吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (4): 887-895.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250404
草苁蓉环烯醚萜苷对大鼠肝脏癌前病变的抑制作用及其机制
- 1.延边大学附属医院临床营养科,吉林 延吉 133000
2.延边大学医学院生物化学与分子生物学 教研室,吉林 延吉 133002
3.山东省临沂市人民医院肿瘤科,山东 临沂 276000
Inhibitory effect of iridoid glycosides from Boschniakia rossica on hepatic preneolasia of rats and its mechanism
Huixian XU1,Hui XU2,Jishu QUAN2( ),Feng ZHENG1,3(
),Feng ZHENG1,3( )
)
- 1.Department of Clinical Nutrition,Affilited Hospital,Yanbian University,Yanji 133002,China
2.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,School of Medical Sciences,Yanbian University,Yanji 133002,China
3.Department of Oncology,People’s Hosptial,Linyi City,Shangdong Province,Linyi 276000,China
摘要:
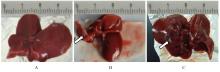
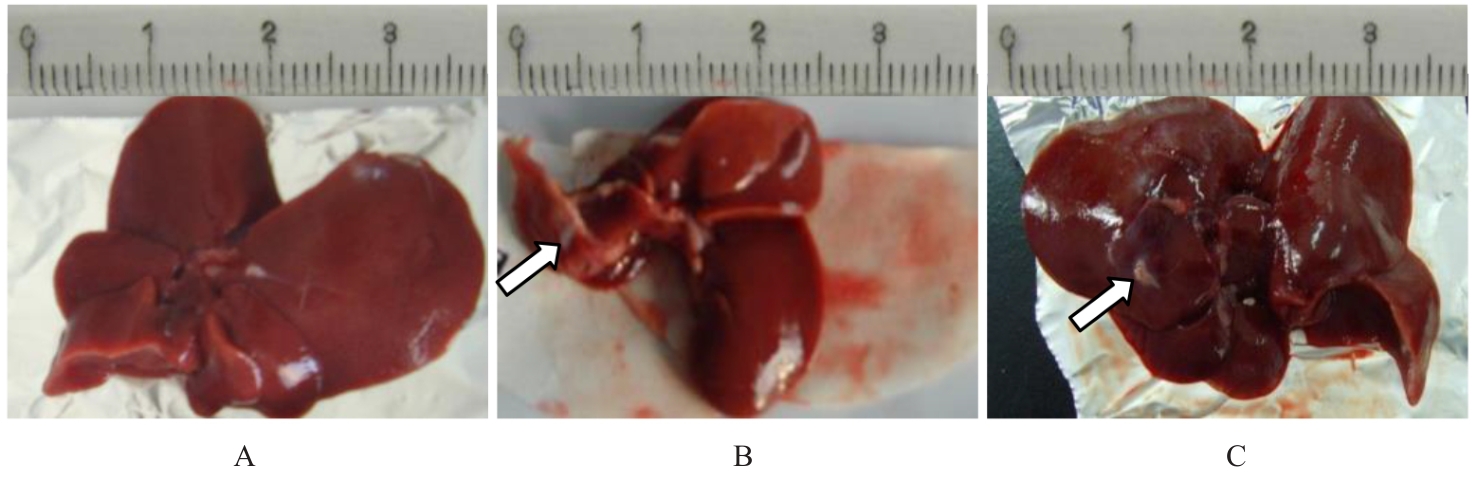
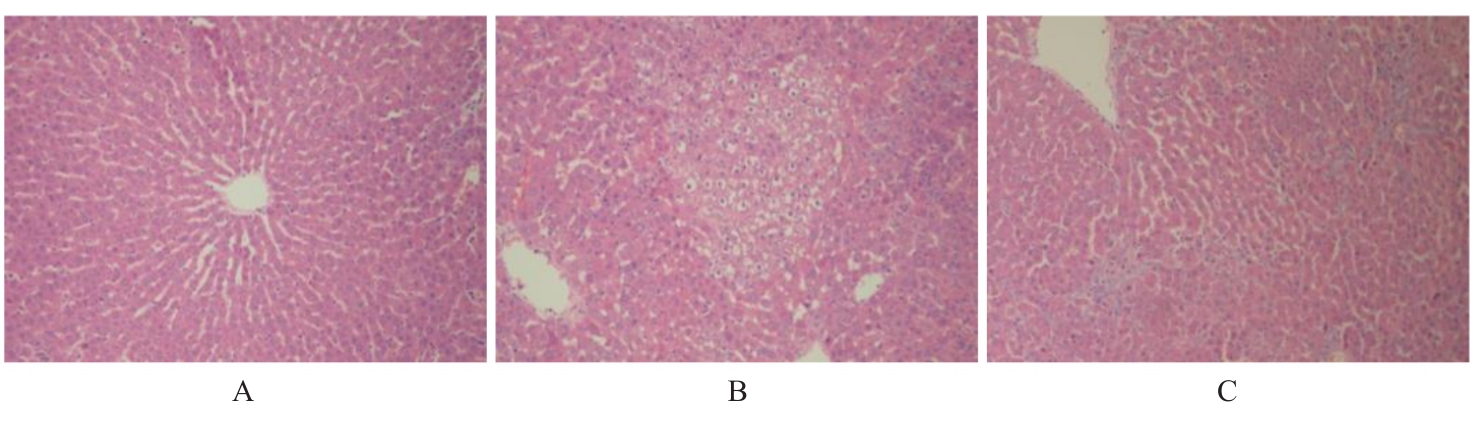
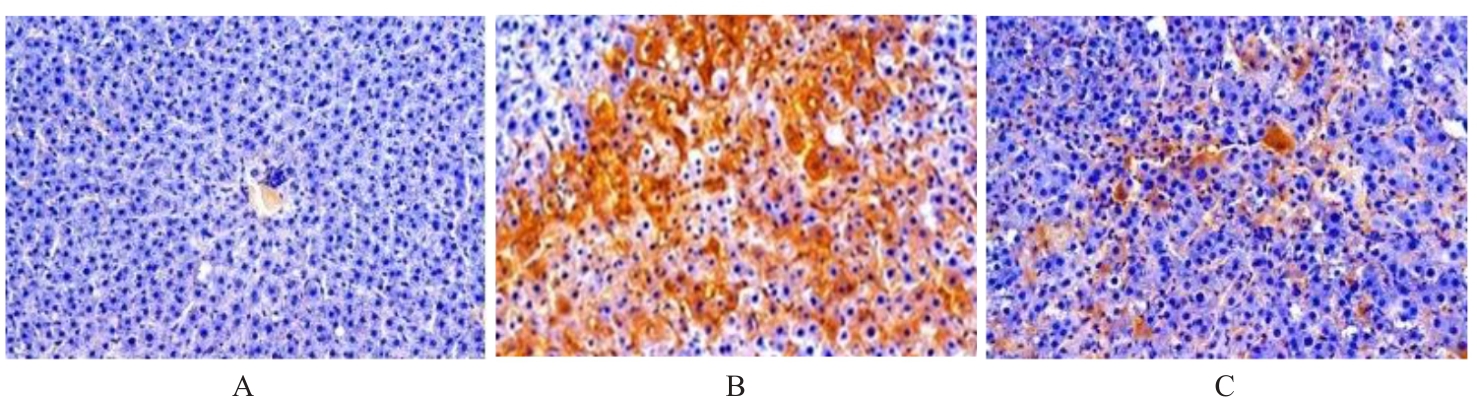
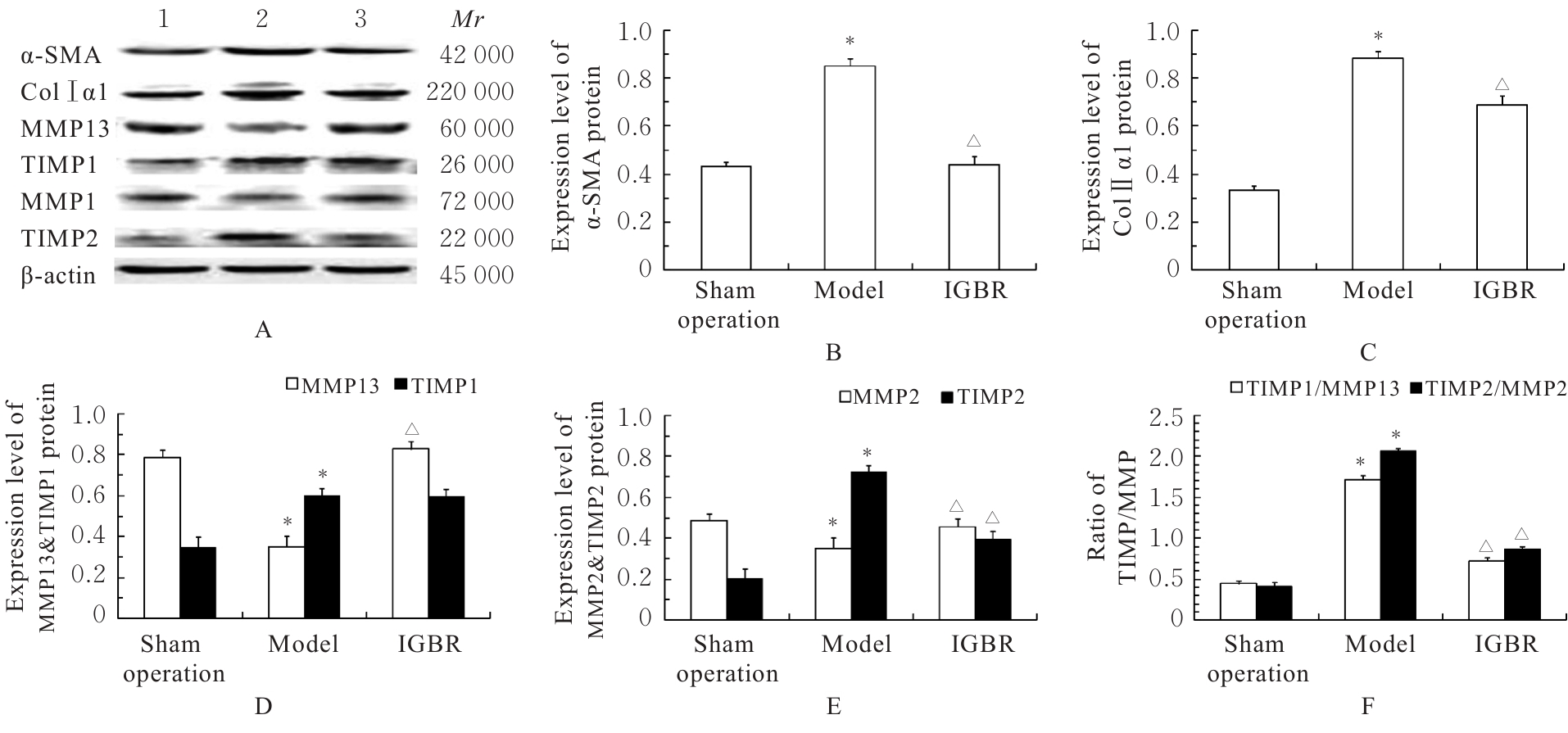
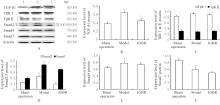
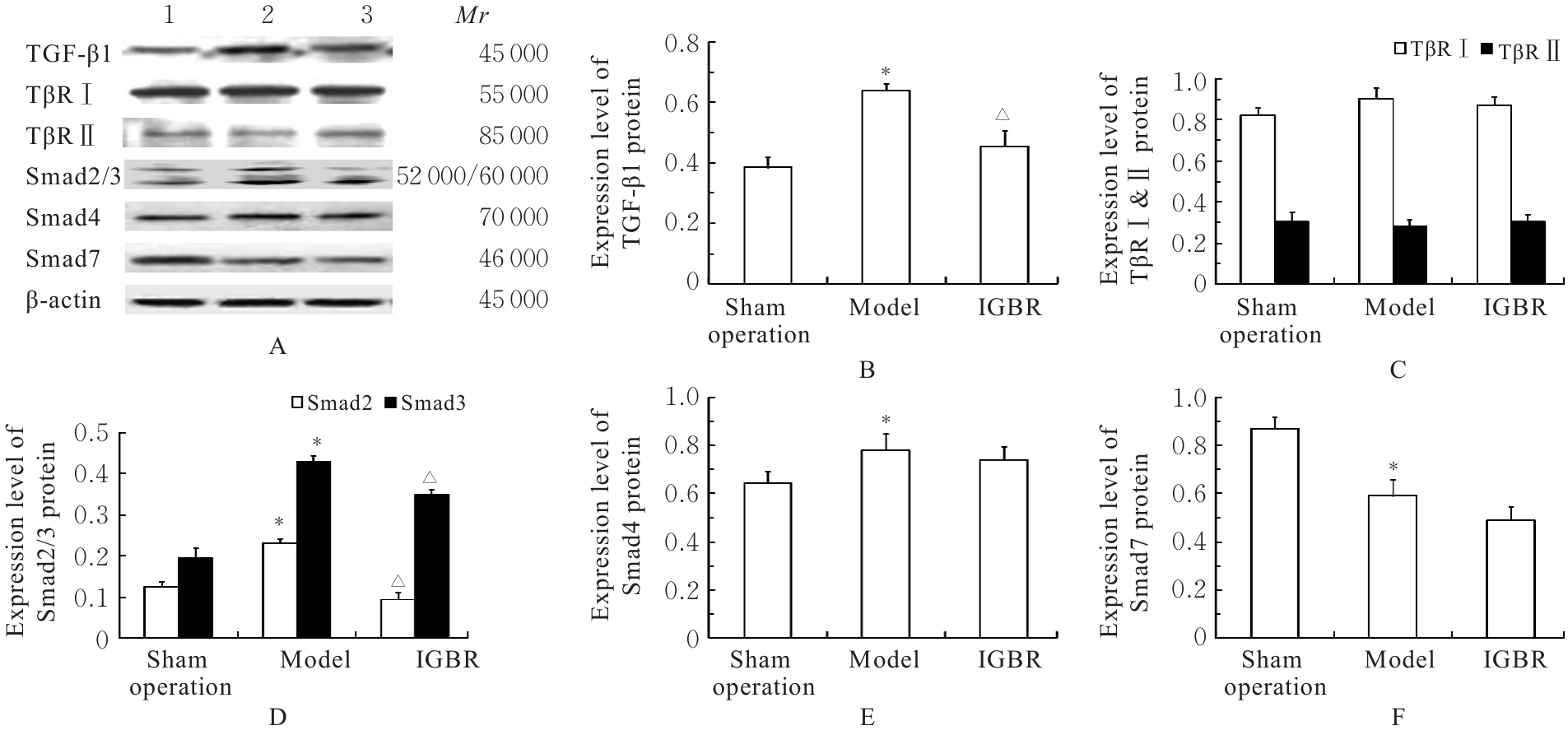
目的 研究草苁蓉环烯醚萜苷(IGBR)对大鼠肝脏癌前病变的防治作用,并阐明其可能的作用机制。 方法 选取30只Wistar大鼠,按照改良Solt-Faber法构建大鼠肝脏癌前病变模型。将制模成功后的大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组和IGBR组,每组10只。取各组大鼠肝组织观察其形态表现,检测各组大鼠肝脏质量、肝脏指数和肝脏再生度,HE染色法观察各组大鼠肝组织病理形态表现,免疫组织化学法检测各组大鼠肝组织中谷胱甘肽-S-转移酶(GST)-Pi蛋白表达情况,比色法检测各组大鼠肝组织和肝线粒体中γ-谷氨酰转肽酶(γ-GT)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、超氧化物岐化酶(SOD)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)和GST活性及丙二醛(MDA)水平,Western