吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (9): 2508-2518.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220106
基于深度强化学习的自动驾驶车辆专用道汇入引导
张健1,2,3( ),李青扬1,3,李丹2,姜夏1,3,雷艳红2,季亚平1,3
),李青扬1,3,李丹2,姜夏1,3,雷艳红2,季亚平1,3
- 1.东南大学 江苏省城市智能交通重点实验室,南京 211189
2.西藏大学 工学院,拉萨 850013
3.东南大学 交通学院,南京 211189
Merging guidance of exclusive lanes for connected and autonomous vehicles based on deep reinforcement learning
Jian ZHANG1,2,3( ),Qing-yang LI1,3,Dan LI2,Xia JIANG1,3,Yan-hong LEI2,Ya-ping JI1,3
),Qing-yang LI1,3,Dan LI2,Xia JIANG1,3,Yan-hong LEI2,Ya-ping JI1,3
- 1.Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Urban ITS,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
2.Institute of Technology,Tibet University,Lhasa 850013,China
3.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
摘要:
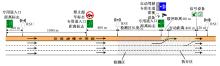
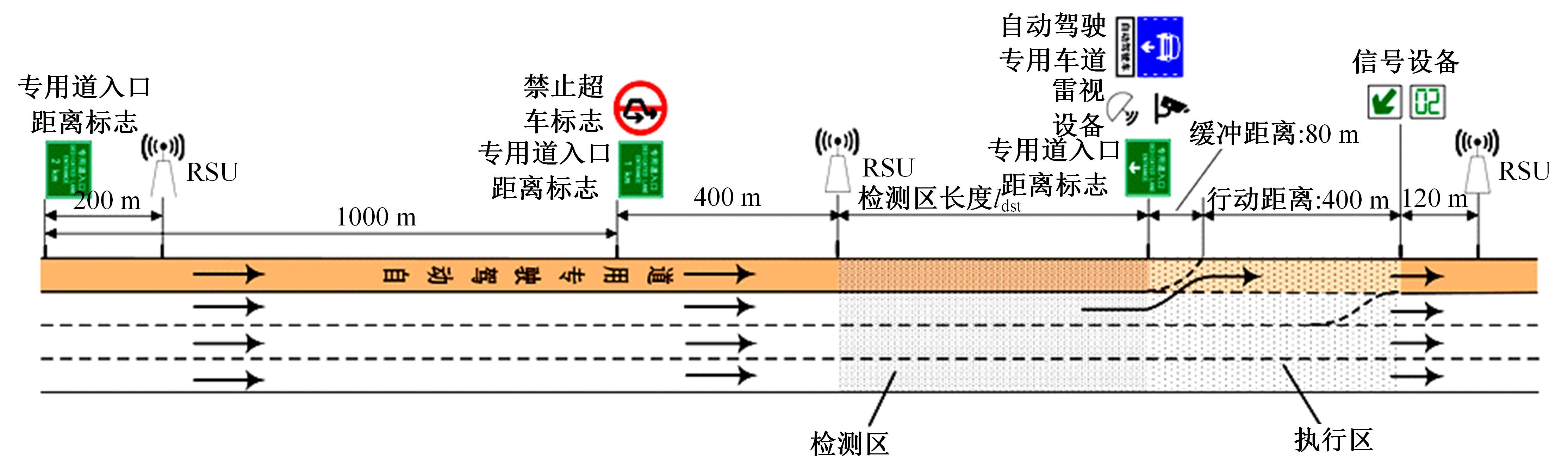
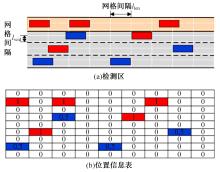
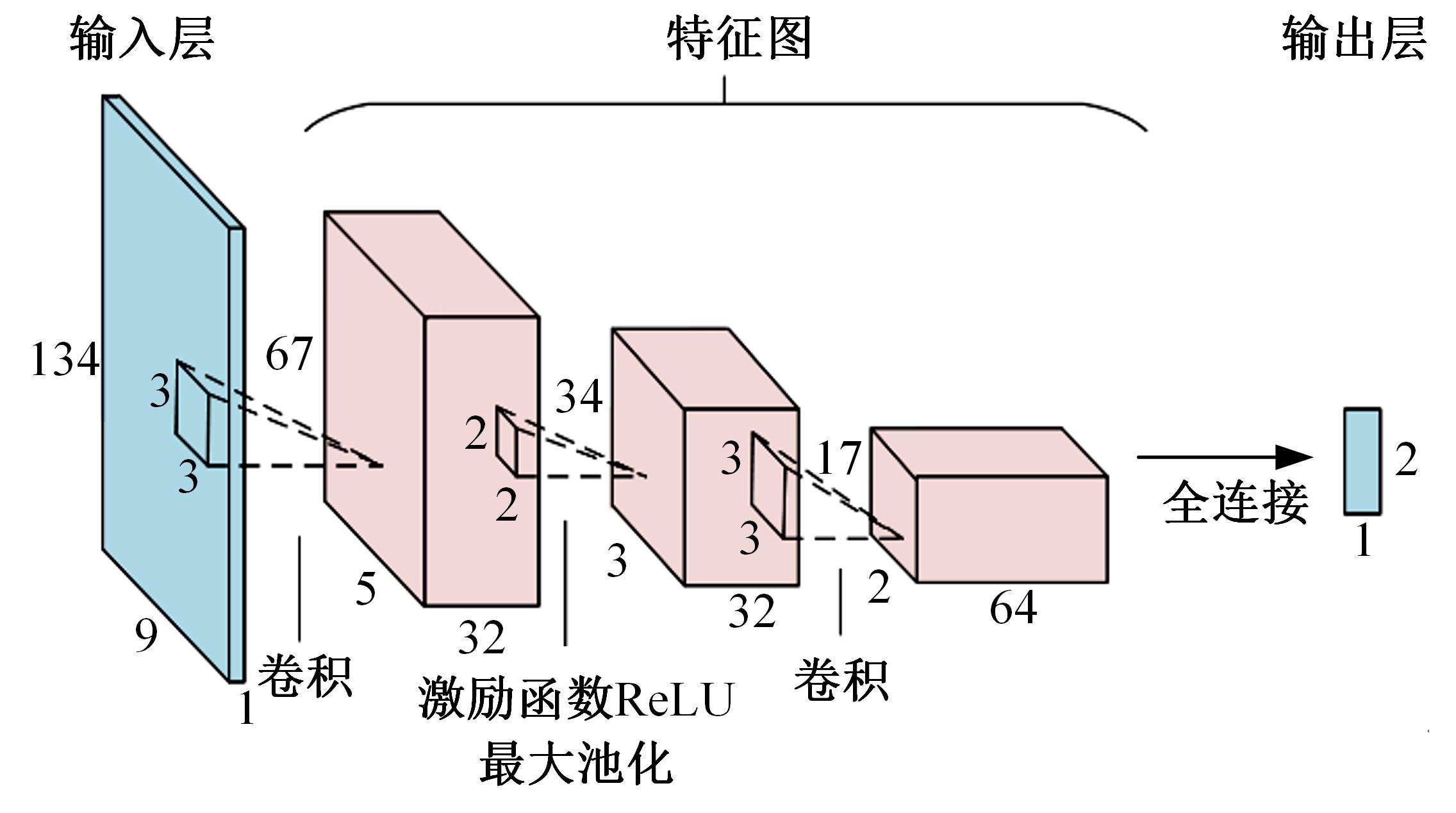
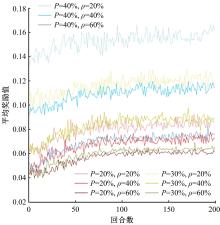
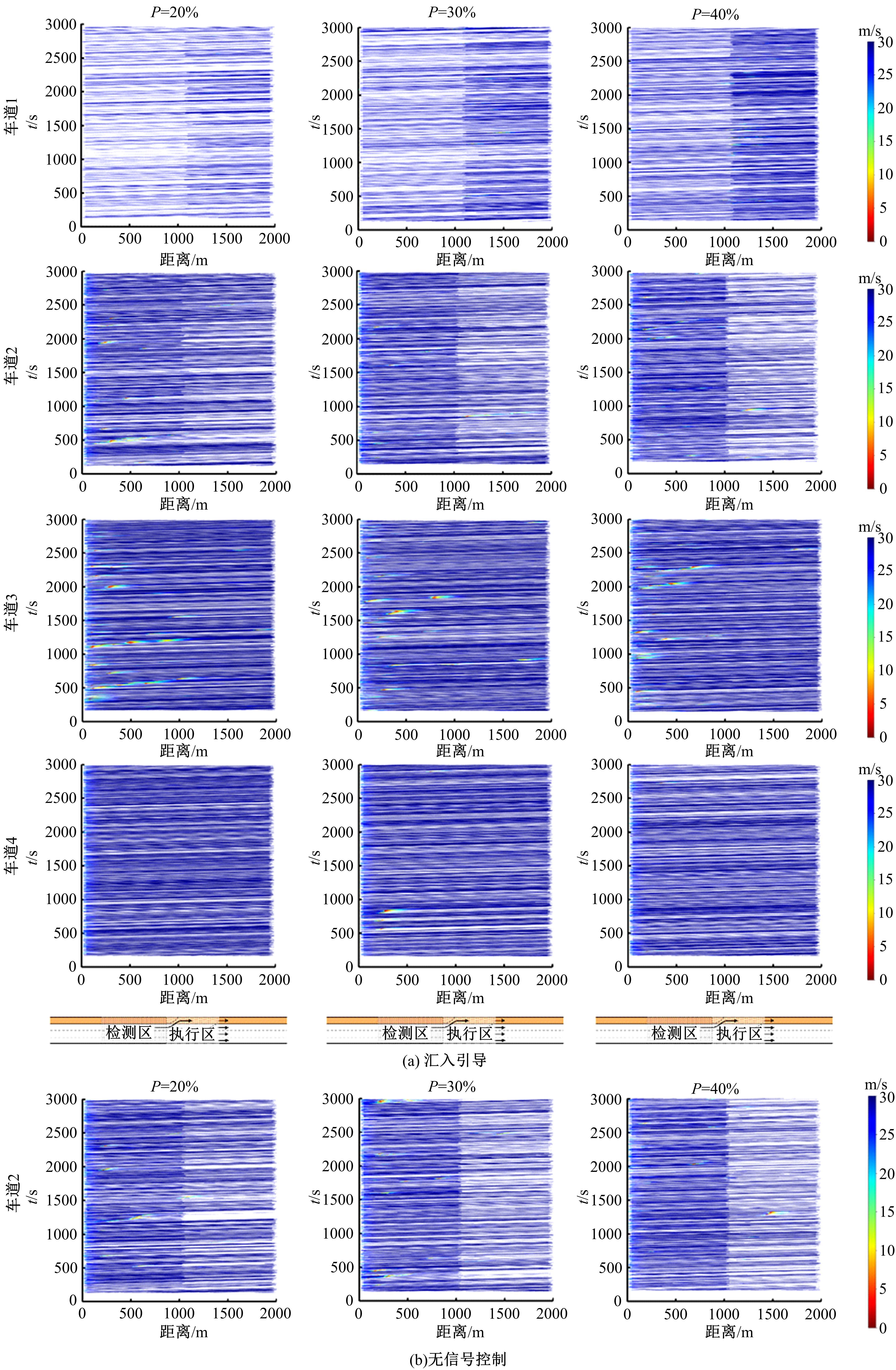
为满足自动驾驶车辆(CAV)与人工驾驶车辆混行过程中安全和效率的需求,自动驾驶车辆专用道应运而生。当高速公路内侧车道设为自动驾驶车辆专用道时,引导自动驾驶车辆从普通车道汇入至专用道的策略研究具有重要的理论意义和实际价值。首先,设计专用道入口并提出车辆控制规则;其次,以使更多自动驾驶车辆换道至专用道为目标,基于深度强化学习,选择换道信号动作引导车辆换道;最后,通过Python语言编译进行数值仿真验证。结果表明:在自动驾驶车辆渗透率、到达专用道自动驾驶车辆比例等不同因素构建的9种场景下,本文算法能够快速收敛;能够有效引导自动驾驶车辆汇入专用道,保证通行效率;相较无信号控制情况,渗透率为20%~40%时,第2车道交通拥堵显著减少;在两段式专用道入口场景下,CAV换道至专用道的比例比单入口场景明显提高。所提出的策略具有较好的适用性,能为工程建设提供参考借鉴。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | 秦严严, 王昊, 王炜. 智能网联环境下的混合交通流LWR模型[J]. 中国公路学报, 2018, 31(11): 147-156. |
| Qin Yan-yan, Wang Hao, Wang Wei. LWR model for mixed traffic flow in connected and autonomous vehicular environments[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018, 31(11): 147-156. | |
| 2 | Becker F, Axhausen K W. Literature review on surveys investigating the acceptance of automated vehicles[J]. Transportation, 2017, 44(6): 1293-1306. |
| 3 | Elliott D, Keen W, Miao L. Recent advances in connected and automated vehicles[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (English Edition), 2019, 6(2): 109-131. |
