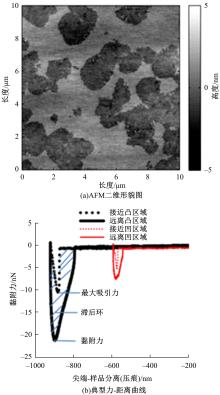
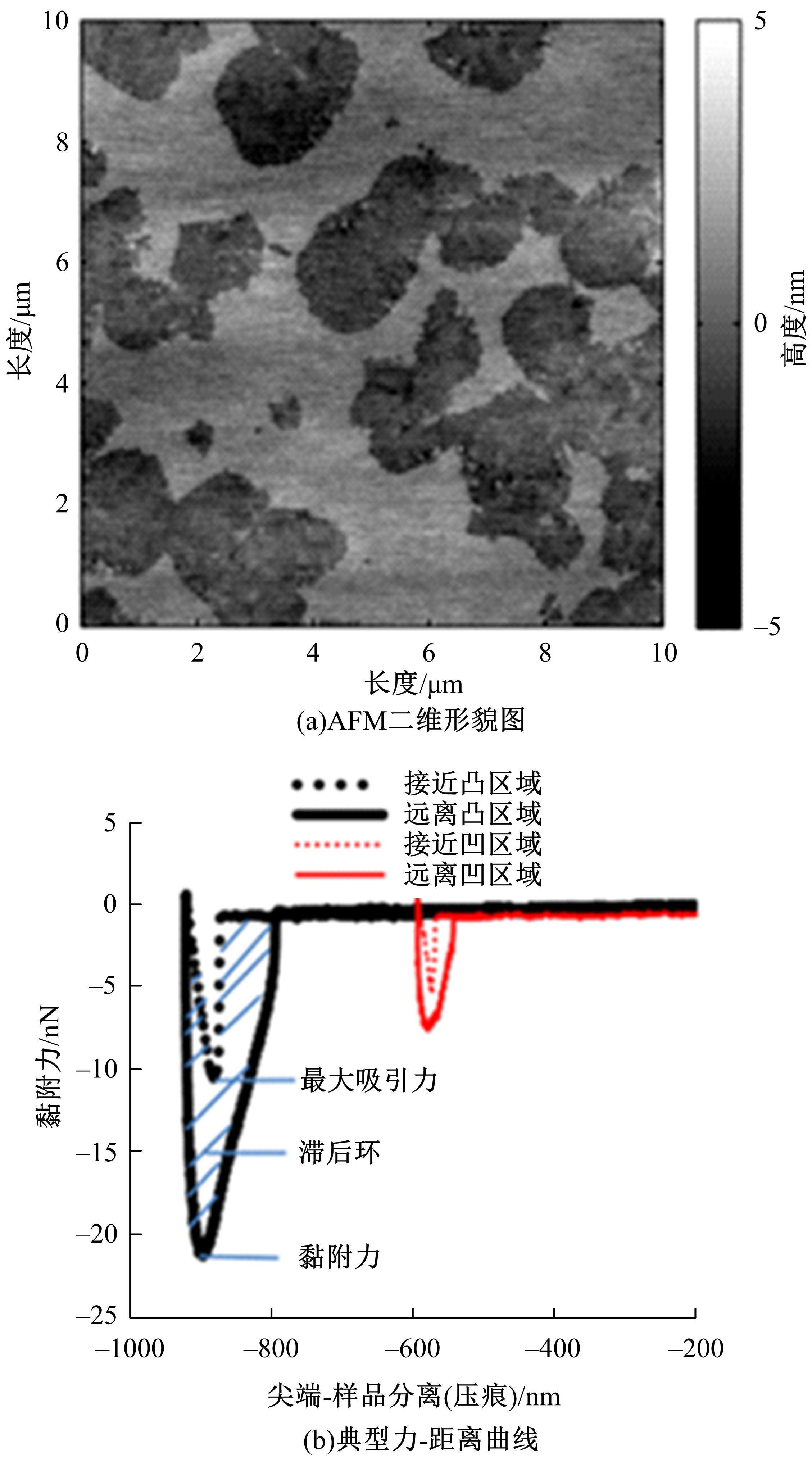
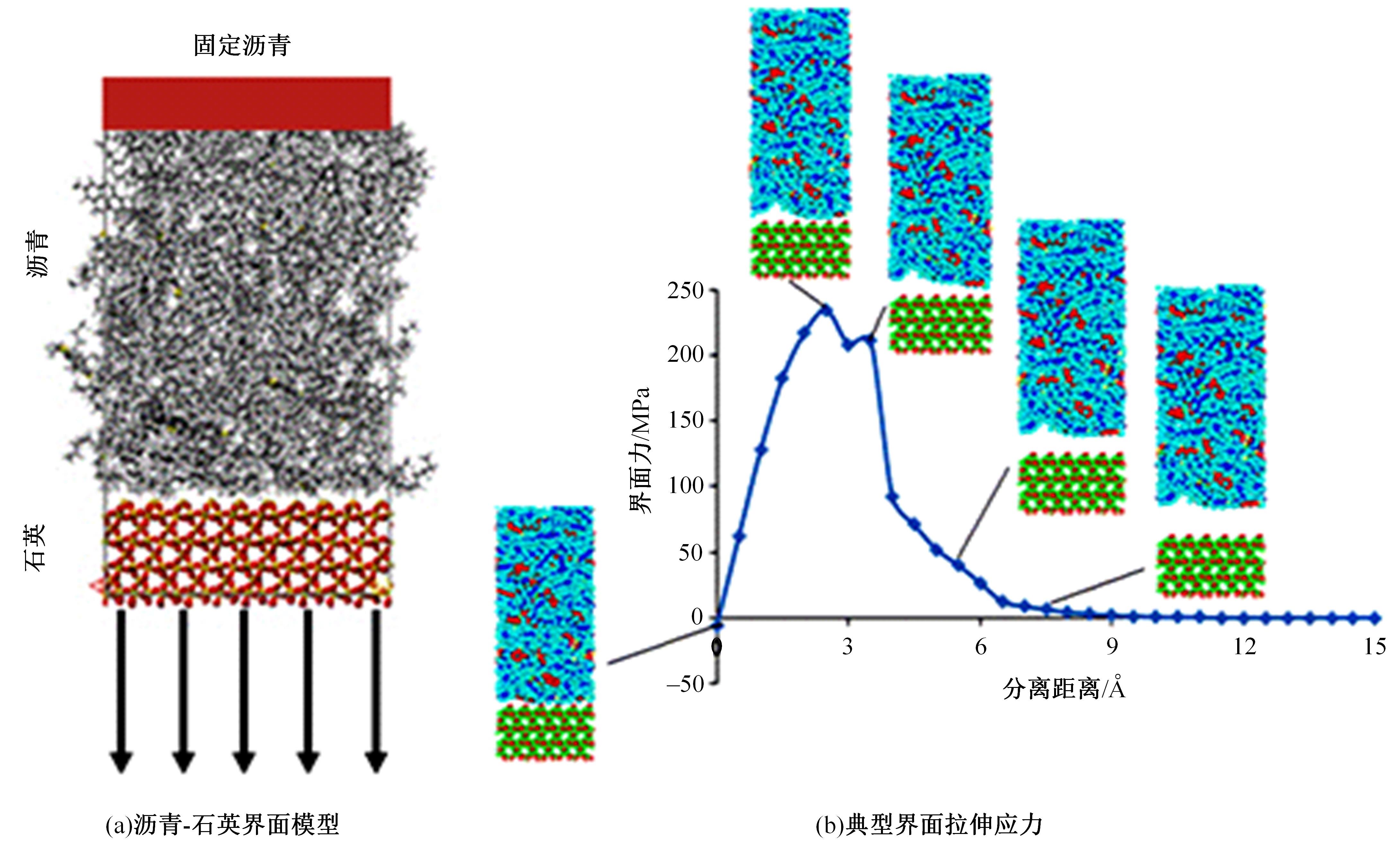
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (9): 2437-2464.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221433
• 综述 • 下一篇
沥青-集料黏附和剥落研究进展
- 1.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710064
2.长安大学 道路施工技术与装备教育部重点实验室,西安 710064
Adhesion and raveling property between asphalt and aggregate: a review
Sheng-qian ZHAO1( ),Zhuo-hong CONG2(
),Zhuo-hong CONG2( ),Qing-long YOU1,Yuan LI1
),Qing-long YOU1,Yuan LI1
- 1.School of Highway,Chang′an University,Xi′an 710064,China
2.Key Laboratory of Road Construction Technology & Equipment of Ministry of Education,Chang′an University,Xi′an 710064,China
摘要:
针对沥青-集料之间的黏附性能,对国内外黏附和剥落机理、评价体系、影响因素和改善措施4个方面的研究成果进行了综述。黏附的形成和失效是涉及物理、化学、热力学及微观力学的复杂过程,界面特征受材料特性、混合料空隙、沥青膜厚及外界环境等因素影响,不同试验体系致力于开发既能模拟损伤发生过程又能评估混合料适用性的方法,进而保证路面使用寿命。最后,结合已有研究内容,对未来研究方向进行了展望。
中图分类号:
- U416.217
| 1 | Guo F, Pei J, Zhang J, et al. Study on the adhesion property between asphalt binder and aggregate: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 256: No. 119474. |
| 2 | Mehrara A, Khodaii A. A review of state of the art on stripping phenomenon in asphalt concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 38: 423-442. |
| 3 | Canestrari F, Cardone F, Graziani A, et al. Adhesive and cohesive properties of asphalt-aggregate systems subjected to moisture damage[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2010, 11(): 11-32. |
| 4 | Caro S, Masad E, Bhasin A, et al. Moisture susceptibility of asphalt mixtures, part 1: mechanisms[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2008, 9(2): 81-98. |
| 5 | Kakar M R, Hamzah M O, Valentin J. A review on moisture damages of hot and warm mix asphalt and related investigations[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2015, 99: 39-58. |
| 6 | Soenen H, Vansteenkiste S, de Maeijer P K. Fundamental approaches to predict moisture damage in asphalt mixtures: state-of-the-art review[J]. Infrastructures, 2020, 5(2): No.20. |
| 7 | 王岚, 罗学东, 张琪, 等. 温拌胶粉改性沥青-集料粘附性及其体系水稳定性分析[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(8): 123-130. |
| Wang Lan, Luo Xue-dong, Zhang Qi, et al. Analysis of adhesion of warm mix rubber powder modified asphalt aggregates and water stability of the system[J]. Materals Reports, 2022, 36(8): 123-130. | |
| 8 | Ghabchi R, Singh D, Zaman M, et al. Micro-structural analysis of moisture-induced damage potential of asphalt mixes containing RAP[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 2016, 44(1): 194-205. |
| 9 | Kim Y R, Little D, Lytton R. Fatigue and healing characterization of asphalt mixtures[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2003, 15(1): 75-83. |
| 10 | Kim Y R, Little D N, Lytton R L. Effect of moisture damage on material properties and fatigue resistance of asphalt mixtures[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2004, 1891(1): 48-54. |
| 11 | Yu X, Burnham N A, Tao M. Surface microstructure of bitumen characterized by atomic force microscopy[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2015, 218: 17-33. |
| 12 | Yao H, Liu J, Xu M, et al. Discussion on molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of the asphalt materials[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 299: No.102565. |
| 13 | McBain J W, Hopkins D G. On adhesives and adhesive action[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1925, 29(2): 188-204. |
| 14 | Canestrari F, Ferrotti G, Cardone F, et al. Innovative testing protocol for evaluation of binder-reclaimed aggregate bond strength[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2014, 2444(1): 63-70. |
| 15 | Petersen J, Plancher H, Ensley E, et al. Chemistry of asphalt-aggregate interaction: relationship with pavement moisture-damage prediction test[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1982, 843: 95-104. |
| 16 | Hefer A W, Little D N, Lytton R L. A synthesis of theories and mechanisms of bitumen-aggregate adhesion including recent advances in quantifying the effects of water[J]. Journal of the Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists, 2005, 74(139): No.e196. |
