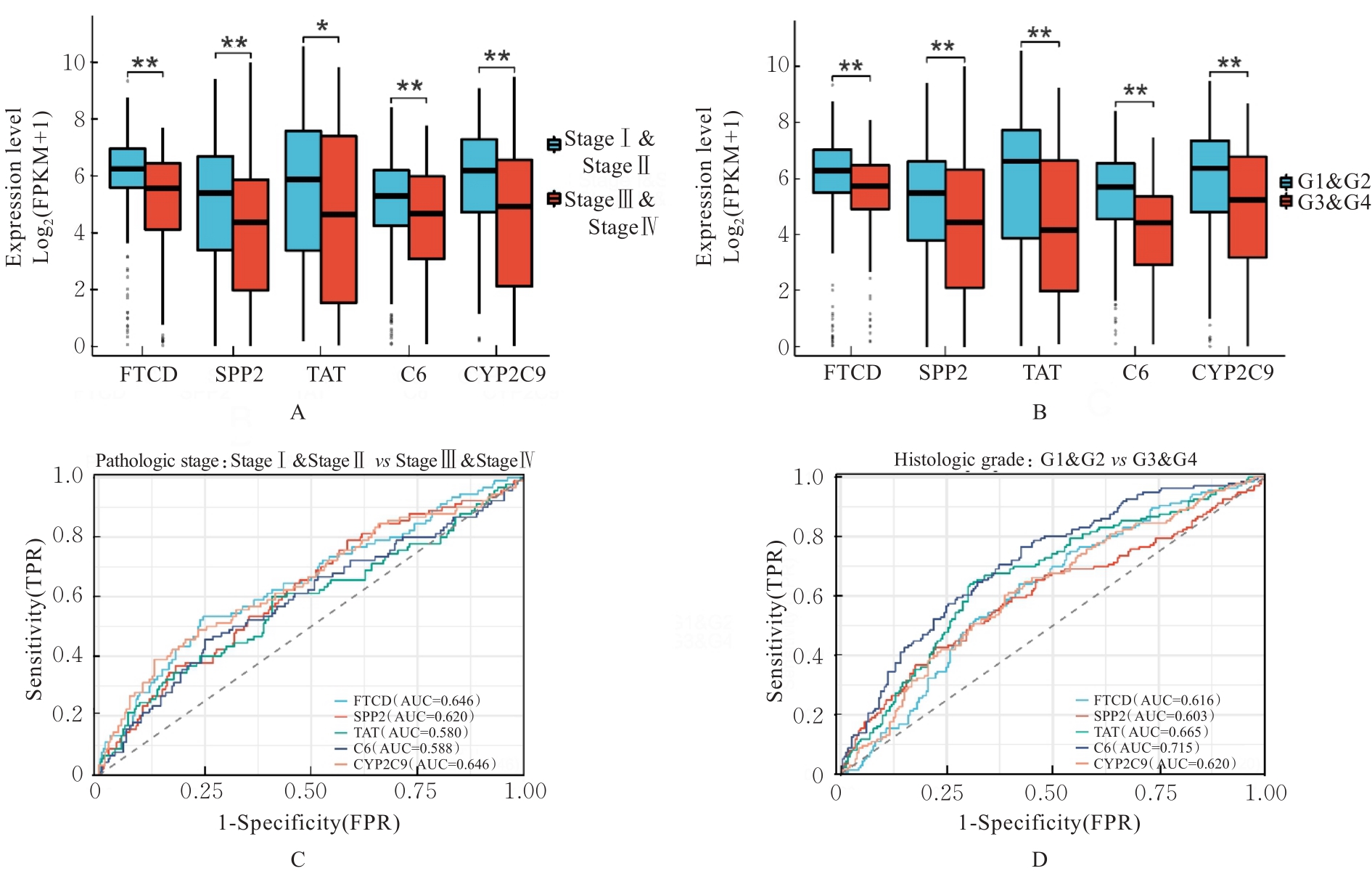
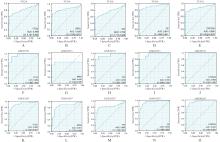
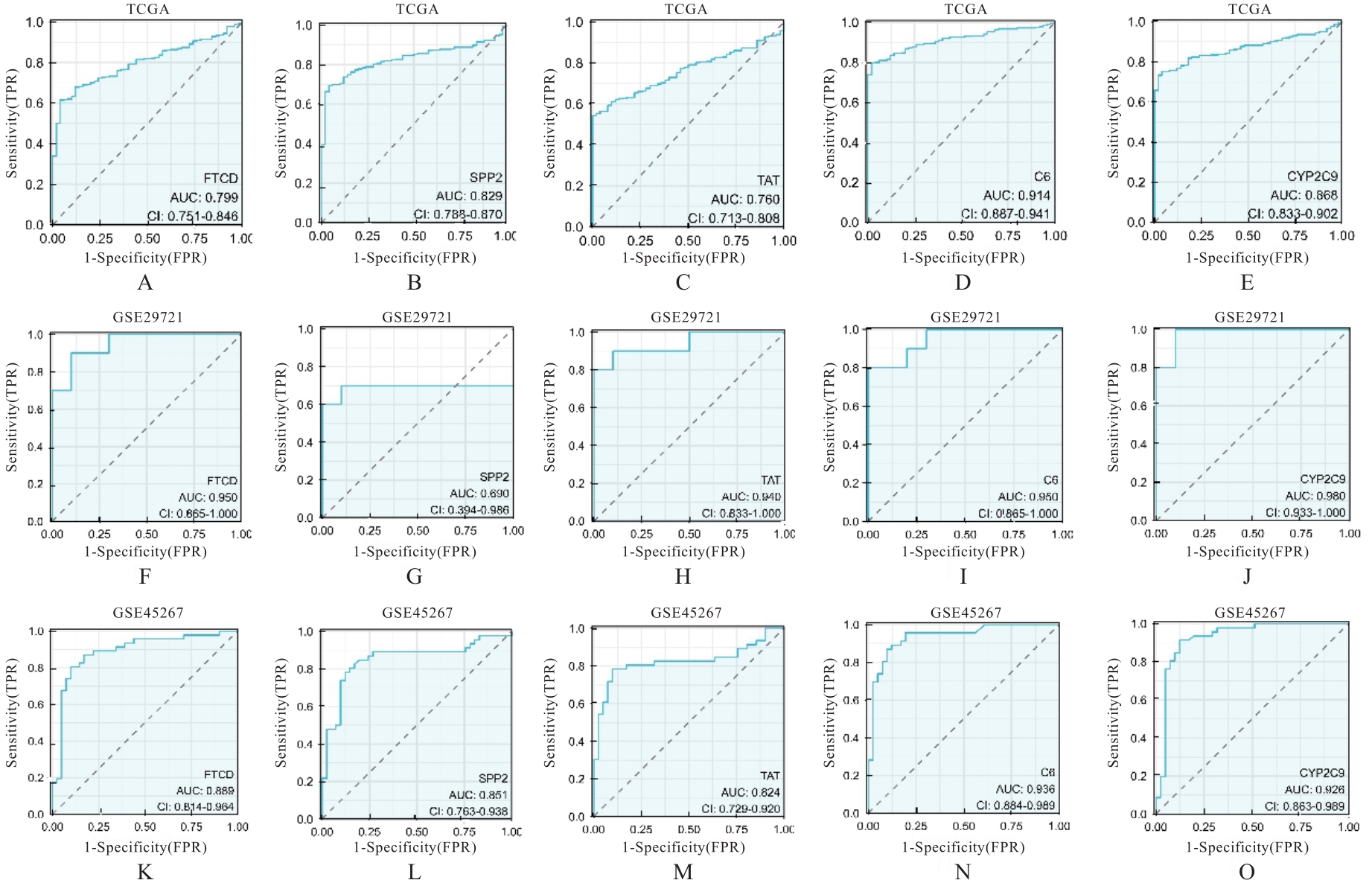
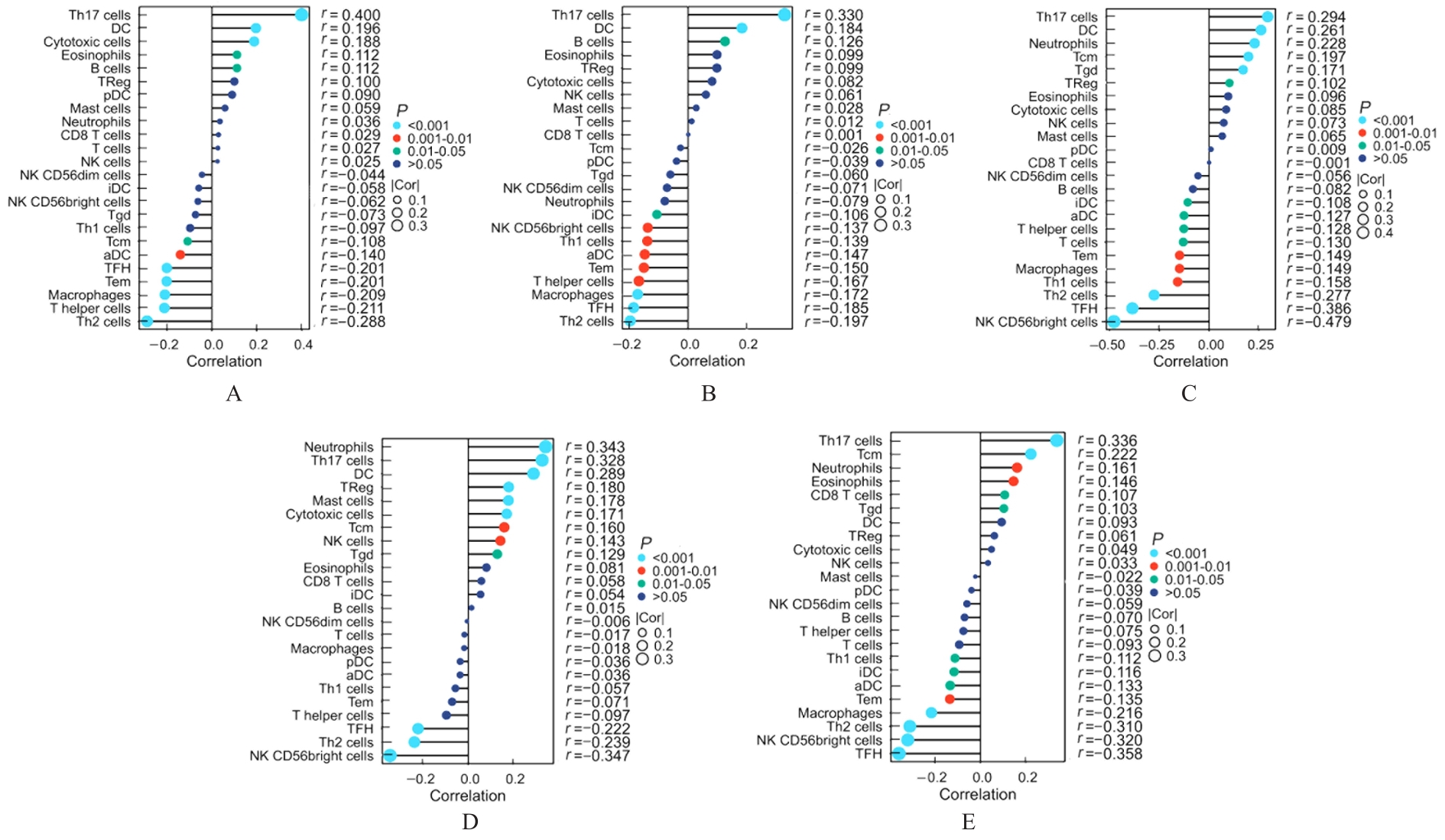
Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1062-1075.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240421
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics analysis on key genes related to prognosis, diagnosis, and immune cell infiltration of hepatocellular carcinoma and their potential therapeutic drugs
Jinlian LI1,2,Lanzhen HUANG3,Xishi HUANG3,Kangzhi LI1,Jiali JIANG4,Miaomiao ZHANG1,Qunying WU1( )
)
- 1.Department of Cell and Genetics,School of Intelligent Medicine and Biotechnology,Guilin Medical University,Guilin 541004,China
2.Joint Laboratory of Transfusion-Transmitted Diseases,Nanning Blood Center,Nanning 530007,China
3.Research Center for Science,Guilin Medical University,Guilin 541004,China
4.School of General Medicine,Guilin Medical University,Guilin 541004,China
-
Received:2023-07-18Online:2024-07-28Published:2024-08-01 -
Contact:Qunying WU E-mail:wuqunying@glmc.edu.cn
CLC Number:
- Q811.4
Cite this article
Jinlian LI,Lanzhen HUANG,Xishi HUANG,Kangzhi LI,Jiali JIANG,Miaomiao ZHANG,Qunying WU. Bioinformatics analysis on key genes related to prognosis, diagnosis, and immune cell infiltration of hepatocellular carcinoma and their potential therapeutic drugs[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1062-1075.
