吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1587-1596.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240612
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
趋化因子CCL19诱导巨噬细胞M1极化对小鼠慢性胰腺炎的促进作用及其机制
- 1.吉林省肿瘤医院检验科,吉林 长春 130012
2.大连理工大学医学部药学系,辽宁 大连 116024
Promotion effect of chemokine CCL19-induced macrophage M1 polarization on chronic pancreatitis in mice and its mechanism
Lianzhi CUI1,Xiaowei ZHANG1,Hua ZHU1,Yue PAN2,Xiuyan YU1( )
)
- 1.Clinical Laboratory,Tumer Hospital,Jilin Province,Changchun 130012,China
2.Department of Pharmacy,School of Medical Science,Dalian University of Technology,Dalian 116024,China
摘要:
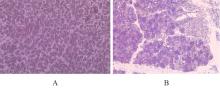
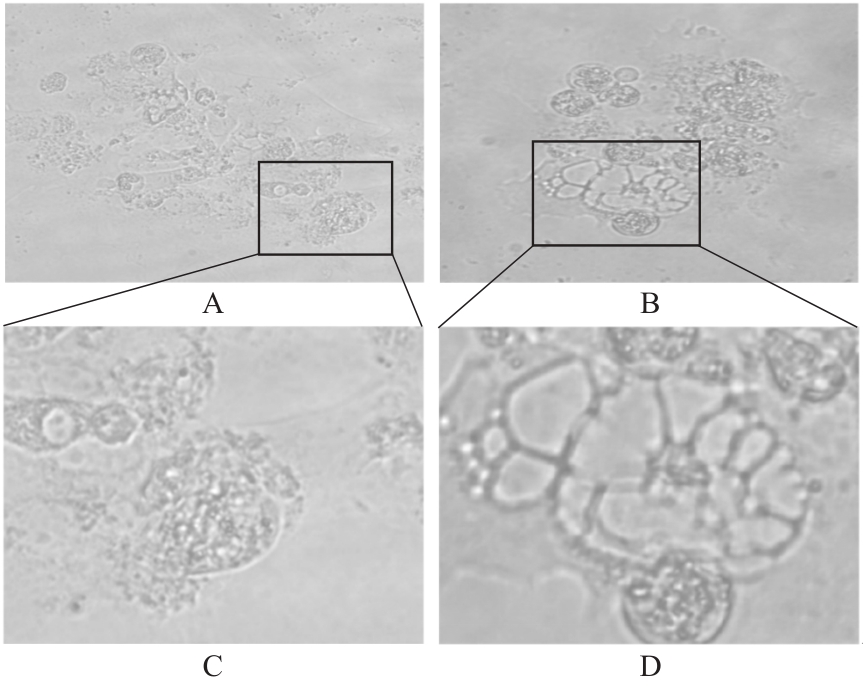
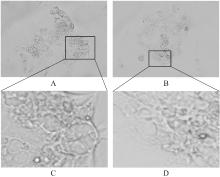
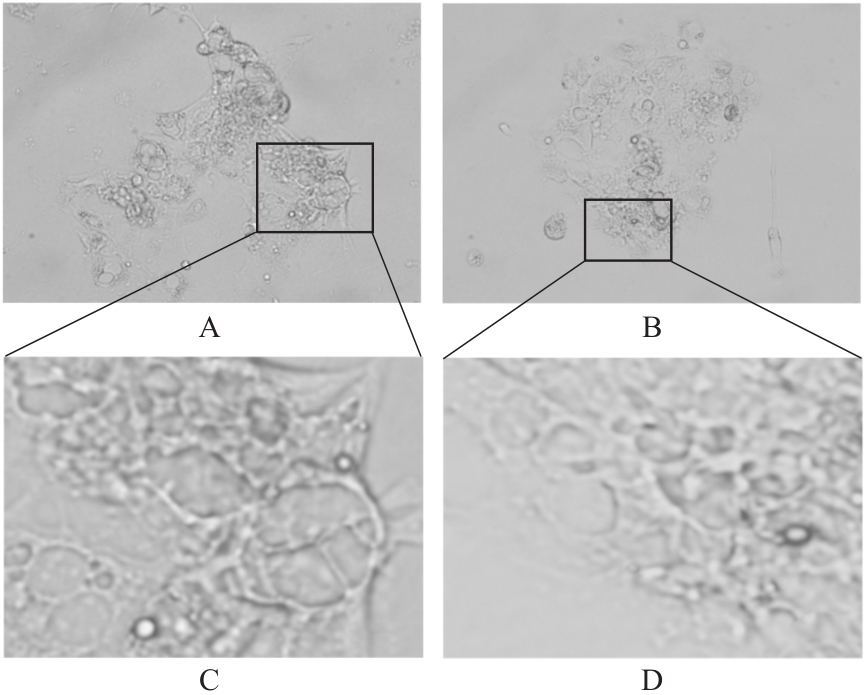
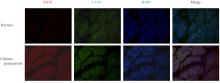
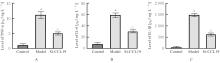
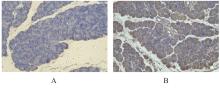
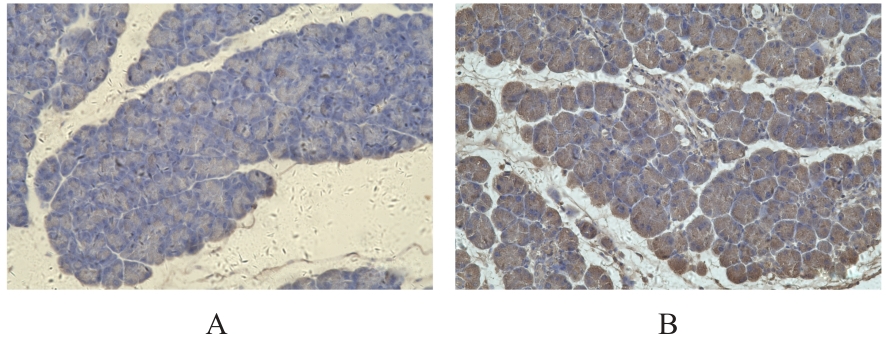
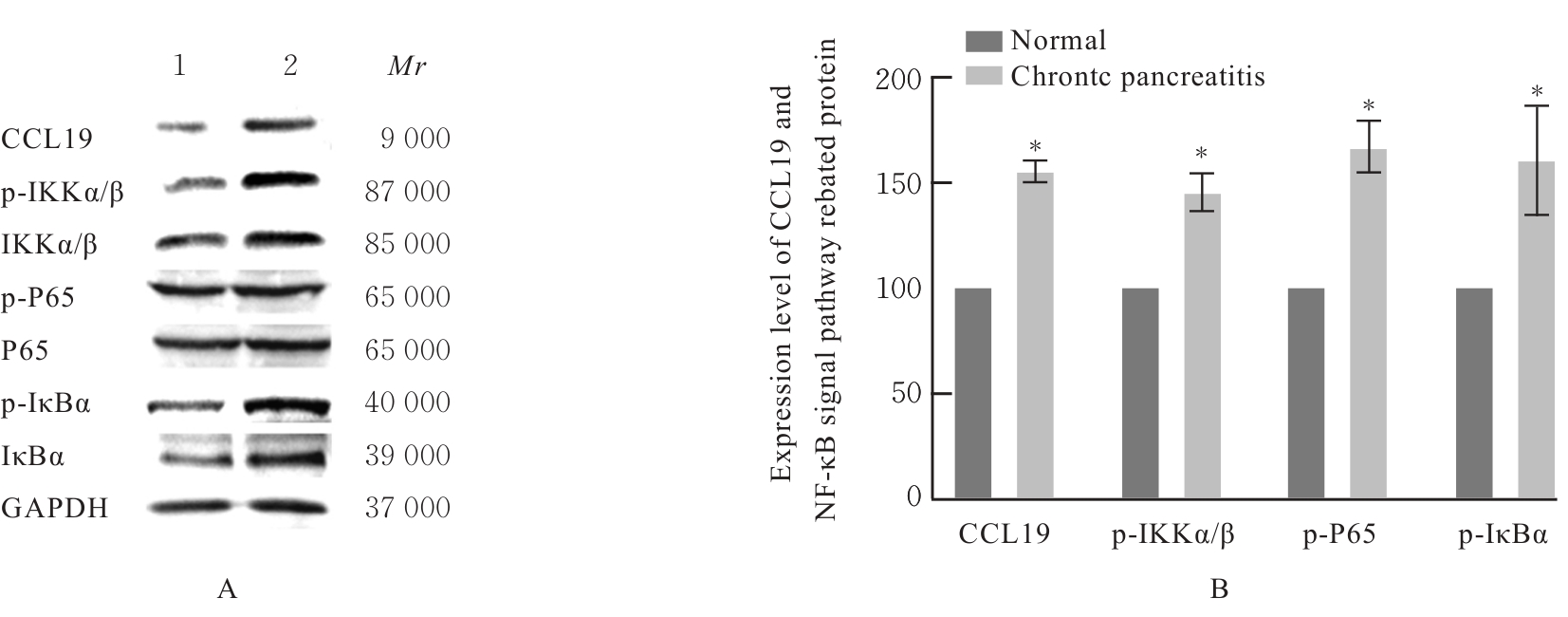
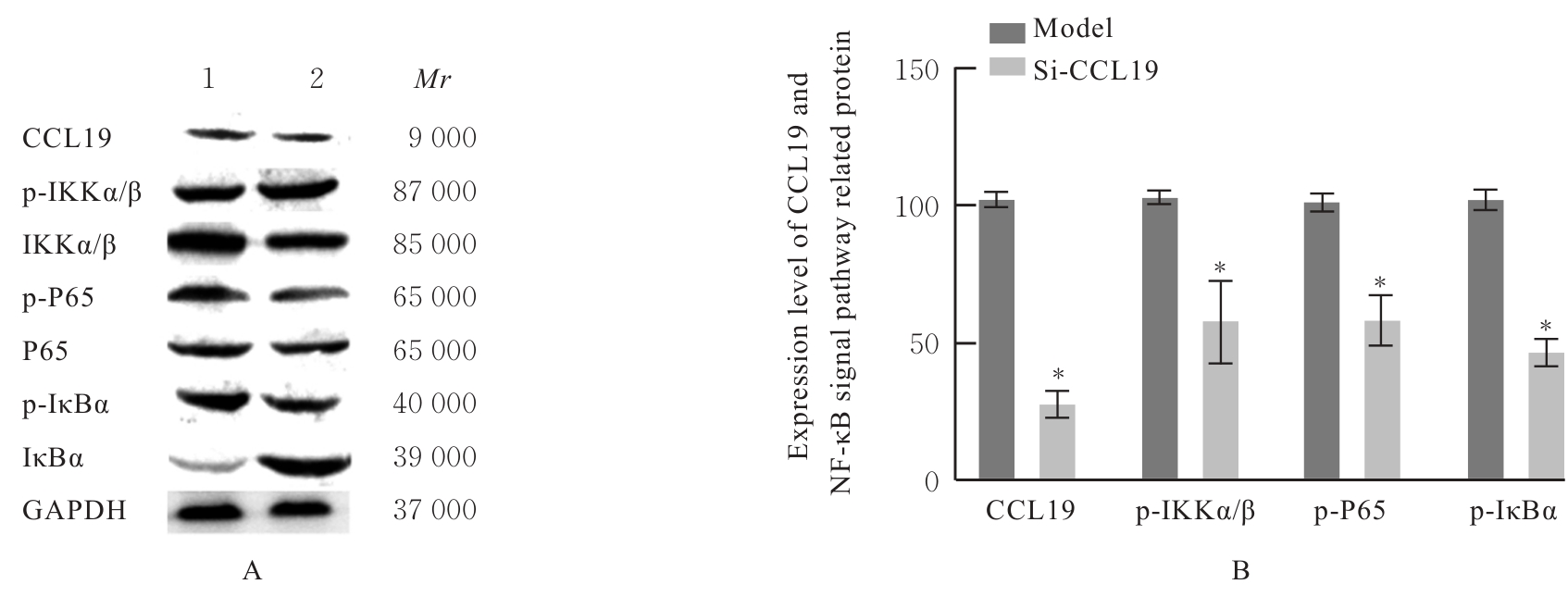
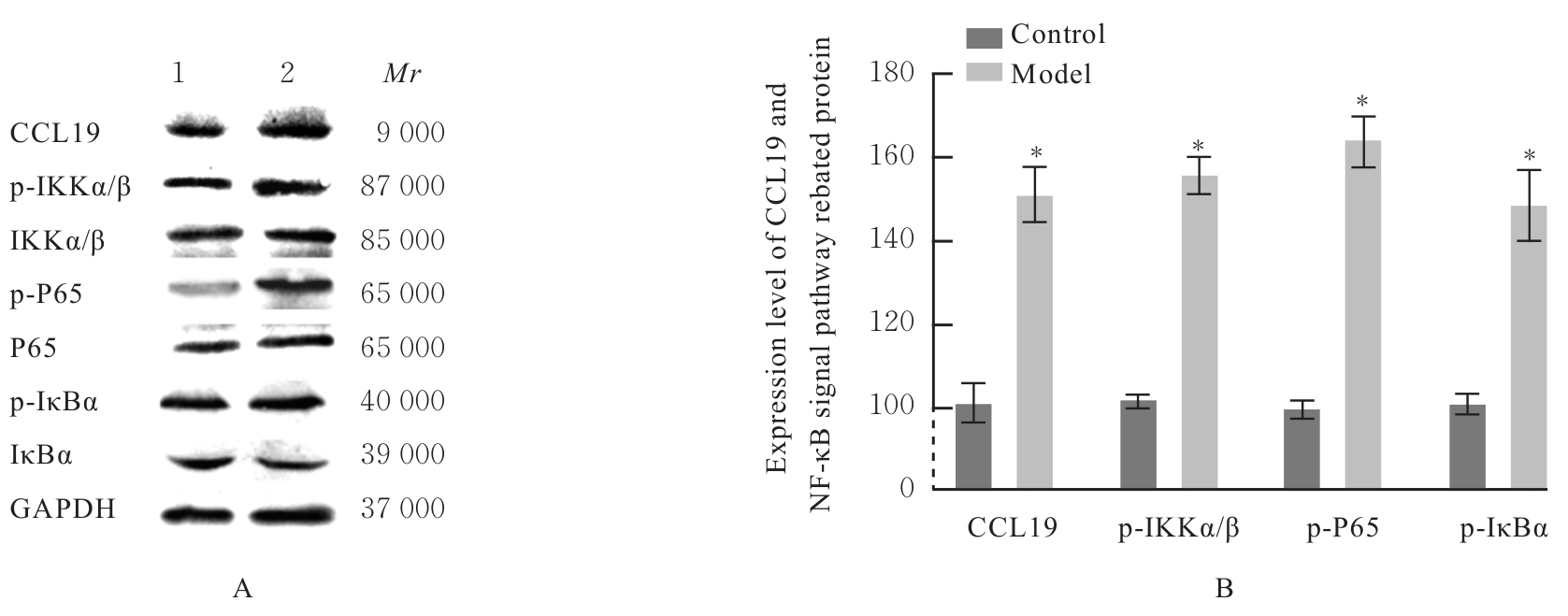
目的 探讨趋化因子C-C基序配体19(CCL19)诱导巨噬细胞M1极化对小鼠慢性胰腺炎的促进作用,并阐明其相关机制。 方法 选取10只雄性C57BL/6N小鼠,提取小鼠胰腺腺泡细胞和腹腔巨噬细胞,构建巨噬细胞-腺泡细胞共培养体系,共培养体系细胞分为对照组、模型组和小干扰RNA CCL19(si-CCL19)组,显微镜下观察各组腺泡细胞形态表现。随机选取40只小鼠,分为正常组和慢性胰腺炎组,每组20只。