| 17 | Huang S C, Branthaver J F, Robertson R E. Interaction of asphalt films with aggregate surfaces in the presence of water[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2002, 3(1): 23-48. |
| 18 | Petersen J C, Plancher H. Model studies and interpretive review of the competitive adsorption and water displacement of petroleum asphalt chemical functionalities on mineral aggregate surfaces[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 1998, 16(1/2): 89-131. |
| 19 | Tan Y, Guo M. Using surface free energy method to study the cohesion and adhesion of asphalt mastic[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 47: 254-260. |
| 20 | 陈燕娟. 酸性集料表面活化技术与粘附机理研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学材料科学与工程学院, 2012. |
| Chen Yan-juan.Surface activation technology of acid aggregate and adhesion mechanism[D]. Xi'an: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chang'an University, 2012. | |
| 21 | 任玉娜. 聚合物改性沥青粘聚性与粘附性研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东)化学化工学院, 2011. |
| Ren Yu-na. Research on cohesion and adhesion properties of polymer modified asphalt[D]. Qingdao: College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, China University of Petroleum, 2011. | |
| 22 | Ensley E K. Multilayer adsorption with molecular orientation of asphalt on mineral aggregate and other substrates[J]. Journal of Applied Chemistry and Biotechnology, 1975, 25(9): 671-682. |
| 23 | 庞骁奕. 基于AFM与表面能原理的沥青与集料粘附特性分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学交通科学与工程学院, 2015. |
| Pang Xiao-yi. Asphalt and aggregate adhesion characteristics analysis based on the principle of AFM and the surface energy[D]. Harbin: School of Transportation Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015. | |
| 24 | Huang S C, Robertson R E. Rheology of thin asphalt films in contact with aggregate[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2006, 7(2): 179-199. |
| 25 | Bagampadde U, Isacsson U, Kiggundu B M. Classical and contemporary aspects of stripping in bituminous mixes[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2004, 5(1): 7-43. |
| 26 | Caro S, Masad E, Bhasin A, et al. Moisture susceptibility of asphalt mixtures, part 2: characterisation and modelling[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2008, 9(2): 99-114. |
| 27 | 周卫峰. 沥青与集料界面粘附性研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学材料科学与工程学院, 2002. |
| Zhou Wei-feng. Study on adhesion of interface between asphalt and aggregate[D]. Xi'an: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chang'an University, 2002. | |
| 28 | 陈斌华. 基于光电比色法的沥青与矿料粘附效应研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学公路学院, 2014. |
| Chen Bin-hua. Based on the photoelectric colormetric method of asphalt and mineral aggregate adhesion effect [D]. Xi'an: School of Highway, Chang'an University, 2014. | |
| 29 | 宋艳茹, 张玉贞. 沥青粘附性能评价方法综述[J]. 石油沥青, 2005(3): 1-6. |
| Song Yan-ru, Zhang Yu-zhen. The evaluating methods' summary of asphalt adhesion[J]. Petroleum Asphalt, 2005(3): 1-6. | |
| 30 | Kanitpong K, Bahia H. Relating adhesion and cohesion of asphalts to the effect of moisture on laboratory performance of asphalt mixtures[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2005, 1901(1): 33-43. |
| 31 | Zhang J, Apeagyei A K, Airey G D, et al. Influence of aggregate mineralogical composition on water resistance of aggregate-bitumen adhesion[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 2015, 62: 45-54. |
| 32 | 徐青杰.沥青-集料黏附性能多尺度分析与评价方法研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学交通运输学院, 2020. |
| Xu Qing-jie. Multi-scale analysis and evaluation method of asphalt-aggregate adhesion [D]. Chongqing: College of Traffic and Transportation, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2020. | |
| 33 | 王威娜, 徐青杰, 周圣雄, 等. 沥青-集料黏附作用评价方法综述[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(13): 2197-2205. |
| Wang Wei-na, Xu Qing-jie, Zhou Sheng-xiong, et al. A review on evaluation methods of asphalt-aggregate adhesion[J]. Materials Reports, 2019, 33(13): 2197-2205. | |
