吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 2371-2379.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220005
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于跨语言预训练模型的朝汉翻译质量评估
- 延边大学 计算机科学与技术学院,吉林 延吉 133002
Korean⁃Chinese translation quality estimation based on cross⁃lingual pretraining model
Ya-hui ZHAO( ),Fei-yu LI,Rong-yi CUI,Guo-zhe JIN,Zhen-guo ZHANG,De LI,Xiao-feng JIN
),Fei-yu LI,Rong-yi CUI,Guo-zhe JIN,Zhen-guo ZHANG,De LI,Xiao-feng JIN
- Department of Computer Science & Technology,Yanbian University,Yanji 133002,China
摘要:
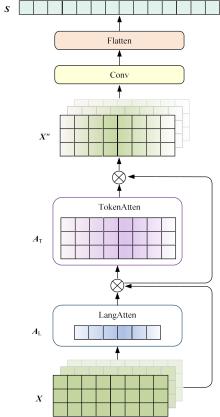
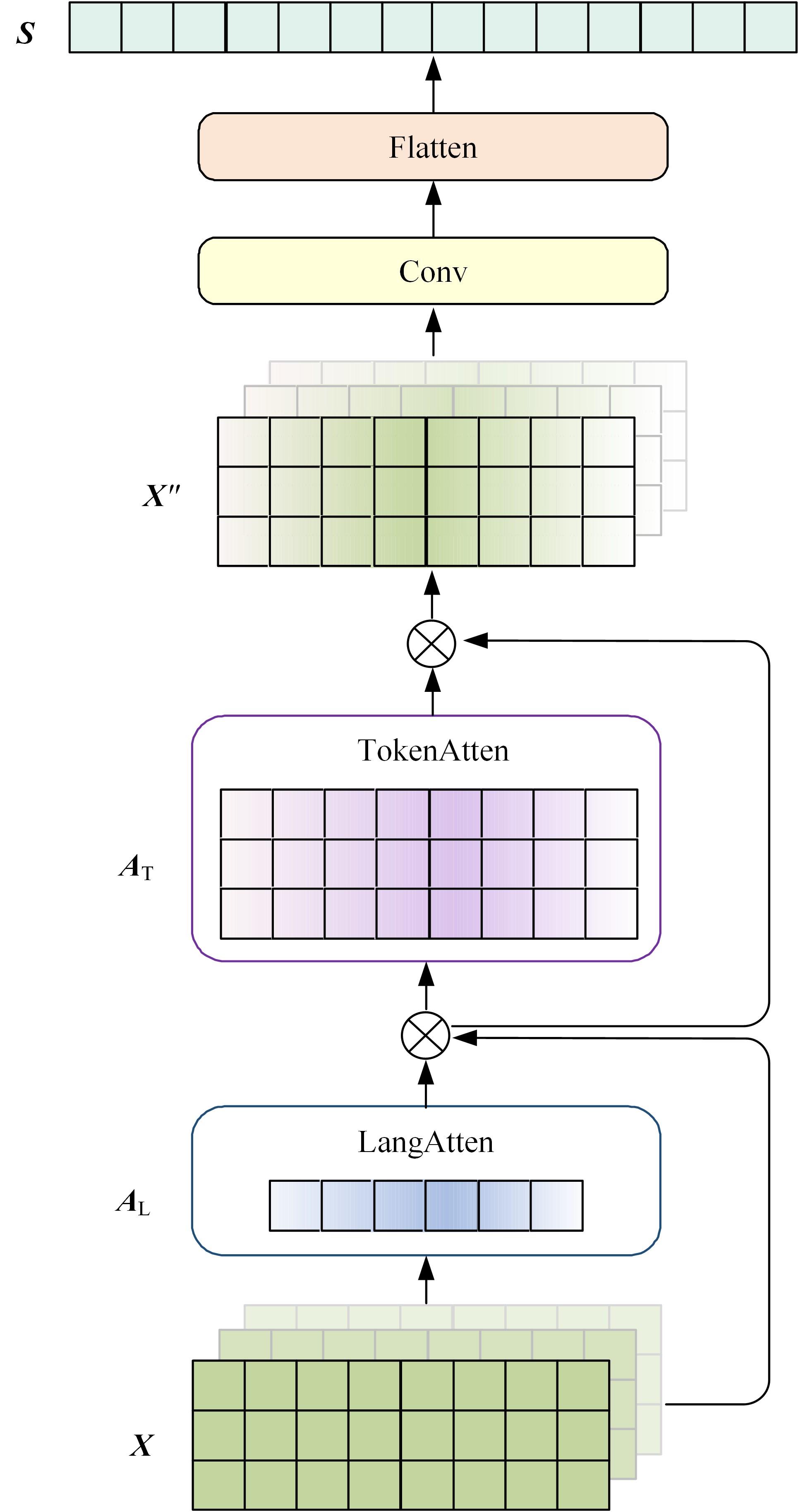
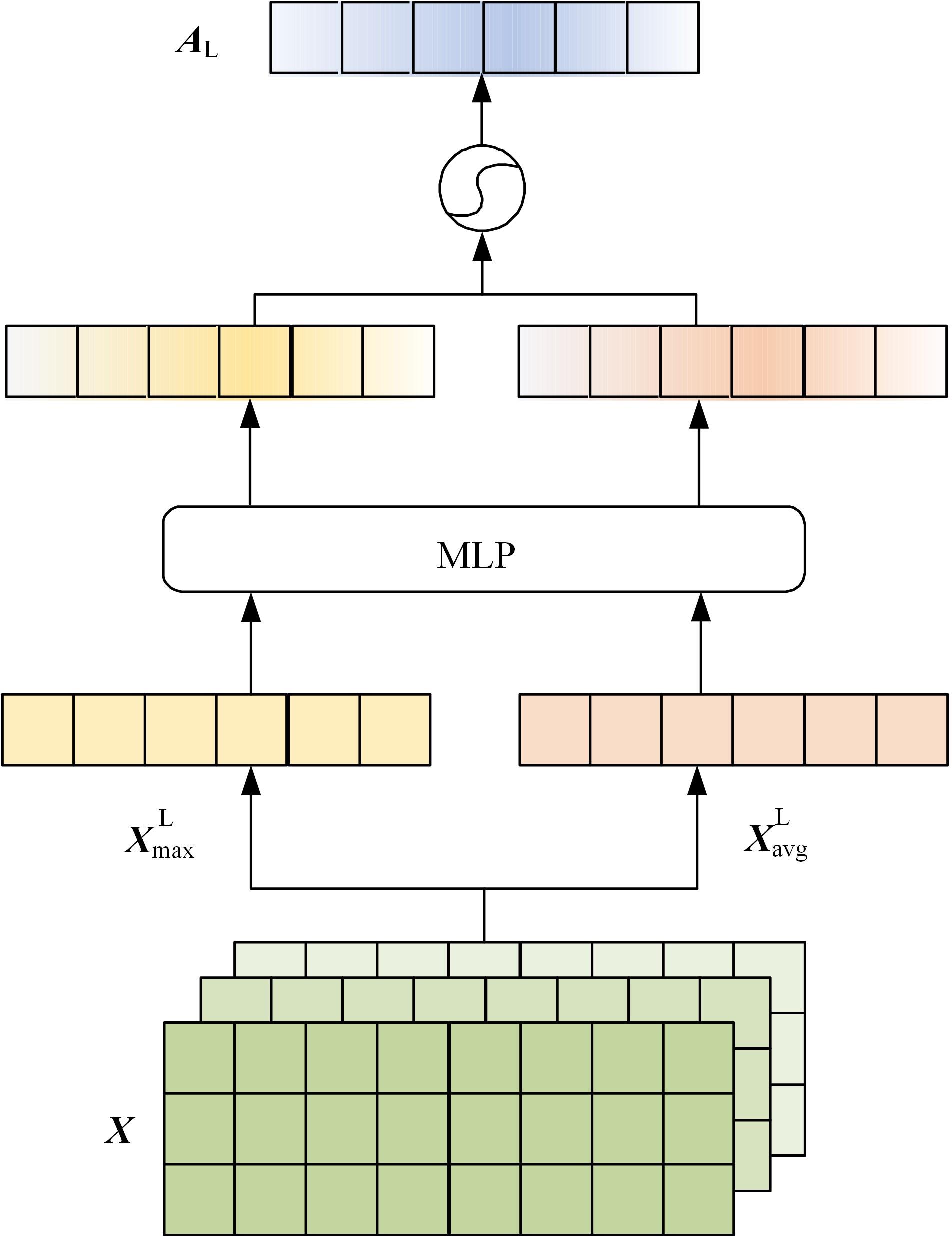
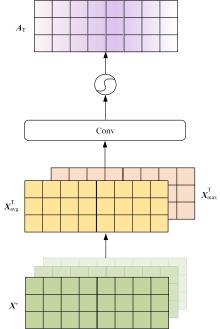
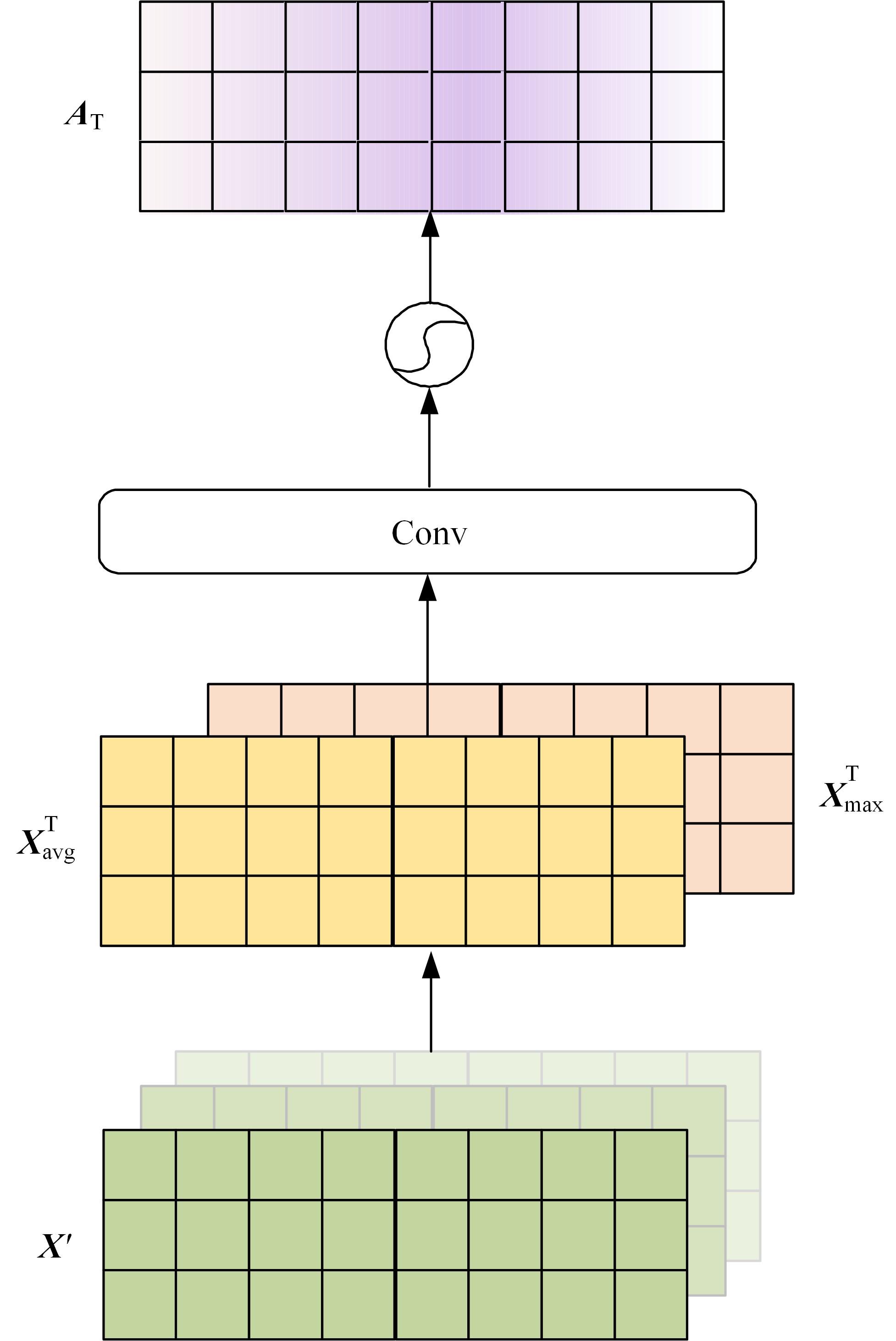
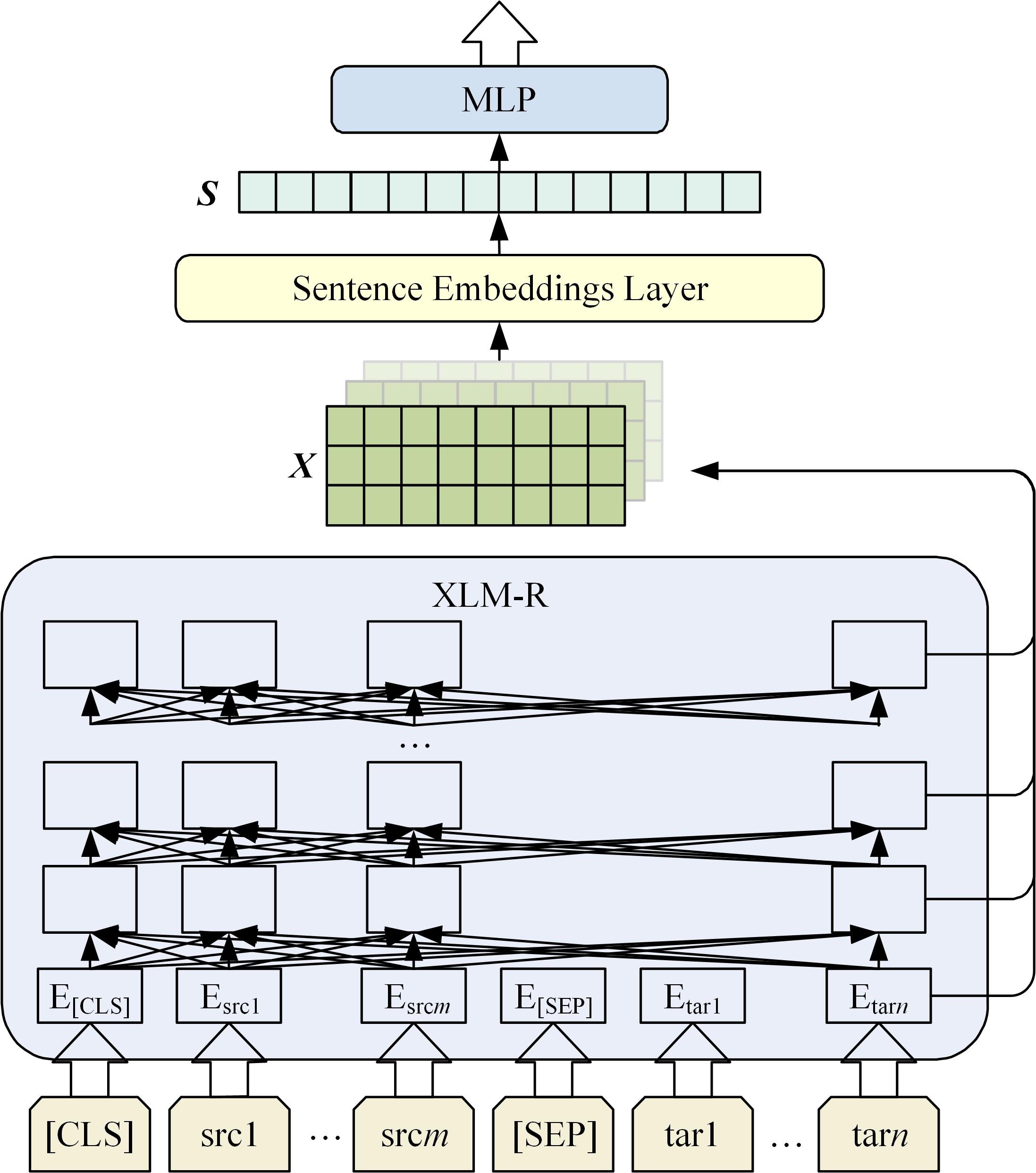
针对主流翻译质量评估框架在低资源语料上表现较差,句子嵌入策略单一的问题,提出了一个基于跨语言预训练模型的朝汉翻译质量评估模型。首先,借鉴注意力思想提出一种融合跨层信息和词项位置的句子嵌入方法;其次,将跨语言预训练模型引入翻译质量评估任务中,缓解朝鲜语低资源环境带来的数据稀疏问题;最后,对句向量进行回归,实现机器翻译质量评估任务。实验结果表明:该模型能有效提升朝汉翻译质量评估任务性能,与质量评估任务领域主流模型QuEst++、Bilingual Expert、TransQuest相比,皮尔逊相关系数分别提升了0.226、0.156、0.034,斯皮尔曼相关系数分别提升了0.123、0.038、0.026。
中图分类号:
- TP391.1
| 1 | Kim H, Lee J. Predictor-estimator using multilevel task learning with stack propagation for neural quality estimation[J]. ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-resource Language Information Processing, 2017, 2: 562-568. |
