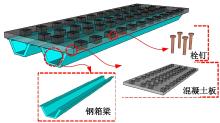
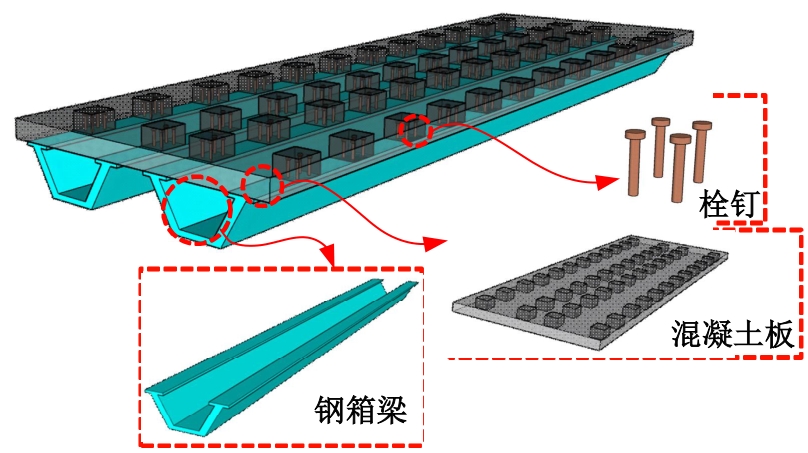
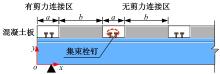
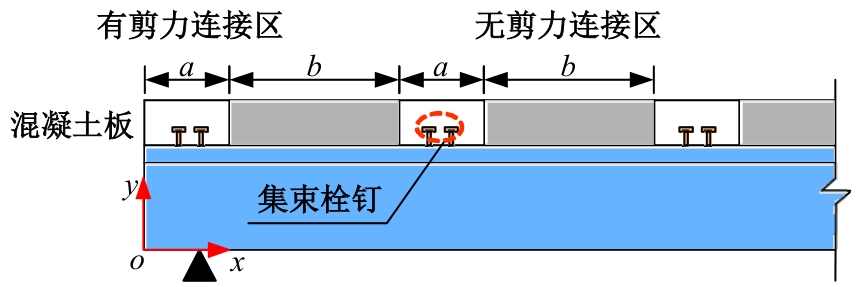
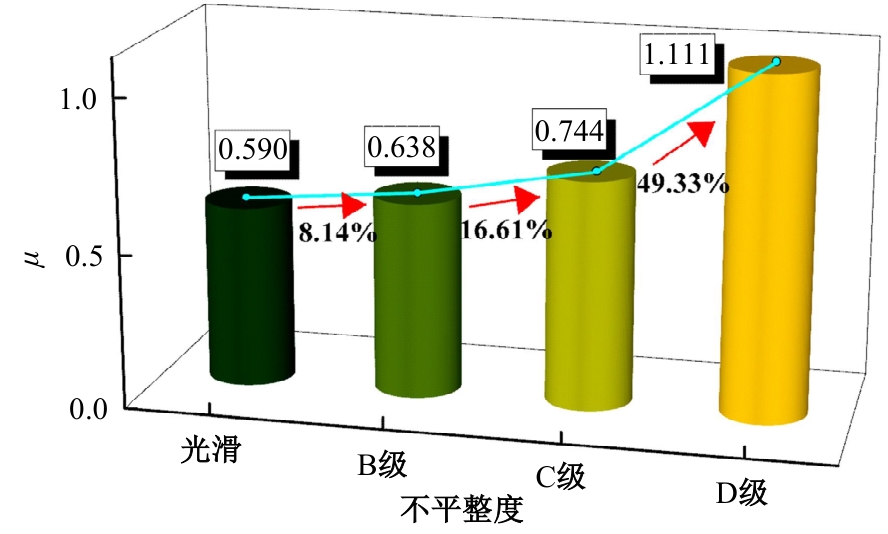
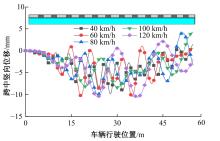
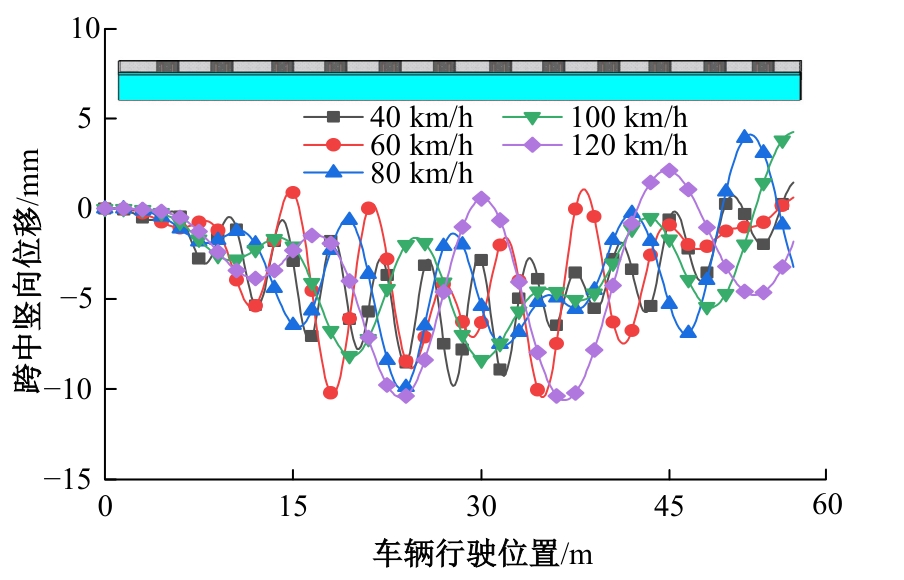
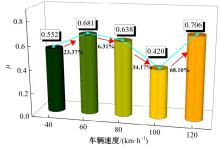
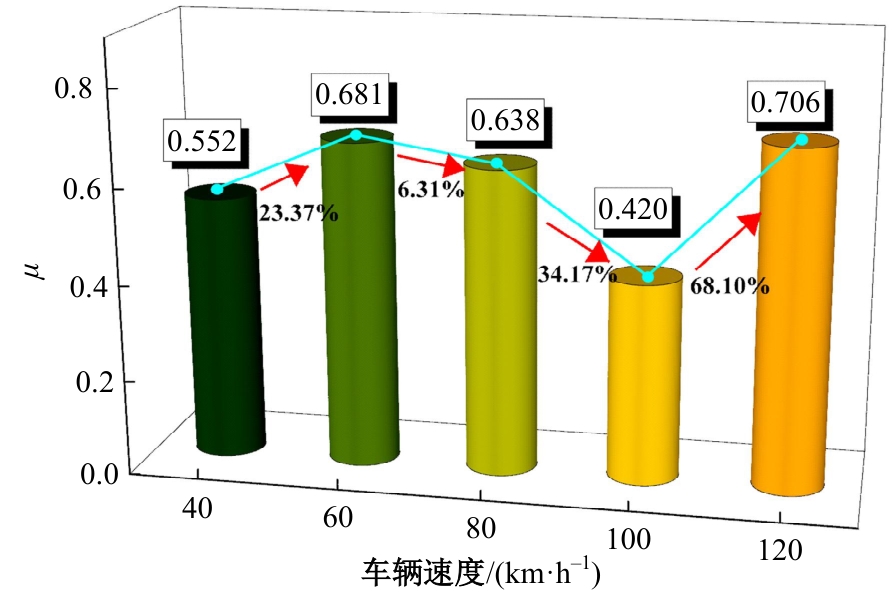
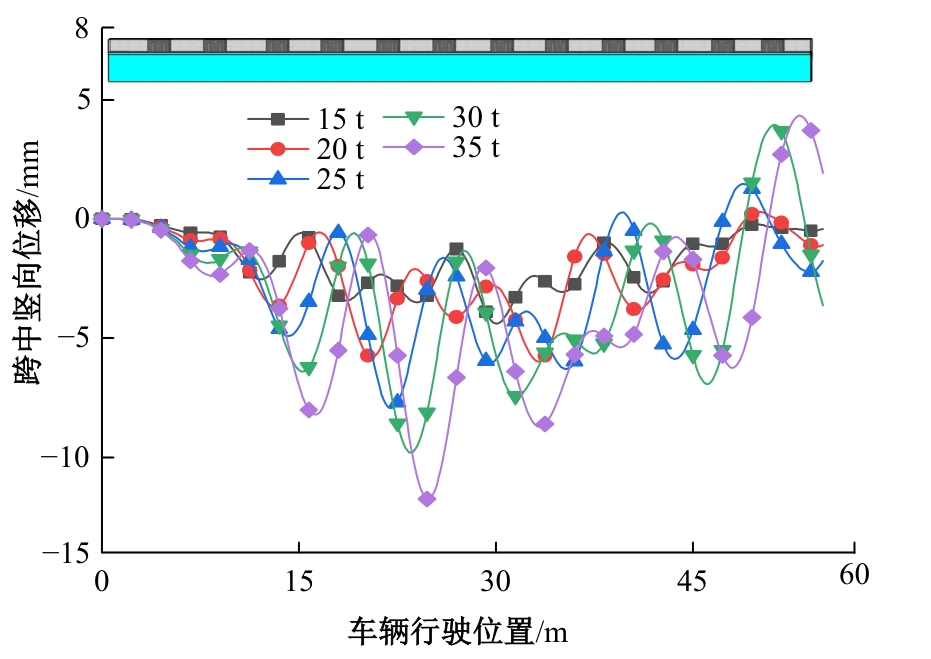
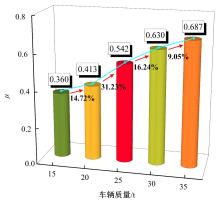
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (7): 2354-2364.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230871
Vibration characteristics of prefabricated steel-concrete composite beam bridges with clustered grouping bolt connection and analysis of vehicle-bridge coupling
Liang FAN1,2( ),Wen ZENG1,Qiang WEN1,Fu-yu ZHAO3,Ying-ming XU4
),Wen ZENG1,Qiang WEN1,Fu-yu ZHAO3,Ying-ming XU4
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Mountain Bridge and Tunnel Engineering,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
3.Southwest Branch,China Construction Eighth Engineering Bureau Co. ,Ltd. ,Chengdu 610041,China
4.Chongqing Kaizhou District Transportation Bureau,Chongqing 405400,China
CLC Number:
- TU318.1
| [1] | 韩万水, 陈艾荣. 侧风与桥梁振动对车辆行驶舒适性影响研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2008, 41(4): 55-60. |
| Han Wan-shui, Chen Ai-rong. Effects of crosswind and bridge motion on ride comfort of road vehicles[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2008, 41(4): 55-60. | |
| [2] | Miguel L F F, Lopez R H, Torii A J, et al. Robust design optimization of TMDs in vehicle–bridge coupled vibration problems[J]. Engineering Structures, 2016, 126(1): 703-711. |
| [3] | Wang L, Kang X, Jiang P. Vibration analysis of a multi-span continuous bridge subject to complex traffic loading and vehicle dynamic interaction[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2016, 20(1): 323-332. |
| [4] | Liu Y, Kong X, Cai C S, et al. Driving effects of vehicle‐induced vibration on long‐span suspension bridges[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2016, 24(2): 1873-1891. |
| [5] | 周勇军, 赵煜, 贺全海, 等. 刚构-连续组合桥梁冲击系数多因素灵敏度分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2012, 31(3): 97-101. |
