吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1861-1872.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221395
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于卫星遥感的路域地质灾害监测方法
- 1.东南大学 交通学院,南京 211102
2.重庆交通大学 土木工程学院,重庆 400074
Monitoring road geological disaster based on satellite remote sensing
Jun-qing ZHU1( ),Xue-ru ZHAO1,Tao MA1(
),Xue-ru ZHAO1,Tao MA1( ),Xiao-ming HUANG1,Hong-zhou ZHU2
),Xiao-ming HUANG1,Hong-zhou ZHU2
- 1.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211102,China
2.School of Civil Engineering,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
摘要:
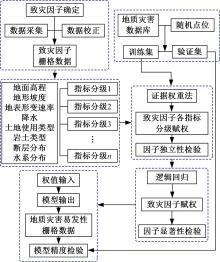
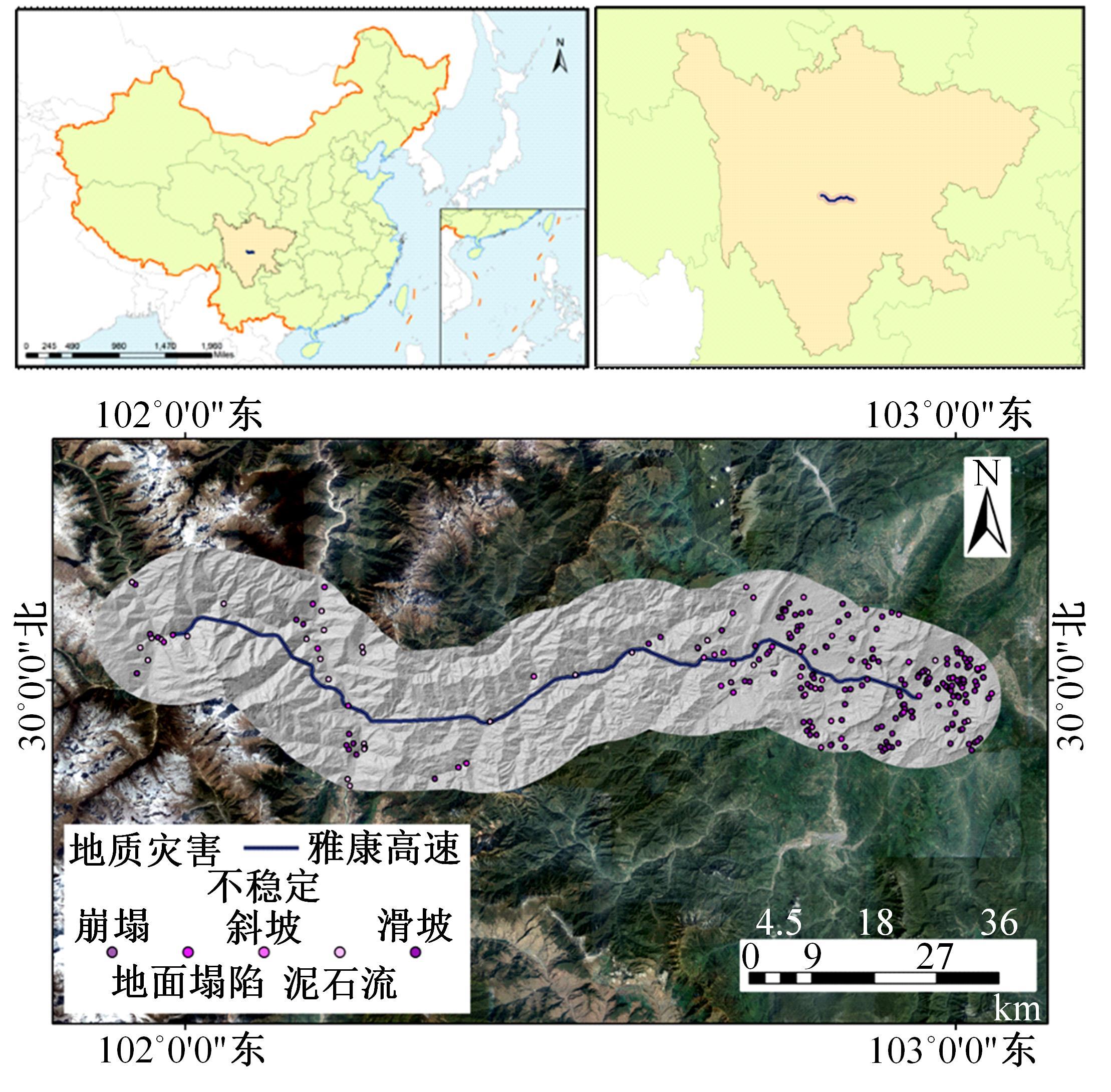
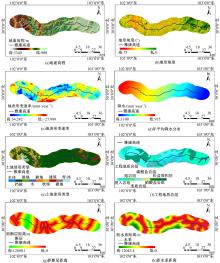
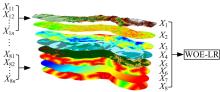
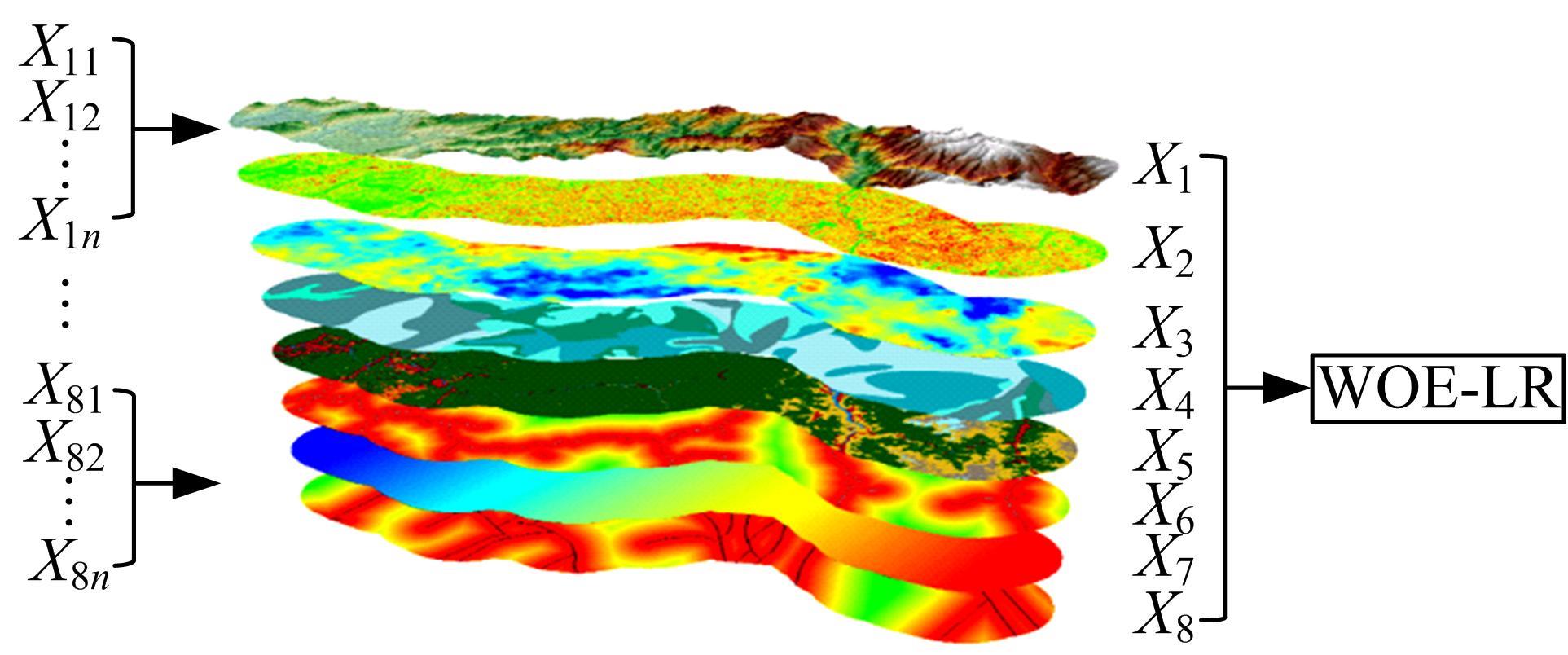
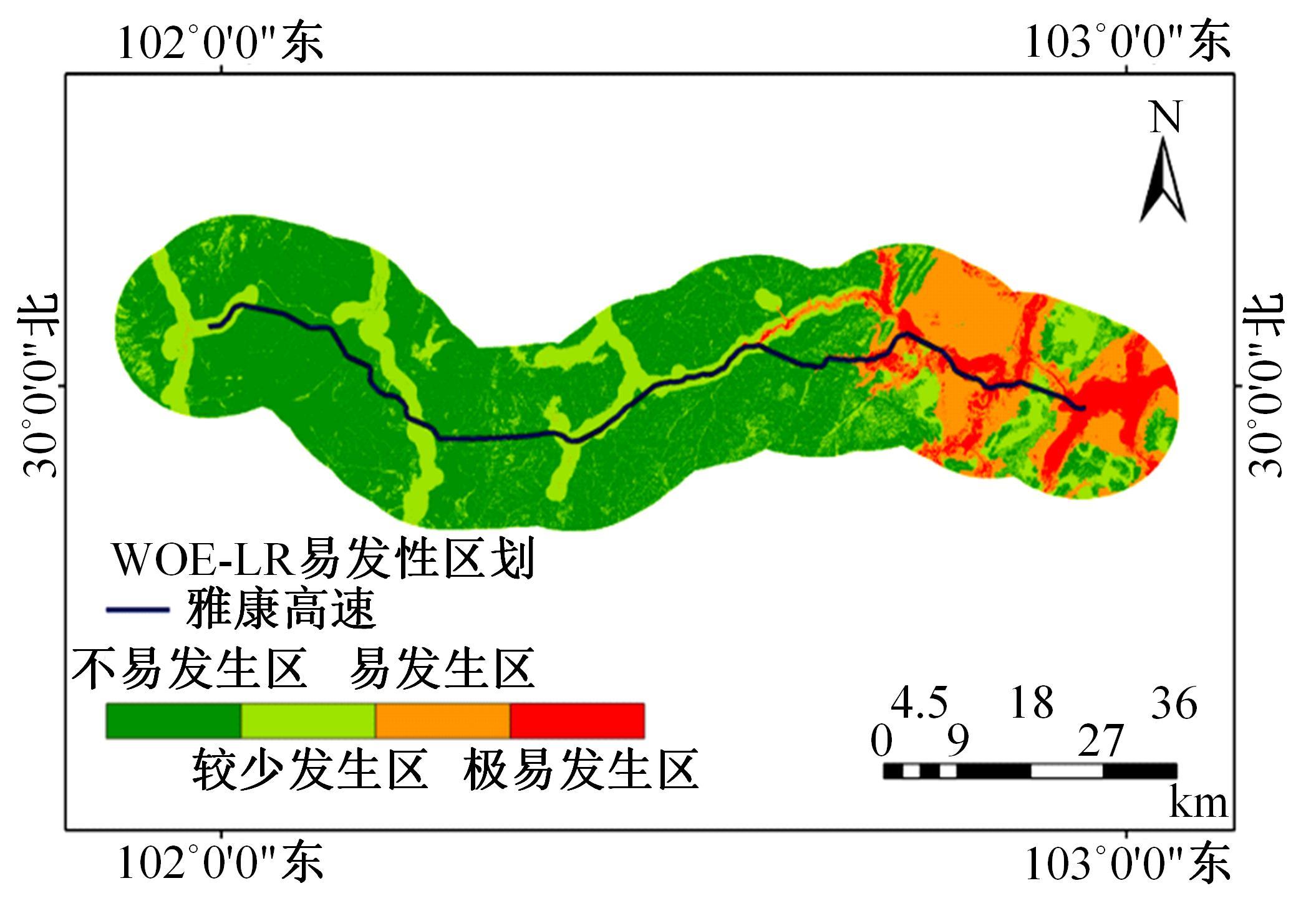
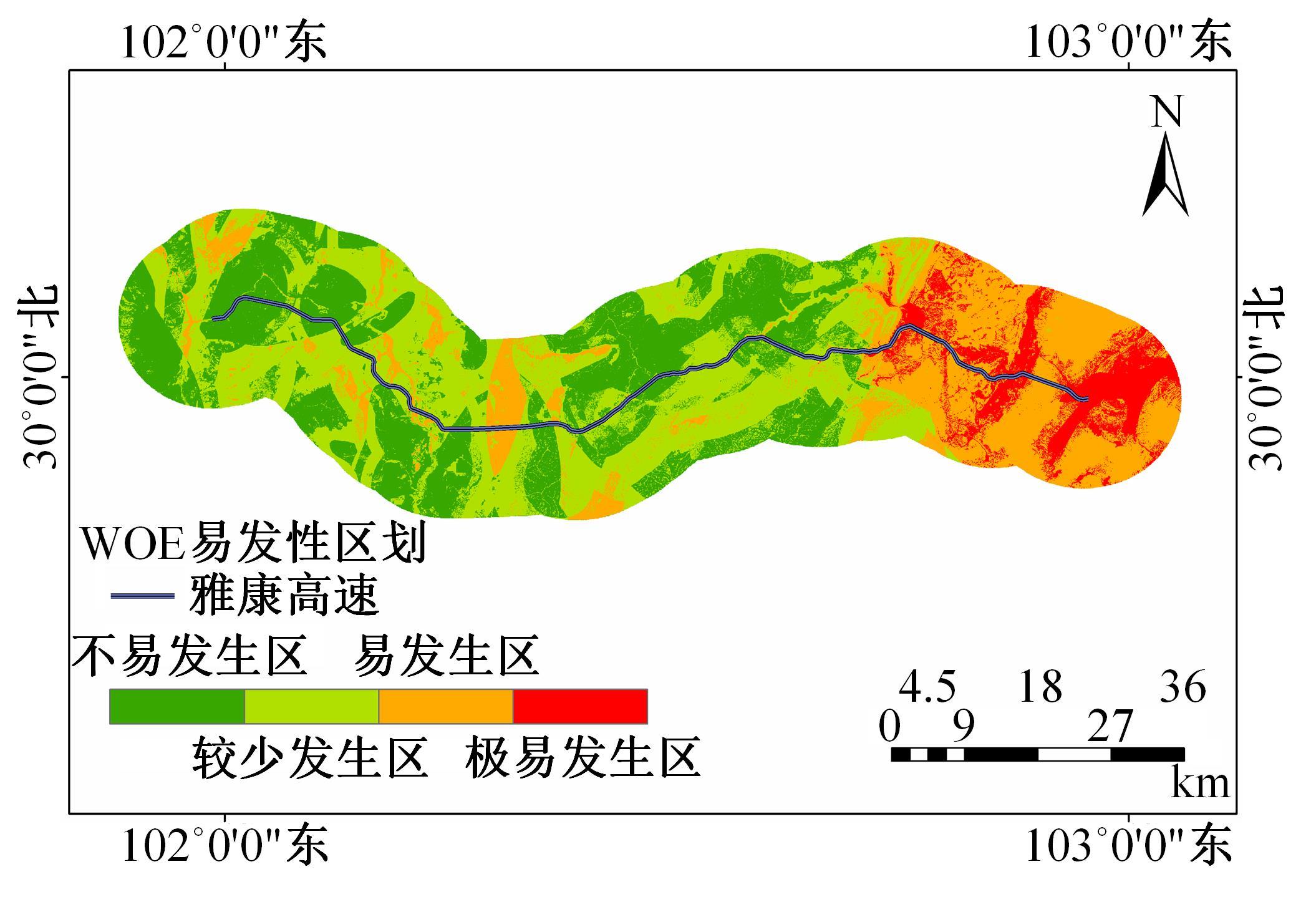
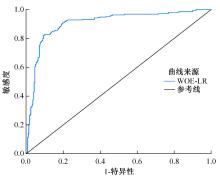
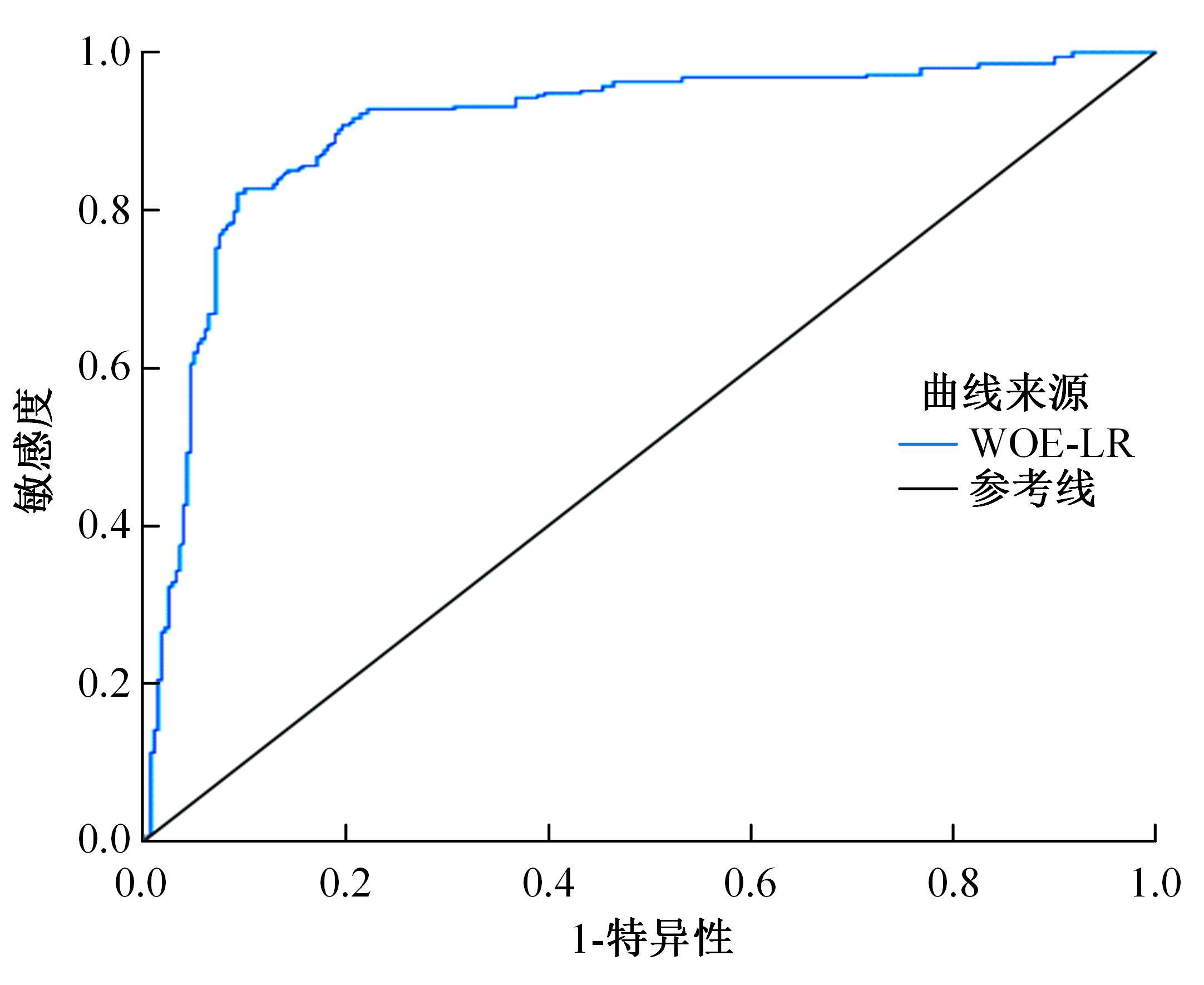
以公路为研究主体,界定了公路沿线研究区范围,构建了路域地质灾害预警监测方法体系。结合公路路域特性,选取地面高程、地形坡度、地表形变速率、降水、土地使用类型、工程地址岩组、断层分布、水系分布8种致灾因子,通过卫星遥感技术对致灾因子进行信息提取,输入至证据权重法和逻辑回归耦合模型,以获取路域范围内的地质灾害易发性计算结果,并对结果进行区域划分,确定预警监测的靶向区域。以四川省雅安至康定高速公路为实例对本文方法进行验证,结果表明,本文方法对以公路为主体的路域研究区特性有良好的数据表征作用;路域地质灾害预警监测精度较高,AUC值为0.906;该方法对公路交通基础设施防灾、抗灾工作具备一定的参考和指导意义。
中图分类号:
- U416
| 1 | 康志成, 李焯芬, 马蔼乃,等. 中国泥石流研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004. |
