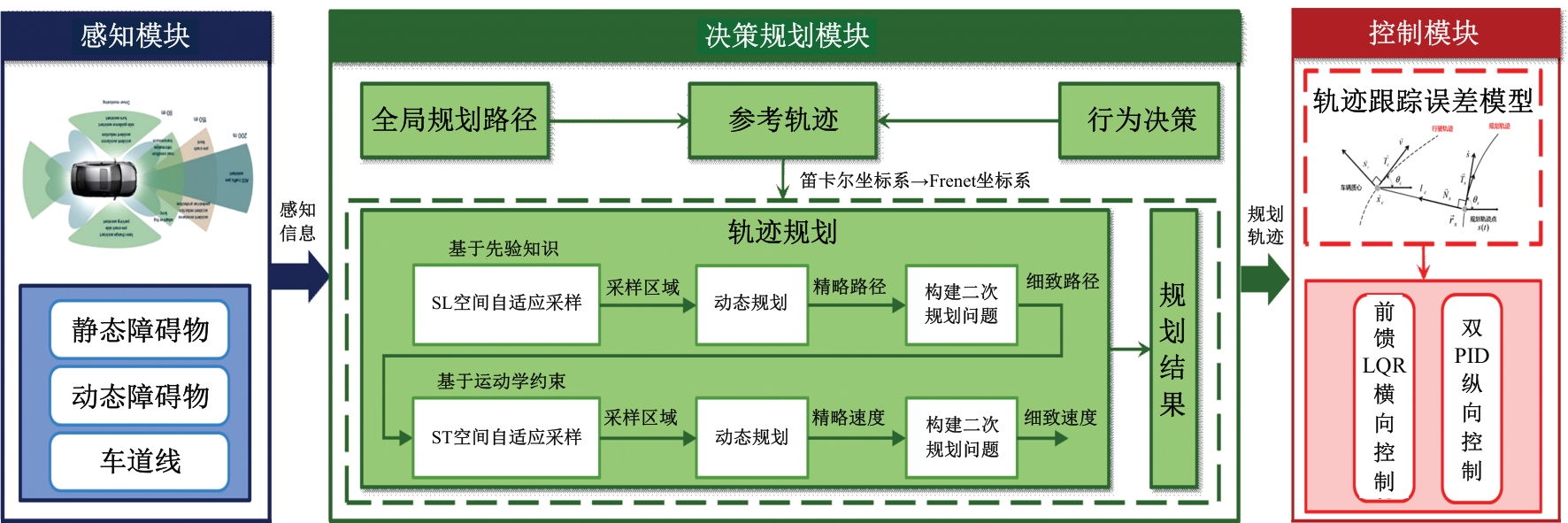
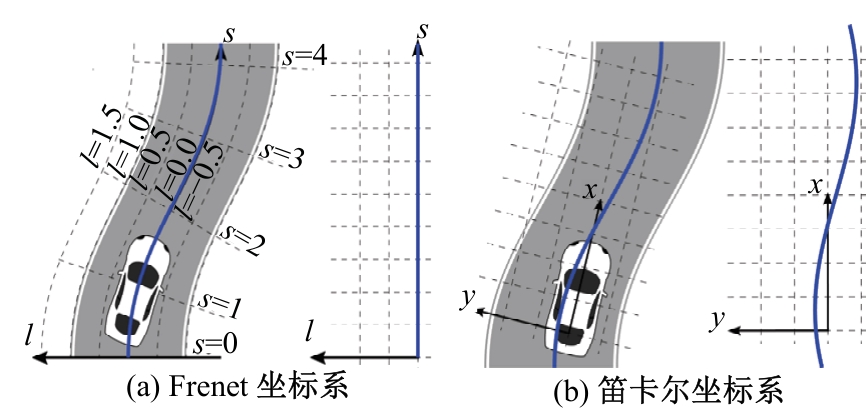
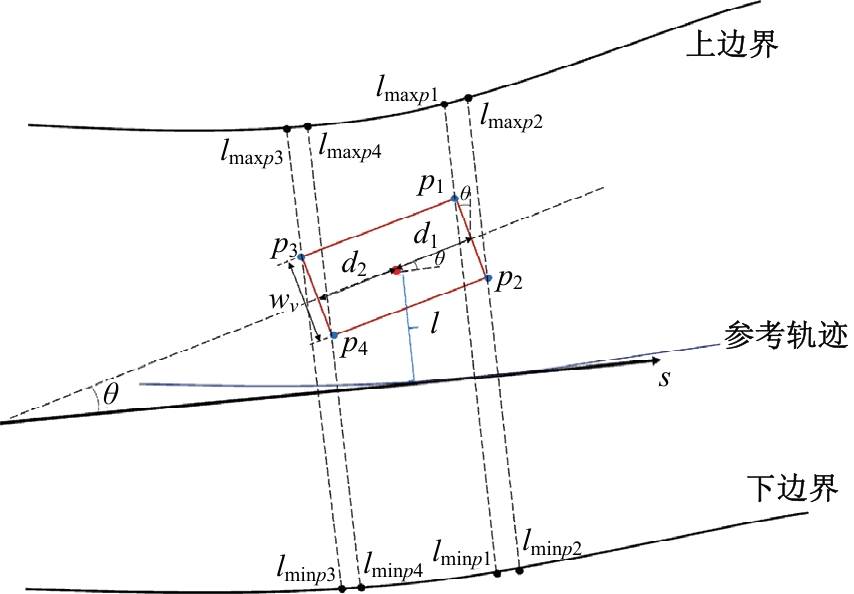
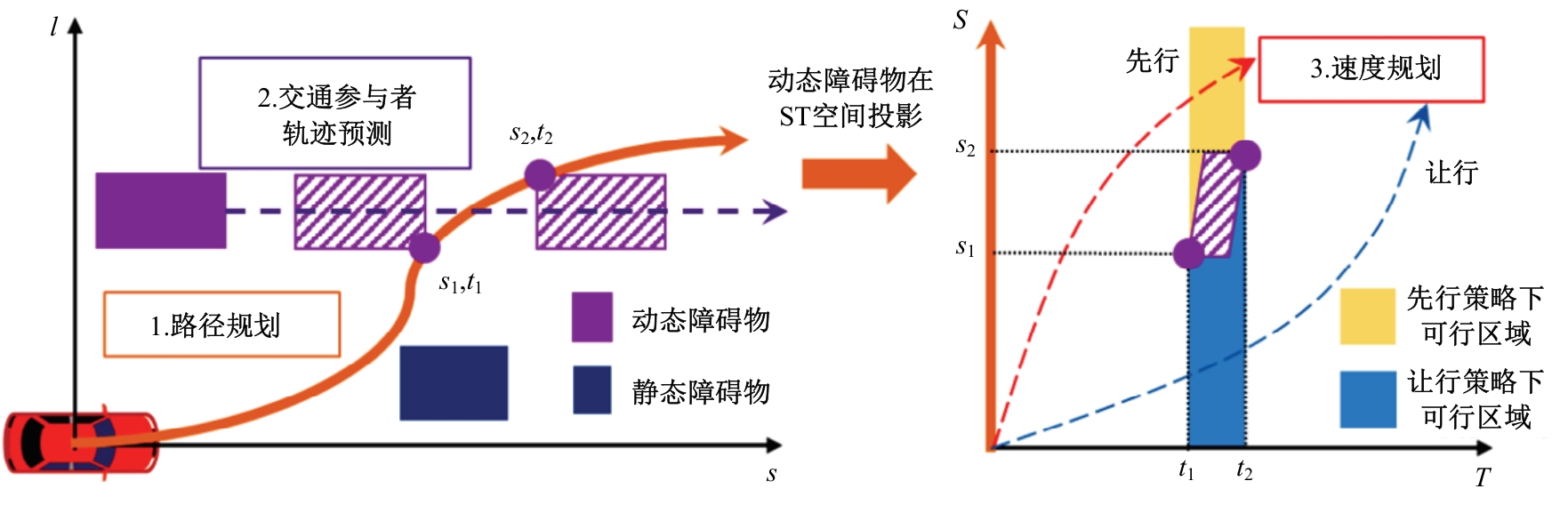
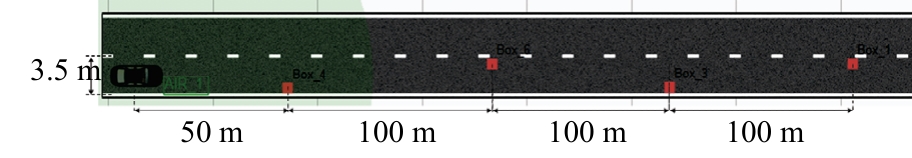
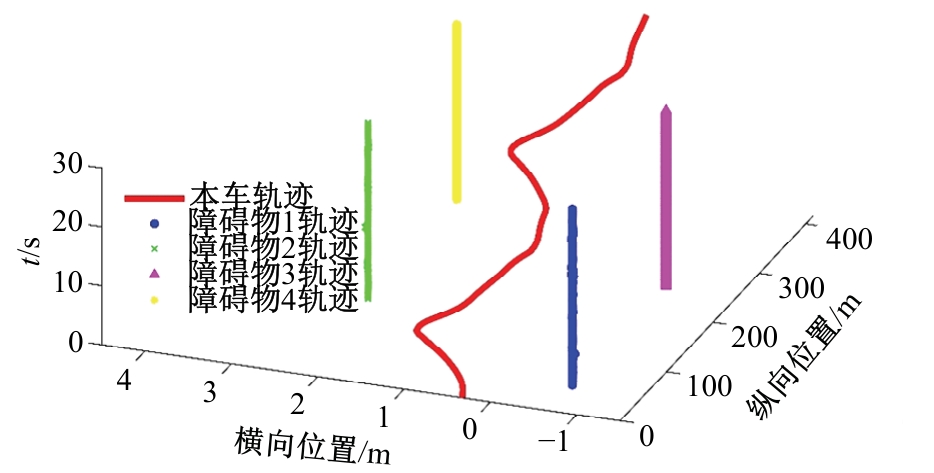
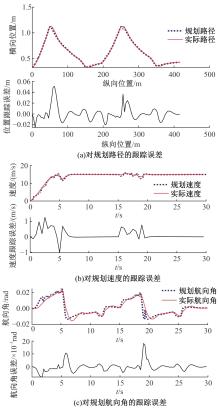
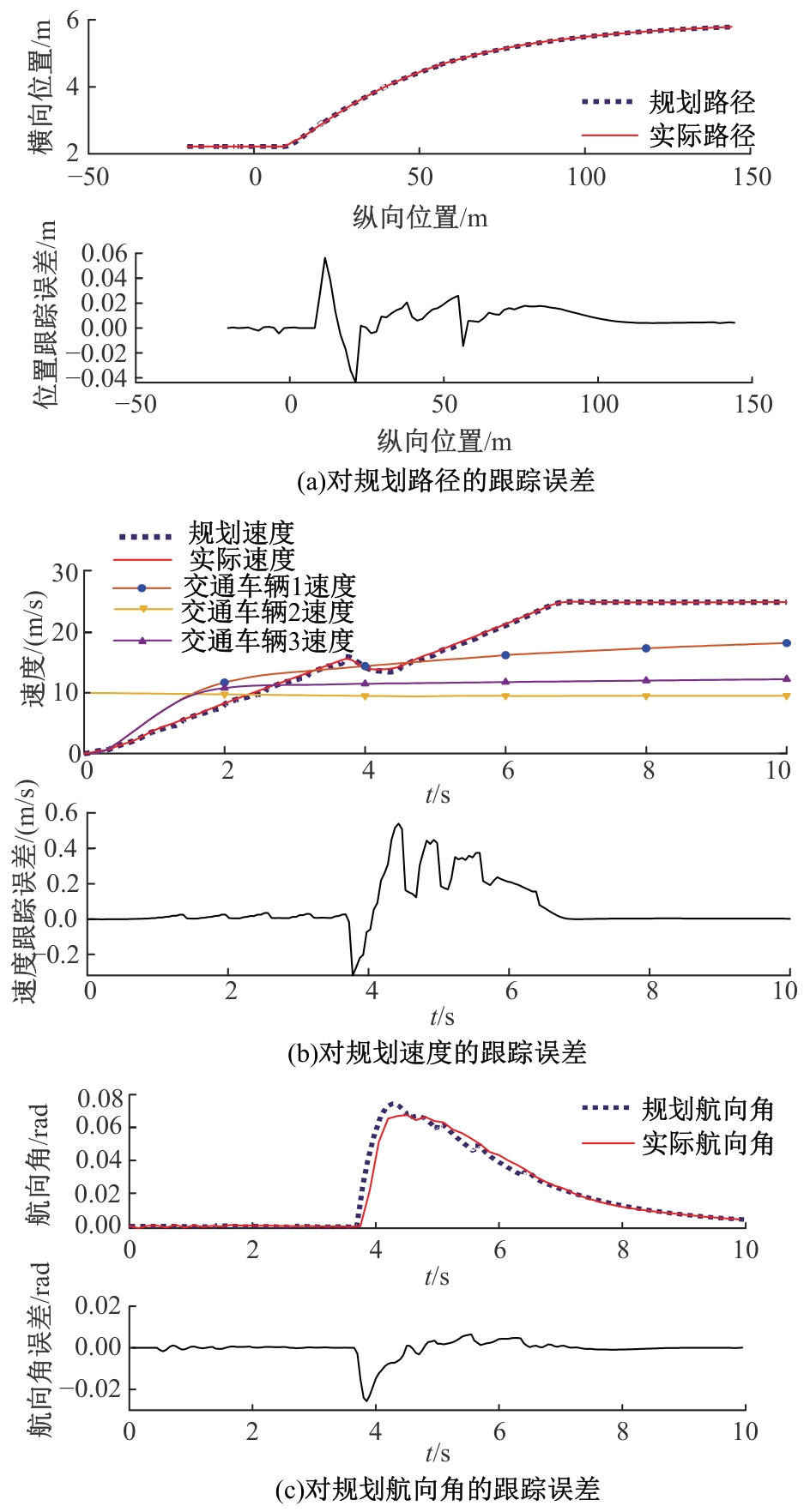
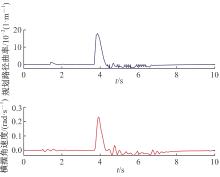
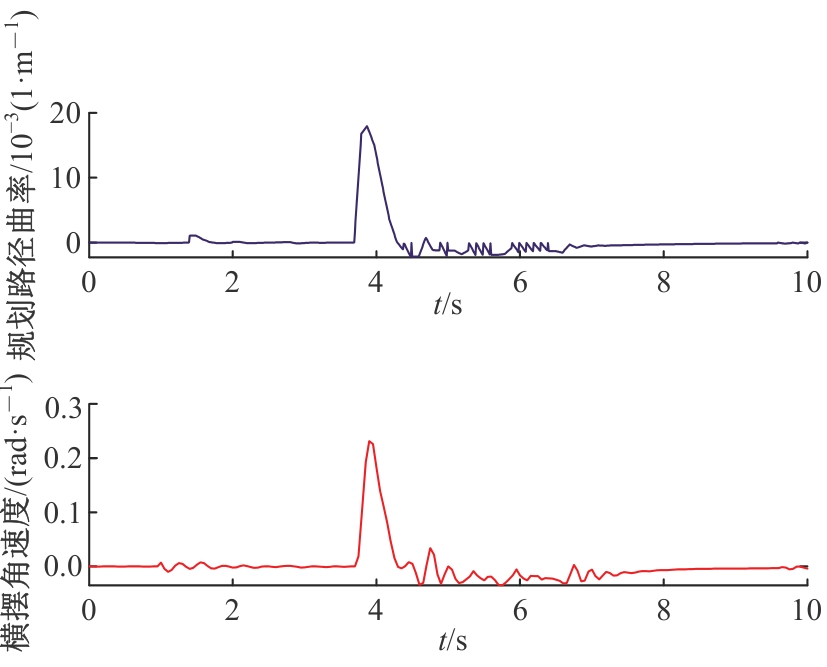
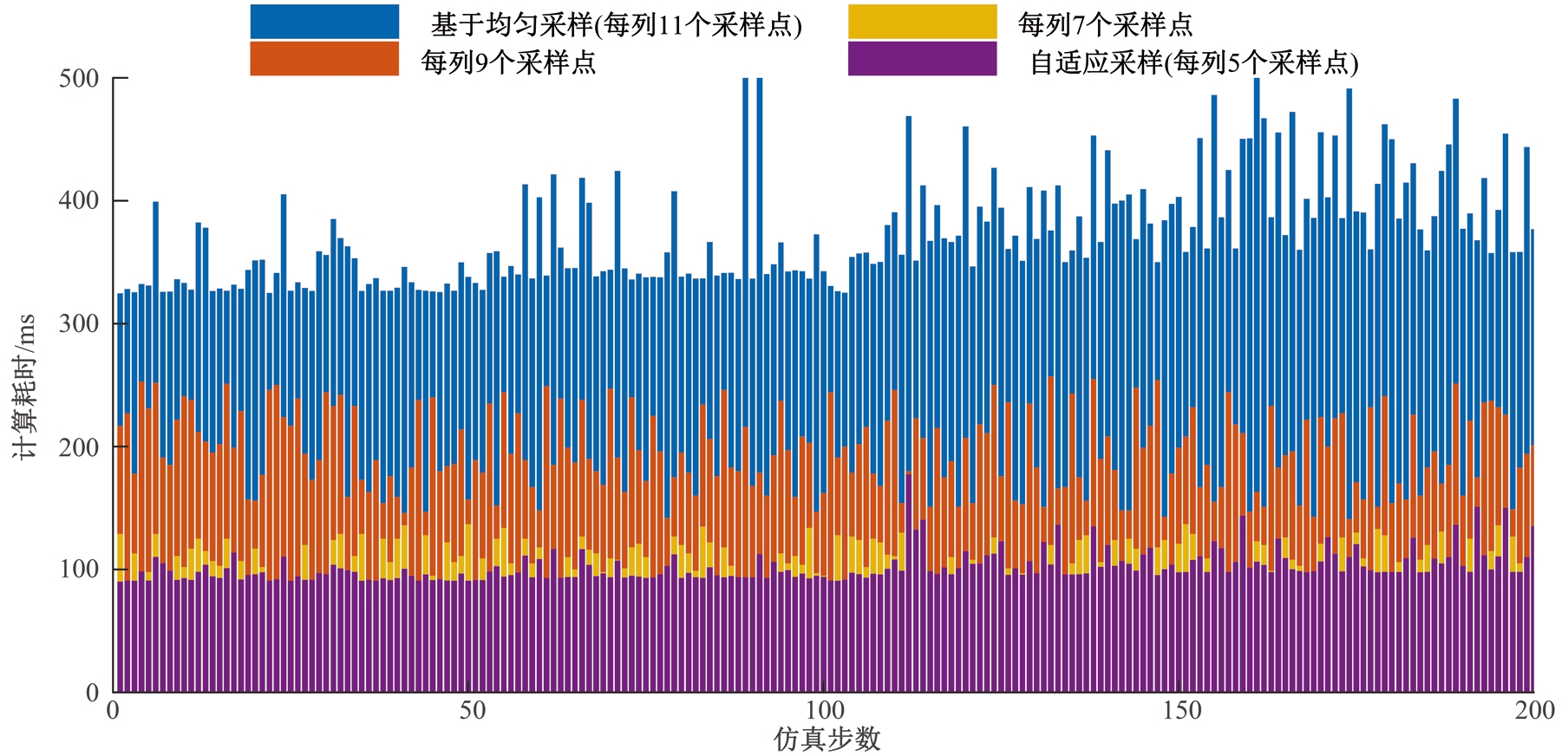
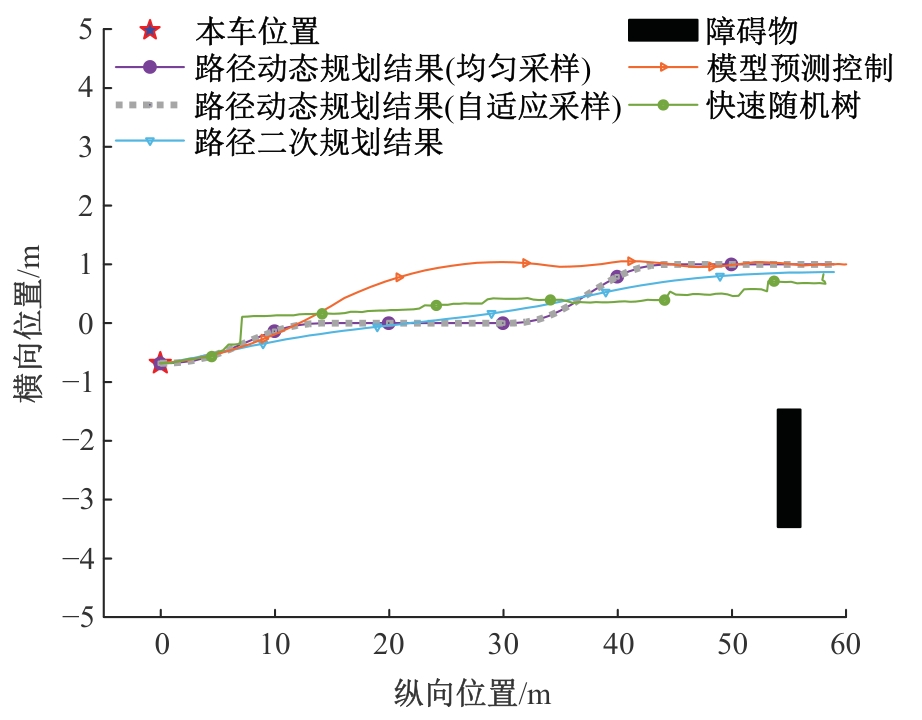
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (8): 2802-2816.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20231236
Trajectory planning for intelligent vehicles based on adaptive sampling
Jun-wu ZHAO1( ),Ting QU1,2,Yun-feng HU1,3(
),Ting QU1,2,Yun-feng HU1,3( )
)
- 1.National Key Laboratory of Automotive Chassis Integration and Bionics,Jilin University,Changchun 130025,China
2.Chongqing Research Institute,Jilin University,Chongqing 401120,China
3.College of Communication Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
CLC Number:
- U270.1
| [1] | Qureshi K N, Abdullah A H. A survey on intelligent transportation systems[J]. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, 2013, 15(5): 629-642. |