| Zhou Yong-jun, Zhao Yu, He Quan-hai, et al. Muti-parameters sensitivity analysis of impact factors for rigid-continuous combined bridge[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 31(3): 97-101. | |
| [6] | 樊小虎, 吴红林. 车桥耦合振动研究方法综述[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2009, 9(14): 4090-4099, 4106. |
| Fan Xiao-hu, Wu Hong-lin. Literature review of addressing interaction of vehicle-bridge vibration[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2009, 9(14): 4090-4099, 4106. | |
| [7] | Gao Y M, Fan L, Yang W, et al. Mechanical behavior of prefabricated steel-concrete composite beams considering the clustering degree of studs[J]. Steel and Composite Structures, 2022, 45(3): 433-444. |
| [8] | 范亮, 邬江红, 谭阳, 等. 集束钉群装配式钢-混组合梁界面滑移特性研究[J]. 建筑结构, 2022, 52(18): 86-91. |
| Fan Liang, Wu Jiang-hong, Tan Yang, et al. Research on interface slip properties of assembled steel-concrete composite beams with cluster nail groups[J]. Building Structure, 2022, 52(18): 86-91. | |
| [9] | 范亮,徐英铭,谭阳.集束群钉式装配组合梁界面滑移计算[J].吉林大学学报:工学版, 2023, 53(9):2533-2541. |
| Fan Liang, Xu Ying-ming, Tan Yang. Interface slip calculation of prefabricated steel-concrete composite beams with clustering studs[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023,53(9): 2533-2541. | |
| [10] | Gao Y, Zhang H H, Jiang B J. Analysis on the vehicle-bridge coupled vibrations of long-span cable-stayed bridge based on multiscale model[J]. Journal of Vibroengineering, 2015, 17(1): 402-410. |
| [11] | 范晨, 王莹, 李兆霞. 以疲劳评估为目标的大跨钢箱梁桥车桥耦合动力分析方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(6): 236-242. |
| Fan Chen, Wang Ying, Li Zhao-xia. Vehicle-bridge coupling dynamic analysis method for the fatigue assessment of a long-span steel box-girder bridge[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(6): 236-242. | |
| [12] | 贺建帅, 李奇, 王君杰. 高铁桥梁震时行车安全性评价的梁端变位限值研究[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2022, 20(5): 1543-1554. |
| He Jian-shuai, Li Qi, Wang Jun-jie. Beam end displacement limits for high-speed railway bridges traffic safety evaluation during earthquake[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2022, 20(5): 1543-1554. | |
