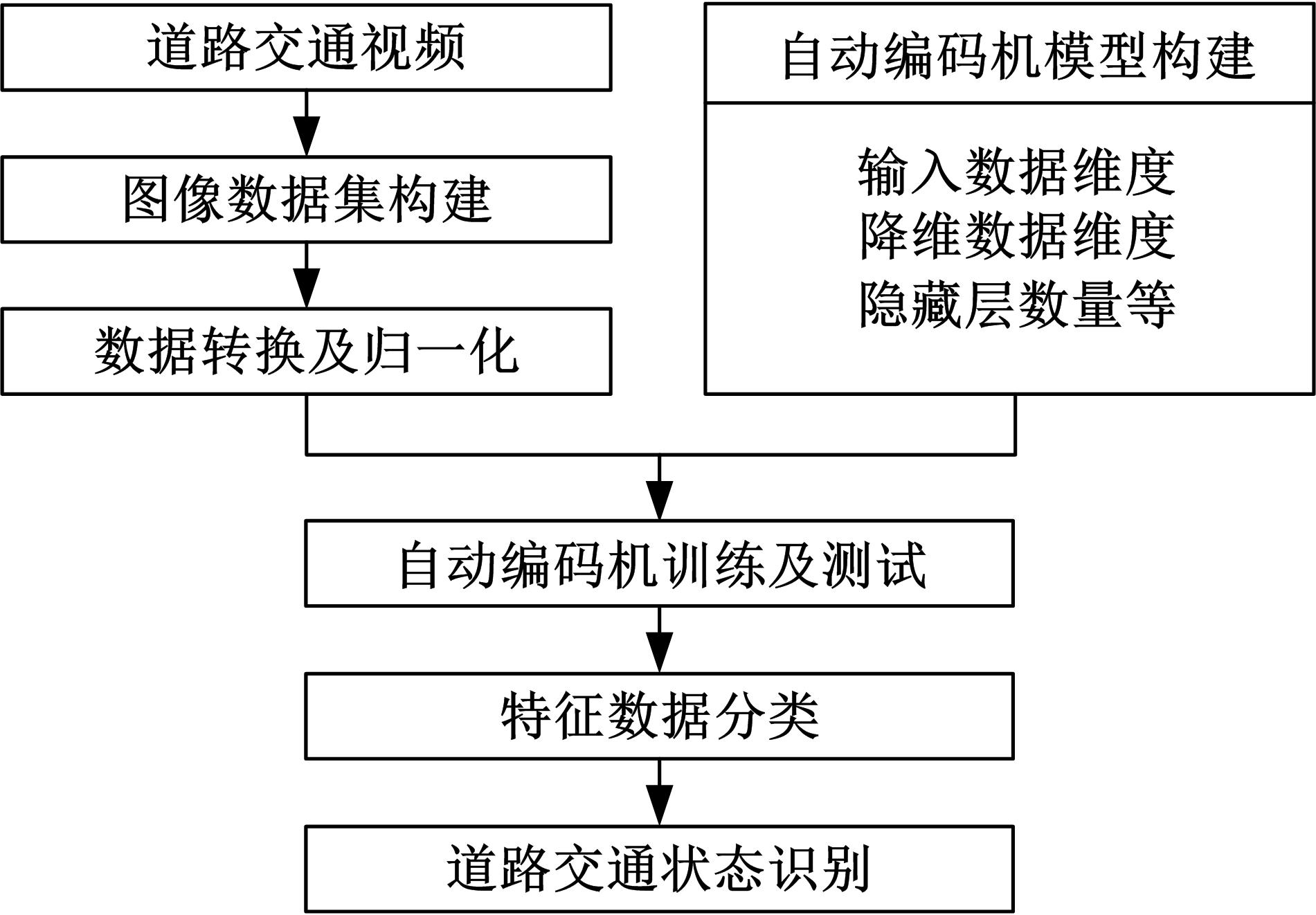
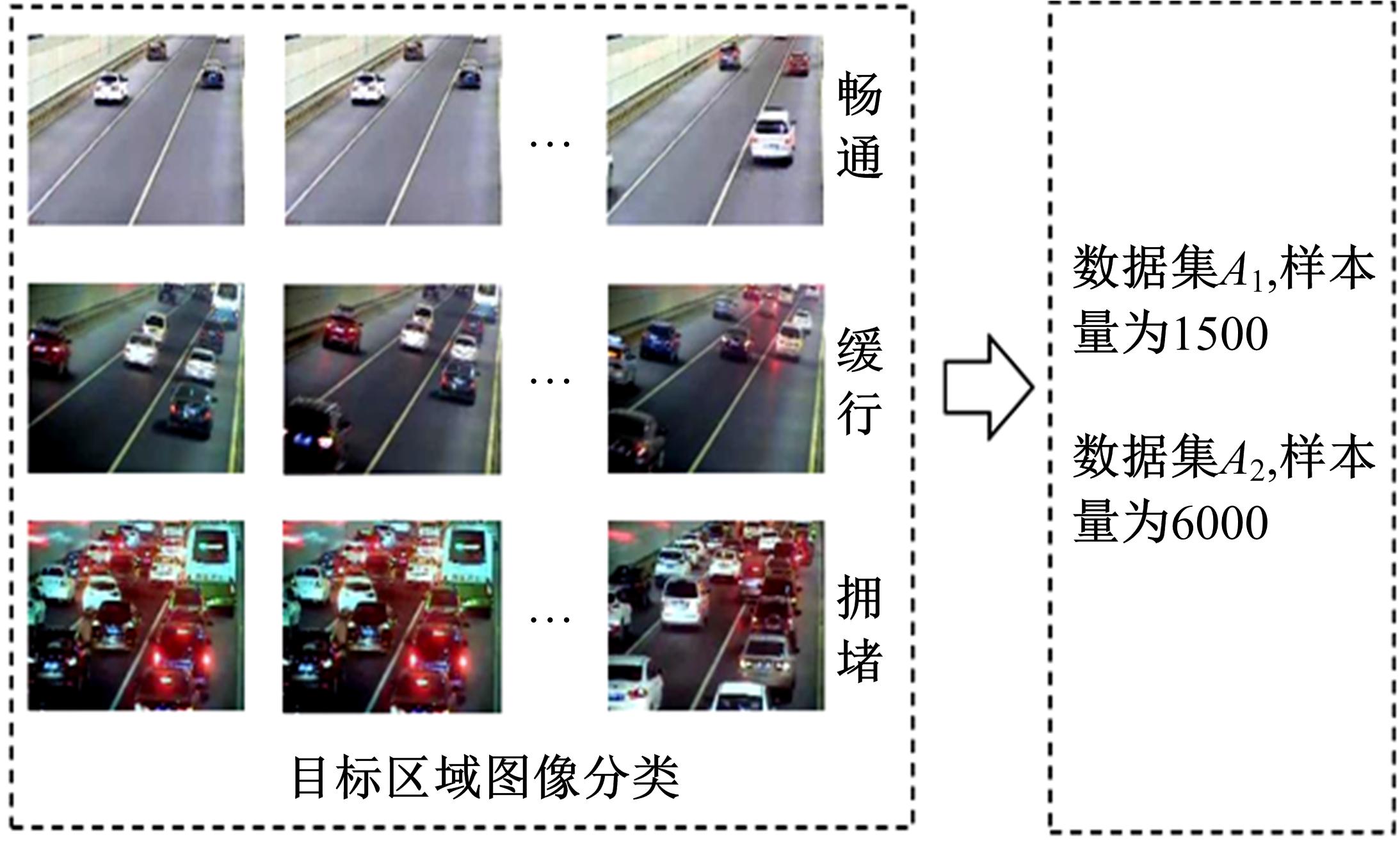
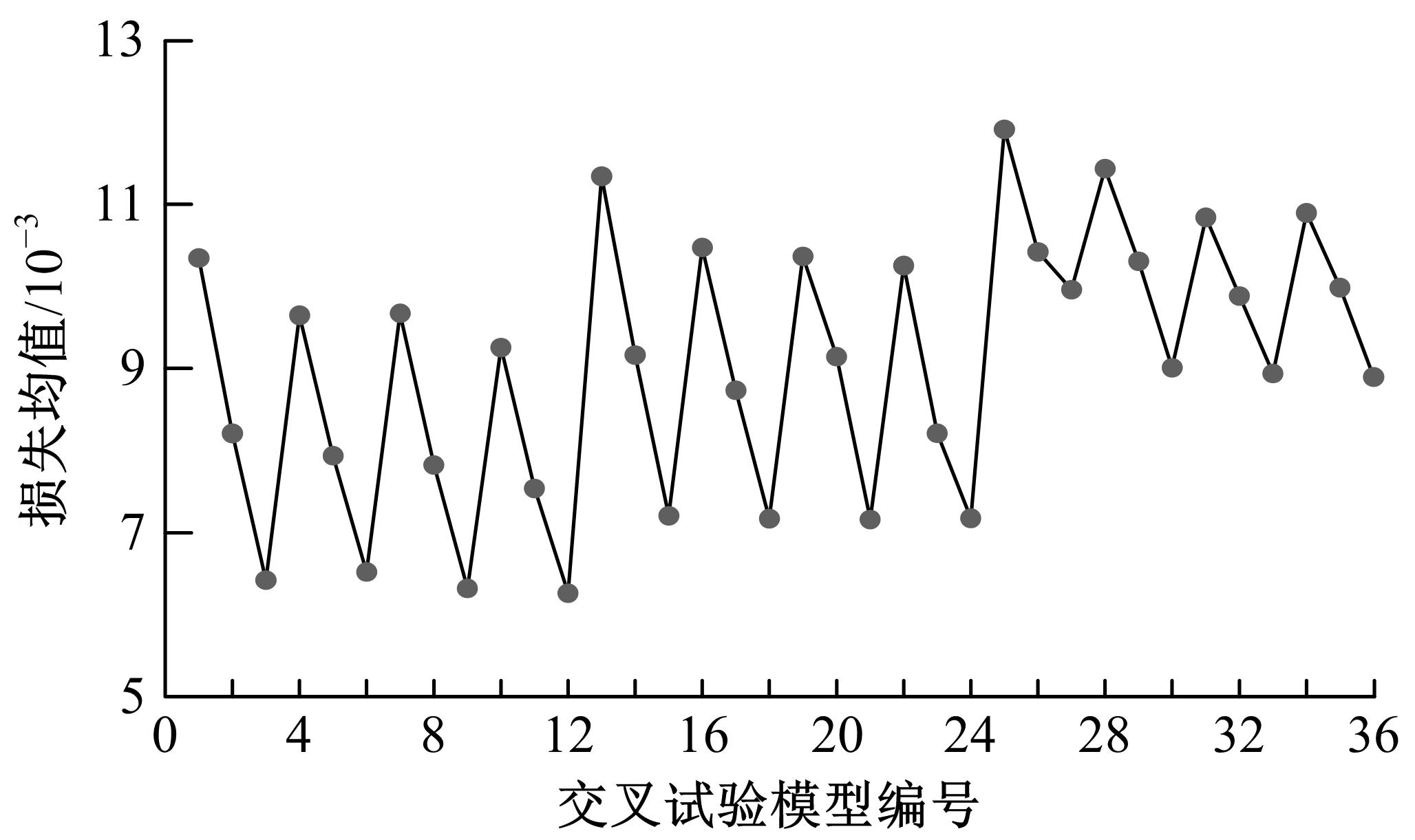
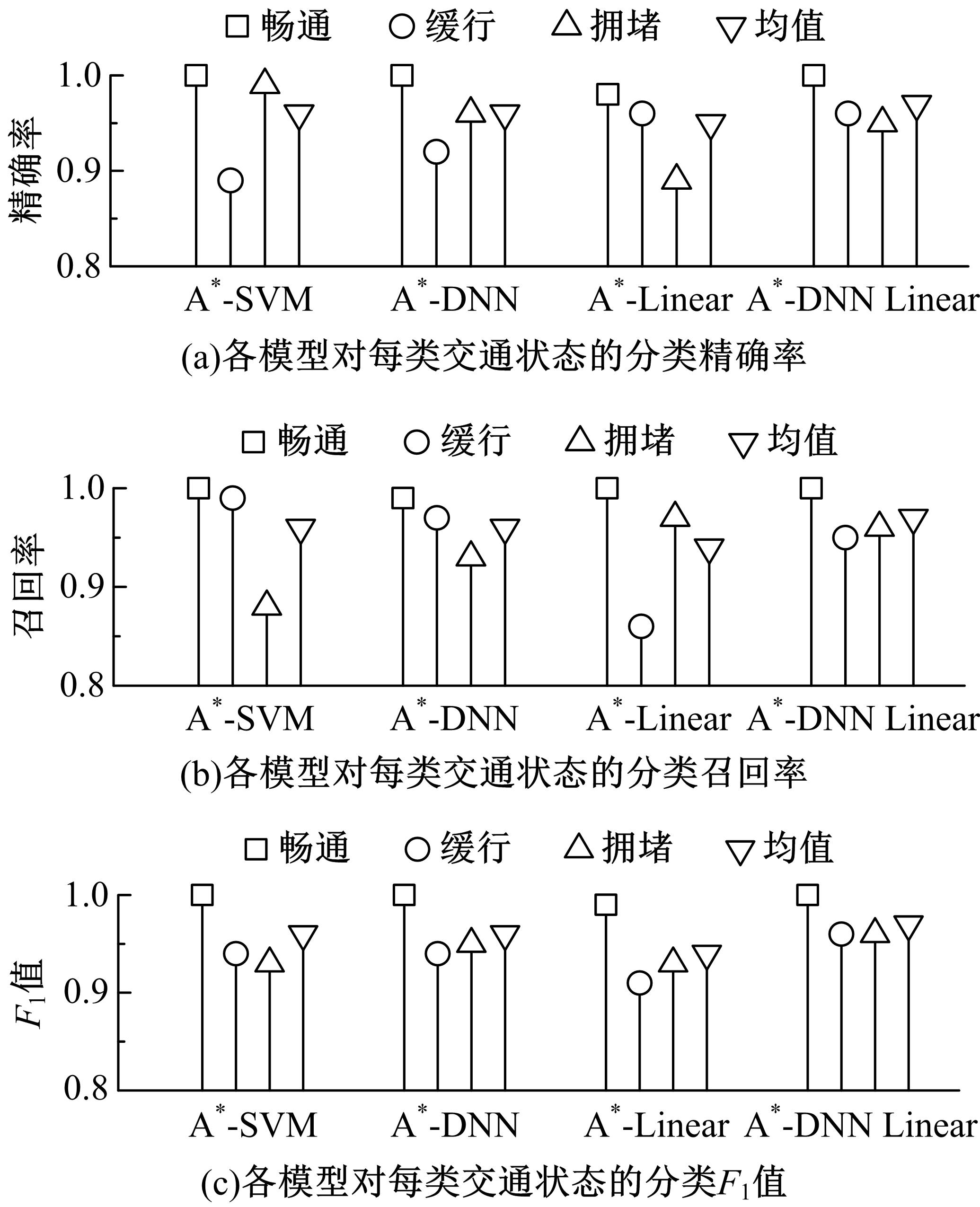
为了及时、有效地识别道路交通状态,提出了结合自动编码机与分类器的视频交通状态识别方法。首先,建立交通状态视频图像数据集,对自动编码机隐藏层和降维数据维度等结构参数进行优化测试。然后,提出自动编码机定量评价方法,选出最优自动编码机模型A*。最后,将A*与线性分类器、支持向量机、深度神经网络、DNN Linear分类方法相结合,构建了4个交通状态识别模型。对前述模型及AlexNet、LeNet、GoogLeNet、VGG16等CNN模型进行训练测试,结果显示:本文模型精确率和召回率均为94.5%~97.1%,
中图分类号:
- U491.1
| 1 | Li L, Hu J, Huang Q, et al. A fuzzy hidden Markov model for traffic status classification based on video features[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computational Engineering in Systems Applications, Beijing, China, 2006: 2050-2055. |
| 2 | Quiros A R F, Bedruz R A, Uy A C, et al. Machine vision of traffic state estimation using fuzzy logic[C]∥IEEE Region 10 Conference, Marina Bay Sands, Singapore, 2016: 2104-2109. |