| 4 | 杜豫川, 刘成龙, 吴荻非, 等. 新一代智慧高速公路系统架构设计[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(4): 203-214. |
| Du Yu-chuan, Liu Cheng-long, Wu Di-fei, et al. Framework of the new generation of smart highway[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(4): 203-214. | |
| 5 | Shladover S E. Connected and automated vehicle systems: introduction and overview[J]. Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 22(3): 190-199. |
| 6 | 冉斌, 谭华春, 张健, 等. 智能网联交通技术发展现状及趋势[J]. 汽车安全与节能学报, 2018, 9(2): 119-130. |
| Ran Bin, Tan Hua-chun, Zhang Jian, et al. Development status and trend of connected automated vehicle highway system[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2018, 9(2): 119-130. | |
| 7 | Ma K, Wang H. Influence of exclusive lanes for connected and autonomous vehicles on freeway traffic flow[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 50168-50178. |
| 8 | Hua X D, Yu W J, Wang W. Influence of lane policies on freeway traffic mixed with manual and connected and autonomous vehicles[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020, 2020: No.3968625. |
| 9 | Ghiasi A, Hussain O, Qian Z. A mixed traffic capacity analysis and lane management model for connected automated vehicles: a markov chain method[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2017, 106: 266-292. |
| 10 | Chen D J, Ahn S, Chitturi M. Towards vehicle automation: roadway capacity formulation for traffic mixed with regular and automated vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2017, 100: 196-221. |
| 11 | Ye L, Yamamoto T. Impact of dedicated lanes for connected and autonomous vehicle on traffic flow throughput[J]. Physica A, 2018, 512: 588-597. |
| 12 | Ye L, Yamamoto T. Modeling connected and autonomous vehicles in heterogeneous traffic flow[J]. Physica A, 2018, 490: 269-277. |
| 13 | Masher D P, Ross D W, Wong P J, et al. Guidelines for design and operation of ramp control systems[R]. Menlo Park: CA United States: Stanford Research Institute,1975. |