| 2 | 自然资源部. 2021年全国地质灾害灾情及2022年地质灾害趋势预测[DP/OL]. [2022-10-04]. |
| 3 | Liu S L, Cui B S, Dong S K, et al. Evaluating the influence of road networks on landscape and regional ecological risk—a case study in lancang river valley of southwest china[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2008, 34(2): 91-99. |
| 4 | 王英杰, 王磊, 荣起国, 等. 基于通径分析与可拓学的公路泥石流危险性评价[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2014, 44(3): 895-900. |
| Wang Ying-jie, Wang Lei, Rong Qi-guo, et al. Danger evaluation of debris flow along highway based on path analysis and extension method[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(3): 895-900. | |
| 5 | 唐川, 张军, 万石云, 等. 基于高分辨率遥感影象的城市泥石流灾害损失评估[J]. 地理科学, 2006, 26(3): 358-363. |
| Tang Chuan, Zhang Jun, Wan Shi-yun, et al. Loss evaluation of urban debris flow hazard using high spatial resolution satellite imagery[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2006, 26(3): 358-363. | |
| 6 | Ilia I, Tsangaratos P. Applying weight of evidence method and sensitivity analysis to produce a landslide susceptibility map[J]. Landslides, 2016, 13(2): 379-397. |
| 7 | 闫怡秋, 杨志华, 张绪教, 等. 基于加权证据权模型的青藏高原东部巴塘断裂带滑坡易发性评价[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(1): 26-37. |
| Yan Yi-qiu, Yang Zhi-hua, Zhang Xu-jiao, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on weight-of-evidence modeling of the Batang fault zone, eastern Tibetan plateau[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(1): 26-37. | |