share this article
Tab.1
Twenty small molecule drugs for potential treatment of HCC"
| Cmap name | Mean | n | Enrichment | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DL-thiorphan | -0.787 | 2 | -0.929 | 0.010 |
| Promethazine | -0.852 | 4 | -0.882 | 0.000 |
| Apigenin | -0.814 | 4 | -0.879 | 0.001 |
| Sanguinarine | -0.742 | 2 | -0.867 | 0.035 |
| Skimmianine | -0.777 | 4 | -0.864 | 0.001 |
| Verteporfin | -0.724 | 3 | -0.858 | 0.006 |
| Repaglinide | -0.792 | 4 | -0.831 | 0.001 |
| Tracazolate | -0.733 | 4 | -0.814 | 0.002 |
| Milrinone | -0.728 | 3 | -0.809 | 0.014 |
| Talampicillin | -0.734 | 4 | -0.805 | 0.003 |
| Dequalinium chloride | -0.730 | 4 | -0.800 | 0.003 |
| Estriol | -0.736 | 4 | -0.791 | 0.004 |
| Chrysin | -0.716 | 3 | -0.790 | 0.019 |
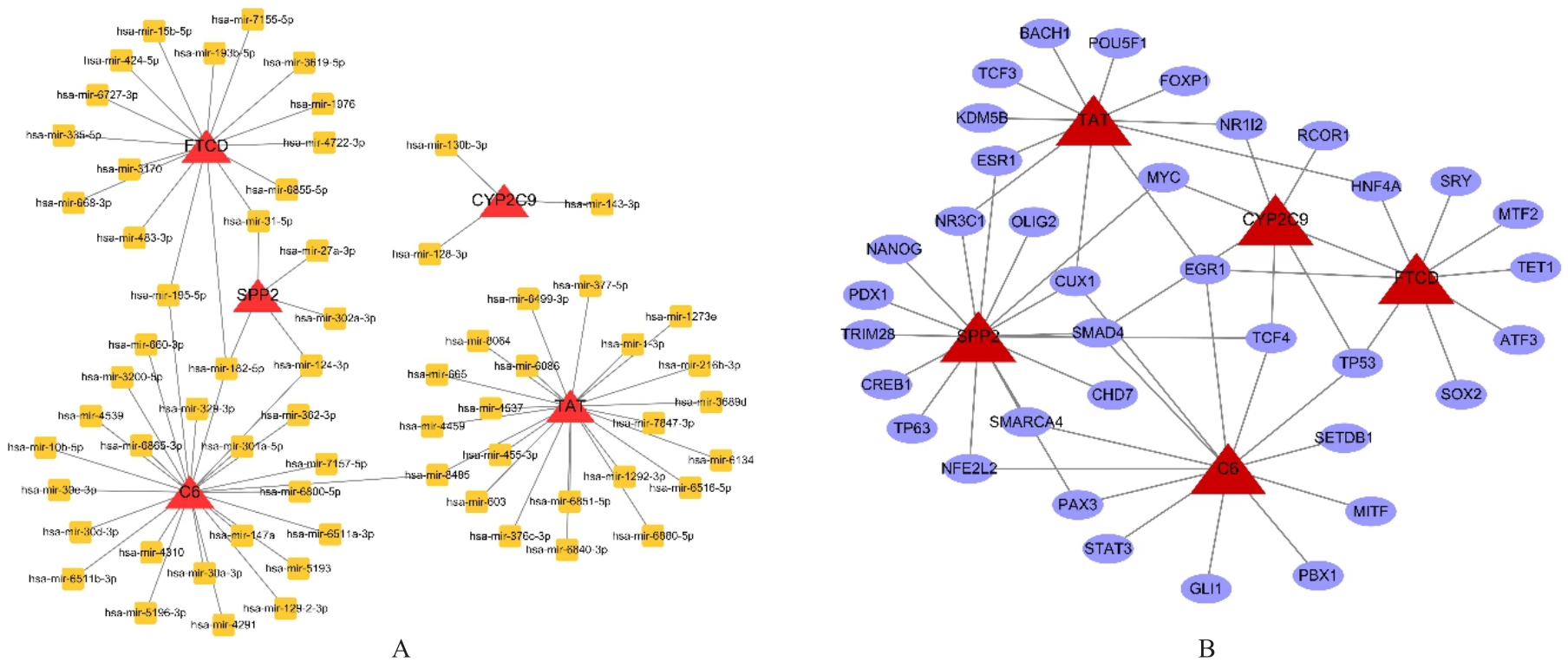
| Monobenzone | -0.721 | 4 | -0.787 | 0.004 |
| Piperidolate | -0.740 | 3 | -0.786 | 0.020 |
| Puromycin | -0.712 | 4 | -0.781 | 0.005 |
| Phenoxybenzamine | -0.698 | 4 | -0.778 | 0.005 |
| Ethaverine | -0.690 | 4 | -0.776 | 0.005 |
| Ursodeoxycholicacid | -0.650 | 3 | -0.775 | 0.023 |
| Trioxysalen | -0.707 | 4 | -0.756 | 0.007 |
| 1 | BRAY F, FERLAY J, SOERJOMATARAM I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. |
| 2 | LLOVET J M, KELLEY R K, VILLANUEVA A, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021, 7(1): 6. |
| 3 | MALUCCIO M, COVEY A. Recent progress in understanding, diagnosing, and treating hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2012, 62(6): 394-399. |
| 4 | BURKHART R A, RONNEKLEIV-KELLY S M, PAWLIK T M. Personalized therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular markers of prognosis and therapeutic response[J]. Surg Oncol, 2017, 26(2): 138-145. |
| 5 | LI B H, XU T C, LIU C H, et al. Liver-enriched genes are associated with the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 11197. |
| 6 | NAULT J C, REYNIÈS A D, VILLANUEVA A, et al. A hepatocellular carcinoma 5-gene score associated with survival of patients after liver resection[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 145(1): 176-187. |
| 7 | TU J X, CHEN J J, HE M M, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of molecular genetic targets and key pathways for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 5153-5162. |