| 34 | Blackman B R, Cui S, Kinloch A J, et al. The development of a novel test method to assess the durability of asphalt road-pavement materials[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 2013, 42: 1-10. |
| 35 | Cui S, Blackman B R, Kinloch A J, et al. Durability of asphalt mixtures: effect of aggregate type and adhesion promoters[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 2014, 54: 100-111. |
| 36 | Mo L T. Damage development in the adhesive zone and mortar of porous asphalt concrete[D]. Netherlands: Faculty of Civil Engineering and Geosciences, Delft University of Technology, 2010. |
| 37 | Kanitpong K, Bahia H U. Role of adhesion and thin film tackiness of asphalt binders in moisture damage of HMA (with discussion)[J]. Journal of the Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists, 2003, 72: 502-528. |
| 38 | Cho D W, Bahia H U. Effects of aggregate surface and water on rheology of asphalt films[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2007, 1998(1): 10-17. |
| 39 | 肖月. 沥青混合料中胶浆-集料粘结性及力学性能研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学材料科学与工程学院, 2008. |
| Xiao Yue. Fracture mechanisms of binder-aggregate system and its effect on properties of asphalt mixtures [D].Wuhan: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, 2008. | |
| 40 | Huang B, Shu X, Dong Q, et al. Laboratory evaluation of moisture susceptibility of hot-mix asphalt containing cementitious fillers[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2010, 22(7): 667-673. |
| 41 | Varveri A, Avgerinopoulos S, Scarpas A. Experimental evaluation of long-and short-term moisture damage characteristics of asphalt mixtures[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2016, 17(1): 168-186. |
| 42 | Collop A C, Choi Y, Airey G. Effects of pressure and aging in SATS test[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2007, 133(11): 618-624. |
| 43 | Abed A H, Qasim Z I, Al-Mosawe H, et al. The effect of hybrid anti-stripping agent with polymer on the moisture resistance of hot-mix asphalt mixtures[J]. Cogent Engineering, 2019, 6(1): No.1659125. |
| 44 | Murshed A M, Tandon V, Nazarian S, et al. Identification of moisture-susceptible asphalt concrete mixes using modified environmental conditioning system[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1998, 1630(1): 106-116. |
| 45 | Al-Swailmi S, Terrel R L. Evaluation of water damage of asphalt Concrete mixtures using the environmental conditioning system (Ecs)(with discussion)[J]. Journal of the Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists, 1992, 61: 405-445. |
| 46 | 任敏达, 冯汉卿, 丛林, 等. 沥青混合料饱水过程的强度演化规律及机理分析[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2022, 25(5): 537-544. |
| Ren Min-da, Feng Han-qing, Cong Lin, et al. Strength evolution law and mechanism analysis of asphalt mixtures during water saturation[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2022, 25(5): 537-544. | |
| 47 | Zhou L, Huang W, Xiao F, et al. Shear adhesion evaluation of various modified asphalt binders by an innovative testing method[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 183: 253-263. |
| 48 | Kim Y R, Lutif J S, Bhasin A, et al. Evaluation of moisture damage mechanisms and effects of hydrated lime in asphalt mixtures through measurements of mixture component properties and performance testing[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2008, 20(10): 659-667. |
| 49 | Copeland A R, Youtcheff J, Shenoy A. Moisture sensitivity of modified asphalt binders: factors influencing bond strength[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2007, 1998(1): 18-28. |
| 50 | Wasiuddin N M, Saltibus N E, Mohammad L N. Novel moisture-conditioning method for adhesive failure of hot-and warm-mix asphalt binders[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2011, 2208(1): 108-117. |
| 51 | Moraes R, Velasquez R, Bahia H U. Measuring the effect of moisture on asphalt-aggregate bond with the bitumen bond strength test[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2011, 2209(1): 70-81. |
| 52 | Mogawer W S, Austerman A J, Bahia H U. Evaluating the effect of warm-mix asphalt technologies on moisture characteristics of asphalt binders and mixtures[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2011, 2209(1): 52-60. |