| 8 | 谭超, 田述军, 李铭杨. 九寨沟地震前后地质灾害对景区通达性影响与对策研究[J]. 公路, 2021, 66(6): 214-221. |
| Tan Chao, Tian Shu-jun, Li Ming-yang. Research on the influence of geological disaster on scenic area accessibility and countermeasures before and after jiuzhaigou earthquake[J]. Highway, 2021, 66(6): 214-221. | |
| 9 | 王昌明, 黄健, 李桥, 等. 基于信息量模型与logistic回归模型耦合的山西吕梁市地质灾害易发性评价研究[J]. 水利水电技术, 2019, 50(3): 132-138. |
| Wang Chang-ming, Huang Jian, Li Qiao, et al. Evaluation of geological hazard vulnerability in lyuliang city in shanxi province based on coupling of information content model and logistic regression model[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2019, 50(3): 132-138. | |
| 10 | 邱曼, 魏云杰. 基于层次分析法的叶城二牧场地质灾害危险性评价[J]. 防灾减灾学报, 2019, 35(3): 9-14. |
| Qiu Man, Wei Yun-jie. The assessment of geological hazard in ermuchang area of yecheng based on analytic hierarchy process[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Reduction, 2019, 35(3): 9-14. | |
| 11 | 林荣福, 刘纪平, 徐胜华, 等. 随机森林赋权信息量的滑坡易发性评价方法[J]. 测绘科学, 2020, 45(12): 131-138. |
| Lin Rong-fu, Liu Ji-ping, Xu Sheng-hua, et al. Evaluation method of landslide susceptibility based on random forest weighted information[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2020, 45(12): 131-138. | |
