吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1756-1764.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230067
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
检测车轨迹偏移对沥青路面磨耗计算误差的影响
- 1.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710064
2.长安大学 特殊地区公路工程教育部重点实验室,西安 710064
Influence of detecting track offset on calculation error of asphalt pavement wearing
Bing HUI1,2( ),Xin-yi YANG1,Le-yang ZHANG1,Yang LI1
),Xin-yi YANG1,Le-yang ZHANG1,Yang LI1
- 1.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.The Key Laboratory of Intelligent Construction and Maintenance of CAAC,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
摘要:
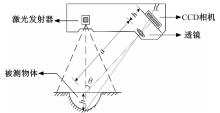
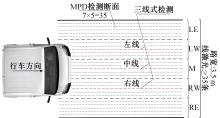
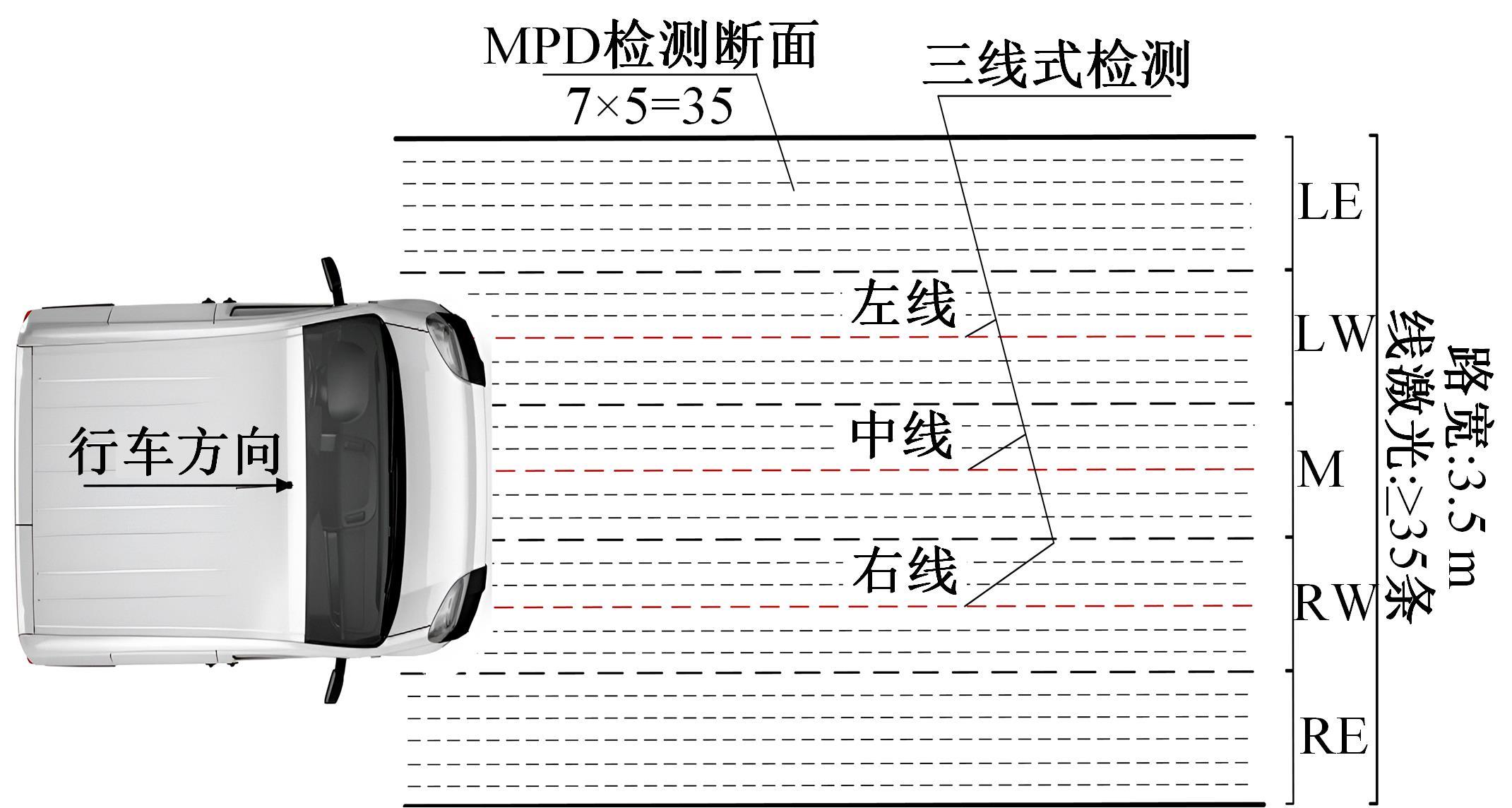
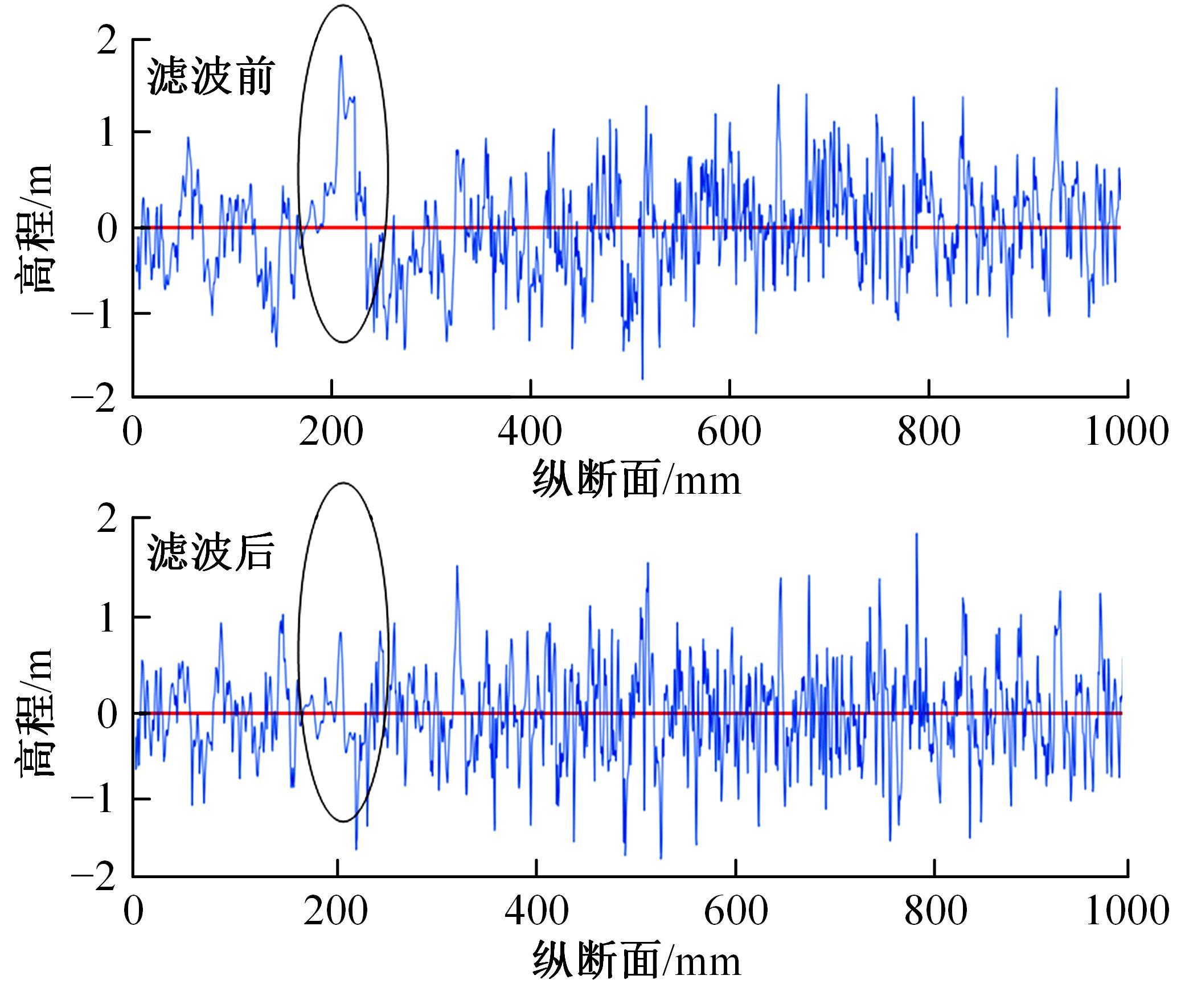
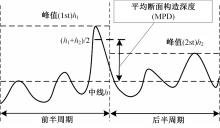
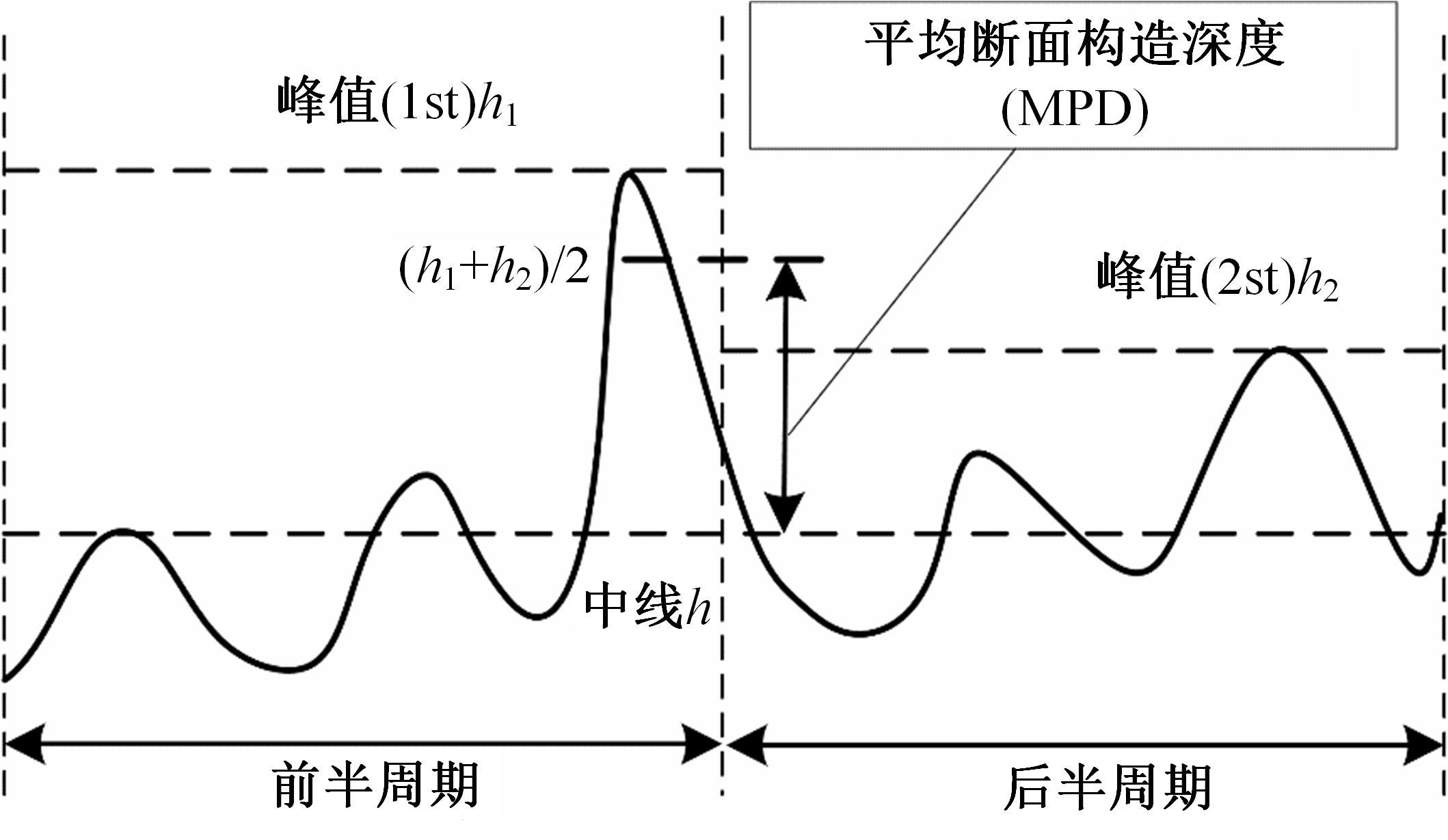
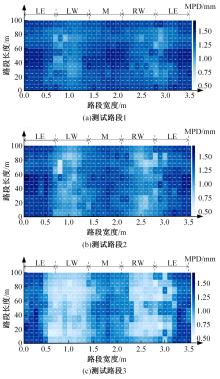
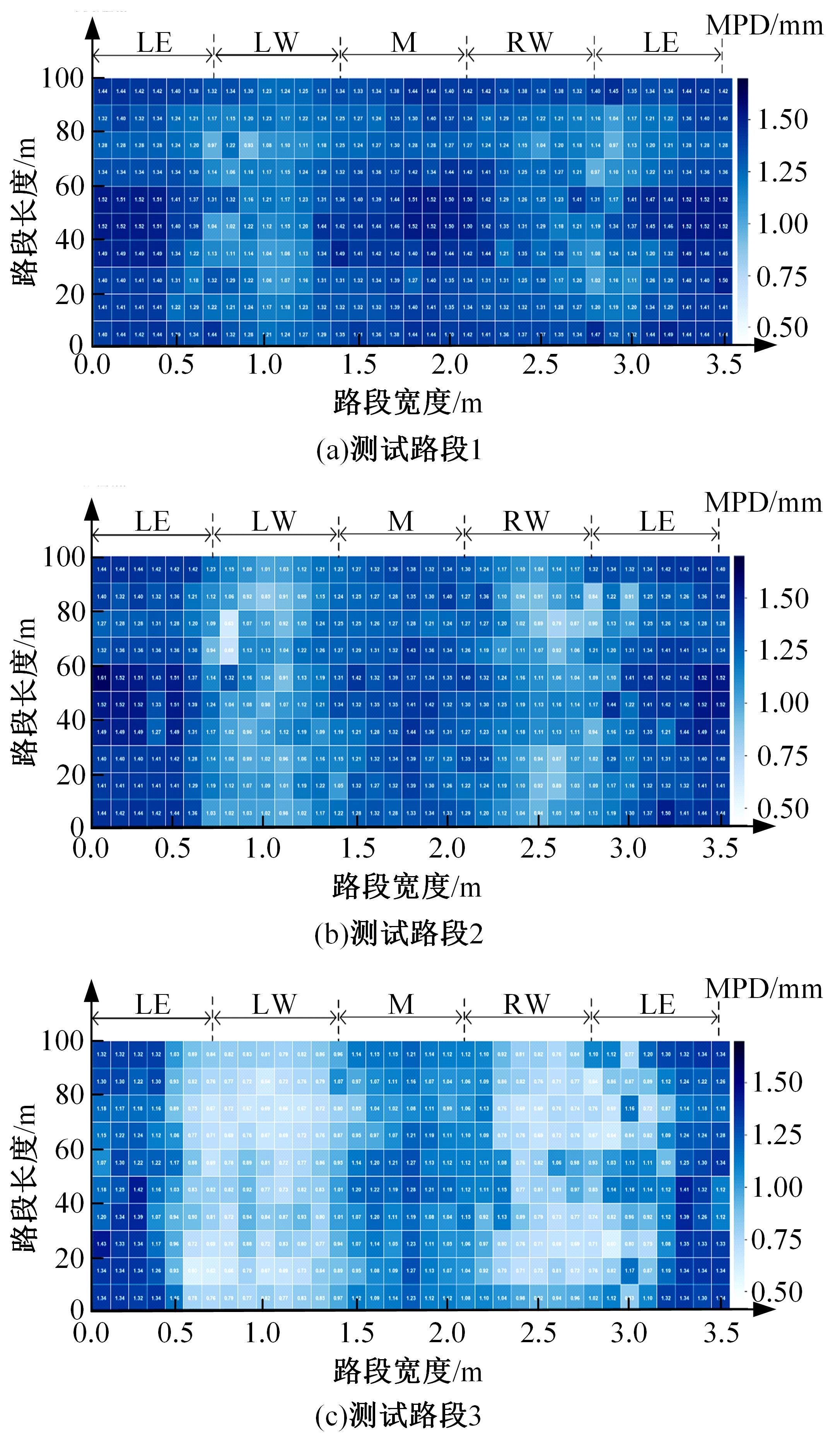
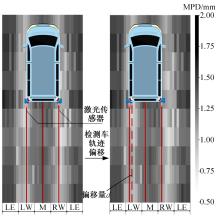
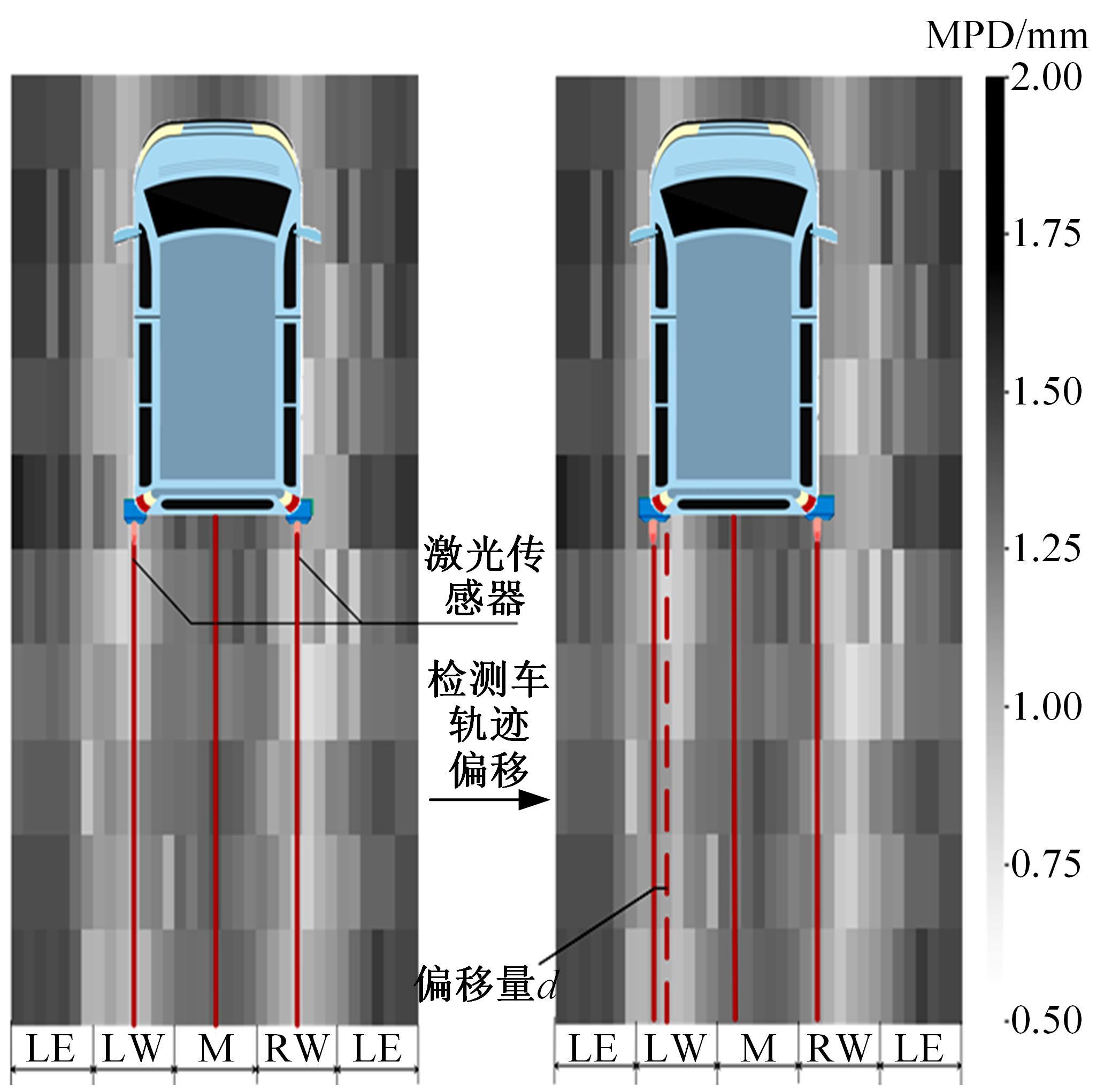
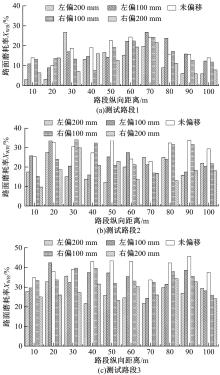
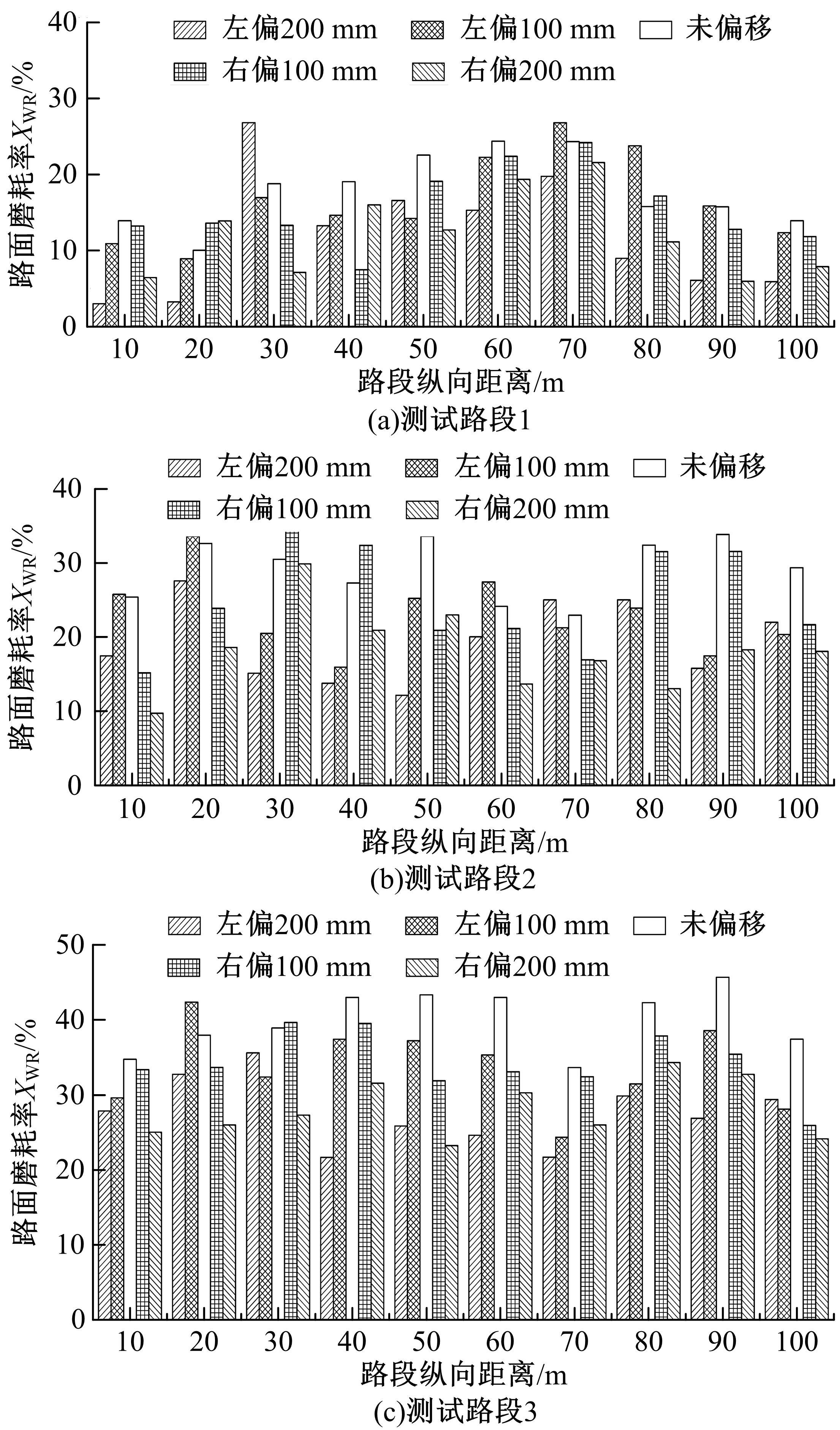
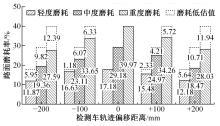
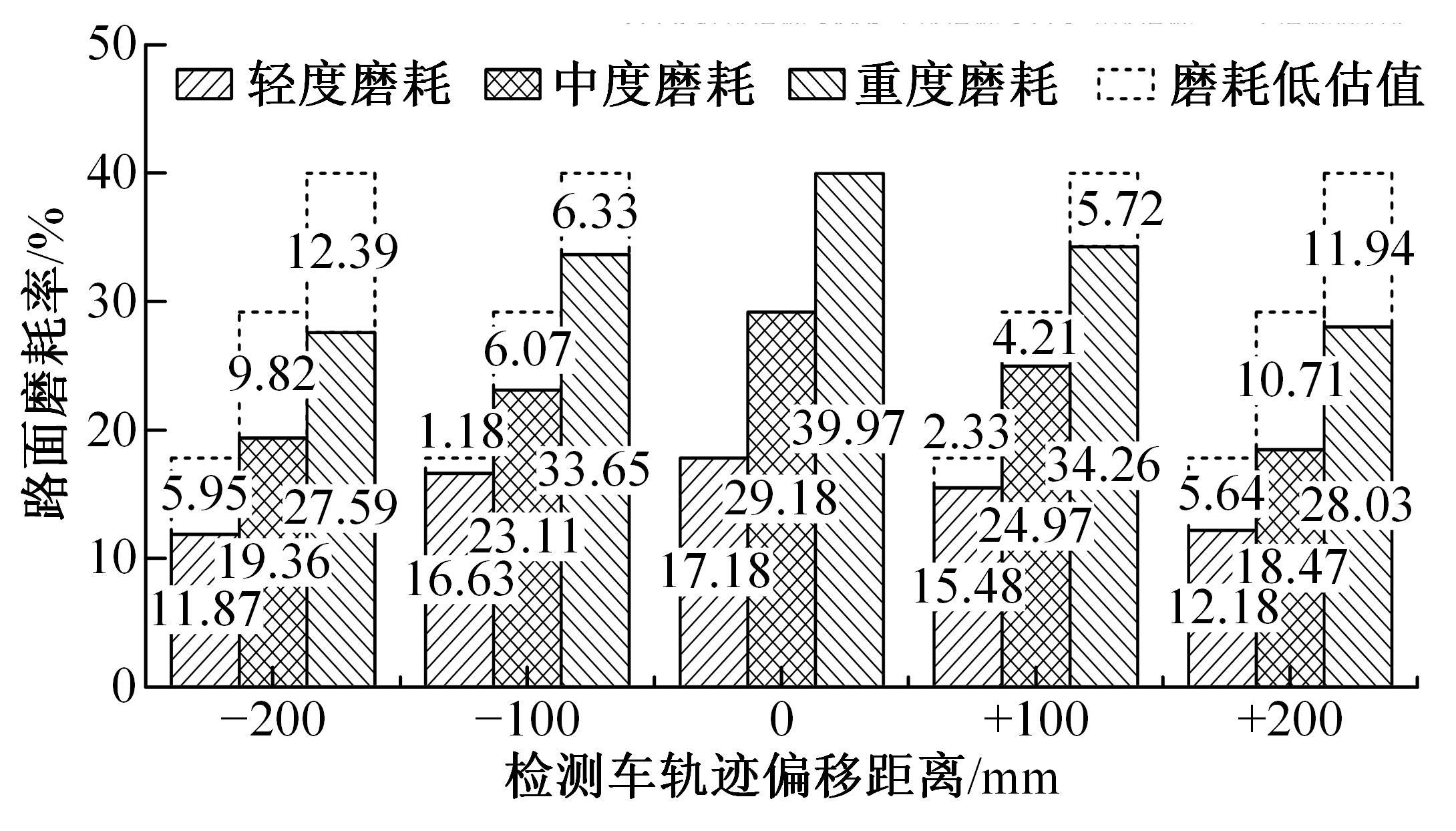
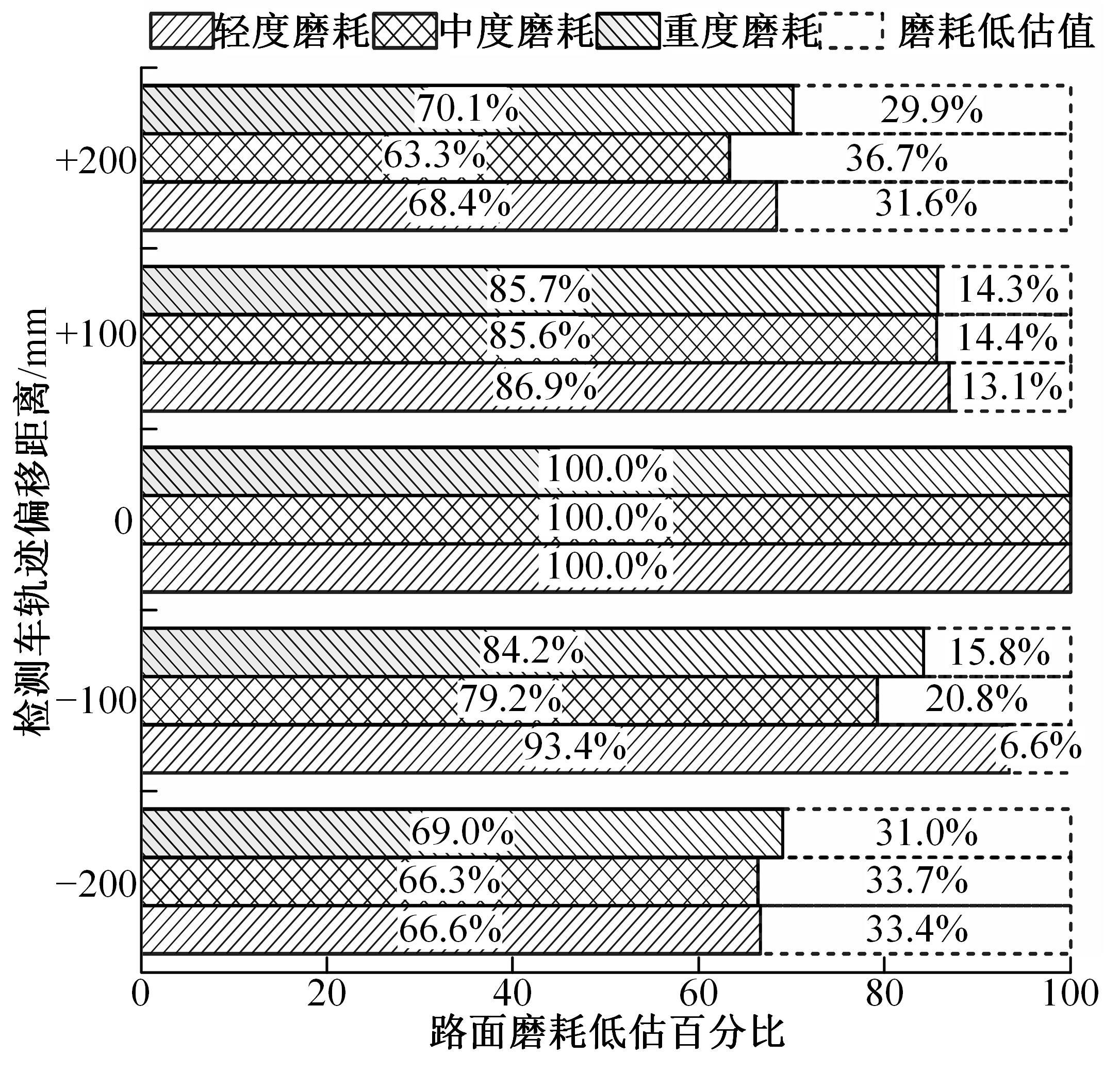