| 53 | Júnior J L L, Babadopulos L F, Soares J B. Moisture-induced damage resistance, stiffness and fatigue life of asphalt mixtures with different aggregate-binder adhesion properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 216: 166-175. |
| 54 | Bagampadde U, Isacsson U, Kiggundu B. Impact of bitumen and aggregate composition on stripping in bituminous mixtures[J]. Materials and Structures, 2006, 39(3): 303-315. |
| 55 | Bagampadde U, Isacsson U, Kiggundu B. Influence of aggregate chemical and mineralogical composition on stripping in bituminous mixtures[J]. The international Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2005, 6(4): 229-239. |
| 56 | 豆莹莹, 李晓民, 姚志杰, 等. 基于表面自由能的再生沥青粘附性及其水稳定性[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2020, 38(4): 648-653. |
| Dou Ying-ying, Li Xiao-min, Yao Zhi-jie, et al. Adhesion and water stability of regenerated asphalt based on surface free energy[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Engineering, 2020, 38(4): 648-653. | |
| 57 | 成志强, 张晓燕, 孔繁盛, 等. 利用表面能理论及拉脱试验分析沥青膜的剥离行为[J]. 材料导报,2020,34():1288-1294. |
| Cheng Zhi-qiang, Zhang Xiao-yan, Kong Fan-sheng,et al. Investigation on stripping behavior of asphalt Film using surface energy theory and pull-off test[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(Sup.2): 1288-1294. | |
| 58 | Wasiuddin N M, Zaman M M, ORear E A. Effect of sasobit and aspha-min on wettability and adhesion between asphalt binders and aggregates[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2008, 2051(1): 80-89. |
| 59 | Bhasin A, Little D N, Vasconcelos K L, et al. Surface free energy to identify moisture sensitivity of materials for asphalt mixes[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2007, 2001(1): 37-45. |
| 60 | Wang W, Shen A, Yang X, et al. Surface free energy method for evaluating the effects of anti-stripping agents on the moisture damage to asphalt mixtures[J]. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology, 2020, 34(18): 1947-1970. |
| 61 | Hamedi G H, Moghadas Nejad F. Using energy parameters based on the surface free energy concept to evaluate the moisture susceptibility of hot mix asphalt[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2015, 16(2): 239-255. |
| 62 | Al-Rawashdeh A S, Sargand S. Performance assessment of a warm asphalt binder in the presence of water by using surface free energy concepts and nanoscale techniques[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2014, 26(5): 803-811. |
| 63 | 王端宜, 郭秀林, 唐成. 基于真实沥青膜厚的沥青与集料黏结性能评价与验证[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2021, 24(3): 624-629. |
| Wang Duan-lin, Guo Xiu-lin, Tang Cheng. Bonding performance evaluation and verification between asphalt and aggregate based on true asphalt film thickness[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2021, 24(3): 624-629. | |
| 64 | Yi J, Pang X, Feng D, et al. Studies on surface energy of asphalt and aggregate at different scales and bonding property of asphalt-aggregate system[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2018, 19(5): 1102-1125. |
| 65 | Moraes R, Velasquez R, Bahia H. Using bond strength and surface energy to estimate moisture resistance of asphalt-aggregate systems[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 130: 156-170. |
| 66 | Guo M, Tan Y, Zhou S. Multiscale test research on interfacial adhesion property of cold mix asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 68: 769-776. |
| 67 | Kim S H, Jeong J H, Kim N. Use of surface free energy properties to predict moisture damage potential of asphalt concrete mixture in cyclic loading condition[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2003, 7(4): 381-387. |
| 68 | Arabani M, Hamedi G H. Using the surface free energy method to evaluate the effects of polymeric aggregate treatment on moisture damage in hot-mix asphalt[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2011, 23(6): 802-811. |
| 69 | Hamedi G H. Effects of polymeric coating the aggregate surface on reducing moisture sensitivity of asphalt mixtures[J]. International Journal of Civil Engineering, 2018, 16(9): 1097-1107. |