| 12 | 徐涵秋. 区域生态环境变化的遥感评价指数[J]. 中国环境科学, 2013, 33(5): 889-897. |
| Xu Han-qiu. A remote sensing index for assessment of regional ecological changes[J]. China Environmental Science, 2013, 33(5): 889-897. | |
| 13 | Yang Z, Zhang Q, Ding X, et al. Analysis of the quality of daily dem generation with geosynchronous insar[J]. Engineering, 2020, 6(8): 913-918. |
| 14 | 陈圣波,于亚凤,杨金中,等. 基于实测光谱指数法的aster遥感数据岩性信息提取[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2016, 46(3): 938-944. |
| Chen Sheng-bo, Yu Ya-feng, Yang Jin-zhong, et al. Lithologic information extraction from aster remote sensing data based on spectral ratio method[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2016, 46(3): 938-944. | |
| 15 | 周超凡, 宫辉力, 陈蓓蓓, 等. 利用数据场模型评价北京地面沉降交通载荷程度[J]. 吉林大学学报: 地球科学版, 2017, 47(5): 1511-1520. |
| Zhou Chao-fan, Gong Hui-li, Chen Bei-bei, et al. Assessment to ground subsidence traffic load in beijing area using data field mode[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2017, 47(5): 1511-1520. | |
| 16 | 章豪, 温剑峰, 陈温清, 等. 对陡坡陡崖引发地质灾害的潜在影响范围进行建模分析[J]. 测绘通报, 2021(6): 117-121, 133. |
| Zhang Hao, Wen Jian-feng, Chen Wen-qing, et al. Modeling and analyzing the potential impact range of geological disasters caused by the escarpments[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2021(6): 117-121, 133. | |