为研究检测车轨迹偏移对沥青路面磨耗程度计算结果的影响,根据实测三维激光高程点云数据重构了3段磨耗等级分别为轻度、中度和重度的路表模型,绘制其全车道平均断面构造深度(MPD)热力分布图。采用三线法计算路面磨耗率XWR,分别模拟检测车向左、右偏移100和200 mm后的测线轨迹,以偏移前、后磨耗率XWR的绝对误差和相对误差为评价指标,分析轨迹偏移对磨耗率计算误差的影响规律。结果表明:检测车轨迹偏移距离越大,路面磨耗率计算的绝对误差和相对误差越大,轻度、中度和重度3个不同严重程度磨耗路段的磨耗率最大绝对误差分别为5.95%、10.71%和12.39%;路面磨耗程度越严重,磨耗率计算误差越大,较大的误差可能产生路面磨耗等级的低估,进而导致路况评价和养护决策的误判;增加测线数量、减小测线间距是降低偏移误差和提升磨耗检测准确性的有效措施。
中图分类号:
- U418.1
| 1 | Guo F C, Pei J Z, Zhang J P, et al. Study on the skid resistance of asphalt pavement: a state-of-the-art review and future prospective[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 303: No.124411. |
| 2 | Li Q J, Zhan Y, Yang G W, et al. Pavement skid resistance as a function of pavement surface and aggregate texture properties[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2020, 21(2): 1-11. |
| 3 | 黄晓明, 郑彬双. 沥青路面抗滑性能研究现状与展望[J].中国公路学报, 2019, 32(4): 32-49. |
| Huang Xiao-ming, Zheng Bin-shuang. Reasearch status and progress for skid resistance performance of asphalt pavement[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(4): 32-49. | |
| 4 | 王元元, 孙璐, 刘卫东, 等. 测量路面三维纹理双目重构算法的约束改进[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(4): 1342-1348. |
| Wang Yuan-yuan, Sun Lu, Liu Wei-dong, et al. Constraint improvement of binocular reconstruction algorithm used to measure pavement three-dimensional texture [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1342-1348. | |
