吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5): 1125-1133.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230503
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
二氧化硫对大鼠急性心肌缺血损伤后心肌纤维化的改善作用及其机制
- 南华大学衡阳医学院附属第一医院心内科,湖南 衡阳 421001
Improvement effect of SO2 on myocardial fibrosis after acute myocardial ischemic injury in rats and its mechanism
Xing LIU,Jiali LIU,Liangui NIE,Maojun LIU,Junxiong ZHAO,Liuyang WANG,Jun YANG( )
)
- Department of Cardiology,First Affiliated Hospital,Hengyang Medical College,University of South China,Hengyang 421001,China
摘要:
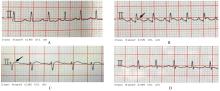
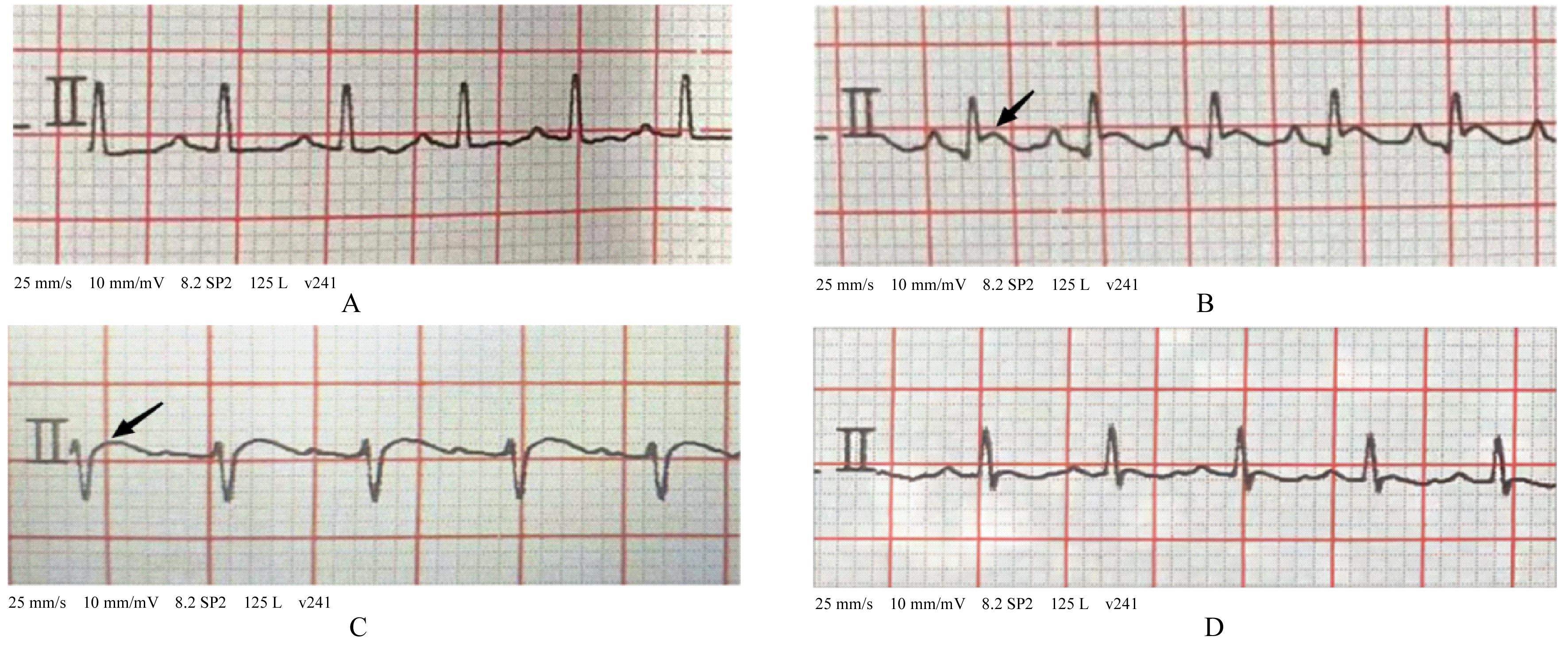
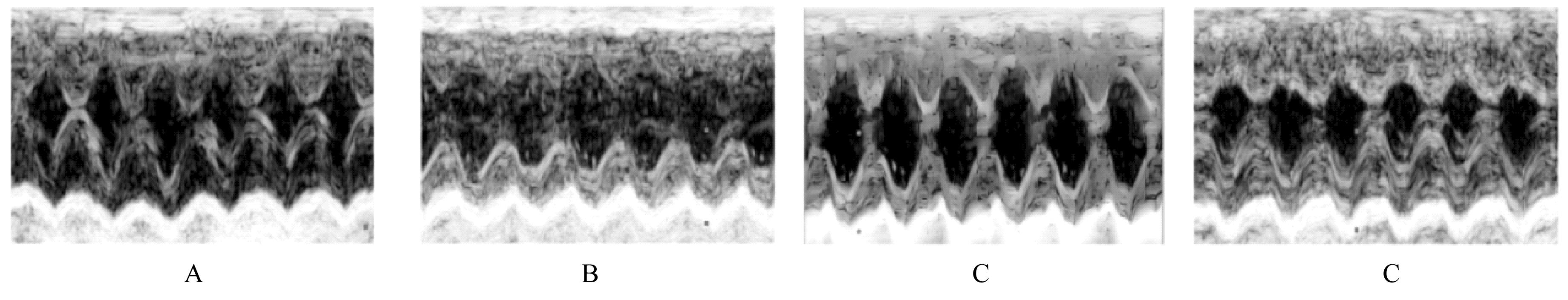
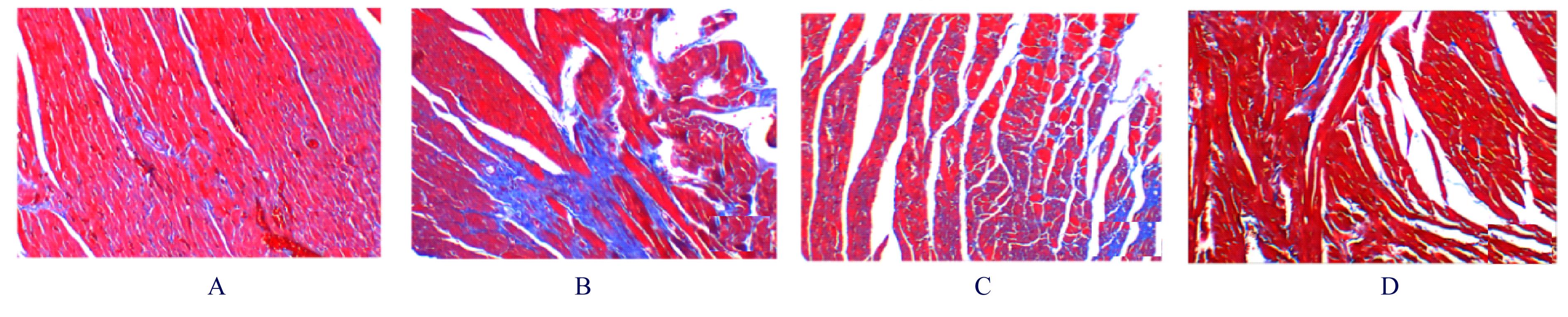