| 70 | 马翔, 胡绪泉, 王丽丽, 等. 基于表面自由能研究水温耦合作用对沥青黏结性能的影响[J]. 森林工程, 2022, 38(4): 140-146. |
| Ma Xiang, Hu Xu-quan, Wang Li-li. Study on the effect of water temperature coupling on asphalt bond performance based on surface free energy[J]. Forest Engineering, 2022, 38(4): 140-146. | |
| 71 | 冯浩浩, 苗强, 李振纲, 等. 基于表面能理论的再生集料与沥青黏附性影响研究[J/OL]. [2022-11-05]. |
| 72 | Hamedi G H, Moghadas N F. Evaluating the effect of mix design and thermodynamic parameters on moisture sensitivity of hot mix asphalt[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2017, 29(2): No.04016207. |
| 73 | Masad E A, Zollinger C, Bulut R, et al. Characterization of HMA moisture damage using surface energy and fracture properties (With Discussion)[J]. Journal of the Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists, 2006, 75: 713-754. |
| 74 | Loeber L, Sutton O, Morel J, et al. New direct observations of asphalts and asphalt binders by scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 1996, 182(1): 32-39. |
| 75 | Das P K, Baaj H, Tighe S, et al. Atomic force microscopy to investigate asphalt binders: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2016, 17(3): 693-718. |
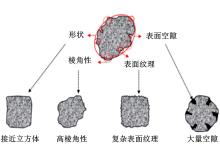
| 76 | Tarefder R, Arifuzzaman M. A study of moisture damage in plastomeric polymer modified asphalt binder using functionalized AFM tips[J]. Journal of Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics, 2011, 9(5): 1-12. |
| 77 | Yao Z, Zhu H, Gong M, et al. Characterization of asphalt materials' moisture susceptibility using multiple methods[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 155: 286-295. |
| 78 | 易军艳, 庞骁奕, 姚冬冬, 等. 基于原子力显微镜技术的沥青与矿料表面粗糙度及黏附特性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(5): 1111-1121. |
| Yi Jun-yan, Pang Xiao-yi, Yao Dong-dong, et al. Characterization of surface roughness and adhesive mechanism of asphalt and mineral aggregate based on atomic force microscopy method[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2017, 34(5): 1111-1121. | |
| 79 | Xu M, Yi J, Feng D, et al. Analysis of adhesive characteristics of asphalt based on atomic force microscopy and molecular dynamics simulation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(19): 12393-12403. |
| 80 | Vasconcelos K L, Bhasin A, Little D N. History dependence of water diffusion in asphalt binders[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2011, 12(5): 497-506. |
| 81 | dos Santos S, Partl M N, Poulikakos L D. Newly observed effects of water on the microstructures of bitumen surface[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 71: 618-627. |
| 82 | Lyne Å L, Wallqvist V, Birgisson B. Adhesive surface characteristics of bitumen binders investigated by atomic force microscopy[J]. Fuel, 2013, 113: 248-256. |
| 83 | Yu X, Burnham N A, Mallick R B, et al. A systematic AFM-based method to measure adhesion differences between micron-sized domains in asphalt binders[J]. Fuel, 2013, 113: 443-447. |
| 84 | 邓越, 孙国强, 余可心, 等. 沥青混合料水损坏微纳观尺度研究方法(1)——AFM的应用[J]. 石油沥青, 2018, 32(1): 31-37. |
| Deng Yue, Sun Guo-qiang, Yu Ke-xin, et al. Micro-Nano scale research methods for moisture damage of asphalt mixtures (1)—the application of AFM[J]. Petroleum Asphalt, 2018, 32(1): 31-37. | |
| 85 | 刘克非, 邓林飞, 郑佳宇, 等. 不同沥青结合料水损害的纳米尺度研究[J]. 材料研究学报, 2016, 30(10): 773-780. |
| Liu Ke-fei, Deng Lin-fei, Zheng Jia-yu, et al. Moisture induced damage of various asphalt binders[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2016, 30(10): 773-780. | |
| 86 | Tarefder R A, Zaman A M. Nanoscale evaluation of moisture damage in polymer modified asphalts[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2010, 22(7): 714-725. |
| 87 | Medendorp C A. Atomic force microscopy method development for surface energy analysis[D]. Kentucky:College of Pharmacy, University of Kentucky, 2011. |
| 88 | Chen Z, Pei J, Li R, et al. Performance characteristics of asphalt materials based on molecular dynamics simulation—a review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 189: 695-710. |
