吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 2350-2357.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211082
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于高分辨率网络的视杯和视盘的联合分割
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
Joint segmentation of optic cup and disc based on high resolution network
Xiao-xin GUO1,2( ),Jia-hui LI1,2,Bao-liang ZHANG1,2
),Jia-hui LI1,2,Bao-liang ZHANG1,2
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbol Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
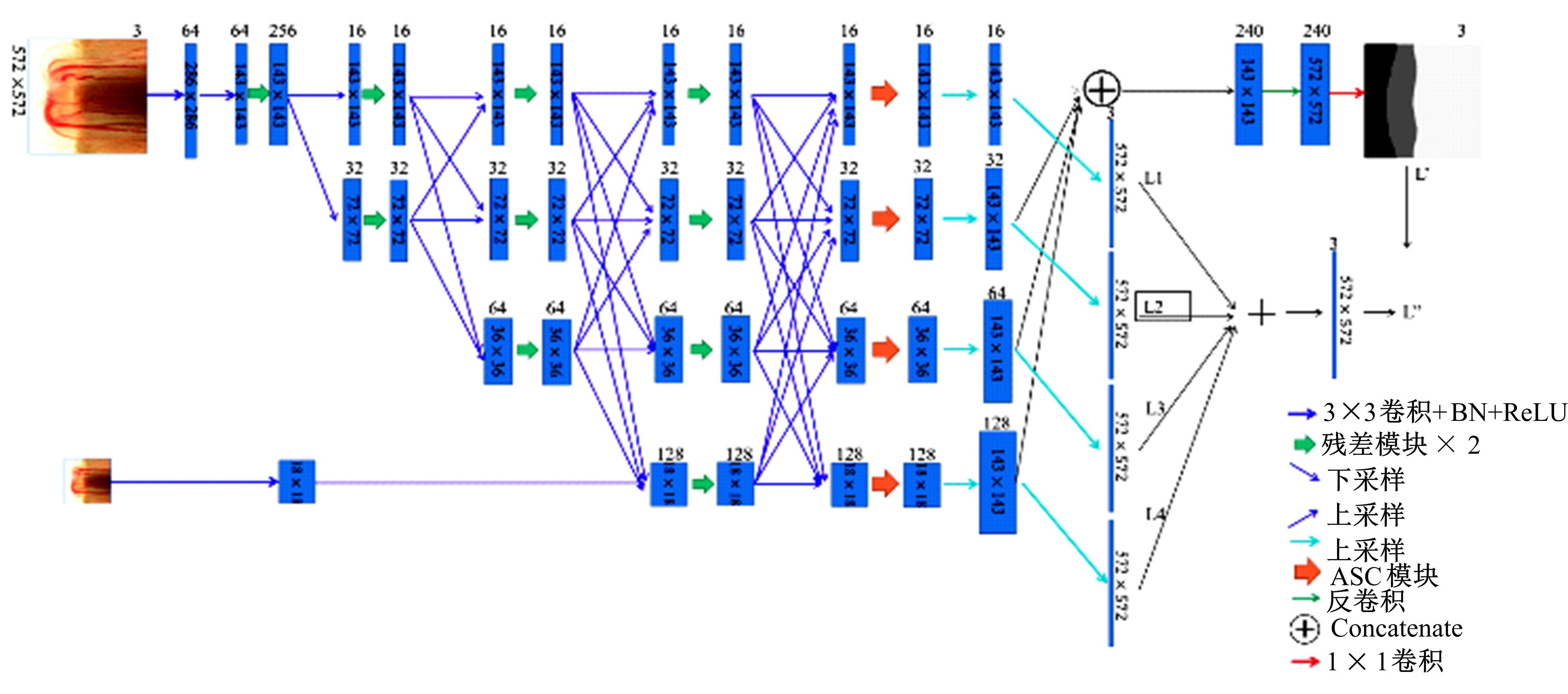
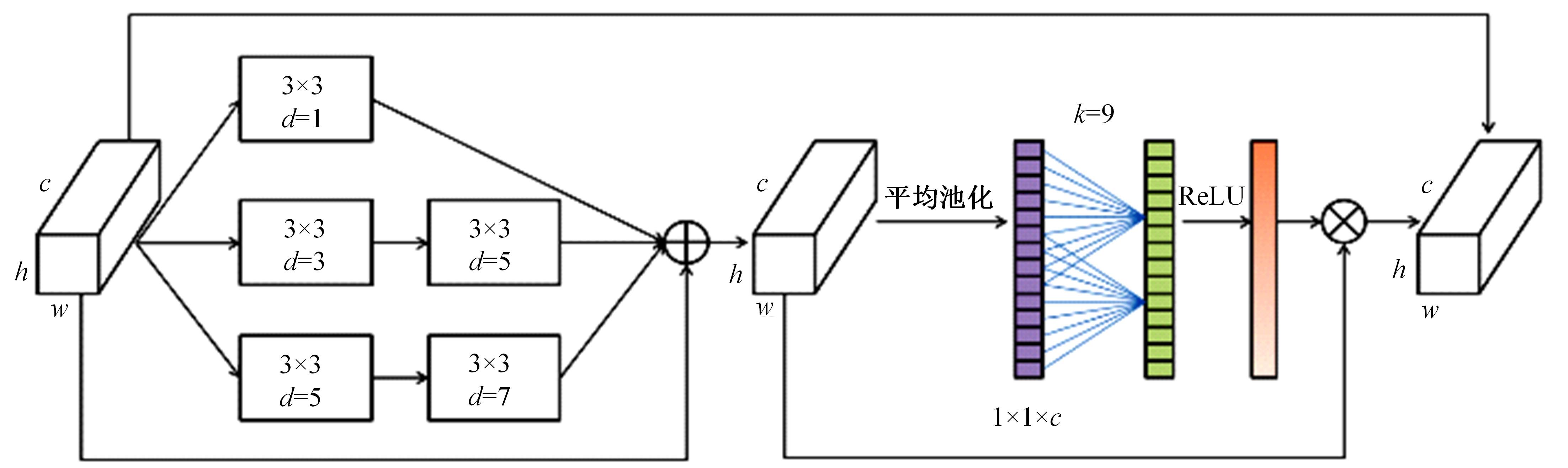
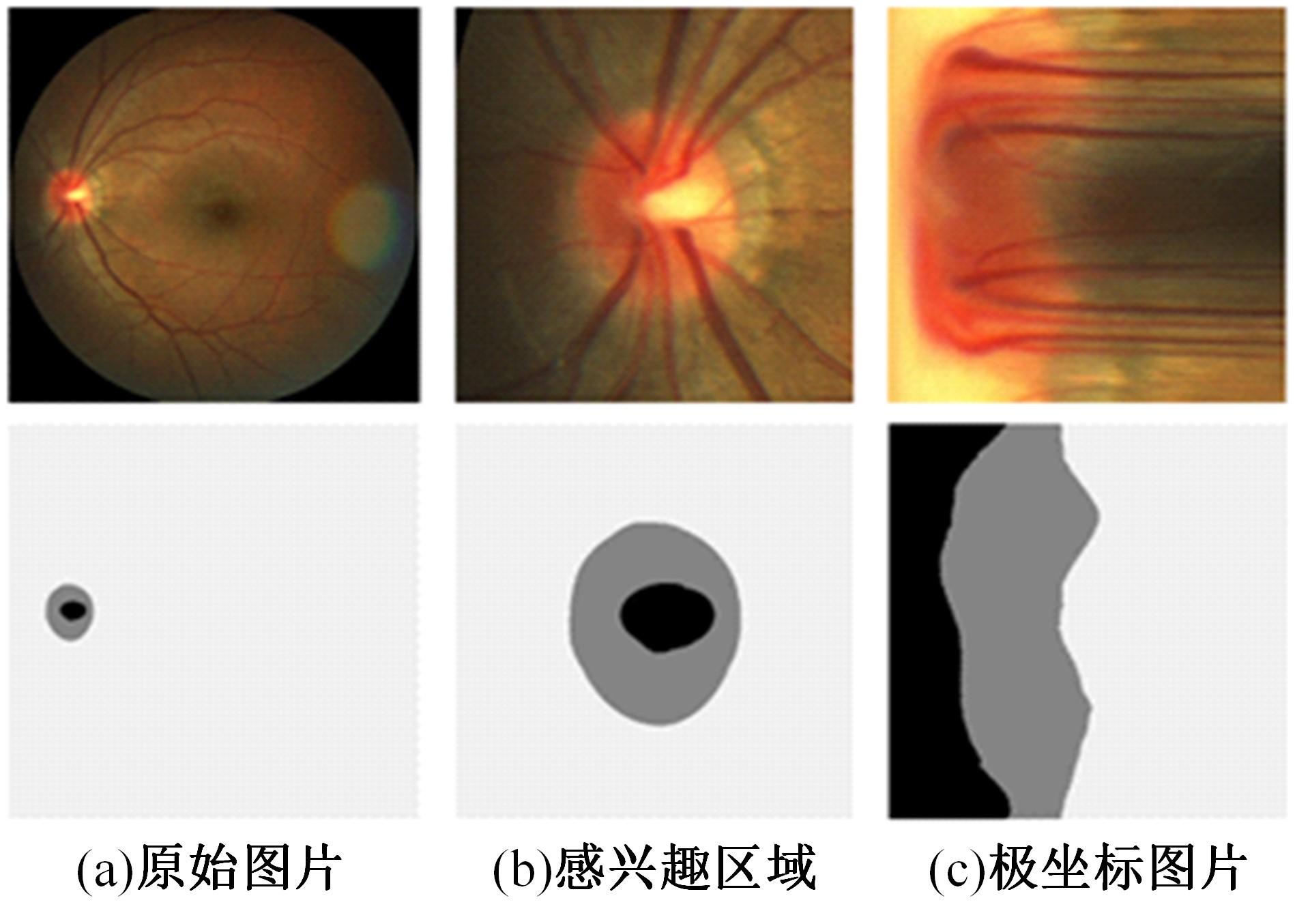
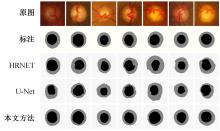
针对在使用视盘(OD)和视杯(OC)的分割测量杯盘比(CDR)来诊断青光眼的过程中,与视盘分割相比视杯分割仍存在分割精度上的困难,提出了一种深度学习体系结构MS-HRNET,用于视杯和视盘的联合分割。它是一种基于HRNET的改进架构。通过在HRNET中添加多尺度输入,可以弥补特征提取过程中的信息丢失。结合多尺度空间和通道注意机制,提取图像深层信息。通过添加侧输出层,指导网络的早期训练。实验表明:该算法在Drishti-GS1和REFUGE数据集上的分割效果优于现有的视杯和视盘分割方法。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Tham Y C, Li X, Wong T Y, et al. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ophthalmology, 2014, 121(11): 2081-2090. |
| 2 | Michelson G, Simone W, Hornegger J, et al. The papilla as screening parameter for early diagnosis of glaucoma[J]. Deutsches Rzteblatt International, 2008, 105(34/35):583-589. |
| 3 | Wong D W K, Liu J, Lim J H, et al. Level-set based automatic cup-to-disc ratio determination using retinal fundus images in ARGALI[C]∥30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vancourer, 2008: 2266-2269. |
| 4 | Inoue N, Yanashima K, Magatani K, et al. Development of a simple diagnostic method for the glaucoma using ocular Fundus pictures[C]∥IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology 27th Annual Conference, Shanghai, China, 2006: 3355-3358. |