| 2 | Takahashi K, Sudoh K, Nakamura S. Automatic machine translation evaluation using source language inputs and cross-lingual language model[C]∥Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Seattle, Washington, United States, 2020: 3553-3558. |
| 3 | Ranasinghe T, Orasan C, Mitkov R. TransQuest: translation quality estimation with cross-lingual transformers[C]∥Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 5070-5081. |
| 4 | Jawahar G, Sagot B, Eddah D. What does BERT learn about the structure of language? [C]∥Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 2019: 3651-3657. |
| 5 | Pires T, Schlinger E, Garrette D. How multilingual is multilingual BERT? [C]∥Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 2019: 4996-5001. |
| 6 | Specia L, Shah K, Desouza J, et al. QuEst: a translation quality estimation framework[C]∥Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, Sofia, Bulgaria, 2013: 79-84. |
| 7 | Fan K, Wang J Y, Li B, et al. "Bilingual Expert" can find translation errors[C]∥Proceedings of the 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, United States, 2019: 6367-6374. |
| 8 | Liu Y H, Ott M, Goyal N, et al. RoBERTa: a robustly optimized bert pretraining approach[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020: 1-15. |
| 9 | Devlin J, Chang M, Lee K, et al. BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]∥Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, United States, 2019: 4171-4186. |
| 10 | Conneau A, Lample G. Cross-lingual language model pretraining[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2019, 32: 7059-7069. |
| 11 | Conneau A, Khandelwal K, Goyal N, et al. Unsupervised cross-lingual representation learning at scale[C]∥Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Seattle, Washington, United States, 2020: 8840-8451. |
| 12 | Arora S, Liang Y Y, Ma T Y. A simple but tough-to-beat baseline for sentence embeddings[C]∥Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017: 1-16. |
| 13 | Conneau A, Kiela D, Schwenk H, et al. Supervised learning of universal sentence representations from natural language inference data[C]∥Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 2017: 670-680. |
| 14 | Logeswaran L, Lee H. An efficient framework for learning sentence representations[C]∥Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Pennsylvania, United States, 2018: 1-16. |
| 15 | Reimers N, Gurevych I, Reimers N, et al. Sentence-BERT: sentence embeddings using siamese BERT-networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Hong Kong, China, 2019: 3982-3992. |