| [2] | 熊璐, 杨兴, 卓桂荣, 等. 无人驾驶车辆的运动控制发展现状综述[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(10): 127-143. |
| Xiong Lu, Yang Xing, Zhuo Gui-rong, et al. Review on motion control of autonomous vehicles[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engneering, 2020, 56(10): 127-143. | |
| [3] | 彭浩楠, 唐明环, 查奇文, 等. 自动驾驶汽车双车道换道最优轨迹规划方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(12): 2852-2863. |
| Peng Hao-nan, Tang Ming-huan, Zha Qi-wen, et al. Optimization-based lane changing trajectory planning approach for autonomous vehicles on two-lane road[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(12): 2852-2863. | |
| [4] | 张利鹏, 苏泰, 严勇. 基于采样区域优化的智能车辆轨迹规划方法[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(14): 276-287. |
| Zhang Li-peng, Su Tai, Yan Yong. Trajectory planning method of intelligent vehicle based on sampling area optimization[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engneering, 2022, 58(14): 276-287. | |
| [5] | 张一鸣, 周兵, 吴晓建, 等. 基于前车轨迹预测的高速智能车运动规划[J]. 汽车工程, 2020, 42(5): 574-580. |
| Zhang Yi-ming, Zhou Bin, Wu Xiao-jian, et al. Motion planning of high speed intelligent vehicle based on front vehicle trajectory prediction[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2020, 42(5): 574-580. | |
| [6] | Chen L, Qin D F, Xu X, et al. A path and velocity planning method for lane changing collision avoidance of intelligent vehicle based on cubic 3-D Bezier curve[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2019, 132: 65-73. |
| [7] | Werling M, Kammel S, Ziegler J, et al. Optimal trajectories for time-critical street scenarios using discretized terminal manifolds[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2012, 31(3): 346-359. |
| [8] | 余卓平, 李奕姗, 熊璐. 无人车运动规划算法综述[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 45(8): 1150-1159. |
| Yu Zhuo-ping, Li Yi-shan, Xiong Lu. A review of the motion planning problem of autonomous vehicle[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2017, 45(8): 1150-1159. | |
| [9] | Fan H Y, Fan Z, Liu C C, et al. Baidu apollo EM motion planner[J]. Arxiv Preprint, 2018, 9: No.180708048. |
| [10] | Lim W, Lee S, Sunwoo M, et al. Hierarchical trajectory planning of an autonomous car based on the integration of a sampling and an optimization method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(2): 613-626. |