| 8 | 刘 迁, 祁国萍, 于华裔, 等. 结肠癌核心基因和独立预后因子筛选的生物信息学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(3): 755-765. |
| 9 | 李 楠, 陈 蕾, 许天敏, 等. 子宫内膜异位症患者细胞外基质相关基因筛选的生物信息学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版), 2022, 48(1): 188-194. |
| 10 | RITCHIE M E, PHIPSON B, WU D, et al. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(7): e47. |
| 11 | MANDREKAR J N. Receiver operating characteristic curve in diagnostic test assessment[J]. J Thorac Oncol, 2010, 5(9): 1315-1316. |
| 12 | LI M H, XIN S Y, GU R Y, et al. Novel diagnostic biomarkers related to oxidative stress and macrophage ferroptosis in atherosclerosis[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 8917947. |
| 13 | SHEN L, ZHOU K G, LIU H, et al. Prediction of mechanosensitive genes in vascular endothelial cells under high wall shear stress[J]. Front Genet, 2021, 12: 796812. |
| 14 | WANG Y Y, KANG H E, XU T Y, et al. CeDR Atlas: a knowledgebase of cellular drug response[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2022, 50(D1): D1164-D1171. |
| 15 | SNAEBJORNSSON M T, JANAKI-RAMAN S, SCHULZE A. Greasing the wheels of the cancer machine: the role of lipid metabolism in cancer[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 31(1): 62-76. |
| 16 | CHAN A W, GILL R S, SCHILLER D, et al. Potential role of metabolomics in diagnosis and surveillance of gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2014, 20(36): 12874-12882. |
| 17 | CHENG X G, GU J, KLAASSEN C D. Adaptive hepatic and intestinal alterations in mice after deletion of NADPH-cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase (Cpr) in hepatocytes[J]. Drug Metab Dispos, 2014, 42(11): 1826-1833. |
| 18 | YAN T M, LU L L, XIE C, et al. Severely impaired and dysregulated cytochrome P450 expression and activities in hepatocellular carcinoma: implications for personalized treatment in patients[J]. Mol Cancer Ther, 2015, 14(12): 2874-2886. |
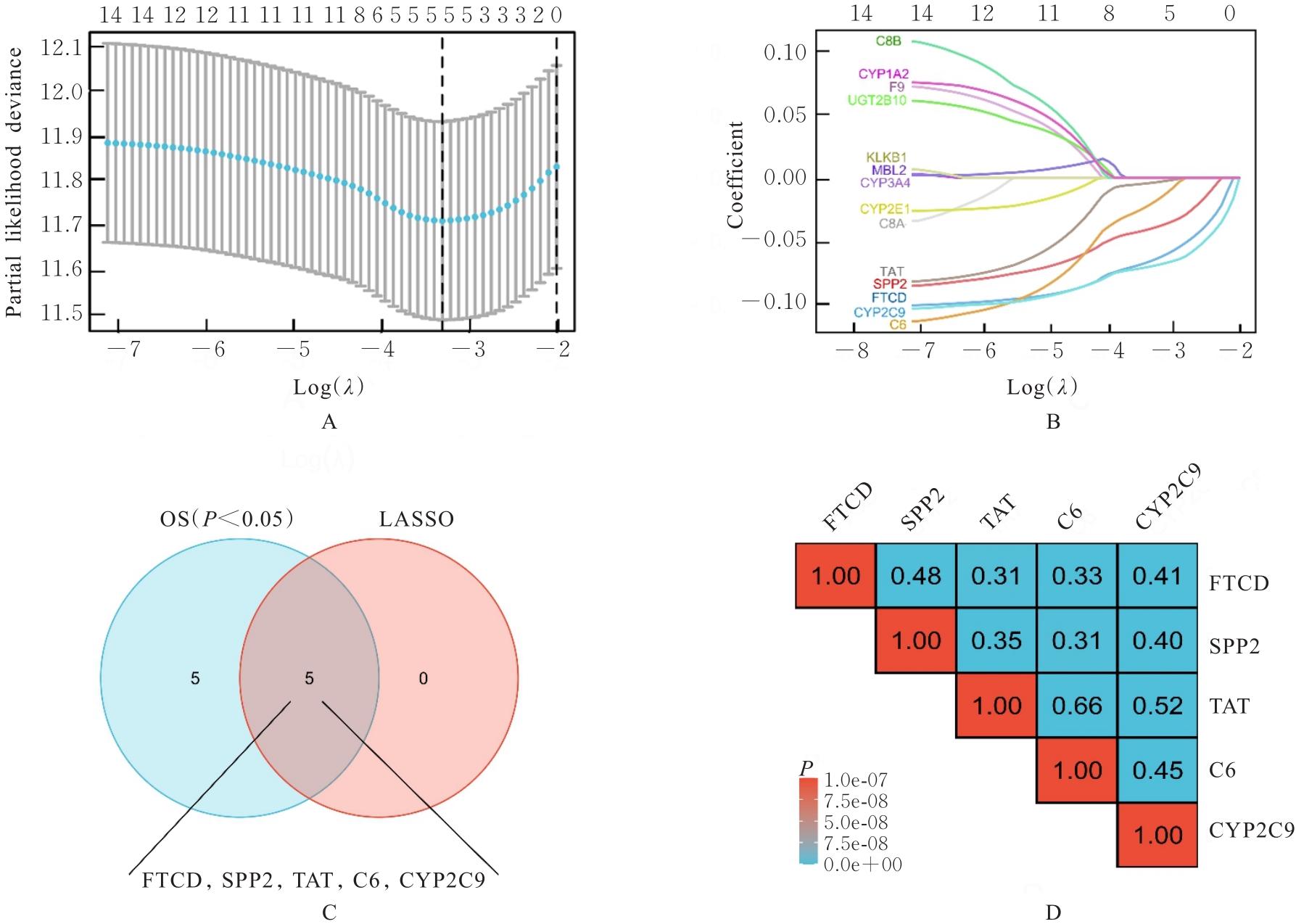
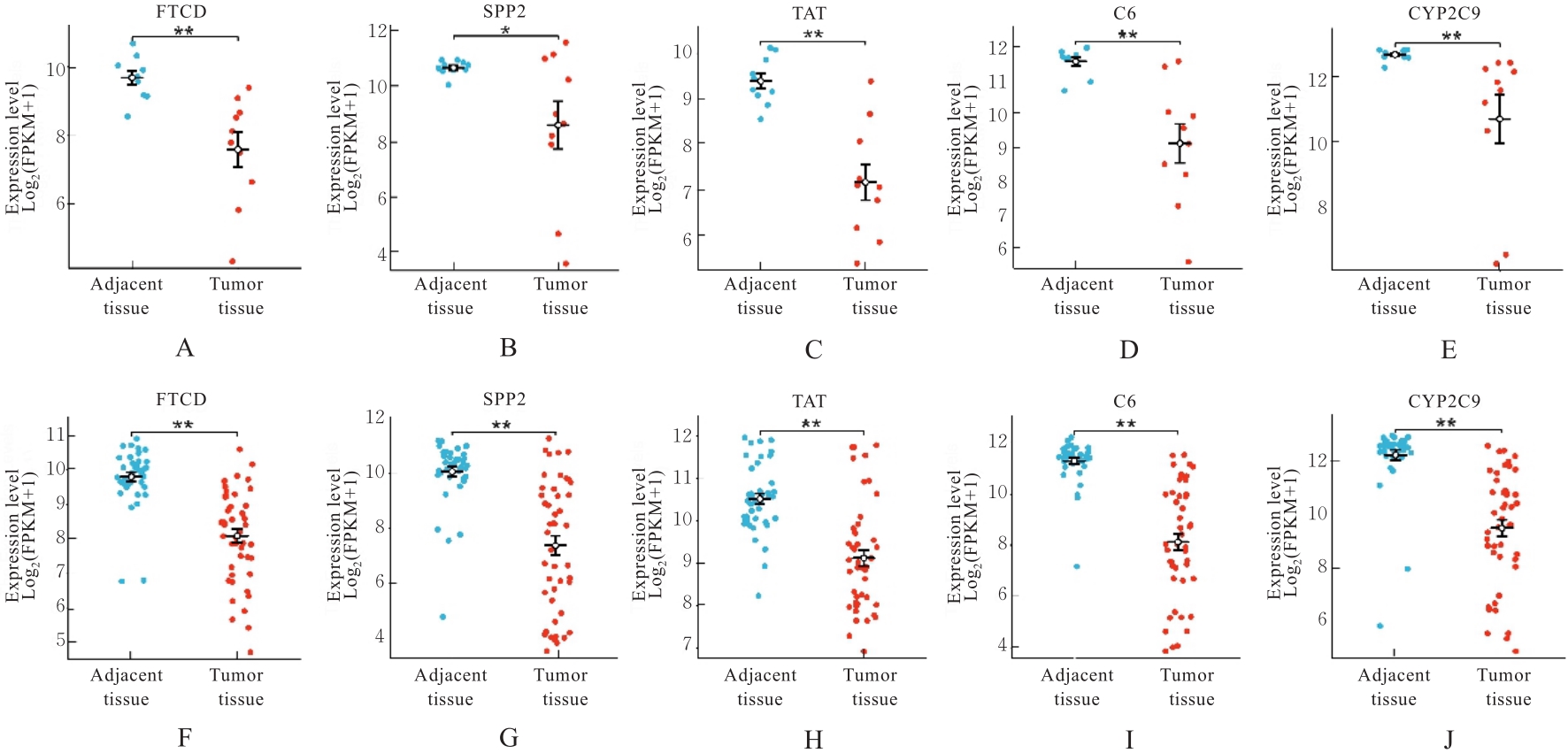
| 19 | YU Z H, GE Y Y, XIE L, et al. Using a yeast two-hybrid system to identify FTCD as a new regulator for HIF-1α in HepG2 cells[J]. Cell Signal, 2014, 26(7): 1560-1566. |
| 20 | LU C Y, FANG S J, WENG Q Y, et al. Integrated analysis reveals critical glycolytic regulators in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2020, 18(1): 97. |