blotting法检测各组大鼠肝组织中α-平滑肌肌动蛋白(α-SMA)、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白α1链(ColⅠα1)、基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)13、MMP2、组织金属蛋白酶抑制剂(TIMP)1、TIMP2、转化生长因子β1(TGF-β1)、TGF-β1受体(TβR)、抗DPP同源物(Smad)2/3、Smad4和Smad7蛋白表达水平。 结果 与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠肝脏质量和肝脏指数升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,IGBR组大鼠肝脏质量、肝脏指数和肝再生度均有下降趋势,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。HE染色法,假手术组大鼠肝小叶结构完整清晰,肝细胞体积大、胞质丰富、嗜酸性,肝细胞以中央静脉为中心单行排列呈条索状向四周放射状排列,肝板间有不规则肝窦,仅于汇管区有少许胶原纤维存在和少量的炎症细胞浸润,肝细胞无变性坏死;模型组大鼠肝细胞失去正常排列,肝小叶结构消失,汇管区有以卵圆细胞为主的小细胞增生,纤维隔内有大量胶原沉积,有较明显纤维组织增生,肝细胞胞浆疏松,发生广泛的变性水肿,水样变性、气球样变性甚至灶状坏死,肝小叶中见增生的嗜碱性肝细胞形成细胞增生区,其细胞胞浆透亮,细胞核位于细胞中央,体积不大,染色质丰富,有1或2个明显核仁,肝小叶内还可见体积增大,细胞核和细胞浆着色浅而透明呈毛玻璃样的透明肝细胞灶;IGBR组大鼠肝小叶结构基本存在,可见肝细胞炎性病变减轻,水肿较轻,可见较多点状坏死或灶状坏死,核异型性大,可见病理性核分裂象或双核。免疫组织化学法,GST-Pi蛋白阳性灶为胞浆染色,呈棕黄色的圆形或类圆形结节;模型组大鼠肝组织中可观察到GST-Pi蛋白阳性灶,提示大鼠肝脏癌前病变模型制作成功。IGBR组大鼠肝组织中可观察到散在的GST-Pi蛋白阳性灶,较模型组明显减少。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠肝组织中γ-GT活性升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,IGBR组大鼠肝组织中γ-GT活性降低(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠肝组织和肝线粒体中GST活性及MDA水平升高(P<0.05),SOD、CAT和GSH-Px活性降低(P<0.05);与模型组比较,IGBR组大鼠肝组织和肝线粒体中GST活性及MDA水平降低(P<0.05),SOD、CAT和GSH-Px活性升高(P<0.05)。Western blotting法,与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠肝组织中α-SMA、ColⅠα1、TIMP1和TIMP2蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),MMP13和MMP2蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),TIMP1/MMP13和TIMP2/MMP2比值升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,IGBR组大鼠肝组织中α-SMA、ColⅠα1和TIMP2蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),MMP13和MMP2蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),TIMP1/MMP13和TIMP2/MMP2比值降低(P<0.05)。与假手术组比较,模型组大鼠肝组织中TGF-β1、Smad2/3和Smad4蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,IGBR组大鼠肝组织中TGF-β1、Smad2/3和Smad7蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05)。 结论 IGBR对大鼠肝脏癌前病变和肝纤维化具有抑制作用,其机制可能与其增强肝组织抗氧化能力、抑制TGF-β/Smad信号通路及调控TIMP/MMP平衡有关。
中图分类号:
- R735.7