| [11] | 唐志荣, 冀杰, 吴明阳, 等. 基于改进人工势场法的车辆路径规划与跟踪[J]. 西南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 40(6): 174-182. |
| Tang Zhi-rong, Ji Jie, Wu Ming-yang, et al. Vehicle path planning and tracking based on improved artificial potential field method[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 40(6): 174-182. | |
| [12] | Lu B, Li G F, Yu H L, et al. Adaptive potential field-based path planning for complex autonomous driving scenarios[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 225294-225305. |
| [13] | Liu Z X, Yuan X F, Huang G M, et al. Two potential fields fused adaptive path planning system for autonomous vehicle under different velocities[J]. ISA Transactions, 2021, 112: 176-185. |
| [14] | Qu T, Chen H, Cao D P, et al. Switching-based stochastic model predictive control approach for modeling driver steering skill[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2014, 16(1): 365-375. |
| [15] | 许芳, 张君明, 胡云峰, 等. 智能车辆路径跟踪横纵向耦合实时预测控制器[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(6): 2287-2294. |
| Xu Fang, Zhang Jun-ming, Hu Yun-feng, et al. Lateral and longitudinal coupling real-time predictive controller for intelligent vehicle path tracking[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2287-2294. | |
| [16] | Qu T, Zhao J W, Gao H H, et al. Multi-mode switching-based model predictive control approach for longitudinal autonomous driving with acceleration estimation[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2020, 14(14): 2102-2112. |
| [17] | Hang P, Lv C, Xing Y, et al. Human-like decision making for autonomous driving: a noncooperative game theoretic approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 22(4): 2076-2087. |
| [18] | Polack P, Altché F, Andréa N B, et al. Guaranteeing consistency in a motion planning and control architecture using a kinematic bicycle model[C]∥Proceeding of the 2018 Annual American Control Conference (ACC). Piscataway, N J: IEEE, 2018: 3981-3987. |
| [19] | Mouhagir H, Talj R, Cherfaoui V, et al. Evidential-based approach for trajectory planning with tentacles, for autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 21(8): 3485-3496. |
| [20] | Ji J L, Yang T K, Xu C, et al. Real-time trajectory planning for aerial perching[C]∥Proceeding of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Piscataway, N J:IEEE, 2022: 10516-10522. |