| 21 | FU L, DONG S S, XIE Y W, et al. Down-regulation of tyrosine aminotransferase at a frequently deleted region 16q22 contributes to the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51(5): 1624-1634. |
| 22 | WANG Q, TANG Q, ZHAO L J, et al. Time serial transcriptome reveals Cyp2c29 as a key gene in hepatocellular carcinoma development[J]. Cancer Biol Med, 2020, 17(2): 401-417. |
| 23 | ROUMENINA L T, DAUGAN M V, PETITPREZ F, et al. Context-dependent roles of complement in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2019, 19(12): 698-715. |
| 24 | HOBART M J, FERNIE B A, DISCIPIO R G, et al. A physical map of the C6 and C7 complement component gene region on chromosome 5p13[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 1993, 2(7): 1035-1036. |
| 25 | OKA R, SASAGAWA T, NINOMIYA I, et al. Reduction in the local expression of complement component 6 (C6) and 7 (C7) mRNAs in oesophageal carcinoma[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2001, 37(9): 1158-1165. |
| 26 | WANG Z, LIAO J, WU S, et al. Recipient C6 rs9200 genotype is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after orthotopic liver transplantation in a Han Chinese population[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2016, 23(6): 157-161. |
| 27 | GARNELO M, TAN A, HER Z, et al. Interaction between tumour-infiltrating B cells and T cells controls the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Gut, 2017, 66(2): 342-351. |
| 28 | CHEN Q F, LI W, WU P H, et al. Significance of tumor-infiltrating immunocytes for predicting prognosis of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(35): 5266-5282. |
| 29 | KUANG D M, PENG C, ZHAO Q Y, et al. Activated monocytes in peritumoral stroma of hepatocellular carcinoma promote expansion of memory T helper 17 cells[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 51(1): 154-164. |
| 30 | SUN K, WANG L, ZHANG Y Y. Dendritic cell as therapeutic vaccines against tumors and its role in therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2006, 3(3): 197-203. |
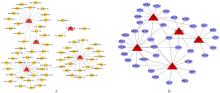
| 31 | WEI L, WANG X W, LV L Y, et al. The emerging role of microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs in drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Cancer, 2019, 18(1): 147. |