| 14 | Smaragdis E, Papageogiou M. Series of new local ramp metering strategies[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2003, 1856: 74-86. |
| 15 | Bellemans T, Schutter B D, Moor B D. Model predictive control for ramp metering of motorway traffic: a case study[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2006, 14(7): 757-767. |
| 16 | 陈德望, 王飞跃, 陈龙. 基于模糊神经网络的城市高速公路入口匝道控制算法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2003(2): 100-105. |
| Chen De-wang, Wang Fei-yue, Chen Long. Freeway ramp control algorithm based on neurofuzzy networks[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2003(2): 100-105. | |
| 17 | 曾筠程, 邵敏华, 孙立军, 等. 基于有向图卷积神经网络的交通预测与拥堵管控[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(12): 239-248. |
| Zeng Yun-cheng, Shao Min-hua, Sun Li-jun, et al. Traffic prediction and congestion control based on directed graph convolution neural network[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(12): 239-248. | |
| 18 | Zhang J, Jiang X, Liu Z, et al. A study on autonomous intersection management: planning-based strategy improved by convolutional neural network[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2021, 25(10): 3995-4004. |
| 19 | Davarynejad M, Hegyi A, Vrancken J, et al. Motorway ramp-metering control with queuing consideration using Q-learning[C]∥2011 14th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Washington, DC, USA, 2011: 1652-1658. |
| 20 | 郑思. 面向快速道路远距离瓶颈的深度强化学习交通流控制策略研究[D]. 南京:东南大学交通学院, 2021. |
| Zheng Si. Research on deep reinforcement learning-based active traffic flow control strategies at distant downstream bottlenecks of expressway[D]. Nanjing: School of Transportation, Southeast University, 2021. | |
| 21 | Belletti F, Haziza D, Gomes G. Expert level control of ramp metering based on multi-task deep reinforcement learning[J]. Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017, 19(4): 1198-1207. |