| 16 | Wang B, Kuo J. SBERT-WK: a sentence embedding method by dissecting BERT-based word models[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2020, 28: 2146-2157. |
| 17 | Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, United States, 2018: 7132-7141. |
| 18 | Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Antibes, France, 2018: 3-19. |
| 19 | 赵亚慧, 杨飞扬, 张振国, 等. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| Zhao Ya-hui, Yang Fei-yang, Zhang Zhen-guo, et al. Korean text structure discovery based on reinforcement learning and attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. | |
| 20 | 李健, 熊琦, 胡雅婷, 等. 基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的中文命名实体识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版,2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| Li Jian, Xiong Qi, Hu Ya-ting, et al. Chinese named entity recognition method based on transformer and hidden markov model[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [1] | 王连明,吴鑫. 基于姿态估计的物体3D运动参数测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2099-2108. |
| [2] | 张则强,梁巍,谢梦柯,郑红斌. 混流双边拆卸线平衡问题的精英差分进化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1297-1304. |
| [3] | 张振海,季坤,党建武. 基于桥梁裂缝识别模型的桥梁裂缝病害识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1418-1426. |
| [4] | 刘培勇,董洁,谢罗峰,朱杨洋,殷国富. 基于多支路卷积神经网络的磁瓦表面缺陷检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1449-1457. |
| [5] | 姜宇,潘家铮,陈何淮,符凌智,齐红. 基于分割方法的繁体中文报纸文本检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1146-1154. |
| [6] | 于鹏,朴燕. 基于多尺度特征的行人重识别属性提取新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1155-1162. |
| [7] | 潘弘洋,刘昭,杨波,孙庚,刘衍珩. 基于新一代通信技术的无人机系统群体智能方法综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 629-642. |
| [8] | 何颖,樊俊松,王巍,孙庚,刘衍珩. 无人机空地安全通信与航迹规划的多目标联合优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 913-922. |
| [9] | 吴振宇,刘小飞,王义普. 基于DKRRT*-APF算法的无人系统轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 781-791. |
| [10] | 陶博,颜伏伍,尹智帅,武冬梅. 基于高精度地图增强的三维目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 802-809. |
| [11] | 薛珊,张亚亮,吕琼莹,曹国华. 复杂背景下的反无人机系统目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 891-901. |
| [12] | 祁贤雨,王巍,王琳,赵玉飞,董彦鹏. 基于物体语义栅格地图的语义拓扑地图构建方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 569-575. |
| [13] | 时小虎,吴佳琦,吴春国,程石,翁小辉,常志勇. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| [14] | 郭鹏,赵文超,雷坤. 基于改进Jaya算法的双资源约束柔性作业车间调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 480-487. |
| [15] | 刘近贞,高国辉,熊慧. 用于脑组织分割的多尺度注意网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 576-583. |
|
||