| 32 | VAN KEUREN-JENSEN K R, MALENICA I, COURTRIGHT A L, et al. MicroRNA changes in liver tissue associated with fibrosis progression in patients with hepatitis C[J]. Liver Int, 2016, 36(3): 334-343. |
| 33 | CAO M Q, YOU A B, ZHU X D, et al. MiR-182-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing FOXO3a[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2018, 11(1): 12. |
| 34 | LAMBERT S A, JOLMA A, CAMPITELLI L F, et al. The human transcription factors[J]. Cell, 2018, 175(2): 598-599. |
| 35 | WU Q, ZHANG B, SUN Y D, et al. Identification of novel biomarkers and candidate small molecule drugs in non-small-cell lung cancer by integrated microarray analysis[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 3545-3563. |
| [1] | Yongjing YANG,Tianyang KE,Shixin LIU,Xue WANG,Dequan XU,Tingting LIU,Ling ZHAO. Synergistic sensitization of apatinib mesylate and radiotherapy on hepatocarcinoma cells invitro [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1009-1015. |
| [2] | Yuanguo WANG,Peng ZHANG. Bioinformatics analysis based on relationship between SSP1 and TGFB1 and occurrence, prognosis, and immune invasion of esophageal adenocarcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1076-1086. |
| [3] | Linghui LIN,Na LI,Xiaoyan YIN,Xiaoling WANG,Yaping HU,Wei LIU,Rui FEI,Xinli TIAN. Bioinformatics anlysis based on three-dimensional structure of Helicobacter pylori hp0169 gene [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 739-748. |
| [4] | Yufei FENG,Shan JIN,Yubing WANG,Yinfei LU,Lijuan PANG,Kejian LIU. Bioinformatics analysis based on immune-related genes and immune cell infiltration of in-stent restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 749-758. |
| [5] | Zijia ZHU,Xia CHEN,Man CUI,Jihong WEN,Ping WANG,Dong SONG. Bioinformatics and molecular docking technology analysis on mechanism of salidroside on key differential genes of triple negative breast cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 759-769. |
| [6] | Yuting LIU,Ying YU,Guizhen LI,Qinxue SHI,Binbin LI. Bioinformatics analysis based on expression of splicing factor SRSF9 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and clinical significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 379-391. |