| 17 | 郭小花, 李小林, 赵振, 等. 青海4·14玉树地震地质作用对地质环境影响分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2011, 19(5): 685-696. |
| Guo Xiao-hua, Li Xiao-lin, Zhao Zhen, et al. Effects of 4·14 Yushu earthquake in qinghai on geological enviroment[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(5): 685-696. | |
| 18 | 孙聿卿. 川藏公路北线泥石流风险评价[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学环境与资源学院, 2021. |
| Sun Yu-qing. Risk assessment of debris flow along the north line of Sichuan-Tibet highway[D]. Mianyang: School of Environment and Resources, Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2021. | |
| 19 | 张锡涛, 刘翔宇, 谢谟文, 等. 基于岩质滑坡引发泥石流的影响范围评价模型[J]. 工程地质学报, 2013, 21(4): 598-606. |
| Zhang Xi-tao, Liu Xiang-yu, Xie Mo-wen, et al. Mathematical model for evaluating affected range of debris flow induced by rock landslide[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2013, 21(4): 598-606. | |
| 20 | 邹强, 王青, 刘延国. 基于GIS与Logistic模型的公路泥石流易发性分析[J]. 水土保持通报, 2014, 34(3): 185-189. |
| Zou Qiang, Wang Qing, Liu Yan-guo. Evaluation method of debris-flow susceptibility using GIS and Logistic model[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 34(3): 185-189. | |
| 21 | Hong H, Ilia I, Tsangaratos P, et al. A hybrid fuzzy weight of evidence method in landslide susceptibility analysis on the Wuyuan area, China[J]. Geomorphology, 2017, 290: 1-16. |
