吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (7): 1966-1977.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221179
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
多温度条件沥青混合料水稳定性评价指标阈值
罗蓉1,2( ),梁宇1,2,牛茏昌3,黄婷婷1,2,苗强1,2
),梁宇1,2,牛茏昌3,黄婷婷1,2,苗强1,2
- 1.武汉理工大学 交通与物流工程学院, 武汉 430063
2.湖北省公路工程技术研究中心, 武汉 430063
3.广州市高速公路有限公司, 广州 510289
Threshold value of water stability evaluation index of asphalt mixture under multi-temperature conditions
Rong LUO1,2( ),Yu LIANG1,2,Long-chang NIU3,Ting-ting HUANG1,2,Qiang MIAO1,2
),Yu LIANG1,2,Long-chang NIU3,Ting-ting HUANG1,2,Qiang MIAO1,2
- 1.School of Transportation and Logistics Engineering,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430063,China
2.Hubei Provincial Highway Engineering Technology Research Center,Wuhan 430063,China
3.Guangzhou Expressway Co. ,Ltd. ,Guangzhou 510289,China
摘要:
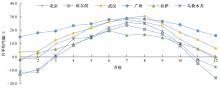
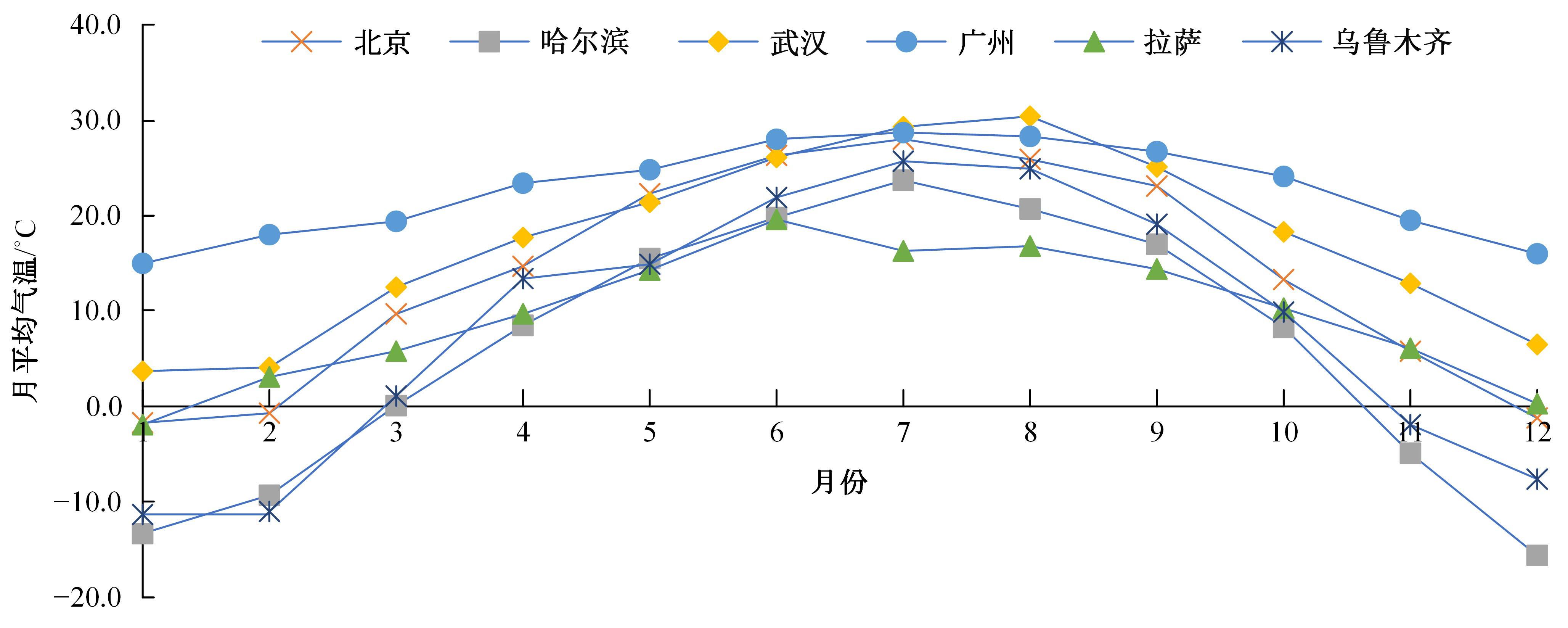
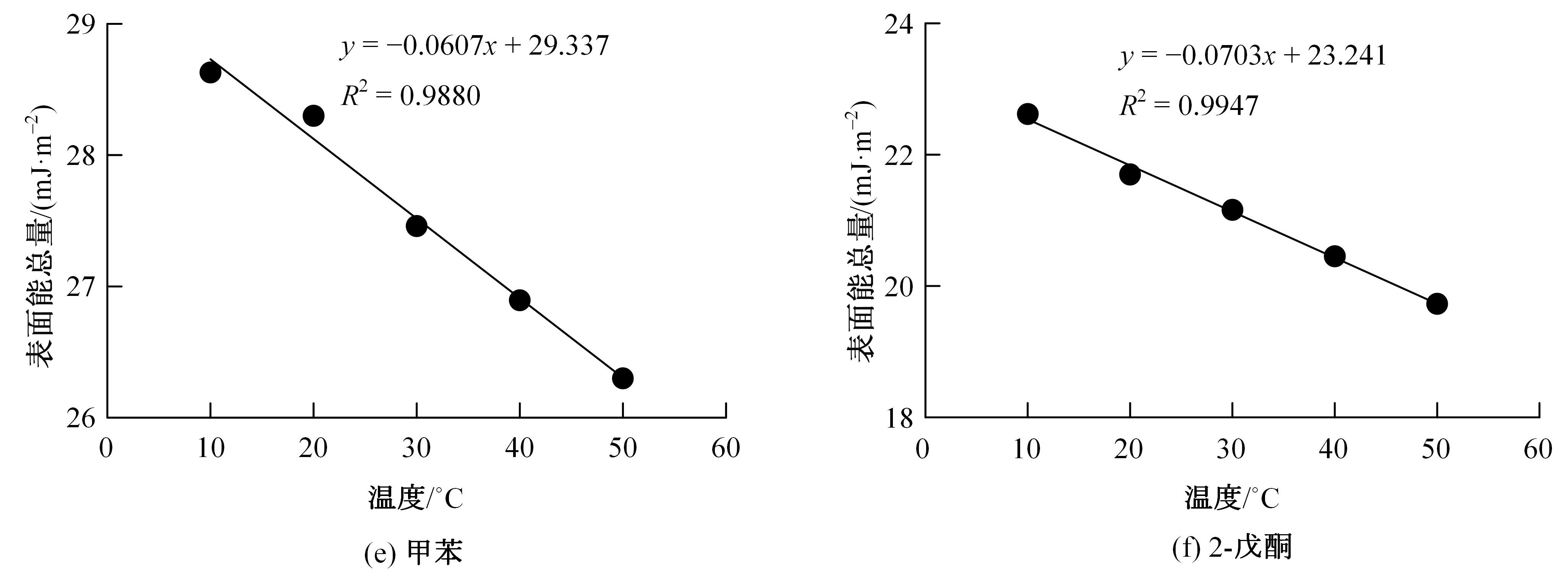
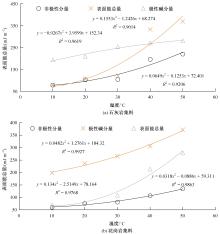
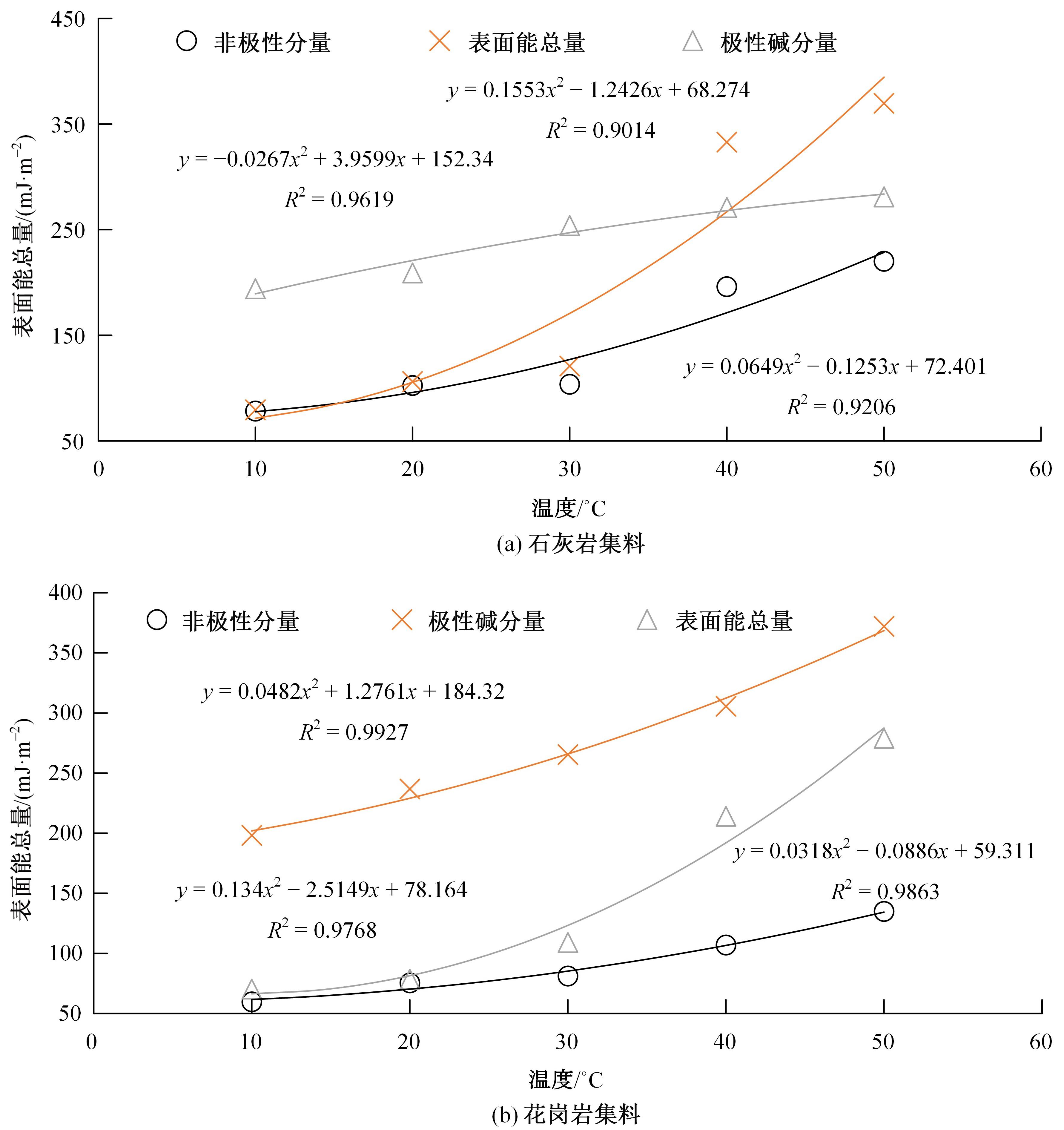
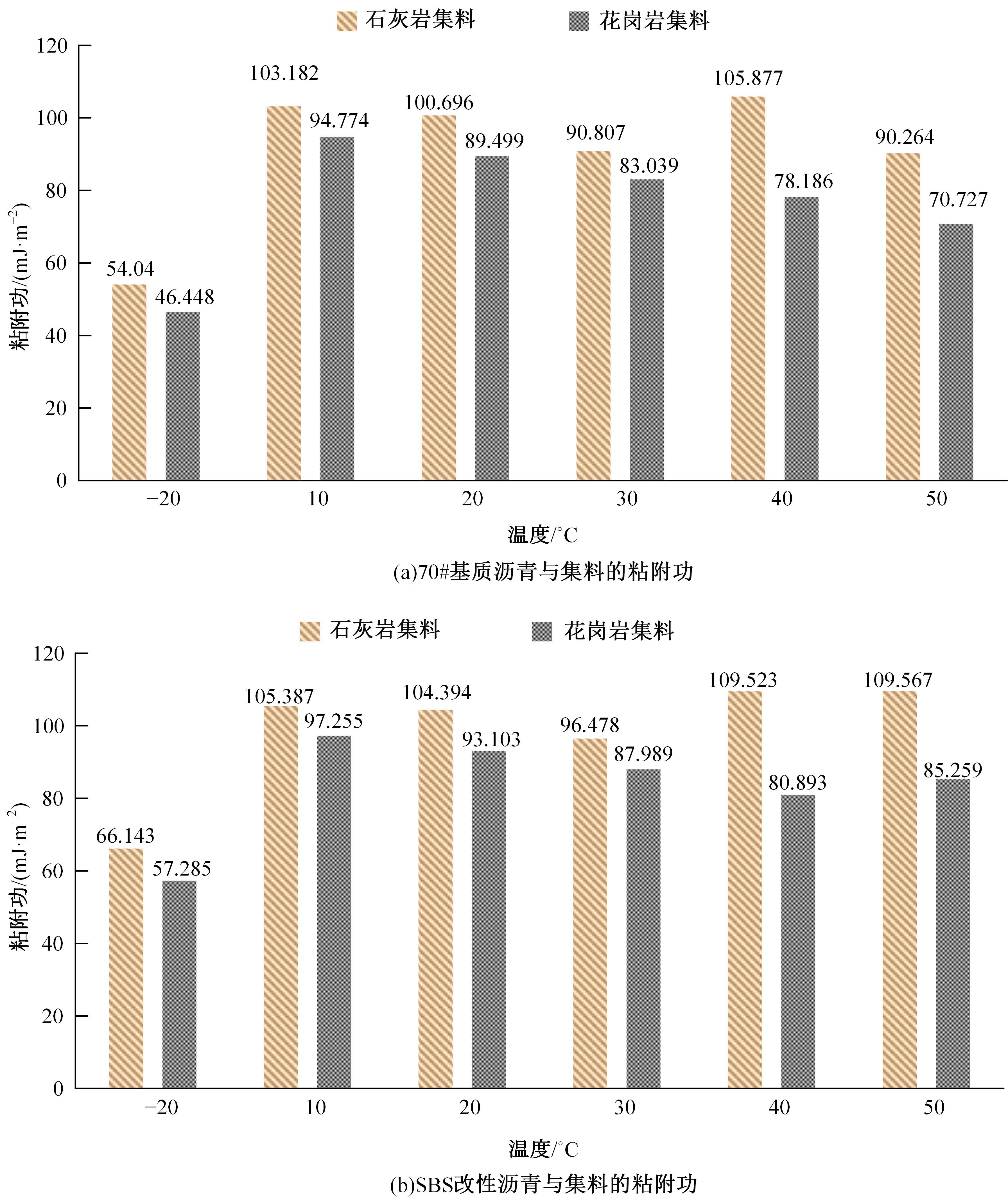
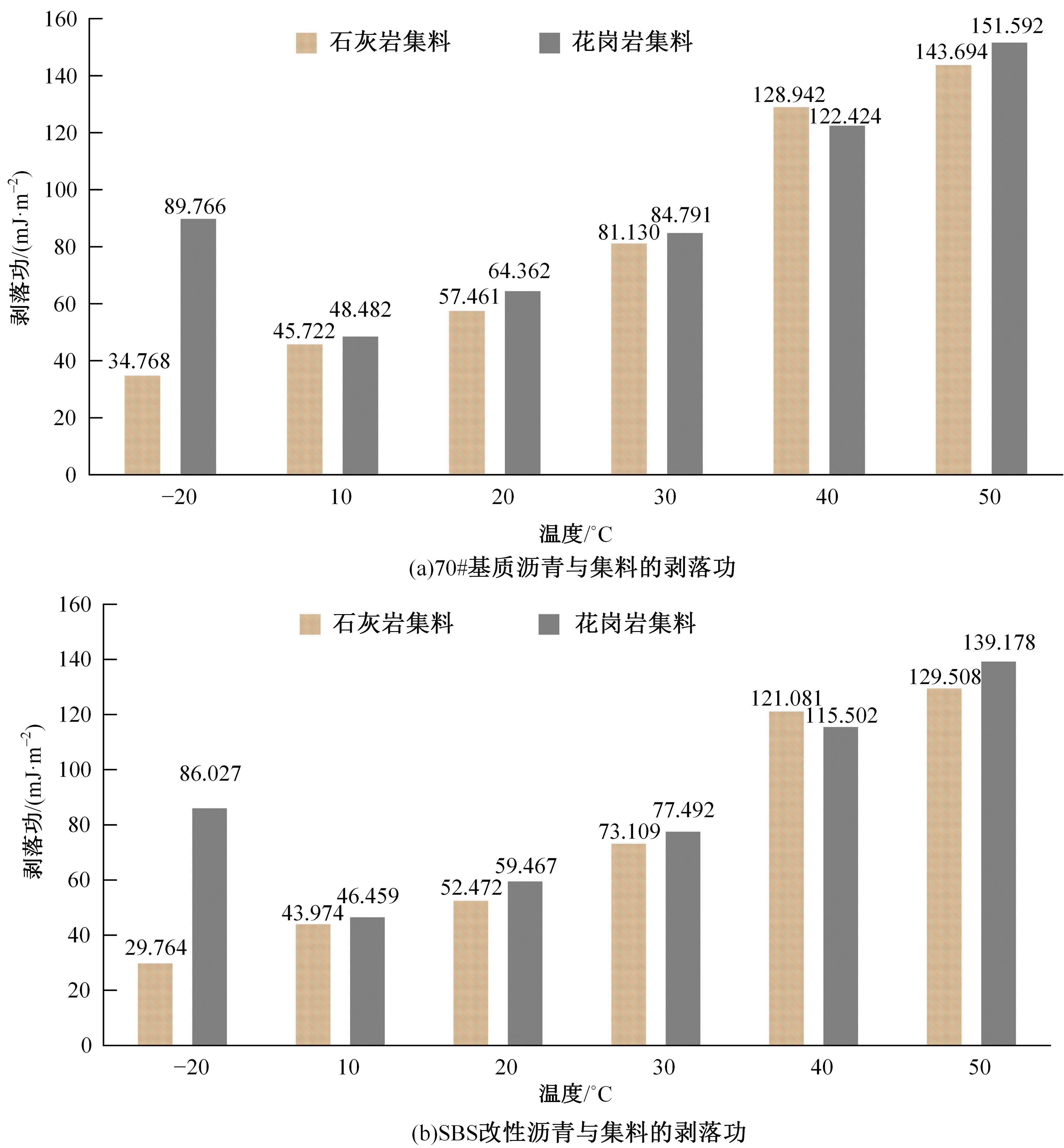
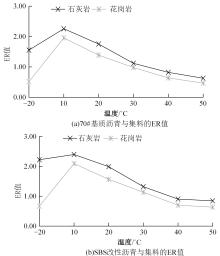
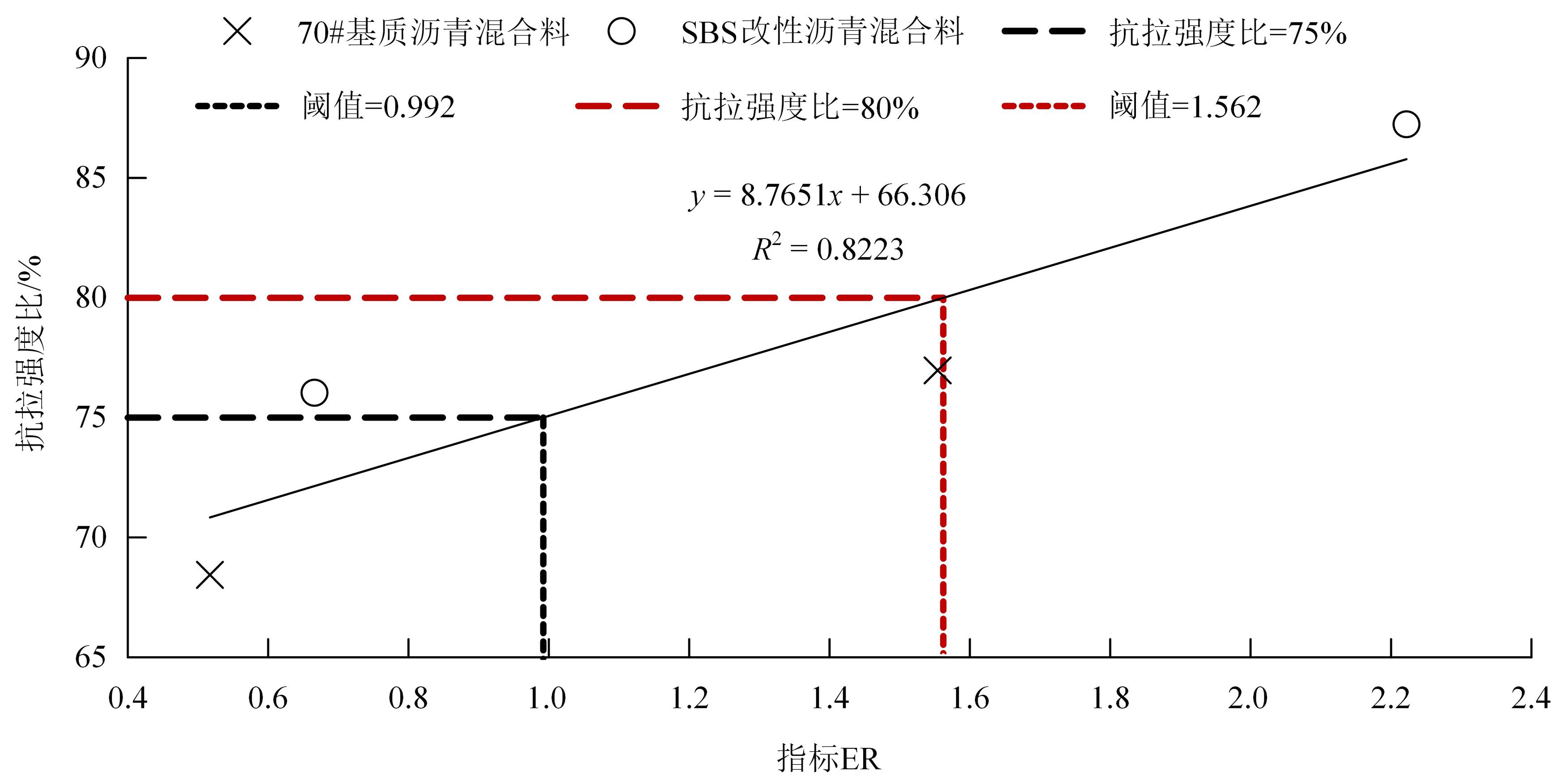
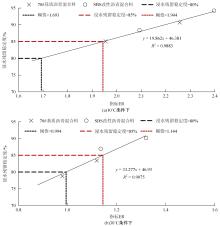
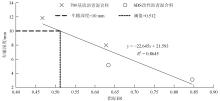
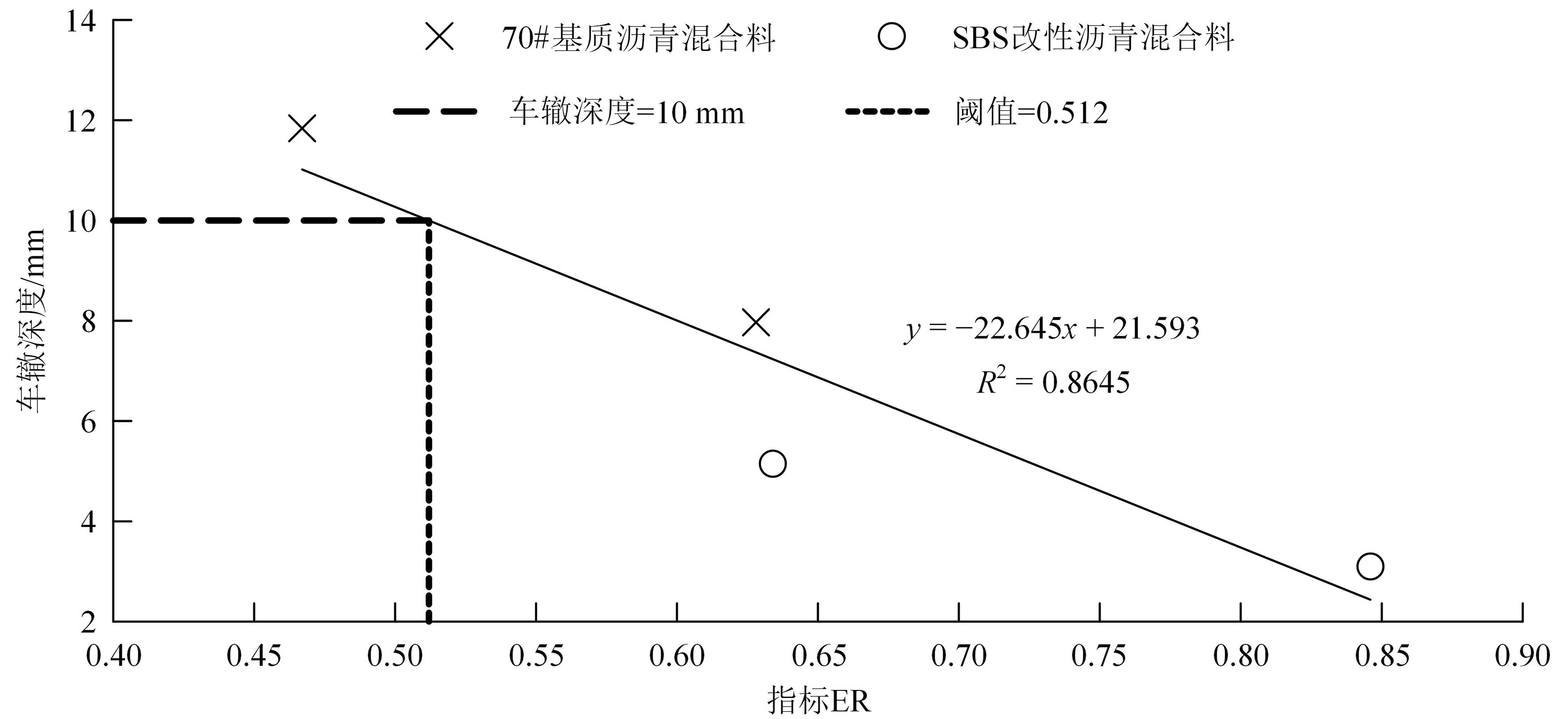
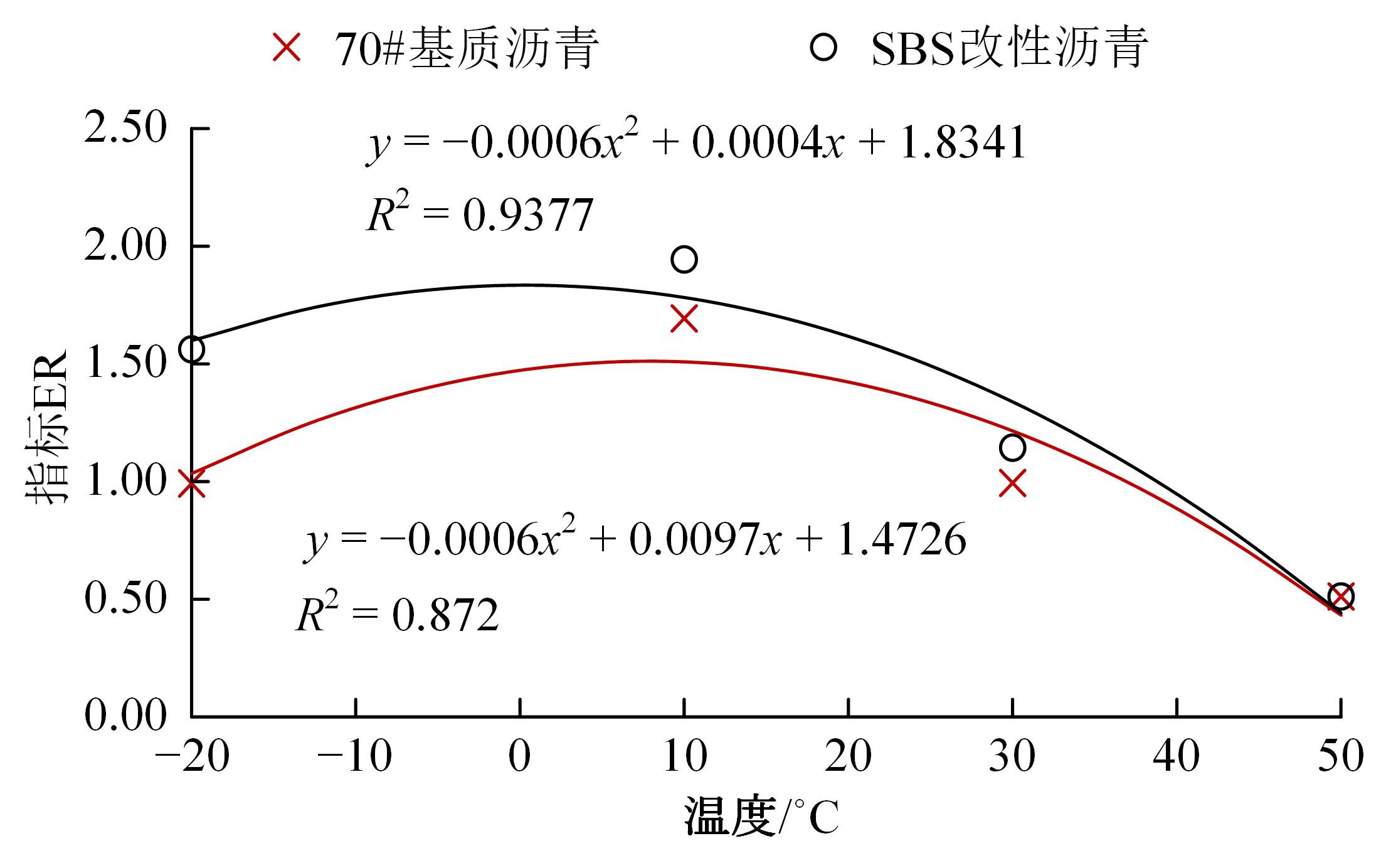
为预防与减少沥青路面水损害的发生,以表面能理论为基础、全国六大区域主要城市月平均气温为依据,结合表面能试验和宏观水稳定性试验两种评价方法来准确评价多温度条件下沥青混合料的水稳定性。首先,测试-20~50 ℃区间内原材料表面能,确定各温度条件下黏附性评价指标ER值;选用4种沥青混合料进行-20 ℃的5次冻融循环劈裂试验、10 ℃和30 ℃的浸水马歇尔试验以及50 ℃的浸水汉堡车辙试验,并借助以上3种宏观试验指标及其技术要求,依次确定对应于各温度点的指标ER阈值。