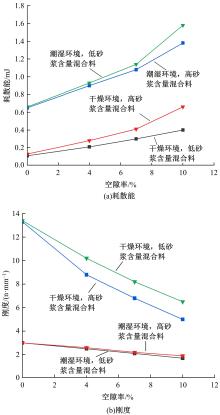
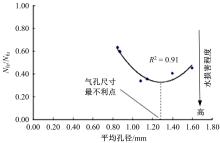
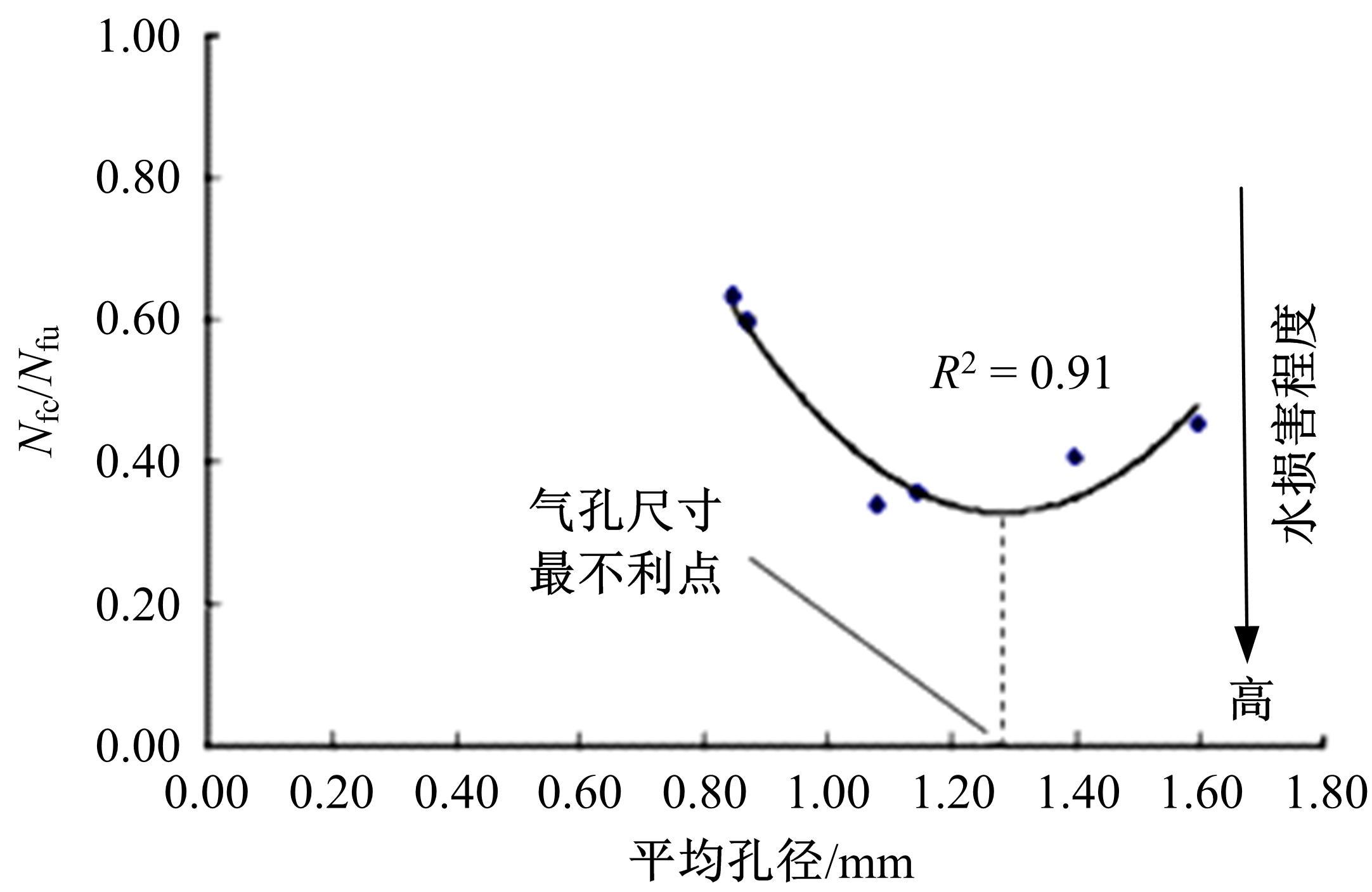
| 89 | Pauli A T, Miknis F, Beemer A, et al. Assessment of physical property prediction based on asphalt average molecular structures[C]∥Chemistry of Petroleum and Emerging Technologies, Washington, DC,USA, 2005, 50(2): 255-259. |
| 90 | Zhang L, Greenfield M L. Analyzing properties of model asphalts using molecular simulation[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2007, 21(3): 1712-1716. |
| 91 | Zhang L, Greenfield M L. Effects of polymer modification on properties and microstructure of model asphalt systems[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2008, 22(5): 3363-3375. |
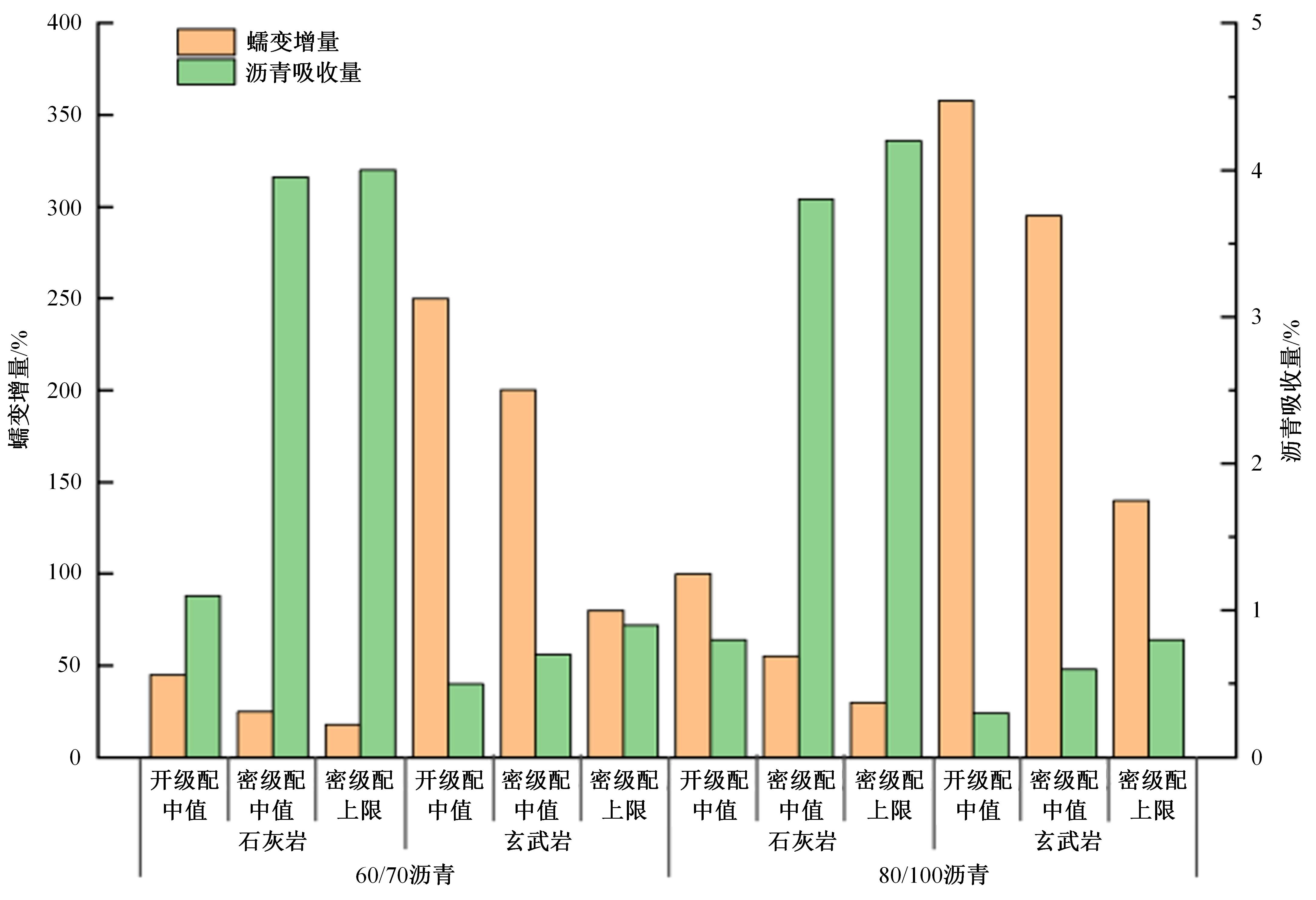
| 92 | Hansen J S, Lemarchand C A, Nielsen E, et al. Four-component united-atom model of bitumen[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2013, 138(9): No.094508. |
| 93 | Li D D, Greenfield M L. Chemical compositions of improved model asphalt systems for molecular simulations[J]. Fuel, 2014, 115: 347-356. |
| 94 | Xu M, Yi J, Qi P, et al. Improved chemical system for molecular simulations of asphalt[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(4): 3187-3198. |
| 95 | 马建民, 孙国强, 胡明君, 等. 沥青混合料水损坏微纳观尺度研究方法(3)—分子动力学模拟[J]. 石油沥青, 2018, 32(3): 42-47, 59. |
| Ma Jian-min, Sun Guo-qiang, Hu Ming-jun, et al.Micro-Nano scale research methods for the moisture damage of asphalt mixtures(3)—molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Petroleum Asphalt, 2018, 32(3): 42-47, 59. | |
| 96 | Sun W, Wang H. Moisture effect on nanostructure and adhesion energy of asphalt on aggregate surface: a molecular dynamics study[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 510: No.145435. |
| 97 | Xu G, Wang H. Molecular dynamics study of interfacial mechanical behavior between asphalt binder and mineral aggregate[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 121: 246-254. |
| 98 | Wang H, Lin E, Xu G. Molecular dynamics simulation of asphalt-aggregate interface adhesion strength with moisture effect[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2017, 18(5): 414-423. |
| 99 | Yao H, Dai Q, You Z. Chemo-physical analysis and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation of moisture susceptibility of nano hydrated lime modified asphalt mixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 101: 536-547. |
| 100 | Zheng C, Shan C, Liu J, et al. Microscopic adhesion properties of asphalt-mineral aggregate interface in cold area based on molecular simulation technology[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 268: No.121151. |
| 101 | Luo L, Chu L, Fwa T. Molecular dynamics analysis of moisture effect on asphalt-aggregate adhesion considering anisotropic mineral surfaces[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 527: No.146830. |
| 102 | Lu Y, Wang L. Nanoscale modelling of mechanical properties of asphalt-aggregate interface under tensile loading[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2010, 11(5): 393-401. |
| 103 | Lu Y, Wang L. Atomistic modelling of moisture sensitivity: a damage mechanisms study of asphalt concrete interfaces[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2017, 18(Sup.3): 200-214. |
| 104 | Swamy A K, Matolia V, Ramana G. Interrelationship between uncompacted void content of aggregates and asphalt concrete properties[J]. Particulate Science and Technology, 2019, 37(5): 623-631. |
| 105 | 王志祥, 李建阁, 张争奇. 集料形态特征对集料-沥青黏附及水稳定性的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2021, 24(5): 1039-1047. |
| Wang Zhi-xiang, Li Jian-ge, Zhang Zheng-qi. Effects of aggregate morphological characteristics on adhesion of aggregate‑asphalt and its moisture stability[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2021, 24(5): 1039-1047. | |
| 106 | 王璐. 沥青-集料界面相结构和粘附机理研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学公路学院, 2014. |
| Wang Lu. Investigation of the interface structure and adhesion mechanism between asphalt and aggregate[D]. Xi'an: School of Highway, Chang'an University, 2014. | |
| 107 | 苏文超. 碎石颗粒形状对沥青混合料性能影响的试验研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学交通运输工程学院, 2013. |
