吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (11): 2669-2675.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220043
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于响应值中心加权卷积特征的图像检索算法
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.长春师范大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130032
3.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
Image retrieval algorithm based on response value center weighted convolution feature
Xiao-ning LI1,2( ),Hong-wei ZHAO1,3,Dan-yang ZHANG1,Yuan ZHANG1(
),Hong-wei ZHAO1,3,Dan-yang ZHANG1,Yuan ZHANG1( )
)
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.College of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun Normal University,Changchun 130032,China
3.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
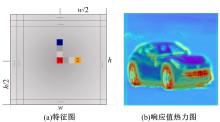
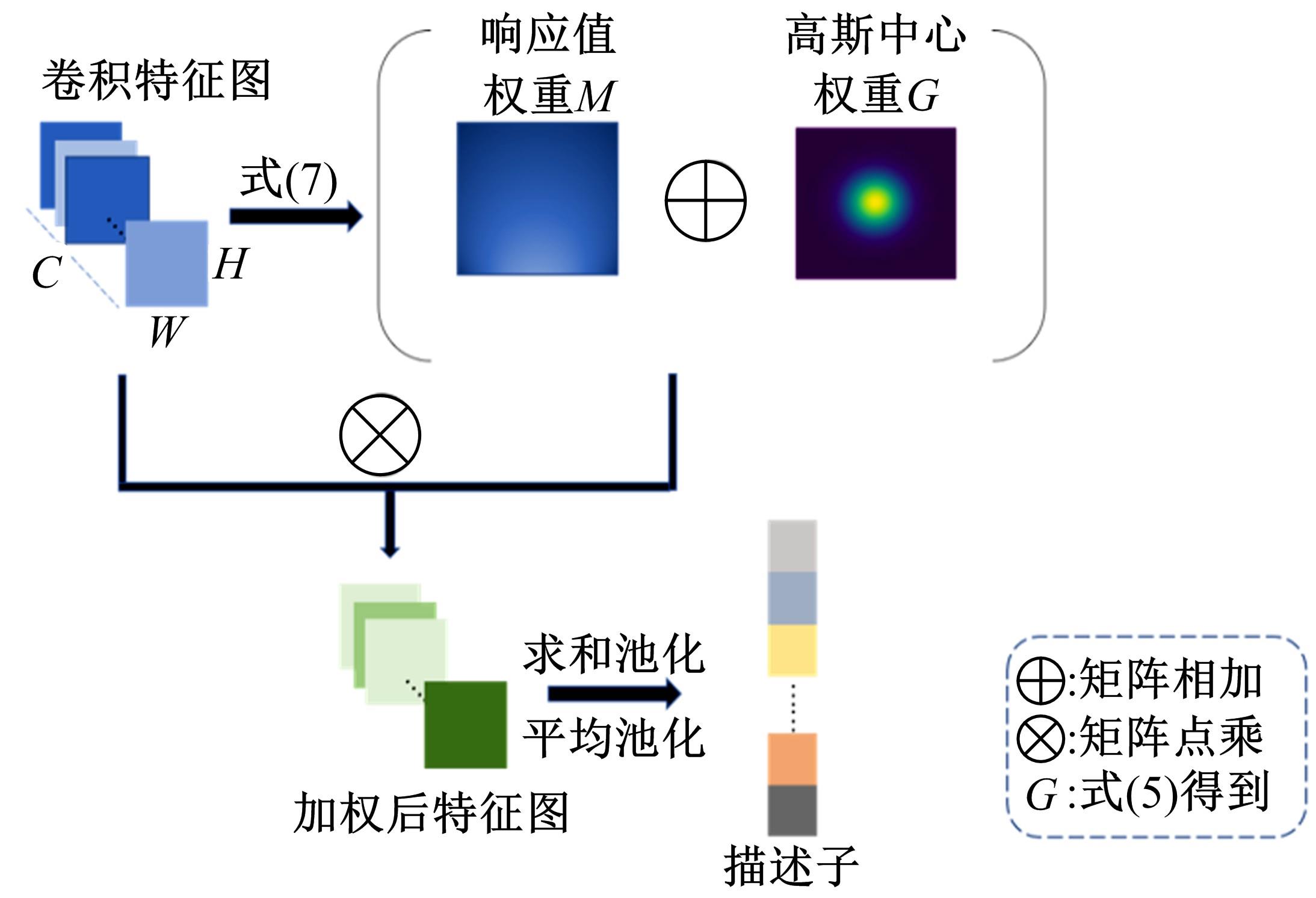
提出一种新颖的基于交叉熵的损失,将该损失应用于经典的卷积神经网络上获得了更优的嵌入空间。设计了一种基于响应值中心加权的卷积特征聚合算法处理神经网络得到的三维卷积特征,该算法通过当前位置响应值以及高斯中心计算获得特征图的空间加权系数,减少了三维卷积特征图降成一维图像特征描述子时的信息丢失,并实现了目标区域的增强。最后,将得到的图像特征描述子用于检索任务。在CUB-200-2011数据集上通过消融实验分别验证了损失函数和响应值中心加权算法的有效性。本文算法在Paris6k、Oxford5k、CUB-200-2011、CARS196四个数据集上较当前已有的检索方法获得了更高的准确率和召回率。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Tolias G, Sicre R, Jégou H. Particular object retrieval with integral max-pooling of CNN activations[J/OL]. [2021-11-18]. |
| 2 | Chen W, Liu Y, Wang W, et al. Deep learning for instance retrieval: a survey[J/OL]. [2021-01-27]. |
| 3 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. |
| 4 | Bell S, Bala K. Learning visual similarity for product design with convolutional neural networks[J]. Transactions on Graphics, 2015, 34(4): 2766959. |
| 5 | Babenko A, Lempitsky V. Aggregating local deep features for image retrieval[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1269-1277. |
| 6 | Razavian A S, Sullivan J, Carlsson S, et al. Visual instance retrieval with deep convolutional networks[J]. ITE Transactions on Media Technology and Applications, 2016, 4(3): 251-258. |
| 7 | Anwaar M U, Labintcev E, Kleinsteuber M. Compositional learning of image-text query for image retrieval[C]∥IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2015: 1140-1149. |
| 8 | He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[J/OL]. [2021-12-10]. |
| 9 | Krause J, Stark M, Deng J, et al. 3D object representations for fine-grained categorization[C]∥In Proceedings of Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 554-561. |
| 10 | Wah C, Branson S, Welinder P, et al. The caltech-UCSD birds-200-2011 dataset[J]. California Institute of Technology, 2011(1): 20111026. |
| 11 | Philbin J, Chum O, Isard M, et al. Object retrieval with large vocabularies and fast spatial matching[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, USA, 2007: 1-8. |
| 12 | Philbin J, Chum O, Isard M, et al. Lost in quantization: Improving particular object retrieval in large scale image databases[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, USA, 2008: 1-8. |
| 13 | Dubey A, Gupta O, Raskar R, et al. Maximum-entropy fine grained classification[C]∥32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems,Montreal, Canada, 2018: 637-647. |