| [13] | 李慧乐, 夏禾. 基于车桥耦合随机振动分析的钢桥疲劳可靠度评估[J]. 工程力学, 2017, 34(2): 69-77. |
| Li Hui-le, Xia He. Fatigue reliability evaluation of steel bridges based on coupling random vibration analysis of train and bridge[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 34(2): 69-77. | |
| [14] | 杨星星. 中小跨径钢桁梁桥的静动力特性研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学土木工程学院, 2018. |
| Yang Xing-xing. Research on static and dynamic characteristics of medium and small span steel truss girder bridges[D]. Yangzhou: College of Civil Engineering,Yangzhou University, 2018. | |
| [15] | 邓露, 陈雅仙, 韩万水, 等. 中小跨径公路混凝土简支梁桥冲击系数研究及建议取值[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(1): 69-78. |
| Deng Lu, Chen Ya-xian, Han Wan-shui, et al. Studying impact factors for short-and medium-span simply supported concrete highway bridges and its suggested values[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(1): 69-78. | |
| [16] | 李喜梅, 王新, 母渤海, 等. 车辆荷载作用下双工字钢-混组合连续梁桥振动控制研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(7): 173-183. |
| Li Xi-mei, Wang Xin, Mu Bo-hai, et al. Research on vibration control of twin-I steel-concrete composite continuous girder bridge under vehicle load[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(7): 173-183. | |
| [17] | 李慧乐. 基于车桥耦合振动的桥梁动应力分析及疲劳性能评估[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学土木工程学院, 2016. |
| Li Hui-le. Dynamic stress analysis and fatigue performance assessment of bridges based on vehicle-bridge coupling vibration[D]. Beijing: College of Civil Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2016. | |
| [18] | Zhang M J, Li Y L, Wang B. Effects of fundamental factors on coupled vibration of wind-rail vehicle-bridge system for long-span cable-stayed bridge[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2016, 23(5): 1264-1272. |
| [19] | Zeng Q, Dimitrakopoulos E G. Seismic response analysis of an interacting curved bridge-train system under frequent earthquakes[J]. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 2016, 45(7): 1129-1148. |
| [20] | 冀伟, 蔺鹏臻, 邓露, 等. 波形钢腹板PC简支箱梁桥的扭转振动频率分析[J]. 振动、测试与诊断, 2017, 37(4): 769-774, 845. |