| 5 | 赵晓华, 刘畅, 亓航, 等. 高速公路交通事故影响因素及异质性分析[J/OL]. [2023-01-25]. |
| 6 | 刘佳雨, 冷军强, 尚平, 等. 冰雪路面下高速公路事故及严重程度影响因素分析[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2022, 54(3): 57-64. |
| Liu Jia-yu, Leng Jun-qiang, Shang Ping, et al. Analysis of traffic crashes and injury severity influence factors for ice-snow covered freeway roads[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2022, 54(3): 57-64. | |
| 7 | 谭忆秋, 李济鲈, 徐慧宁. 冰雪路面摩擦特性与运营风险管控研究综述[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(7): 1-17. |
| Tan Yi-qiu, Li Ji-lu, Xu Hui-ning. Review on friction characteristics and operation risk intelligent management of ice and snow pavement[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(7): 1-17. | |
| 8 | Han C D, Lin H H, Bo X. Experimental investigation on skid resistance of asphalt pavement under various slippery conditions[J]. International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2015, 18(6): 485-499. |
| 9 | 杨国峰, 王浩仰, 潘玉利. 基于多线纹理的路面磨耗检测及评价方法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2016, 29(3): 35-40. |
| Yang Guo-feng, Wang Hao-yang, Pan Yu-li. Detection and evaluation methods of pavement wearing based on multi-line texture[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(3): 35-40. | |
| 10 | 亓祥宇, 黄宗才, 岳晋伟, 等. 路面磨耗指数PWI与路面抗滑性能指数SRI相关性分析及对PQI的影响[J]. 公路交通科技:应用技术版, 2020, 16(6): 150-157. |