| [7] | Liping CHEN,Li HAN,Hua BIAN,Liye PANG. Bioinformatics analysis based on differentially expressed genes and screening of traditional Chinese medicine for treatment of severe bronchial asthma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 411-421. |
| [8] | Xiaoyan WANG,Hao ZHANG,Zehao GUO,Jun CAO,Zhijing MO. Screening of UBE2S interacting protein and construction of prognostic model in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 168-177. |
| [9] | Minqi NING,Yong HE,Bingshu LI,Guotao HUANG,Xiaohu ZUO,Zhihan ZHAO,Wuyue HAN,Li HONG. Bioinformatics analysis based on pelvic organ prolapse related aging genes of GEO Database and LASSO regression algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 178-187. |
| [10] | Xiaopeng YU,Renyi YANG,Zuomei HE,Puhua ZENG. Establishment and validation of nomogram of cancer specific survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma with negative alpha fetoprotein based on SEER Database [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 188-197. |
| [11] | Zixu YANG,Chang SU,Boyuan WANG,Chong LIU,Minghe LI. Bioinformatics analysis on molecular subtypes and clinical characteristics of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on genes associated with lactate metabolism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 198-207. |
| [12] | Yong DONG,Lingyao XU,Jing HUA,Han LIANG,Dongya LIU,Junbo ZHAO,Zhenglu SUN,Cheng CHENG,Shutang WEI. Effect of macrophage exosomal lncRNA HULC on migration, invasion,and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1217-1226. |
| [13] | Wenjun DENG,Liantao HU,Binnan ZHAO,Xinyu DONG,Xuebin LI,Jie LI,Xinyan YANG,Xiaoli GUO,Yue LI,Yikun QU,Weiqun WANG. Effect of CXC chemokine ligand 10 on proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1227-1233. |
| [14] | Yaqi XU,Yanyu WANG,Wenjing ZHANG,Mei HAN,Huaxia MU,Xi YANG,Weixiao BU,Zikun TAO,Yujia KONG,Fuyan SHI,Suzhen WANG. Bioinformatics analysis on screening of key genes of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and its relationship with prognosis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1243-1252. |
| [15] | Yiming ZHAO,Haiyang XU. Bioinformatics analysis on related genes and candidate pathways of glioblastoma multiforme [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1280-1289. |
|