| 22 | 徐胜华, 刘纪平, 王想红, 等. 熵指数融入支持向量机的滑坡灾害易发性评价方法——以陕西省为例[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2020, 45(8): 1214-1222. |
| Xu Sheng-hua, Liu Ji-ping, Wang Xiang-hong, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment method incorporating index of entropy based on support vector machine:a case study of Shaanxi province[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(8): 1214-1222. | |
| 23 | 张晓东, 刘湘南, 赵志鹏, 等. 信息量模型、确定性系数模型与逻辑回归模型组合评价地质灾害敏感性的对比研究[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(3): 602-610. |
| Zhang Xiao-dong, Liu Xiang-nan, Zhao Zhi-peng, et al. Comparative study of geological hazards susceptibility assessment: constraints from the information value+logistic regression model and the CF+logistic regression model[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(3): 602-610. | |
| 24 | Agterberg F. A modified weights-of-evidence method for regional mineral resource estimation[J]. Natural Resources Research, 2011, 20(2): 95-101. |
| 25 | Saier W, Chen J, Zhou W, et al. Debris-flow susceptibility assessment and validation based on logistic regression model: an example from the Benzilan-Changbo segment of the upper Jinshajiang river[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(3): 611-622. |
| 26 | 范强, 巨能攀, 向喜琼, 等. 证据权法在滑坡易发性分区中的应用——以贵州桐梓河流域为例[J]. 灾害学, 2015, 30(1): 124-129. |