| Bian Xiang-yu, Huang Zong-cai, Yue Jin-wei, et al. Correlation analysis of pavement wear index PWI and pavement skid resistance index SRI and its influence on PQI[J]. Highway Transportation Technology (Applied Technology Edition), 2020, 16(6): 150-157. | |
| 11 | 赵可成, 徐志枢, 朱益军, 等. 路面磨耗指数PWI在高速公路养护中的应用[C]∥中国公路学会养护与管理分会第十届学术年会论文集, 中国, 深圳, 2020: 191-196. |
| 12 | Tsai Y C, Wu Y C, Ai C B, et al. Critical assessment of measuring concrete joint faulting using 3D continuous pavement profile data[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2012, 138(11): 1291-1296. |
| 13 | 李清泉, 邹勤, 张德津. 利用高精度三维测量技术进行路面破损检测[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2017, 42(11): 1549-1564. |
| Li Qing-quan, Zou Qin, Zhang De-jin. Road pavement defect detection using high precision 3D surveying technology[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2017, 42(11): 1549-1564. | |
| 14 | Bennett C R, Solminihac H D, Chamorro A, et al. Data Collection Technologies for Road Management[M]. Washington DC: The World Bank, 2006. |
| 15 | . 公路技术状况评定标准 [S]. |
| 16 | 王浩仰, 杨国峰, 潘玉利. 基于路面构造深度的沥青路面磨耗状况预测研究[J]. 公路, 2019, 64(1): 59-65. |
| Wang Hao-yang, Yang Guo-feng, Pan Yu-li. Prediction of asphalt pavement wear condition based on pavement structure depth[J]. Highway, 2019, 64(1): 59-65. | |
| 17 | 张丽娜, 何东坡, 徐文远, 等. 季冻区沥青路面PWI与SRI的相关性研究[J]. 公路, 2022, 67(7): 109-116. |