| Ji Wei, Lin Peng-zhen, Deng Lu, et al. Analysis the torsional vibration frequencies of PC box girder bridge with corrugated steel webs[J]. Journal of Vibration,Measurement & Diagnosis, 2017, 37(4): 769-774, 845. | |
| [21] | 罗锟, 王鹏生, 雷晓燕, 等. 轨道-箱梁耦合振动模型试验设计与验证[J]. 铁道学报, 2023, 45(2): 139-145. |
| Luo Kun, Wang Peng-sheng, Lei Xiao-yan, et al. Model test design and verification of track-box girder coupling Vibration[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2023, 45(2): 139-145. | |
| [22] | Deng L, Yu Y, Zou Q, et al. State-of-the-art review of dynamic impact factors of highway bridges[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2015, 20(5): 1-14. |
| [23] | 邓露, 王维. 公路桥梁动力冲击系数研究进展[J]. 动力学与控制学报, 2016, 14(4): 289-300. |
| Deng Lu, Wang Wei. Research progress on dynamic impact factors of highway bridge[J]. Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2016, 14(4): 289-300. | |
| [24] | 聂建国, 刘明, 叶列平. 钢-混凝土组合结构[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2005. |
| [25] | 安里鹏, 李德建, 胡立华, 等. 高速公路大跨度连续梁桥车桥耦合动力响应与参数影响分析[J]. 应用力学学报, 2015, 32(6): 942-949, 1099. |
| An Li-peng, Li De-jian, Hu Li-hua, et al. Vehicle-bridge coupled dynamic response and parameter influence analysis on highway large span continuous girder bridge[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2015, 32(6): 942-949, 1099. | |
| [26] | 桂水荣. 基于桥面不平顺公路梁桥车桥耦合随机振动研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学土木工程学院, 2017. |
| Gui Shui-rong. Research of deck irregularity excitation on highway vehicle-bridge coupling random vibrations[D]. Nanjing: College of Civil Engineering,Southeast University, 2017. | |
| [27] | 桂水荣, 陈水生, 万水. 基于路面一致激励车桥耦合非平稳随机振动分析[J]. 振动、测试与诊断, 2018, 38(5): 908-915, 1077. |
| Gui Shui-rong, Chen Shui-sheng, Wan Shui. Analysis of consistent stimulus of road roughness on vehicle-bridge coupling nonstationary random vibrations[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2018, 38(5): 908-915, 1077. | |
| [28] | 徐华. 考虑车桥耦合振动的正交异性钢桥面板疲劳性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学土木工程学院, 2021. |
| Xu Hua. Fatigue behavior of orthotropic steel deck considering vehicle bridge coupling vibration[D]. Chongqing: College of Civil Engineering,Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2021. | |
