吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 2971-2983.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210526
基于无监督变形网络的三维模型稠密对应关系计算
- 1.兰州交通大学 电子与信息工程学院,兰州 730070
2.兰州交通大学 测绘与地理信息学院,兰州 730070
Dense correspondence calculation of 3D models based on unsupervised deformed network
- 1.School of Electronic and Information Engineering,Lanzhou Jiaotong University,Lanzhou 730070,China
2.Faculty of Geomatics,Lanzhou Jiaotong University,Lanzhou 730070,China
摘要:
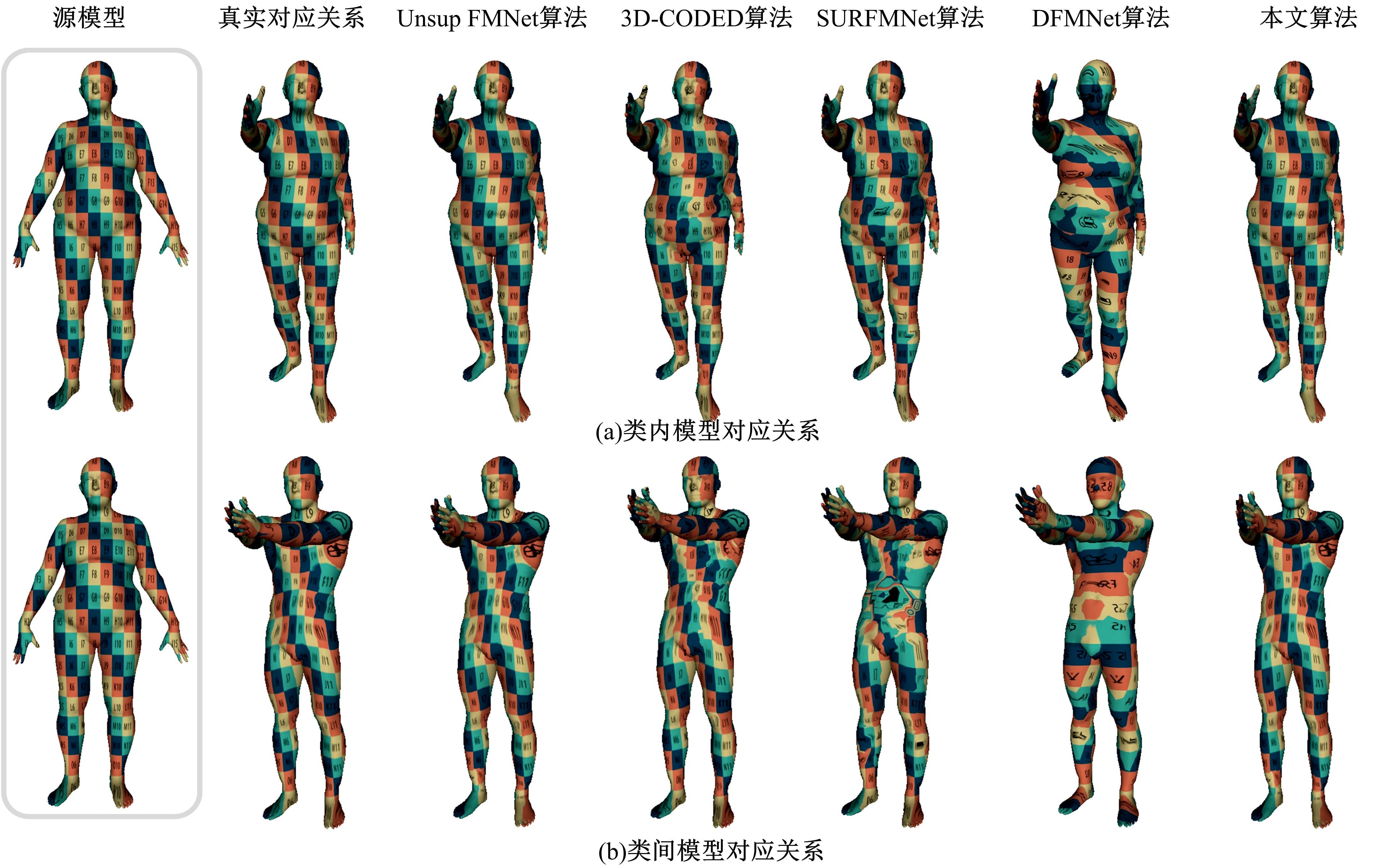
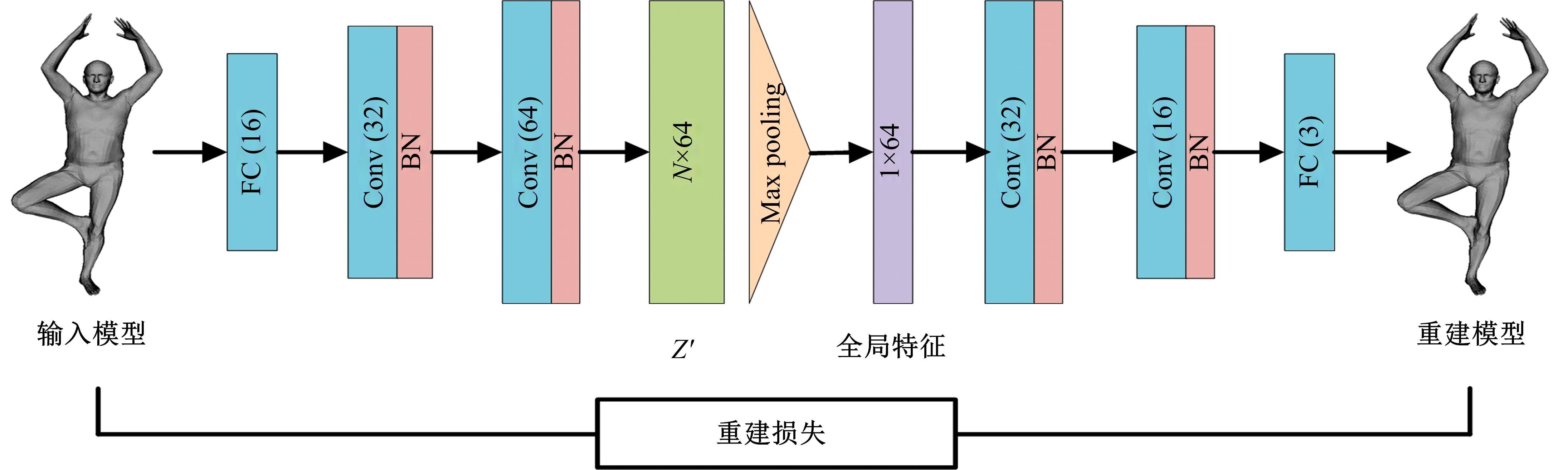
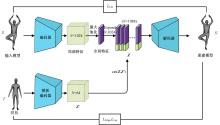
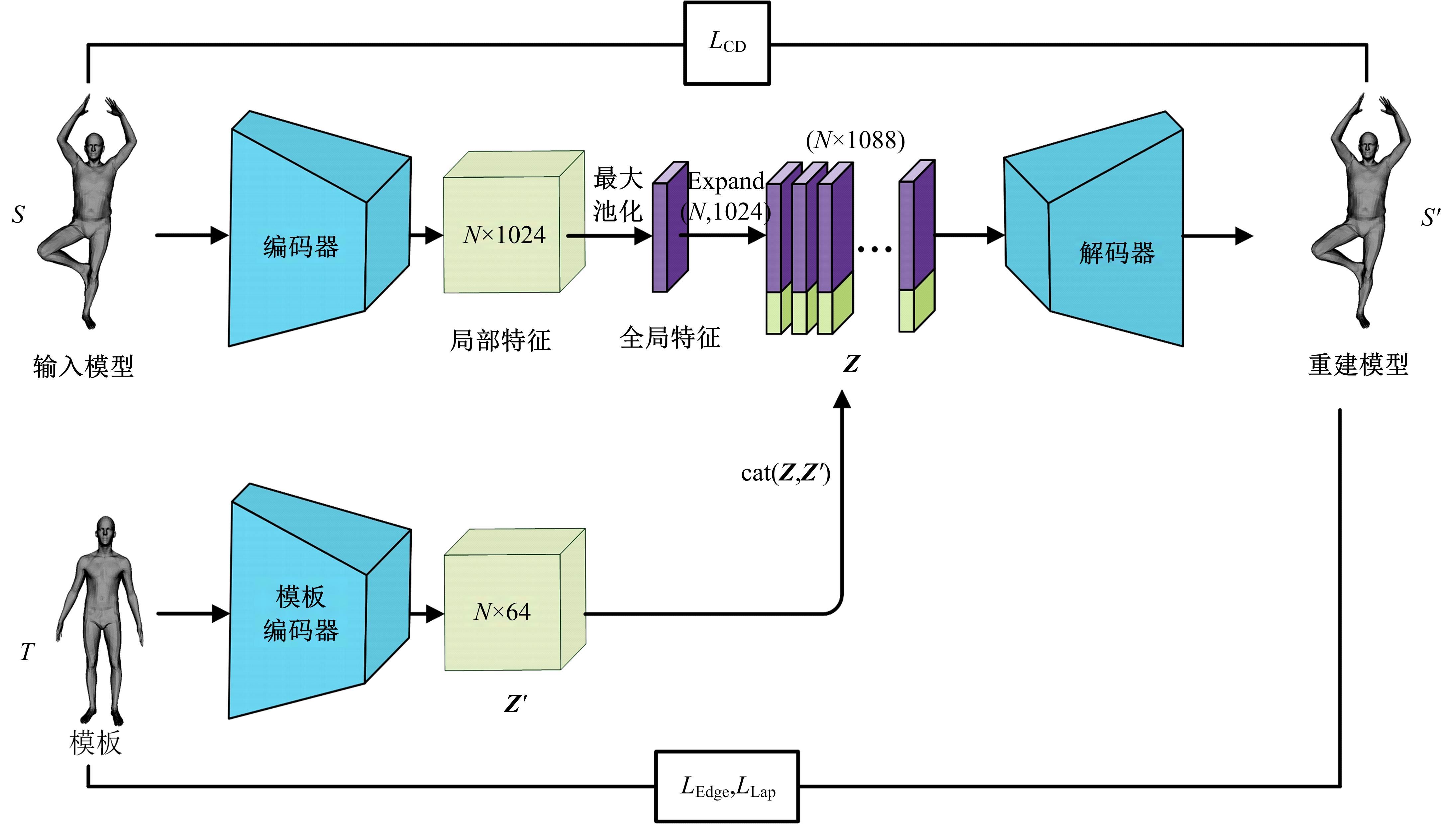
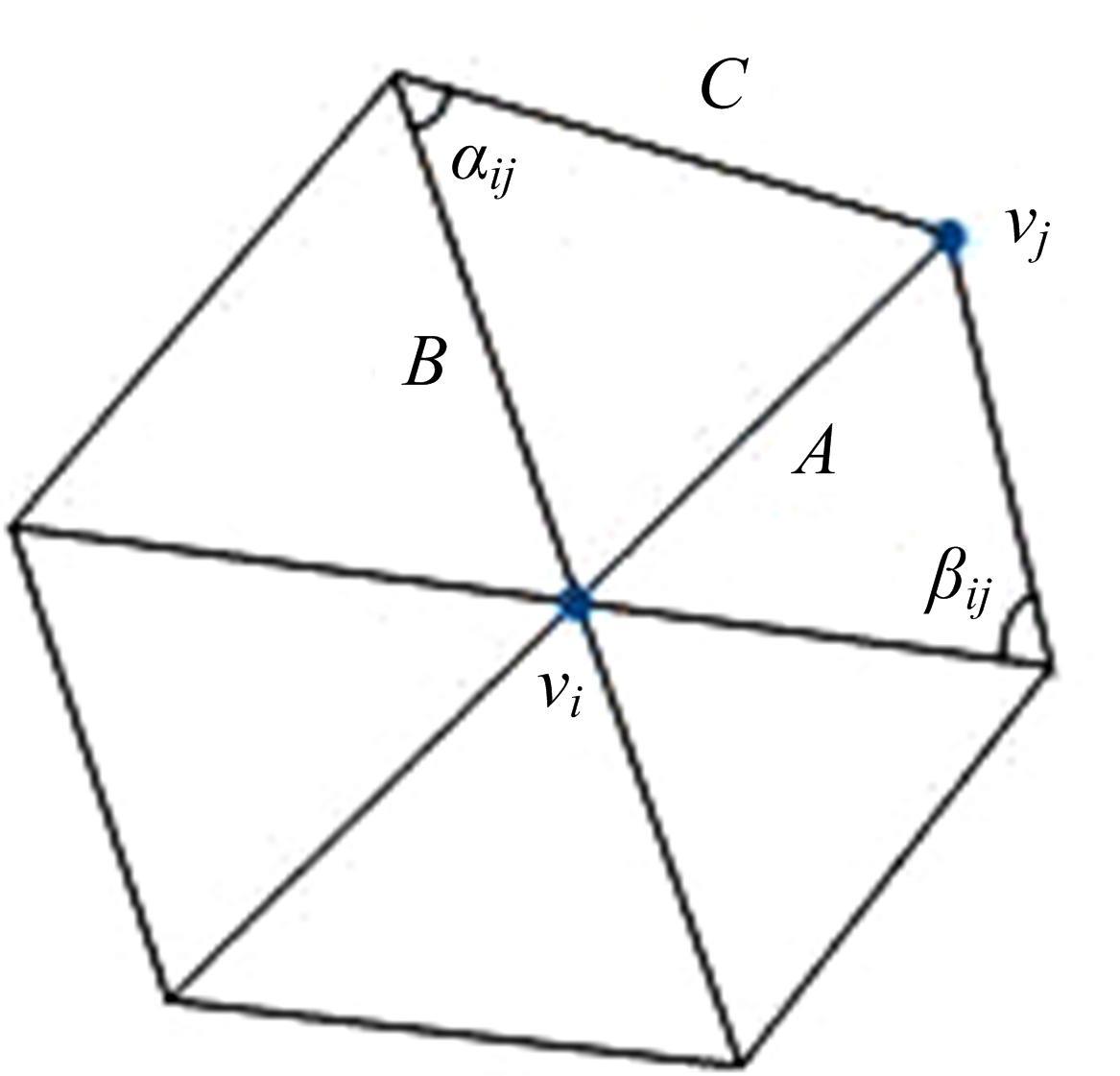
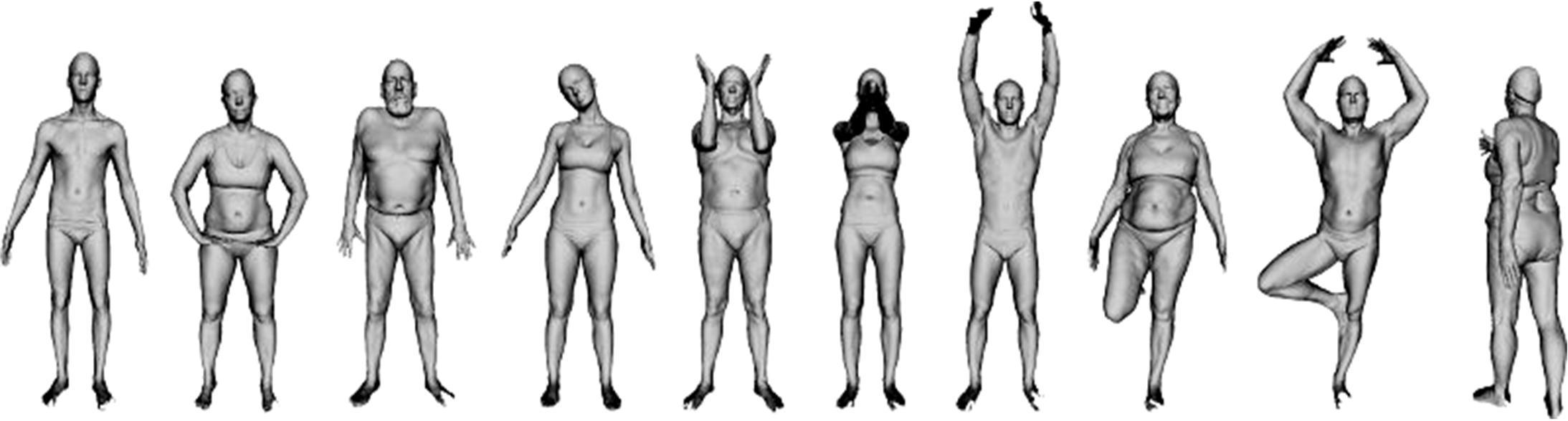
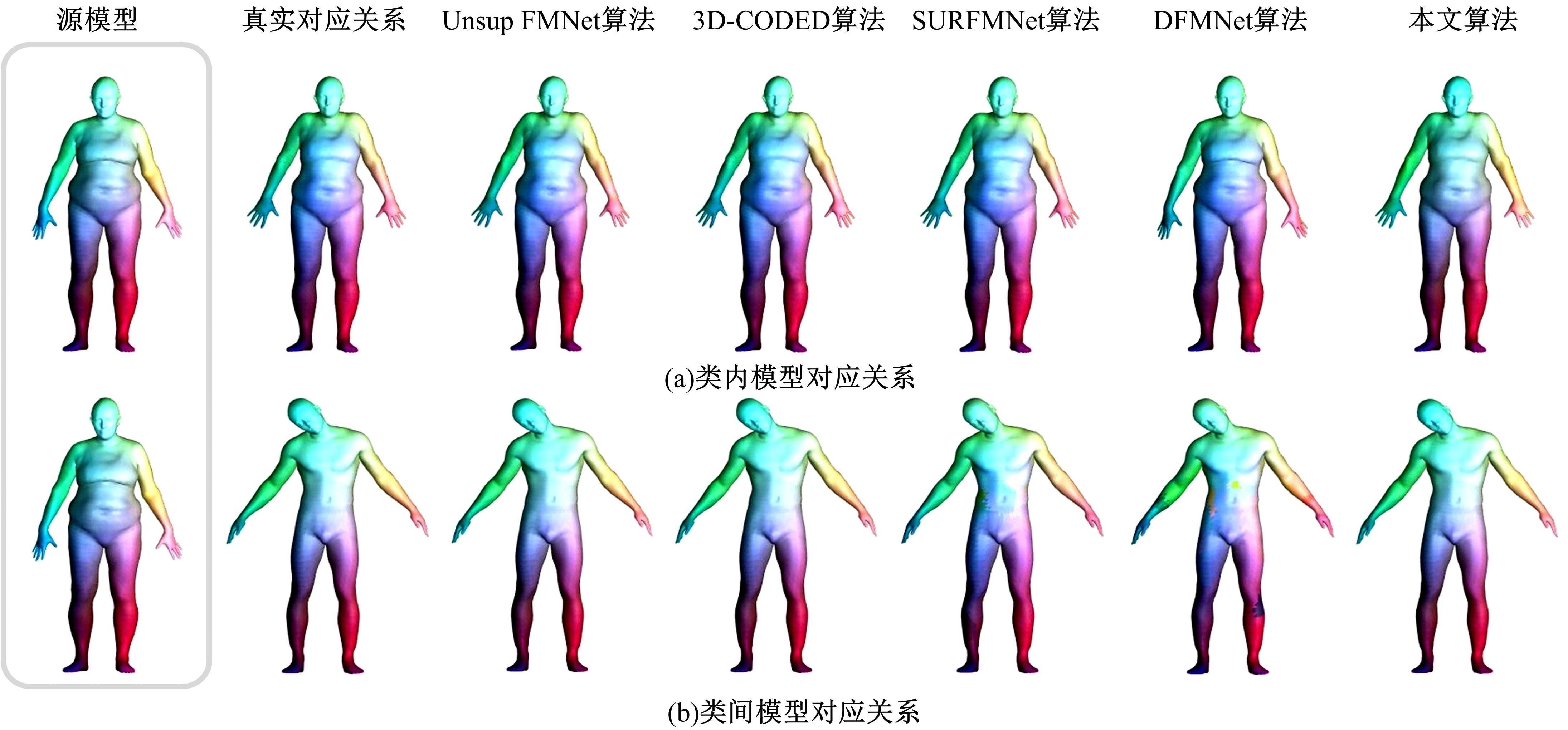
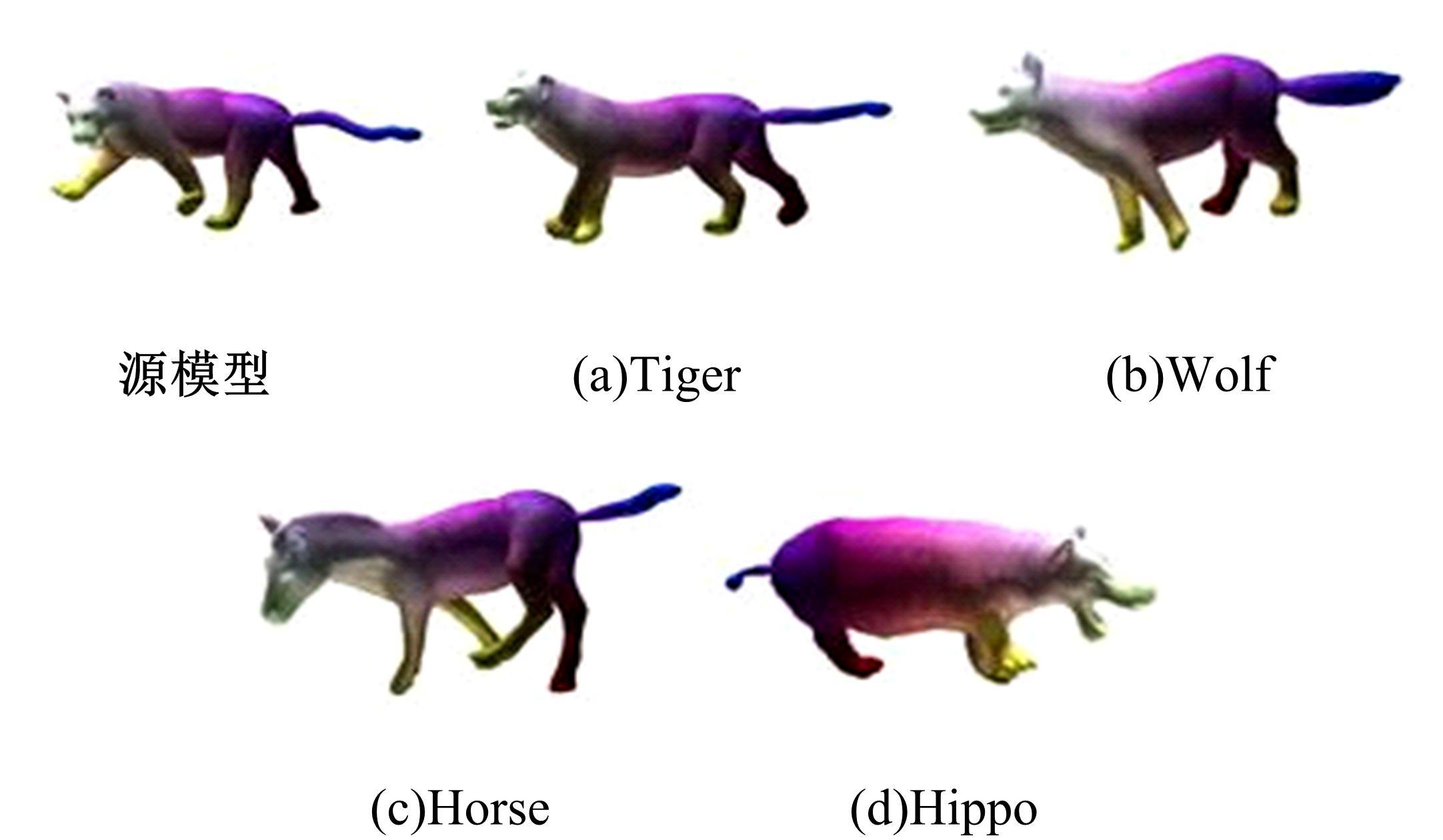
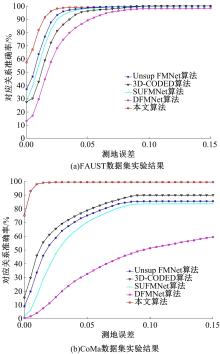
针对利用深度学习方法计算三维模型间稠密对应关系时算法泛化能力较差的问题,提出了一种基于无监督变形网络的对应关系的计算方法。首先,通过基于螺旋卷积的模板特征提取网络计算非参数化模板的局部特征描述符;其次,在模板变形网络中利用编码器获取输入模型的全局特征,并与模板的局部特征描述符拼接,将拼接后的特征输入到解码器中计算模板的变形模型;最后,通过最近邻搜索算法计算变形模型与输入模型之间的稠密对应关系。实验结果表明,在具有相同训练样本的条件下,本文算法与目前主流算法相比得到了更精确的稠密对应关系,且具有更强的泛化能力。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Corman T, Ovsjanikov M, Chambolle A. Supervised descriptor learning for non-rigid shape matching[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV), Switzerland, Zurich, 2014: 283-298. |