| Zhang Li-na, He Dong-po, Xu Wen-yuan, et al. Research on the Correlation between PWI and SRI of asphalt pavement in seasonal frozen area[J]. Highway, 2022, 67(7): 109-116. | |
| 18 | Simpson A L. Measurement of rutting in asphalt pavements[D]. Austin, USA: The University of Texas at Austin, 2001. |
| 19 | Simpson A L. Characterization of transverse profile[J]. Transportation Research Record Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 1999, 1655(1): 185-191. |
| 20 | 马荣贵, 王建锋, 李平. 沥青路面构造深度精确检测方法研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(8): 265-268. |
| Ma Rong-gui, Wang Jian-feng, Li Ping. Research on high precision measurement of pavement texture depth[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(8): 265-268. | |
| 21 | 窦光武. 非接触式路面构造深度量值溯源技术[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 34(6): 70-78. |
| Dou Guang-wu. Contactless metrological traceability technology of pavement texture depth[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 34(6): 70-78. | |
| 22 | 王迪. 基于多点激光检测技术的车辙深度算法对比及横向偏移误差研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学公路学院, 2014. |
| Wang Di. Point-based laser rut detection technology on depth algorithm contrast and offset error research[D]. Xi'an: School of Highway, Chang'an University, 2014. | |
| 23 | 惠冰, 李甜甜, 王迪. 检测车辆横向偏移对车辙深度计算误差分析[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 36(3): 1-6, 12. |
| Hui Bing, Li Tian-tian, Wang Di. Calculation error analysis of detecting lateral offset of vehicle on rut depth[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 36(3): 1-6, 12. | |
| 24 | Liu Y Y, Wang Y Y, Cai X Y, et al. The detection effect of pavement 3D texture morphology using improved binocular reconstruction algorithm with laser line constraint[J]. Measurement, 2020, 157: No.107638. |
| 25 | Qiu S, Wang K C P, Wang W J, et al. Reducing the effect of inaccurate lane identification on PP69-10-based rut characterization[J]. Journal of Infrastructure Systems, 2015, 22(1): No. 04015009. |
| 26 | Hui B, Tsai Y, Guo M, et al. Critical assessment of the impact of vehicle wandering on rut depth measurement accuracy using 13-point based lasers[J]. Measurement, 2018, 123: 246-253. |
| 27 | Luo W, Liu L, Li L. Measuring rutting dimension and lateral position using 3D line scanning laser and inertial measuring unit[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 111: No. 103056. |
| 28 | Tsai Y C, Li F, Kaul V, et al. Characterizing point-based transverse pavement rut measurement errors using emerging 3D continuous profile-based laser technology[C]∥Structural Materials Technology (SMT) Conference, New York, USA, 2010: No.108. |