| 5 | Blanco M, Penedo M G, Barreira N, et al. Localization and extraction of the optic disc using the fuzzy circular hough transform[C]∥International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Soft Computing, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2006: 712-721. |
| 6 | Sevastopolsky A. Optic disc and cup segmentation methods for glaucoma detection with modification of U-Net convolutional neural network[J]. Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, 2017, 27(3): 618-624. |
| 7 | Fu H, Cheng J, Xu Y, et al. Joint optic disc and cup segmentation based on multi-label deep network and polar transformation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(7): 1597-1605. |
| 8 | Wang S, Yu L, Yang X, et al. Patch-based output space adversarial learning for joint optic disc and cup segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(11): 2485-2495. |
| 9 | Zilly J, Buhmann J M, Mahapatra D. Glaucoma detection using entropy sampling and ensemble learning for automatic optic cup and disc segmentation[J]. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics, 2017, 55: 28-41. |
| 10 | Gu Z, Cheng J, Fu H, et al. Ce-net: context encoder network for 2d medical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(10): 2281-2292. |
| 11 | Tabassum M, Khan T M, Arsalan M, et al. CDED-Net: Joint segmentation of optic disc and optic cup for glaucoma screening[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 102733-102747. |
| 12 | Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Long Beach, 2019: 5693-5703. |