| [1] | Jin-wu GAO,Shao-long SUN,Shun-yao WANG,Bing-zhao GAO. Speed fluctuation suppression strategy of range extender based on motor torque compensation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2475-2486. |
| [2] | Gui-shen YU,Xin CHEN,Yue TANG,Chun-hui ZHAO,Ai-jia NIU,Hui CHAI,Jing-xin NA. Effect of laser surface treatment on the shear strength of aluminum-aluminum bonding joints [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(8): 2555-2569. |
| [3] | Mei-xia JIA,Jian-jun HU,Feng XIAO. Multi⁃physics simulation method of vehicle motor under varying working conditions based on multi⁃software combination [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1862-1872. |
| [4] | Chun XIAO,Zi-chun YI,Bing-yin ZHOU,Shao-rui ZHANG. Fuzzy energy management strategy of fuel cell electric vehicle based on improved pigeon⁃inspired optimization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1873-1882. |
| [5] | Xue-wei SONG,Ze-ping YU,Yang XIAO,De-ping WANG,Quan YUAN,Xin-zhuo LI,Jia-wen ZHENG. Research progress on the performance changes of lithium⁃ion batteries after aging [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1817-1833. |
| [6] | Wei-dong LI,Cao-yuan MA,Hao SHI,Heng CAO. An automatic driving decision control algorithm based on hierarchical reinforcement learning [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1798-1805. |
| [7] | Dang LU,Yan-ru SUO,Yu-hang SUN,Hai-dong WU. Estimation of tire camber and sideslip combined mechanical characteristics based on dimensionless expression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(5): 1516-1524. |
| [8] | Zhen-hai GAO,Cheng-yuan ZHENG,Rui ZHAO. Review of active safety verification and validation for autonomous vehicles in real and virtual scenarios [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1142-1162. |
| [9] | Tao ZHANG,Huang-da LIN,Zhong-jun YU. Real-time rolling optimization control method for gearshift of hybrid electric vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1215-1224. |
| [10] | Dang LU,Xiao-fan WANG,Hai-dong WU. Analysis of uniform distribution characteristics of contact pressure of TWEEL tires [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 811-819. |
| [11] | Xin CHEN,Xiang-yuan ZHANG,Zi-tao WU,Gui-shen YU,Li-fei YANG. Effect of process sequence on tensile shear properties of PFSSW joints for automotive aluminum sheets [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 468-475. |
| [12] | Jun-long QU,Wen-ku SHI,Sheng-yi XUAN,Zhi-yong CHEN. Parameter design method of multiple dynamic vibration absorbers for suppressing multi-frequency resonance of automotive powertrain [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 444-455. |
| [13] | Jun-nian WANG,Yu-jing CAO,Zhi-ren LUO,Kai-xuan LI,Wen-bo ZHAO,Ying-yi MENG. Online detection algorithm of road water depth based on binocular vision [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 175-184. |
| [14] | Hong-yu HU,Zheng-guang ZHANG,You QU,Mu-yu CAI,Fei GAO,Zhen-hai GAO. Driver behavior recognition method based on dual-branch and deformable convolutional neural networks [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 93-104. |
| [15] | Cao TAN,Hao-xin REN,Wen-qing GE,Ya-dong SONG,Jia-yu LU. Improved active disturbance rejection control for hydraulic vibration stages based on the direct-drive valve [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 84-92. |
|
||