| 29 | 李清泉, 雷波, 毛庆洲, 等. 利用激光三角法进行快速车辙检测[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2010, 35(3): 302-307. |
| Li Qing-quan, Lei Bo, Mao Qing-zhou, et al. A fast method for pavement ruts measuring with laser triangulation[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2010, 35(3): 302-307. | |
| 30 | Hua L X, Lu Y, Deng J H, et al. 3D reconstruction of concrete defects using optical laser triangulation and modified spacetime analysis[J]. Automation in Construction, 2022, 142: No.104469. |
| 31 | Wang K C P, Li L, Luo W, et al. Potential measurement of pavement surface texture based on three-dimensional image data[C]∥Transportation Research Board 91st Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 2012: No. 12-4046. |
| 32 | Li L, Wang K C P, Li Q, et al. Impacts of sample size on calculation of pavement texture indicators with 1 mm 3D surface data[J]. Periodica Polytechnica Transportation Engineering, 2017, 46(1): 42-49. |
| 33 | . 公路路基路面现场测试规程 [S]. |
| [1] | 杨柳,王创业,王梦言,程阳. 设置自动驾驶小客车专用车道的六车道高速公路交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2043-2052. |
| [2] | 周正峰,于晓涛,陶雅乐,郑茂,颜川奇. 基于灰色关联分析的树脂与弹性体高黏沥青高温性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2078-2088. |
| [3] | 马涛,马源,黄晓明. 基于多元非线性回归的智能压实关键参数最优解[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2067-2077. |