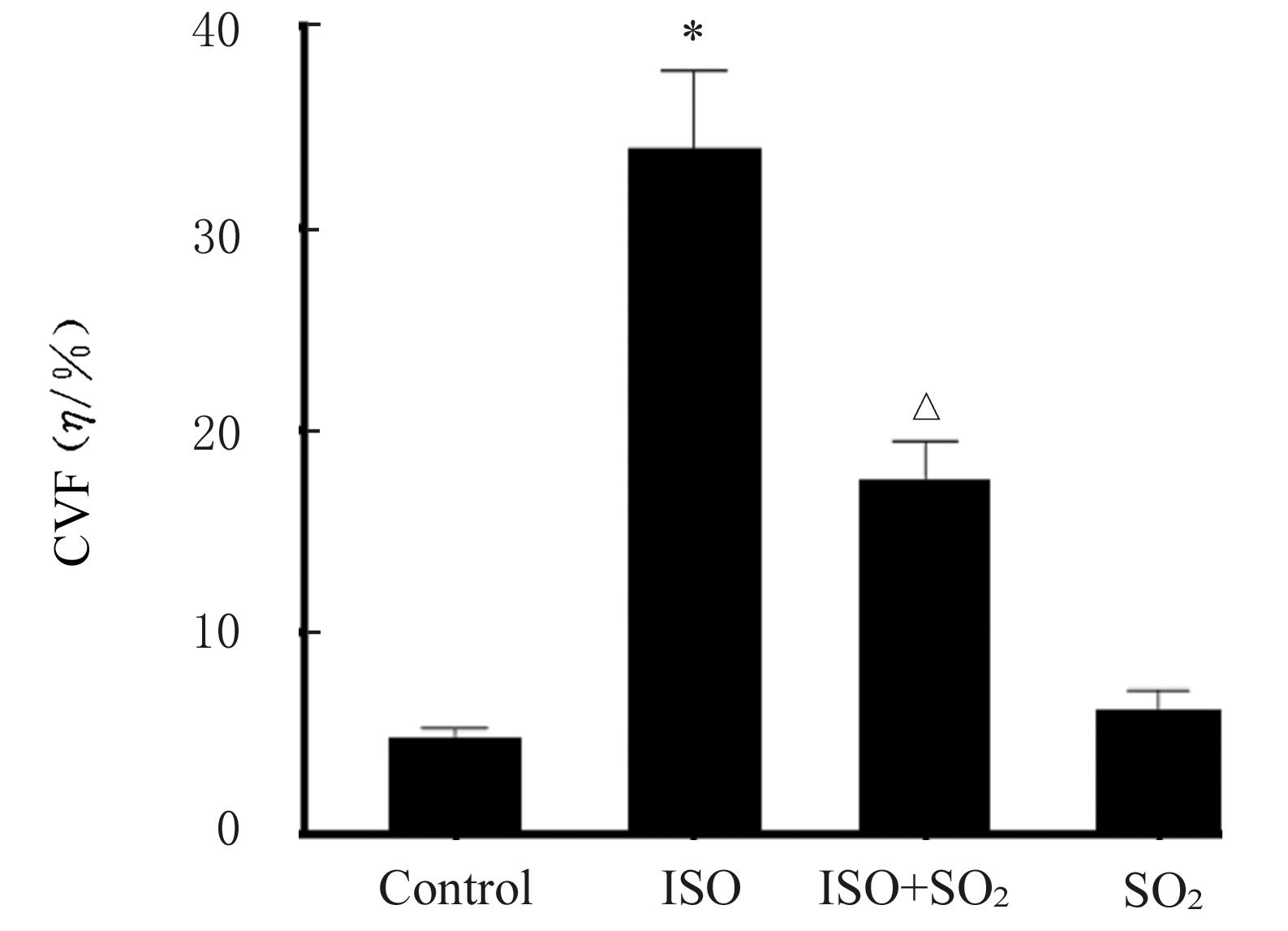
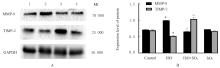
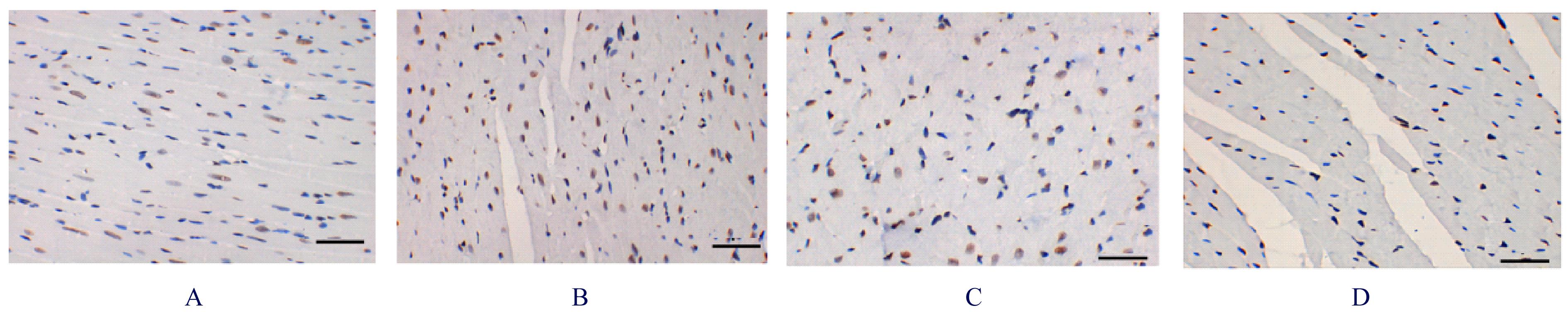
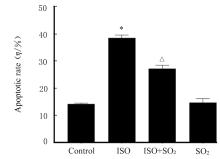
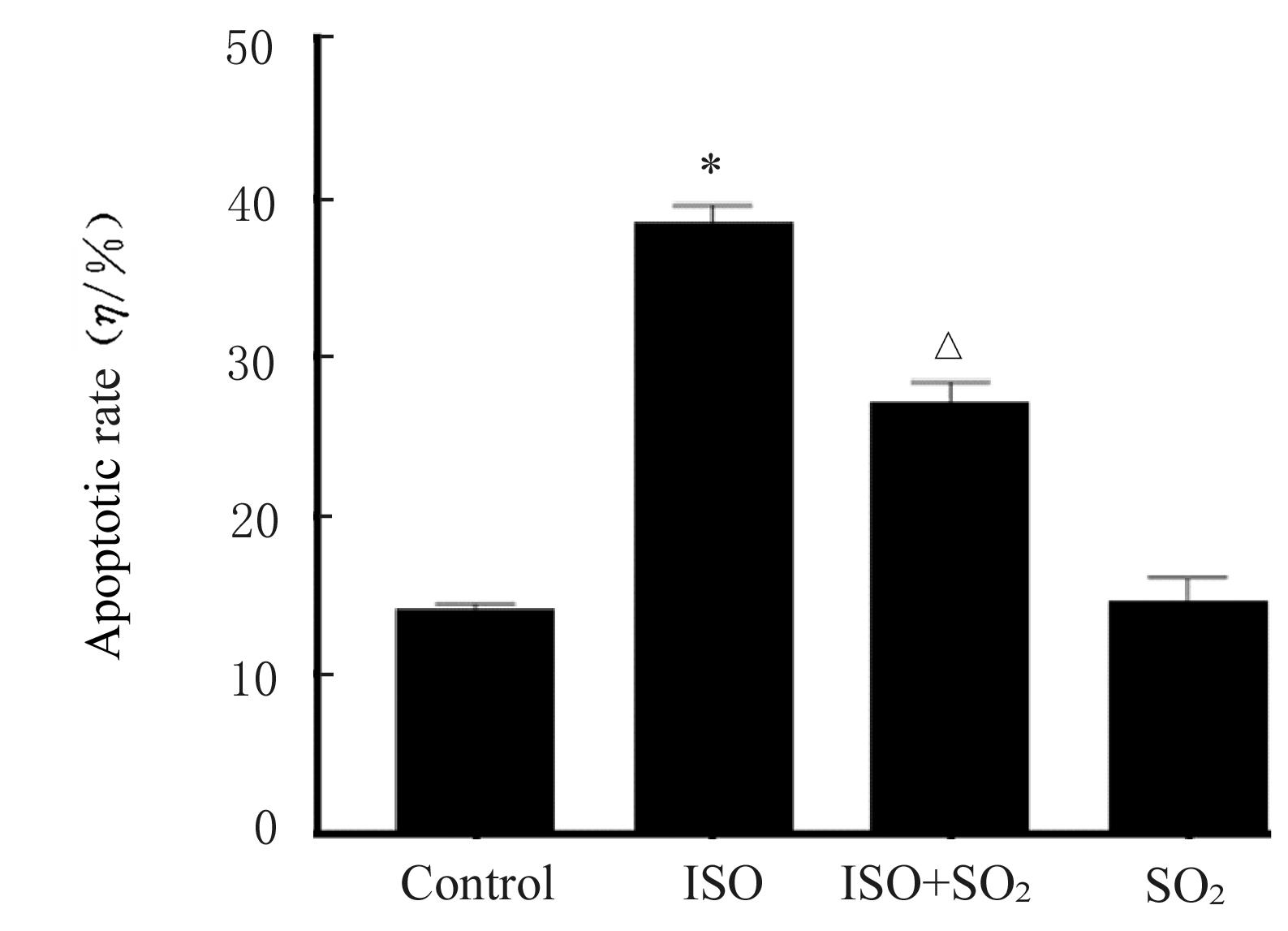
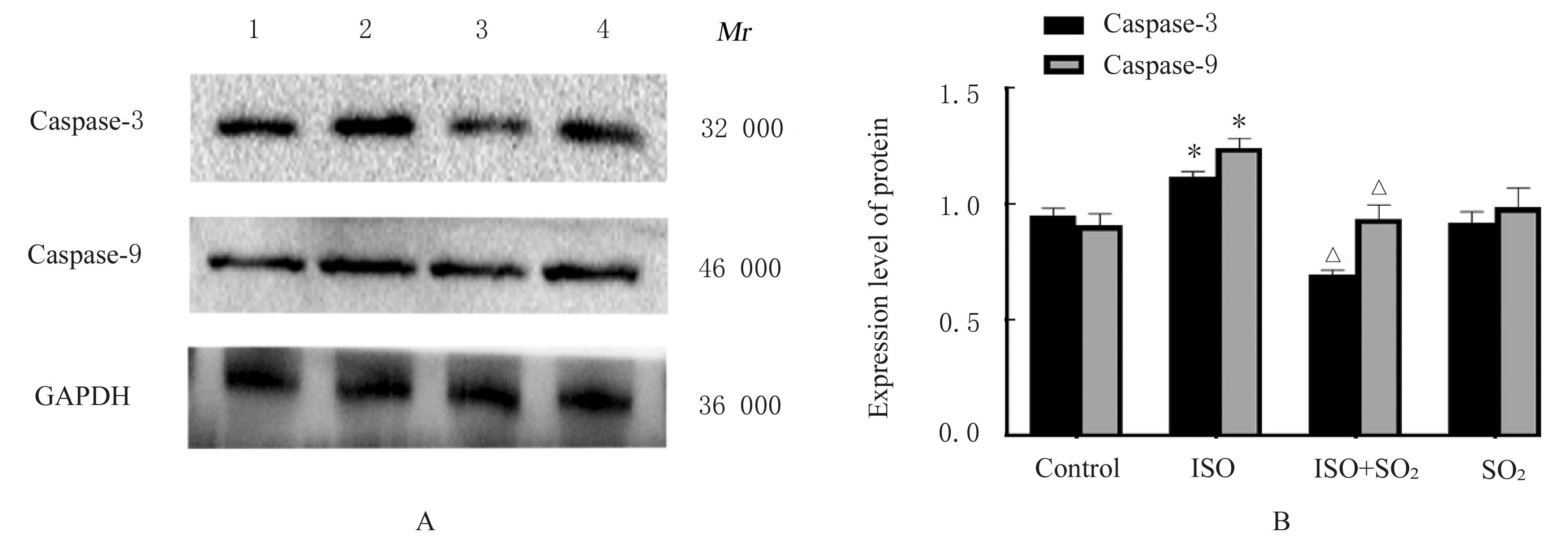
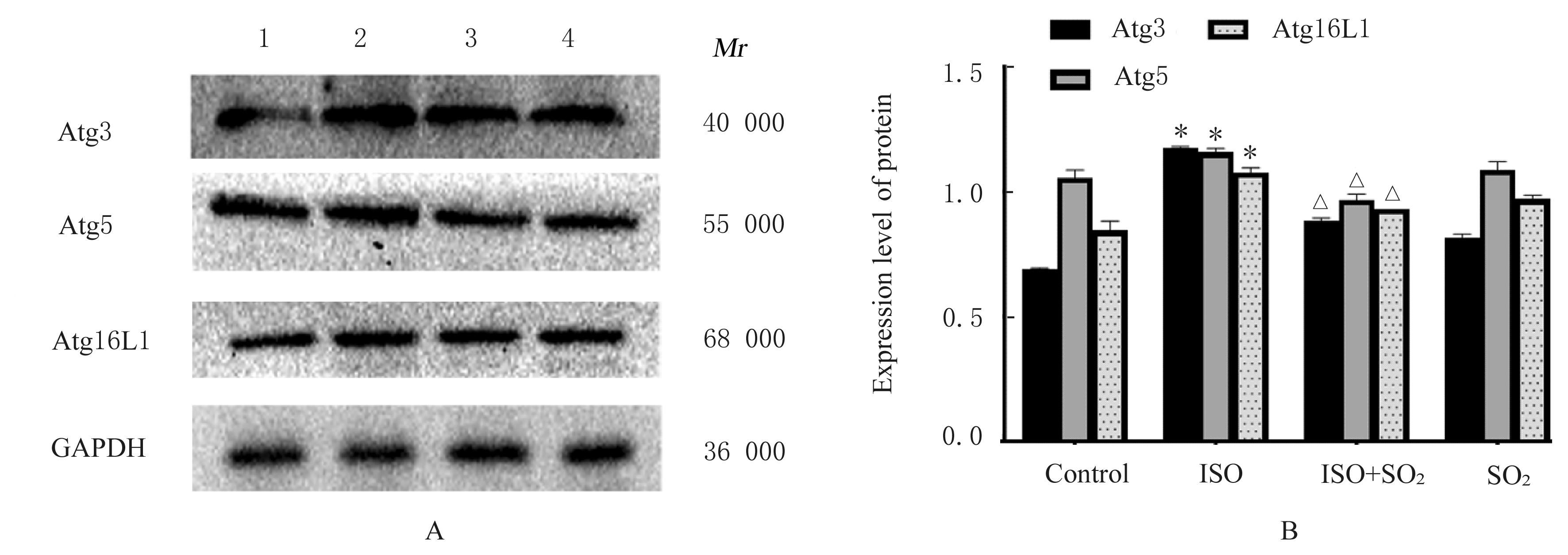
目的 观察二氧化硫(SO2)对大鼠急性心肌缺血损伤后心肌纤维化(MF)的影响,并探讨其作用机制。 方法 24只雄性SD大鼠随机分为对照组(不处理)、异丙肾上腺素(ISO)组(给予ISO)、ISO+SO2组(给予ISO+SO2)和SO2组(给予SO2),每组6只。