| [29] | 王运金, 桂水荣, 陈水生. 连续梁桥车桥耦合振动分析的数值解法[J]. 华东交通大学学报, 2007(4): 25-29. |
| Wang Yun-jin, Gui Shui-rong, Chen Shui-sheng. An efficient algorithm for coupled vibration analysis of continuous bridges under moving vehicle[J]. Journal of East China Jiaotong University, 2007(4): 25-29. | |
| [30] | 周勇, 薛宇欣, 李冉冉, 等.桥梁冲击系数理论研究和应用进展[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(4): 31-50. |
| Zhou Yong, Xue Yu-xin, Li Ran-ran, et al. State-of-the-art of theory and applications of bridge dynamics load allowance[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(4): 31-50. | |
| [31] | 韩万水, 马麟, 院素静, 等.路面粗糙度非一致激励对车桥耦合振动系统响应影响分析[J].土木工程学报, 2011, 44(10): 81-90. |
| Han Wan-shui, Ma Lin, Yuan Su-jing, et al. Analysis of the effect of inconsistent stimulus of surface roughness on vehicle-bridge coupling vibrations[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2011, 44(10): 81-90. |
| [1] | Ge-dong JIANG,Hao WANG,Ya-bin JING. Influence of contact thermal resistance on temperature rise characteristics of high⁃speed ball screw [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(6): 1915-1922. |
| [2] | Yong-jun ZHOU,Feng-rui MU,Cheng CAI,Fan YANG. Influence factors of preload loss in cable clamp bolt of suspension bridge based on orthogonal experiment method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(4): 1188-1196. |
| [3] | Dang LU,Xiao-fan WANG,Hai-dong WU. Analysis of uniform distribution characteristics of contact pressure of TWEEL tires [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(3): 811-819. |
| [4] | Bao-dong LIU,Fang LI,Xiao-xi WANG,Meng GAO. Flexural stiffness and bearing capacity of corrugated steel plate composite structures reinforced by concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2502-2510. |
| [5] | Yu-xin XUE,Yong-jun ZHOU,Ye-lu WANG,Kai-xiang FAN,Yu ZHAO. Application of dynamic load allowance test method of simply supported girder bridge based on suspension hammer system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2557-2567. |
| [6] | Hua-min LIU,Shu-han YANG,Yi LI,Ce LIANG,Qi-gang Han. Thrust rod ball hinge bionic surface improvement and finite element analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2733-2740. |