| 13 | Zhao H S, Qi X J, Shen X Y, et al. Icnet for real-time semantic segmentation on high-resolution images[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2018: 405-420. |
| 14 | Sun K, Zhao Y, Jiang B, et al. High-resolution representations for labeling pixels and regions[J]. arXiv Preprint Arxiv:. |
| 15 | Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, 2017: 4700-4708. |
| 16 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Veges, 2016: 770-778. |
| 17 | Wang Q L, Wu B G, Zhu P E, et al. ECA-net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:. |
| 18 | 袁伟,许文波,周甜.一种深度学习分割遥感影像道路的损失函数[J].中国空间科学技术,2021,41(4):134-141. |
| Yuan Wei, Xu Wen-bo, Zhou Tian. A loss function of road segmentation in remote sensing image by deep learning[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2021,41(4):134-141. | |
| 19 | Orlando J I, Fu H, Breda J B, et al. Refuge challenge: A unified framework for evaluating automated methods for glaucoma assessment from fundus photographs[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2020, 59: 101570. |
| 20 | Sivaswamy J, Krishnadas S R, Joshi G D, et al. Drishti-gs: retinal image dataset for optic nerve head (onh) segmentation[C]∥IEEE 11th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging,Beijing, China, 2014: 53-56. |
| 21 | Fu H, Cheng J, Xu Y, et al. Disc-aware ensemble network for glaucoma screening from fundus image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(11): 2493-2501. |
| 22 | Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. Segnet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. |
| 23 | Liu S, Hong J, Lu X, et al. Joint optic disc and cup segmentation using semi-supervised conditional GANs[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2019, 115: 103485. |