| 22 | 葛家丽. 基于车辆簇的高速公路路侧单元部署研究[D]. 济南: 山东科技大学交通学院, 2020. |
| Ge Jia-li. Research on freeway road side unit deployment based on vehicle clusters[D]. Jinan: School of Transportation, Shandong University of Science and Technology, 2020. | |
| 23 | 陈瑜. 高速公路作业区安全分析及交通组织管理方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学交通科学与工程学院, 2006. |
| Chen Yu. The safety analysis and organization & management method study of freeway work zone[D]. Harbin: School of Transportation Science & Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2006. | |
| 24 | 石茂清. 道路交通安全设施设计研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学交通运输与物流学院, 2005. |
| Shi Mao-qing. Study on design of traffic safety facilities[D]. Chengdu: School of Transportation and Logistics, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2005. | |
| 25 | 孙玲, 张静, 周瀛, 等. 车路协同环境下自动驾驶专用车道入口区域设计[J]. 公路交通科技, 2020, 37(): 122-129. |
| Sun Ling, Zhang Jing, Zhou Ying, et al. Design of entrance area of automatic driving special lane in vehicle-infrastructure collaborative environment[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2020, 37(Sup.1): 122-129. | |
| 26 | Milanés V, Shladover S E. Modeling cooperative and autonomous adaptive cruise control dynamic responses using experimental data[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2014, 48: 285-300. |
| 27 | Xue Y, Wang X, Cen B L, et al. Study on fuel consumption in the Kerner-Klenov-Wolf three-phase cellular automaton traffic flow model[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2020, 102(1): 1-10. |
| 28 | Wang C H, Hwang M C. Value-based deep reinforcement learning for adaptive isolated intersection signal control[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2018, 12(9): 1005-1010. |
| 29 | Schaul T, Quan J, Antonoglou I, et al. Prioritized experience replay[C]∥Proceeding of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2016: 322-355. |
| 30 | 武毅. 基于三相交通流理论的元胞自动机模型研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学交通学院, 2018. |