| Su Wen-chao. Experimental study on gravel particle shape effect on the performance of asphalt mixture[D]. Changsha: School of Traffic & Transportation Engineering, Changsha University, 2013. | |
| 108 | Airey G, Collop A, Zoorob S, et al. The influence of aggregate, filler and bitumen on asphalt mixture moisture damage[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2008, 22(9): 2015-2024. |
| 109 | Cala A, Caro S, Lleras M, et al. Impact of the chemical composition of aggregates on the adhesion quality and durability of asphalt-aggregate systems[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 216: 661-672. |
| 110 | 虞将苗, 周文理. 宏纳观多尺度集料-沥青粘附性评价[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(2): 2052-2056. |
| Yu Jiang-miao, Zhou Wen-li. Experimental study on gravel particle shape effect on the performance of asphalt mixture[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(2): 2052-2056. | |
| 111 | Blazek J, Sebor G, Maxa D. Effect of aggregate composition on asphalt-aggregate adhesion[J]. Petroleum and Coal, 2000, 42(1): 46-51. |
| 112 | Huang M, Zhang H, Gao Y, et al. Study of diffusion characteristics of asphalt-aggregate interface with molecular dynamics simulation[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2021, 22(3): 319-330. |
| 113 | Wang H, Wang J, Chen J. Micromechanical analysis of asphalt mixture fracture with adhesive and cohesive failure[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2014, 132: 104-119. |
| 114 | Hossain M I, Tarefder R A. Identifying damage in asphalt matrix materials surrounding an aggregate particle[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 49: 536-546. |
| 115 | Abo Q S, Al S H. Effect of aggregate properties on asphalt mixtures stripping and creep behavior[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2007, 21(9): 1886-1898. |
| 116 | 豆莹莹, 魏定邦, 李晓民, 等. 沥青-集料界面黏附性衰减机理研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2019, 22(5): 771-779. |
| Dou Ying-ying, Wei Ding-bang, Li Xiao-min,et al. Adhesion attenuation mechanism of asphalt-aggregate interface[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2019, 22(5): 771-779. | |
| 117 | Kutay M E, Aydilek A H. Pore pressure and viscous shear stress distribution due to water flow within asphalt pore structure[J]. Computer Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2009, 24(3): 212-224. |
| 118 | Noguera J A H, Quintana H A R, Gómez W D F. The influence of water on the oxidation of asphalt cements[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 71: 451-455. |
| 119 | 张吉哲, 王静, 李岩, 等. 沥青胶浆-集料界面水盐侵蚀损伤规律研究[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(16): 21-29. |
| Zhang Ji-zhe, Wang Jing, Li Yan. Study on water and salt erosion damage of asphalt mortar-aggregate interface[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(16): 21-29. | |
| 120 | 成志强, 张晓燕, 孔繁盛. 水分在沥青膜中的扩散特征[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2021, 24(2): 399-404. |
| Cheng Zhi-qiang, Zhang Xiao-yan, Kong Fan-sheng. Moisture diffusion property into asphalt film[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2021, 24(2): 399-404. | |
| 121 | Caro S, Masad E, Bhasin A, et al. Probabilistic modeling of the effect of air voids on the mechanical performance of asphalt mixtures subjected to moisture diffusion[J]. Asphalt Paving Technology, 2010, 79: 221-228. |
| 122 | Masad E, Castelblanco A, Birgisson B. Effects of air void size distribution, pore pressure, and bond energy on moisture damage[J]. Journal of Testing and Evaluation, 2006, 34(1): 15-23. |
| 123 | Arambula E, Masad E, Martin A E. Influence of air void distribution on the moisture susceptibility of asphalt mixes[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2007, 19(8): 655-664. |
| 124 | Schram S, Abdelrahman M. Effects of asphalt film thickness on field performance[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering (English Edition), 2020, 5(7): 600-628. |
| 125 | Kiggundu B M, Roberts F L. Stripping in HMA mixtures: state-of-the-art and critical review of test methods[EB/OL]. [2022-11-04]. |