| Fan Qiang, Ju Neng-pan, Xiang Xi-qiong, et al. Application of weights of evidence method in landslide susceptibility zoning—a case study on Tongzi rver basin in Guizhou[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2015, 30(1): 124-129. | |
| 27 | 韩用顺, 孙湘艳, 刘通, 等. 基于证据权-投影寻踪模型的藏东南地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 山地学报, 2021, 39(5): 672-686. |
| Han Yong-shun, Sun Xiang-yan, Liu Tong, et al. Susceptibility evaluation of geological hazards based on evidence weight-projection pursuitmodel in southeast Tibet, China[J]. Mountain Research, 2021, 39(5): 672-686. | |
| 28 | Ozdemir A, Altural T. A comparative study of frequency ratio, weights of evidence and logistic regression methods for landslide susceptibility mapping: Sultan mountains, SW Turkey[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 64: 180-197. |
| 29 | 袁飞云, 李永林, 郑斌. 四川藏区高速公路斜坡地质灾害防范对策[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2018, 29(2): 23-27. |
| Yuan Fei-yun, Li Yong-lin, Zheng Bin. Prevention countermeasures for geohazard of sichuan tibetan area expressway[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2018, 29(2): 23-27. |
| [1] | 马涛,马源,黄晓明. 基于多元非线性回归的智能压实关键参数最优解[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2067-2077. |
| [2] | 王宁,马涛,陈丰,付永强. 影响智能骨料感知的关键因素及数据分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1799-1808. |
| [3] | 李崛,张安顺,张军辉,钱俊峰. 级配碎石基层结构动力响应模型测试及数值分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1782-1789. |