试验结果表明:在-20、10、30、50 ℃条件下,基质沥青混合料的指标ER阈值分别为0.992、1.693、0.994和0.512;改性沥青混合料的指标ER阈值分别为1.562、1.944、1.144和0.512。进而以多温度条件下沥青混合料水稳定性评价指标阈值为基础,建立基质沥青混合料阈值与温度的关系模型为
中图分类号:
- U416.217
| 1 | Tan Y, Guo M. Using surface free energy method to study the cohesion and adhesion of asphalt mastic[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 47(10):254-260. |
| 2 | 韩森, 刘亚敏, 徐鸥明, 等. 材料特性对沥青-集料界面粘附性的影响[J]. 长安大学学报:自然科学版, 2010(3):10-13, 74. |
| Han Sen, Liu Ya-min, Xu Ou-ming, et al. Effect of material properties on adhesion of asphalt-aggregate interface[J]. Journal of Chang'an University: Natural Science Edition, 2010(3) :10-13, 74. | |
| 3 | 王勇. 基于表面能理论的沥青与集料粘附性研究[D]. 长沙:湖南大学土木工程学院, 2010. |
| Wang Yong. Study on adhesion between asphalt and aggregate based on surface energy theory[D]. Changsha:College of Civil Engineering, Hunan University, 2010. | |
| 4 | 张恺, 罗蓉, 张德润. 基于表面自由能理论的彩色树脂类沥青材料润湿性分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2016(5):34-40. |
| Zhang Kai, Luo Rong, Zhang De-run. Wettability analysis of colored resin asphalt materials based on surface free energy theory[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016(5): 34-40. | |
| 5 | 邓冲, 罗蓉, 钟昆志. 沥青-集料表面能指标与沥青混合料路用性能关系研究[J]. 公路, 2019(10):8-13. |
| Deng Chong, Luo Rong, Zhong Kun-zhi. Research on the relationship between asphalt-aggregate surface energy index and asphalt mixture road performance [J]. Highways, 2019(10) : 8-13. | |
| 6 | Little D N, Bhasin A. Using surface energy measurements to select materials for asphalt pavements[R]. Austin:Texas A & M University, 2006. |