| 2 | Litany O, Remez T, Rodolà E, et al. Deep functional maps: structured prediction for dense shape correspondence[C]∥International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5659-5667. |
| 3 | Chen Q, Koltun V. Robust non-rigid registration by convex optimization[C]∥International Conference on Computer Vision, Chile, Santiago, 2015: 2039-2047. |
| 4 | Van K, Zhang H, Hamarneh G, et al. A survey on shape correspondence[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2011, 30(6): 1681-1707. |
| 5 | Groueix T, Fisher M, Kim V, et al. 3D-CODED: 3D correspondences by deep deformation[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 235-251. |
| 6 | Gao L, Yang J, Wu T, et al. SDM-NET: deep generative network for structured deformable mesh[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, 38(6): 1-15. |
| 7 | Wu N, Song S, Khosla A, et al. 3D ShapeNets: a deep representation for volumetric shapes[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Boston, USA, 2015: 1912-1920. |
| 8 | Tan Q, Gao L, Lai Y, et al. Mesh-based autoencoders for localized deformation component analysis[C]∥AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2017: 247-263. |
| 9 | Gong W, Chen L, Michael B, et al. SpiralNet++: a fast and highly efficient mesh convolution operator[C]∥International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 4141-4148. |
| 10 | Fukushima K. Neocognitron: a self-organizing neural network model for a mechanism of pattern recognition unaffected by shift in position[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 1980, 36(4): 193-202. |
| 11 | Facundo M, Sapiro G. Theoretical and computational framework for isometry invariant recognition of point cloud data[J]. Foundations of Computational Mathematics, 2005, 5(3): 313-347. |
| 12 | Alexander M, Michael M, Ron K, et al. Generalized multidimensional scaling: a framework for isometry-invariant partial surface matching[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2006, 103(5): 1168-1172. |
| 13 | Rusinkiewicz S, Levoy M. Efficient variants of the ICP algorithm[C]∥Proceedings Third International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling, Quebec, Canada, 2001: 145-152. |