| [7] | Yong-xin SUN,Peng-zhen LIN,Zi-jiang YANG,Wei JI. Calculation method for crack width of UHPC beams considering bond slip effect [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2600-2608. |
| [8] | Xue-lian GUO,Wan-shui HAN,Tao WANG,Kai ZHOU,Xiu-shi ZHANG,Shu-ying ZHANG. Assessment method of resistant overturning stability safety factors of curved bridge under customized transport vehicles [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2229-2237. |
| [9] | Ce LIANG,Min LI,Yi LI,Ji-cai LIANG,Qi-gang HAN. Numerical simulation on friction characteristics of rubber bushing with bionic flexible surfaces [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2181-2186. |
| [10] | Lin XIAO,Huan-bo WEI,Xing WEI,Zhi-rui KANG. Numerical analysis on cracking behavior of concrete slab due to corrosion expansion of stud connector in steel-concrete composite beam [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1958-1965. |
| [11] | Jian-xiao ZHENG,Wen-bo WANG,Jin-song LIU,Li-ming ZHOU,Yu LI. Moisture-electro-mechanical coupling smoothed finite element method based on asymptotic homogenization [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 1876-1886. |
| [12] | Han-hui HUANG,Kang-ming CHEN,Qing-xiong WU. Flexural behavior of composite continuous girders with concrete-filled steel tubular truss chords [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1665-1676. |
| [13] | Chun-lei ZHANG,Chang-yu SHAO,Qing-tian SU,Chang-yuan DAI. Experimental on positive bending behaviour of composite bridge decks with steel-fiber-reinforced concrete and longitudinal bulb-flat ribs [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1634-1642. |
| [14] | Chang-jiang SHAO,Hao-meng CUI,Qi-ming QI,Wei-lin ZHUANG. Longitudinal seismic mitigation of near⁃fault long⁃span RC soft⁃lighten arch bridge based on viscous damper [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1355-1367. |
| [15] | Qiu ZHAO,Peng CHEN,Yu-wei ZHAO,Ao YU. Overall mechanical performance of jointless bridges with arch structure behind abutment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1016-1027. |
|
||