| 7 | Liu Y W, Apeagyei A, Ahmad N, et al. Examination of moisture sensitivity of aggregate-bitumen bonding strength using loose asphalt mixture and physico-chemical surface energy property tests[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2014, 15(7):657-670. |
| 8 | 中华人民共和国国家统计局. 2021中国统计年鉴(资源和环境)[M]. 北京:中国统计出版社, 2021. |
| 9 | 李剑. 高速公路沥青路面早期水损害防治措施研究[D]. 西安:长安大学公路学院, 2003. |
| Li Jian. Research on prevention and control measures of Early water damage in asphalt pavement of expressway[D]. Xi 'an: School of Highway,Chang 'an University, 2003. | |
| 10 | 交通部公路科学研究所. 公路沥青路面施工技术规范[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社, 2004. |
| 11 | 交通部公路科学研究所. 公路工程沥青及沥青混合料试验规程[M]. 北京:人民交通出版社, 2011. |
| 12 | 陈龙龙. 高温多雨地区桥面铺装层设计与施工工艺研究[D]. 武汉:武汉理工大学交通学院, 2019. |
| Chen Long-long. Research on design and construction technology of bridge deck pavement in high temperature and rainy area[D].Wuhan: School of Transportation,Wuhan University of Technology, 2019. | |
| 13 | Zhao Q, Liu Y, Abel E W. Effect of temperature on the surface free energy of amorphous carbon films[J]. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2004, 280(1):174-183. |
| 14 | Bahramian A. Evaluating surface energy components of asphalt binders using Wilhelmy plate and Sessile drop techniques[J]. Highway & Railway Engineering, 2013. |
| 15 | 中华人民共和国交通部. 公路工程集料试验规程: [S]. 北京:人民交通出版社,2005. |
| 16 | Tex-242-F. Hamburg wheel-tracking test [S]. |
| [1] | 李义,白亚赛,梁继才,姚卫国,梁策. 轿车内饰件包覆成型过程温度场变化对制件成型质量的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1887-1893. |