| [4] | 黄晓明,赵润民. 道路交通基础设施韧性研究现状及展望[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1529-1549. |
| [5] | 司春棣,崔亚宁,许忠印,凡涛涛. 层间粘结失效后桥面沥青铺装层细观力学行为分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1719-1728. |
| [6] | 李岩,张久鹏,陈子璇,黄果敬,王培. 基于PCA-PSO-SVM的沥青路面使用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1729-1735. |
| [7] | 赵晓康,胡哲,张久鹏,裴建中,石宁. 基于光纤传感技术的路面结冰智能监测研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1566-1579. |
| [8] | 刘状壮,郑文清,郑健,李轶峥,季鹏宇,沙爱民. 基于网格化的路表温度感知技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1746-1755. |
| [9] | 郑睢宁,何锐,路天宇,徐紫祎,陈华鑫. RET/胶粉复合改性沥青制备及其混合料性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1381-1389. |
| [10] | 魏海斌,韩栓业,毕海鹏,刘琼辉,马子鹏. 智能感知道路主动除冰雪系统及实验技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1411-1417. |
| [11] | 杨帆,李琛琛,李盛,刘海伦. 温缩作用下双层连续配筋混凝土路面配筋率设计参数对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1122-1132. |
| [12] | 关博文,邸文锦,王发平,吴佳育,张硕文,贾治勋. 干湿循环与交变荷载作用下混凝土硫酸盐侵蚀损伤[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1112-1121. |
| [13] | 刘状壮,张有为,季鹏宇,Abshir Ismail Yusuf,李林,郝亚真. 电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 523-530. |
| [14] | 魏海斌,马子鹏,毕海鹏,刘汉涛,韩栓业. 基于力学响应分析方法的导电橡胶复合路面铺装技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 531-537. |
| [15] | 陈栩,曹超飞,尚静,黄明星,艾长发,任东亚. 动静水环境作用下级配离析对沥青混合料水损害的影响评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 210-219. |
|
||