| 3 | 崔华, 袁超, 魏泽发, 等. 利用FCM对静态图像进行交通状态识别[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 44(6): 85-90. |
| Cui Hua, Yuan Chao, Wei Ze-fa, et al. Traffic state recognition using state images and FCM[J]. Journal of Xidian University(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 44(6): 85-90. | |
| 4 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012, 25(2): 1097-1105. |
| 5 | Ostrom Q T, Bauchet L, Davis F G, et al. The epidemiology of gliomain in adults: a "state of the science" review[J]. Neuro-Oncology, 2014, 16(7): 896-913. |
| 6 | Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Boston, USA, 2015: 1-9. |
| 7 | 李映, 龚红丽, 梁佳熙, 等. 基于KSVD和PCA的SAR图像目标特征提取[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2010, 40(5): 1336-1339. |
| Li Ying, Gong Hong-li, Liang Jia-xi, et al. SAR image target feature extraction based on KSVD and PCA[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2010, 40(5): 1336-1339. | |
| 8 | 侯阿临, 廖庆, 靳志娟, 等. 计算全息图的人工神经网络压缩算法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2013, 43(): 21-24. |
| Hou A-lin, Liao Qing, Jin Zhi-juan, et al. Compression algorithm of computer-generated hologram based on artificial neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2013, 43(Sup.1): 21-24. | |
| 9 | Gao S, Zhang Y, Jia K, et al. Single sample face recognition via learning deep supervised autoencoders[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2015, 10(10): 2108-2118. |
| 10 | Zhao C, Wan X, Zhao G, et al. Spectral-spatial classification of hyperspectral imagery based on stacked sparse autoencoder and random forest[J]. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 2017, 50(1): 47-63. |
| 11 | Ge P, Ren C X, Dai D Q, et al. Dual adversarial autoencoders for clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(4): 1417-1424. |