| 14 | Sun J, Ovsjanikov M, Guibas L. A concise and provably informative multi-scale signature-based on heat diffusion[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2009, 28(5): 1383-1392. |
| 15 | Aubry M, Schlickewei U, Cremers D. The wave kernel signature: a quantum mechanical approach to shape analysis[C]∥International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 1626-1633. |
| 16 | 杨军, 闫寒, 王茂正. 融合特征描述符约束的3维等距模型对应关系计算[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2016, 21(5): 628-635. |
| Yang Jun, Yan Han, Wang Mao-zheng. Correspondence calculation of 3D isometric model fused with feature descriptor constraints[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2016, 21(5): 628-635. | |
| 17 | Solomon J, Nguyen A, Butscher A, et al. Soft maps between surfaces[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2012, 31(5): 1617-1626. |
| 18 | Kim V G, Li W, Mitra N J, et al. Exploring collections of 3D models using fuzzy correspondences[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2012, 31(4): No.54. |
| 19 | Lipman Y, Funkhouser T A. Mobius voting for surface correspondence[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2009, 28(3):1-12. |
| 20 | Ovsjanikov M, Quentin M, Facundo M, et al. One point isometric matching with the heat kernel[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2010, 29(5): 1555-1564. |
| 21 | Masci J, Boscaini D, Bronstein M, et al. Geodesic convolutional neural networks on Riemannian manifolds[C]∥International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 37-45. |
| 22 | Ovsjanikov M, Ben-Chen M, Solomon J, et al. Functional maps: a flexible representation of maps between shapes[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2012, 31(4): 1-11. |
| 23 | 杨军, 闫寒. 校准三维模型基矩阵的函数映射的对应关系计算[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2018, 43(10): 1518-1525. |
| Yang Jun, Yan Han. Correspondence calculation of functional maps for calibrating the base matrix of 3D model[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(10): 1518-1525. | |
| 24 | Wu Y, Yang J, Zhao J. Partial 3D shape functional correspondence via fully spectral eigenvalue alignment and upsampling refinement[J]. Computers & Graphics, 2020, 92: 99-113. |