| 126 | Gao J, Guo C, Liu Y. Measurement of pore water pressure in asphalt pavement and its effects on permeability[J]. Measurement, 2015, 62: 81-87. |
| 127 | Li S, Zhang H, Sun L. Development and simulation measurement of dynamic hydraulic pressure[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2007, 35(7): No.915. |
| 128 | Lei Y, Hu X, Wang H, et al. Effects of vehicle speeds on the hydrodynamic pressure of pavement surface: measurement with a designed device[J]. Measurement, 2017, 98: 1-9. |
| 129 | 王英, 杨熙, 姜继斌, 等. 动水冲刷作用下季冻区沥青混合料水损害发展的细观过程[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(10): 50-56. |
| Wang Ying, Yang Xi, Jiang Ji-bin.The micro process of water damage in asphalt mixture in seasonal frozen area under the dynamic water erosion[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(10): 50-56. | |
| 130 | Feng D, Yi J, Wang D, et al. Impact of salt and freeze-thaw cycles on performance of asphalt mixtures in coastal frozen region of China[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2010, 62(1): 34-41. |
| 131 | Kutay M E, Aydilek A H. Dynamic effects on moisture transport in asphalt concrete[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2007, 133(7): 406-414. |
| 132 | Kringos N, Scarpas T, Kasbergen C, et al. Modelling of combined physical-mechanical moisture-induced damage in asphaltic mixes, part 1: governing processes and formulations[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2008, 9(2): 115-128. |
| 133 | 周璐, 黄卫东, 吕泉, 等. 不同改性剂对沥青黏结及抗水损害性能的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2021, 24(2): 377-384. |
| Zhou Lu, Huang Wei-dong, Lv Quan,et al. Effects of various modifiers on the bond property and moisture damage resistance of asphalt[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2021, 24(2): 377-384. | |
| 134 | 季节, 马榕达, 郑文华, 等. TLA和DCLR对沥青与集料黏附性的影响[J]. 重庆交通大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 37(1): 54-61. |
| Ji Jie, Ma Rong-da, Zheng Wen-hua, et al. Effect of DCLR and TLA on adhesion characteristics of asphalt and aggregate[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University(Natural Science), 2018, 37(1): 54-61. | |
| 135 | Chakravarty H, Sinha S. Moisture damage of bituminous pavements and application of nanotechnology in its prevention[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2020, 32(8): No.03120003. |
| 136 | Oliviero R C, Teltayev B, Angelico R. Adhesion promoters in bituminous road materials: a review[J]. Applied Sciences, 2017, 7(5): No.524. |
| [1] | 杨柳,王创业,王梦言,程阳. 设置自动驾驶小客车专用车道的六车道高速公路交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2043-2052. |
| [2] | 周正峰,于晓涛,陶雅乐,郑茂,颜川奇. 基于灰色关联分析的树脂与弹性体高黏沥青高温性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2078-2088. |
| [3] | 马涛,马源,黄晓明. 基于多元非线性回归的智能压实关键参数最优解[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2067-2077. |
| [4] | 王宁,马涛,陈丰,付永强. 影响智能骨料感知的关键因素及数据分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1799-1808. |
| [5] | 黄晓明,赵润民. 道路交通基础设施韧性研究现状及展望[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1529-1549. |
| [6] | 张哲,付伟,张军辉,黄超. 循环荷载下冻融路基黏土长期塑性行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1790-1798. |
| [7] | 张青霞,侯吉林,安新好,胡晓阳,段忠东. 基于车辆脉冲响应的路面不平度识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1765-1772. |
| [8] | 姜屏,陈业文,陈先华,张伟清,李娜,王伟. 改性石灰土在干湿和冻融循环下的无侧限抗压性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1809-1818. |
| [9] | 司春棣,崔亚宁,许忠印,凡涛涛. 层间粘结失效后桥面沥青铺装层细观力学行为分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1719-1728. |
| [10] | 李岩,张久鹏,陈子璇,黄果敬,王培. 基于PCA-PSO-SVM的沥青路面使用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1729-1735. |
| [11] | 赵晓康,胡哲,张久鹏,裴建中,石宁. 基于光纤传感技术的路面结冰智能监测研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1566-1579. |
| [12] | 惠冰,杨心怡,张乐扬,李扬. 检测车轨迹偏移对沥青路面磨耗计算误差的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1756-1764. |
| [13] | 李崛,张安顺,张军辉,钱俊峰. 级配碎石基层结构动力响应模型测试及数值分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1782-1789. |
| [14] | 李博,李欣,芮红,梁媛. 基于变分模态分解和灰狼优化极限学习机的隧道口边坡位移预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1853-1860. |
| [15] | 刘状壮,郑文清,郑健,李轶峥,季鹏宇,沙爱民. 基于网格化的路表温度感知技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1746-1755. |
|