| 12 | Cheng H, Koc L, Harmsen J, et al. Wide & deep learning for recommender systems[C]∥Conference on Recommender Systems, New York, USA, 2016: 7-10. |
| [1] | 宋震,李俊良,刘贵强. 基于深度学习和限幅模糊的变转速液压动力源恒流量预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1106-1110. |
| [2] | 袁哲明,袁鸿杰,言雨璇,李钎,刘双清,谭泗桥. 基于深度学习的轻量化田间昆虫识别及分类模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1131-1139. |
| [3] | 李锦青,周健,底晓强. 基于循环生成对抗网络的学习型光学图像加密方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1060-1066. |
| [4] | 王殿海,沈辛夷,罗小芹,金盛. 车均延误最小情况下的相位差优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 511-523. |
| [5] | 张健,吴坤润,杨敏,冉斌. 智能网联环境下交叉口双环自适应控制模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 541-548. |
| [6] | 宋现敏,张明业,李振建,王鑫,张亚南. 动态公交专用道的设置及其仿真分析评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1677-1686. |
| [7] | 赵宏伟,刘晓涵,张媛,范丽丽,龙曼丽,臧雪柏. 基于关键点注意力和通道注意力的服装分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770. |
| [8] | 谌华,郭伟,闫敬文,卓文浩,吴良斌. 基于深度学习的SAR图像道路识别新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1778-1787. |
| [9] | 贾洪飞,丁心茹,杨丽丽. 城市潮汐车道优化设计的双层规划模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 535-542. |
| [10] | 尹超英,邵春福,王晓全,熊志华. 考虑空间异质性的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 543-548. |
| [11] | 郜峰利,陶敏,李雪妍,何昕,杨帆,王卓,宋俊峰,佟丹. 基于深度学习的CT影像脑卒中精准分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 678-684. |
| [12] | 张大伟,祝海涛. 考虑行人差异性的人群疏散最优决策理论模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 549-556. |
| [13] | 常玉林,袁才鸿,孙超,张鹏. 基于改进元胞传输模型的城市路网实际阻抗计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 132-139. |
| [14] | 隋振,姜源. 基于MIMO类脑情感学习回路的横-纵向综合控制驾驶员模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 140-146. |
| [15] | 宗长富,文龙,何磊. 基于欧几里得聚类算法的三维激光雷达障碍物检测技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 107-113. |
|
||