HE染色观察2组小鼠胰腺组织病理形态表现,免疫荧光染色法观察2组小鼠胰腺组织中角质蛋白19(CK19)、淀粉酶、M1型巨噬细胞相关标志物诱导型一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)和F4/80表达情况及各组共培养体系细胞中腺泡细胞形态表现及CK19和淀粉酶表达情况,酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)法检测2组小鼠血清和各组共培养体系细胞中肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素(IL)-6和IL-1β水平,免疫组织化学法观察2组小鼠胰腺组织中CCL19蛋白表达情况,Western blotting法检测2组小鼠胰腺组织和各组共培养体系细胞中CCL19蛋白和关键蛋白核因子κB(NF-κB)信号通路相关蛋白P65、磷酸化P65(p-P65)、κB抑制物激酶α/β(IKKα/β)、磷酸化IKKα/β(p-IKKα/β)、IκBα和磷酸化IκBα(p-IκBα)表达水平。 结果 HE染色,正常组小鼠胰腺组织腺泡细胞的紧密排列;与正常组比较,慢性胰腺炎组小鼠胰腺组织腺泡细胞产生了明显的空泡化,即腺泡细胞导管化,小鼠胰腺炎模型制备成功。免疫荧光染色法,与对照组比较,模型组腺泡细胞严重的空泡化明显,CK19表达明显增加,淀粉酶表达明显减少;与模型组比较,si-CCL19组中腺泡细胞导管化程度降低,CK19表达明显减少,淀粉酶表达明显增加;与正常组比较,慢性胰腺炎组小鼠胰腺组织中淀粉酶表达明显减少,CK19和M1型巨噬细胞标志物iNOS及F4/80表达均明显增加。ELISA法,与正常组比较,慢性胰腺炎组小鼠血清中TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与对照组比较,模型组细胞中TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,si-CCL19组细胞中TNF-α、IL-6和IL-1β水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。免疫组织化学法,与正常组比较,慢性胰腺炎组小鼠胰腺组织中CCL19蛋白表达明显增加。Western blotting法,与正常组比较,慢性胰腺炎组小鼠胰腺组织中CCL19蛋白表达水平和NF-κB信号通路相关蛋白p-IKKα/β、p-P65及p-IκBα蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05)。与对照组比较,模型组细胞中CCL19、p-IKKα/β、p-P65和p-IκBα蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,si-CCL19组细胞中CCL19、p-IKKα/β、p-P65和p-IκBα蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05)。 结论 CCL19通过NF-κB信号通路促进巨噬细胞M1型极化,诱导炎症微环境的产生,促进胰腺炎的发生发展。
中图分类号:
- R364.5