| [4] | 张青霞,侯吉林,安新好,胡晓阳,段忠东. 基于车辆脉冲响应的路面不平度识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1765-1772. |
| [5] | 刘状壮,郑文清,郑健,李轶峥,季鹏宇,沙爱民. 基于网格化的路表温度感知技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1746-1755. |
| [6] | 金辰,曾孟源,吴荻非. 基于振动传递的水泥混凝土路面接缝损伤感知[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1736-1745. |
| [7] | 赵晓康,胡哲,张久鹏,裴建中,石宁. 基于光纤传感技术的路面结冰智能监测研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1566-1579. |
| [8] | 杨帆,李琛琛,李盛,刘海伦. 温缩作用下双层连续配筋混凝土路面配筋率设计参数对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1122-1132. |
| [9] | 孙雅珍,郑直,黄伟明,王金昌. 基于状态空间法的含裂缝水泥路面结构分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 188-196. |
| [10] | 叶奋,胡诗园. 考虑旧水泥路面接缝传荷能力的超薄罩面力学特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2636-2643. |
| [11] | 杨彦海,崔宏,杨野,张怀志,刘赫. 冻融循环作用对非饱和乳化沥青冷再生混合料性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2352-2359. |
| [12] | 于晓贺,罗蓉,柳子尧,黄婷婷,束裕. 沥青路面典型裂缝湿度场数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2343-2351. |
| [13] | 时成林,王勇,吴春利,宋文祝. 路堤挡土墙主动土压力计算方法修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1394-1403. |
| [14] | 郭庆林,刘强,吴春利,李黎丽,李懿明,刘富春. 导电沥青及混合料裂缝局部温度场及愈合效果[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1386-1393. |
| [15] | 姚玉权,仰建岗,高杰,宋亮. 基于性能-费用模型的厂拌再生沥青混合料优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 585-595. |
|
||