ISO组和ISO+SO2组大鼠连续2 d腹腔注射大剂量ISO (50 mg·kg-1·d-1)构建急性心肌缺血损伤模型。造模成功后,ISO+SO2组和SO2组大鼠给予Na2SO3溶液(0.54 mmol·kg-1·d-1)和NaHSO3溶液(0.18 mmol·kg-1·d-1),连续4周,对照组和ISO组大鼠给予等量生理盐水。检测4组大鼠血浆肌钙蛋白水平和心电图,超声心动图检测4组大鼠左室短轴缩短率(LVFS)和左室射血分数(LVEF),Masson染色检测4组大鼠心肌组织中胶原沉积情况并计算胶原体积分数(CVF),Tunel染色检测4组大鼠心肌细胞凋亡率,Western blotting法检测4组大鼠心肌组织中自噬相关蛋白3(Atg3)、自噬相关蛋白5(Atg5)、自噬相关蛋白16L1(Atg16L1)、含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶3(Caspase-3)、含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶9(Caspase-9)、基质金属蛋白酶8(MMP-8)和金属蛋白酶组织抑制物2(TIMP-2)蛋白表达水平。 结果 与对照组比较,ISO组和ISO+SO2组大鼠心电图ST段明显抬高,肌钙蛋白水平升高(P<0.05),提示急性心肌缺血损伤大鼠造模成功;与对照组比较,ISO组大鼠LVFS和LVEF降低(P<0.05),心肌组织中CVF升高(P<0.05),心肌细胞凋亡率升高(P<0.05),心肌组织中Atg3、Atg5、Atg16L1、Caspase-3、Caspase-9和MMP-8蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05),TIMP-2蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05);与ISO组比较,ISO+SO2组大鼠LVFS和LVEF升高(P<0.05),心肌组织中CVF降低(P<0.05),心肌细胞凋亡率降低(P<0.05),心肌组织中Atg3、Atg5、Atg16L1、Caspase-3、Caspase-9和MMP-8蛋白表达水平降低(P<0.05),TIMP-2蛋白表达水平升高(P<0.05)。 结论 SO2可以改善大鼠急性心肌缺血损伤后MF,其机制可能与抑制心肌细胞过度自噬并减少心肌细胞凋亡有关。
中图分类号:
- R542.2