| 24 | Xu Y, Lu S, Li H, et al. Mixed maximum loss design for optic disc and optic cup segmentation with deep learning from imbalanced samples[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(20): 19204401. |
| [1] | 唐菲菲,周海莲,唐天俊,朱洪洲,温永. 融合动静态变量的滑坡多步位移预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1833-1841. |
| [2] | 田彦涛,黄兴,卢辉遒,王凯歌,许富强. 基于注意力与深度交互的周车多模态行为轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
| [3] | 吕卫,韩镓泽,褚晶辉,井佩光. 基于多模态自注意力网络的视频记忆度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1211-1219. |
| [4] | 田彦涛,许富强,王凯歌,郝子绪. 考虑周车信息的自车期望轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 674-681. |
| [5] | 欧阳继红,郭泽琪,刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [6] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [7] | 陈晓雷,孙永峰,李策,林冬梅. 基于卷积神经网络和双向长短期记忆的稳定抗噪声滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 296-309. |
| [8] | 周大可,张超,杨欣. 基于多尺度特征融合及双重注意力机制的自监督三维人脸重建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2428-2437. |
| [9] | 王德兴,吴若有,袁红春,宫鹏,王越. 基于多尺度注意力融合和卷积神经网络的水下图像恢复[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1396-1404. |
| [10] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [11] | 刘元宁,吴迪,朱晓冬,张齐贤,李双双,郭书君,王超. 基于YOLOv3改进的用户界面组件检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1026-1033. |
| [12] | 赵海英,周伟,侯小刚,张小利. 基于多任务学习的传统服饰图像双层标注[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 293-302. |
| [13] | 赵宏伟,刘晓涵,张媛,范丽丽,龙曼丽,臧雪柏. 基于关键点注意力和通道注意力的服装分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770. |
| [14] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| [15] | 欧阳丹彤,肖君,叶育鑫. 基于实体对弱约束的远监督关系抽取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 912-919. |
|
||