| 14 | Zhang X F, Zhou F, Lin Y Q, et al. Embedding label structures for fine-grained feature representation[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1114-1123. |
| 15 | Wei X S, Luo J H, Wu J X, et al. Selective convolutional descriptor aggregation for fine-grained image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(6): 2868-2881. |
| 16 | Zhang X, Zhou F, Lin Y, et al. Embedding label structures for fine-grained feature representation[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1114-1123. |
| 17 | Song H O, Yu X, Jegelka S, et al. Deep metric learning via lifted structured feature embedding[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las VegasLas,USA,2016: 4004-4012. |
| 18 | Song H O, Jegelka S, Rathod V, et al. Deep metric learning via facility location[C]∥30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5382-5390. |
| 19 | Sohn K. Improved deep metric learning with multi-class n-pair loss objective[C]∥Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 29, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 1857-1865. |
| 20 | Chen H, Chen C L, Tang X O. Local similarity-aware deep feature embedding[J/OL]. [2021-10-27]. |
| 21 | Wei X S, Luo J H, Wu J, et al. Selective convolutional descriptor aggregation for fine-grained image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(6): 2868-2881. |
| 22 | Zheng X W, Ji R R, Sun X S, et al. Centralized ranking loss with weakly supervised localization for fine-grained object retrieval[C]∥27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 1226-1233. |
| 23 | Zheng X W, Ji R R, Sun X X, et al. Towards optimal fine grained retrieval via decorrelated centralized loss with normalize-scale layer[C]∥In Proceedings of Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, USA, 2019: 9291-9298. |
| [1] | 高金武,贾志桓,王向阳,邢浩. 基于PSO-LSTM的质子交换膜燃料电池退化趋势预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2192-2202. |
| [2] | 周丰丰,朱海洋. 基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法SEE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1834-1841. |
| [3] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [4] | 李晓英,杨名,全睿,谭保华. 基于深度学习的不均衡文本分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1889-1895. |
| [5] | 申铉京,张雪峰,王玉,金玉波. 像素级卷积神经网络多聚焦图像融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| [6] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [7] | 赵宏伟,张健荣,朱隽平,李海. 基于对比自监督学习的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1850-1856. |
| [8] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [9] | 胡丹,孟新. 基于时变网格的对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1896-1903. |
| [10] | 王军,徐彦惠,李莉. 低能耗支持完整性验证的数据融合隐私保护方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1657-1665. |
| [11] | 周丰丰,张亦弛. 基于稀疏自编码器的无监督特征工程算法BioSAE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1645-1656. |
| [12] | 高明华,杨璨. 基于改进卷积神经网络的交通目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| [13] | 康耀龙,冯丽露,张景安,陈富. 基于谱聚类的高维类别属性数据流离群点挖掘算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1422-1427. |
| [14] | 王文军,余银峰. 考虑数据稀疏的知识图谱缺失连接自动补全算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1428-1433. |
| [15] | 陈雪云,贝学宇,姚渠,金鑫. 基于G⁃UNet的多场景行人精确分割与检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 925-933. |
|
||