| [2] | 李春凯,代悦,王嘉昕,顾玉芬,石玗,席保龙. 焊剂对焊接熔池液态金属表面张力的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1555-1562. |
| [3] | 李祖仲,李梦园,刘卫东,庞萧萧,唐豪,张学磊,马晨杨. 蔗渣纤维表面改性及其沥青混合料路用性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1738-1745. |
| [4] | 孙雅珍,薛博欣,孙岩,王志臣,潘嘉伟. 考虑非均匀性的沥青混合料开裂行为细观模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1708-1718. |
| [5] | 江虹,徐洪亮. 基于自纠正最小和的LDPC译码改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1136-1143. |
| [6] | 林新华,周子栋,邵淑芳,林威,张瑞. 双轴倾角传感器温度补偿方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 558-563. |
| [7] | 杨悦,赵培雷,马天惠,贾剑明. 碳纳米管掺杂3YSZ陶瓷的低温闪烧[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 394-399. |
| [8] | 高海龙,徐一博,刘坤,李春阳,卢晓煜. 基于多源数据融合的高速公路路网短时交通流参数实时预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 155-161. |
| [9] | 卫星,高亚杰,康志锐,刘宇辰,赵骏铭,肖林. 低温环境下栓钉环焊缝焊接残余应力场数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 198-208. |
| [10] | 赵胜前,丛卓红,游庆龙,李源. 沥青-集料黏附和剥落研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2437-2464. |
| [11] | 宫亚峰,吴树正,毕海鹏,谭国金. 基于现场监测技术的装配式箱涵温度场及冻胀分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2321-2331. |
| [12] | 杨悦,马天惠,赵培雷,贾剑明. 快速热压烧结制备立方相Li7La3Zr2O12固态电解质[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2272-2276. |
| [13] | 李新宇,凌贤长,曲娜. 考虑温度效应的冻结膨胀土统计损伤模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2339-2349. |
| [14] | 翁渊瀚,李南. 基于时间序列模型的文本数据压缩存储算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2109-2114. |
| [15] | 袁野. 温度和车辆作用下梁式桥梁结构固有频率分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1702-1710. |
|
||