| Wu Yi. Research on cellular automated traffic flow model for three-phase theory[D]. Changchun: College of Transportation, Jilin University, 2018. | |
| 31 | 舒凌洲, 吴佳, 王晨. 基于深度强化学习的城市交通信号控制算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2019, 39(5): 1495-1499. |
| Shu Ling-zhou, Wu Jia, Wang Chen. Urban traffic signal control based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2019, 39(5): 1495-1499. |
| [1] | 郑植,袁佩,金轩慧,魏思斯,耿波. 桥墩复合材料柔性防撞护舷试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2581-2590. |
| [2] | 李建华,王泽鼎. 考虑路径耗时的城市汽车分布式充电桩选点规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2298-2303. |
| [3] | 李洪涛,王琳虹,李俊达. 公路交叉口照明和限速对视觉搜索能力的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2287-2297. |
| [4] | 巫威眺,曾坤,周伟,李鹏,靳文舟. 基于多源数据和响应面优化的公交客流预测深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [5] | 程国柱,盛林,赵浩,冯天军. 基于危险度分析的信号交叉口专用相位设置条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1962-1969. |
| [6] | 何永明,陈世升,冯佳,万亚楠. 基于高精地图的超高速公路虚拟轨道系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2016-2028. |
| [7] | 薛志佳,王召阳,张久鹏,晏长根,许子凯,张英立,黄晓明,马涛. 泥石流作用下道路结构韧性分析及提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1773-1781. |
| [8] | 刘振亮,赵存宝,吴云鹏,马迷娜,马龙双. 数据驱动的公路桥梁网络全寿命抗震韧性评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1695-1701. |
| [9] | 贾洪飞,徐英俊,杨丽丽,王楠. 商品车多式联运联盟成员选择及利益分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
| [10] | 孙超,尹浩为,汤文蕴,褚昭明. 交通需求估计下的检测器布局和手机数据扩样推断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1070-1077. |
| [11] | 常玉林,徐文倩,孙超,张鹏. 车联网环境下考虑遵从程度的混合流量逐日均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1085-1093. |
| [12] | 田彦涛,季言实,唱寰,谢波. 深度强化学习智能驾驶汽车增广决策模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 682-692. |
| [13] | 姚荣涵,徐文韬,郭伟伟. 基于因子长短期记忆的驾驶人接管行为及意图识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 758-771. |
| [14] | 肖雪,李克平,彭博,昌满玮. 基于决策-规划迭代框架的智驾车换道行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 746-757. |
| [15] | 马敏,胡大伟,舒兰,马壮林. 城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
|