| 25 | Salti S, Tombari F, Di S. Shot: unique signatures of histograms for surface and texture description[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2014, 125(8): 251-264. |
| 26 | Qi C, Su H, Mo K, et al. PointNet: deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 2017: 652-660. |
| 27 | Lu D, Fang Y. Meta deformation network: meta functional for shape correspondence[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 6647-6660. |
| 28 | Groueix T, Fisher M, Kim V G, et al. Unsupervised cycle-consistent deformation for shape matching[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2019, 38(5): 123-133. |
| 29 | Vestner M, Litman R, Rodola E, et al. Product manifold filter: non-rigid shape correspondence via kernel density estimation in the product space[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Honolulu, Hawaii, 2017: 6681-6690. |
| 30 | Federica B, Javier R, Matthew L, et al. Faust: dataset and evaluation for 3D mesh registration[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Columbus, USA, 2014: 3794-3801. |
| 31 | Varol G, Romero J, Martin X, et al. Learning from synthetic humans[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 2017: 109-117. |
| 32 | Ranjan A, Bolkart T, Sanyal S, et al. Generating 3D faces using convolutional mesh autoencoders[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 704-720. |
| 33 | Zuffi S, Kanazawa A, Jacobs D, et al. 3D menagerie: modeling the 3D shape and pose of animals[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 2017: 6365-6373. |
| 34 | Matthew L, Naureen M, Javier R, et al. Smpl: a skinned multi-person linear model[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2015, 34(6): 283-298. |
| 35 | Lowe D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110. |
| 36 | Halimi O, Litany O, Rodola E, et al. Unsupervised learning of dense shape correspondence[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4370-4379. |
| 37 | Roufosse J M, Sharma A, Ovsjanikov M. Unsupervised deep learning for structured shape matching[C]∥International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 5659-5667. |
| [1] | 祁贤雨,王巍,王琳,赵玉飞,董彦鹏. 基于物体语义栅格地图的语义拓扑地图构建方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 569-575. |
| [2] | 时小虎,吴佳琦,吴春国,程石,翁小辉,常志勇. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| [3] | 郭鹏,赵文超,雷坤. 基于改进Jaya算法的双资源约束柔性作业车间调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 480-487. |
| [4] | 刘近贞,高国辉,熊慧. 用于脑组织分割的多尺度注意网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 576-583. |
| [5] | 赵宏伟,张健荣,朱隽平,李海. 基于对比自监督学习的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1850-1856. |
| [6] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [7] | 胡丹,孟新. 基于时变网格的对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1896-1903. |
| [8] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [9] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [10] | 周丰丰,朱海洋. 基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法SEE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1834-1841. |
| [11] | 周丰丰,张亦弛. 基于稀疏自编码器的无监督特征工程算法BioSAE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1645-1656. |
| [12] | 王军,徐彦惠,李莉. 低能耗支持完整性验证的数据融合隐私保护方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1657-1665. |
| [13] | 王生生,姜林延,杨永波. 基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
| [14] | 康耀龙,冯丽露,张景安,陈富. 基于谱聚类的高维类别属性数据流离群点挖掘算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1422-1427. |
| [15] | 王文军,余银峰. 考虑数据稀疏的知识图谱缺失连接自动补全算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1428-1433. |
|