吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (7): 2078-2088.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210991
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于灰色关联分析的树脂与弹性体高黏沥青高温性能评价
周正峰1,2( ),于晓涛1,2,陶雅乐1,2,郑茂3,颜川奇1,2(
),于晓涛1,2,陶雅乐1,2,郑茂3,颜川奇1,2( )
)
- 1.西南交通大学 土木工程学院,成都 610031
2.西南交通大学 道路工程四川省重点实验室,成都 610031
3.四川省交通建设集团股份有限公司,成都 610047
High-temperature performance evaluation of resin and elastomer high viscosity asphalt based on grey correlation analysis
Zheng-feng ZHOU1,2( ),Xiao-tao YU1,2,Ya-le TAO1,2,Mao ZHENG3,Chuan-qi YAN1,2(
),Xiao-tao YU1,2,Ya-le TAO1,2,Mao ZHENG3,Chuan-qi YAN1,2( )
)
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu 610031,China
2.Highway Engineering Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province,Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu 610031,China
3.Sichuan Transportation Construction Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Chengdu 610047,China
摘要:
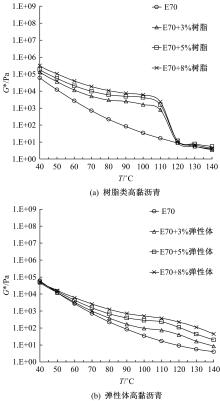
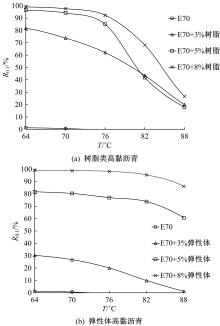
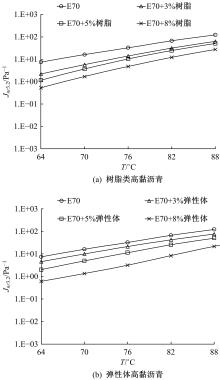
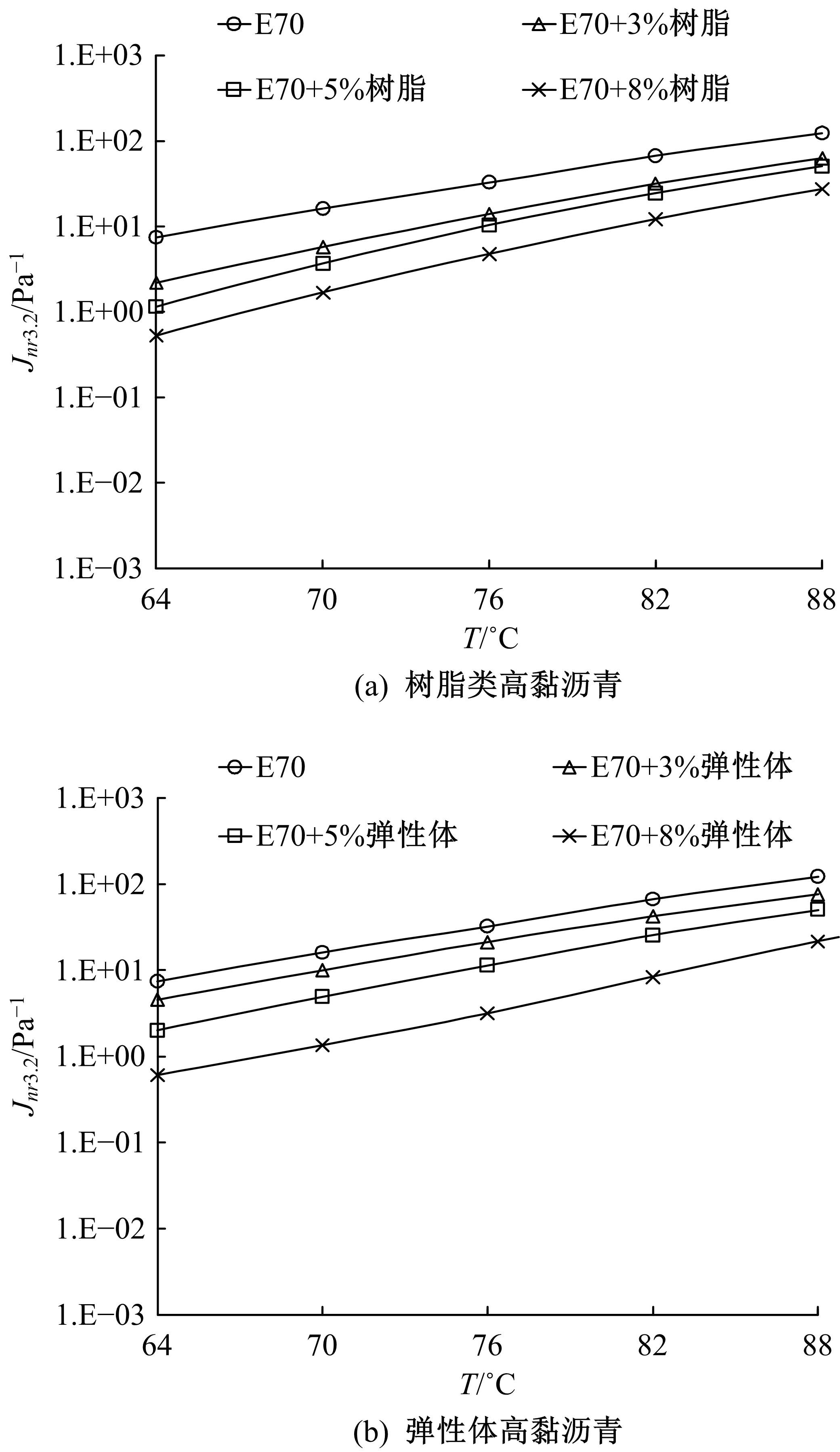
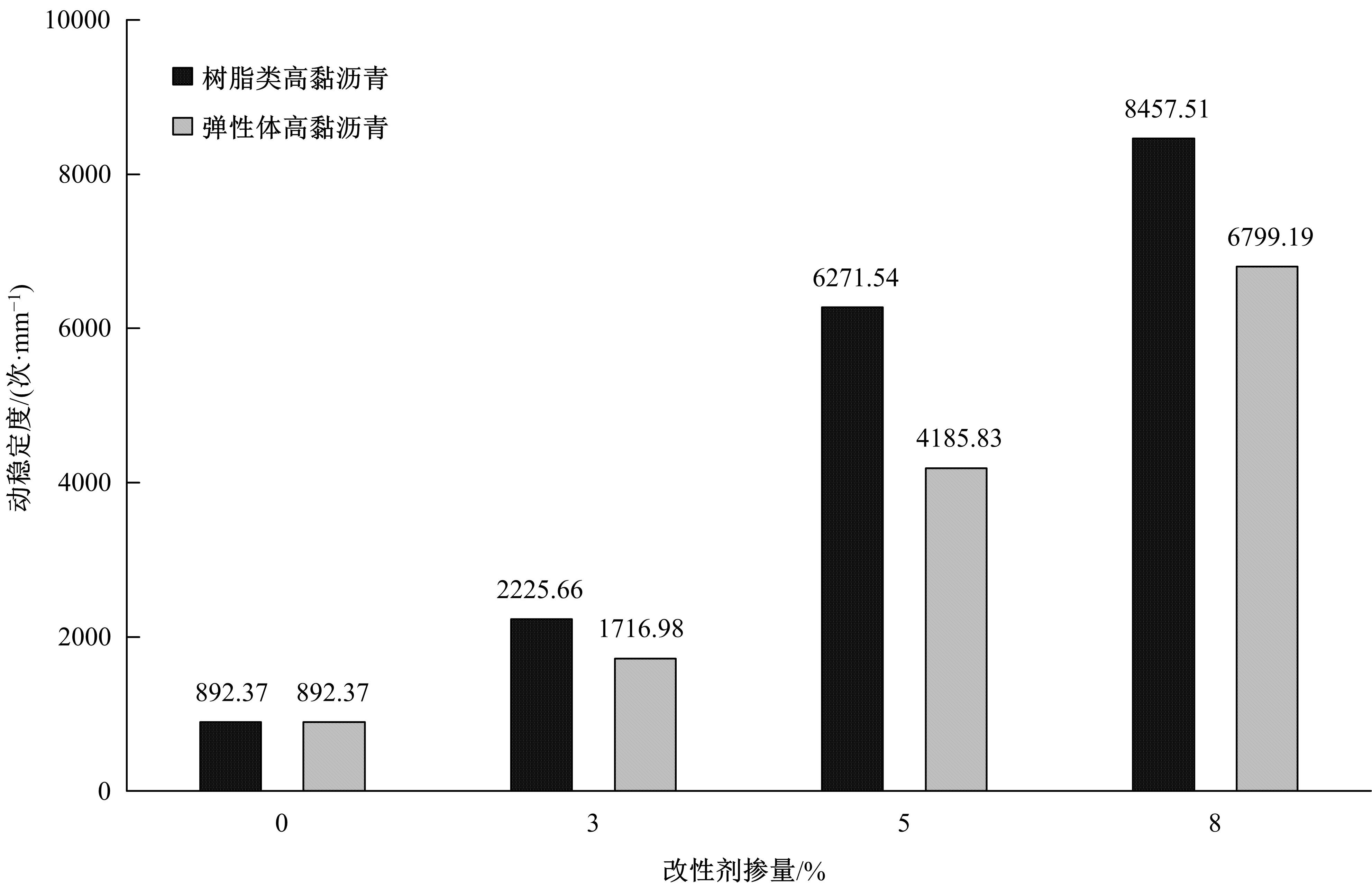
通过透射电子显微镜扫描(TEM)、流变试验,以及常规性能测试,分析树脂高黏沥青与弹性体高黏沥青的路用性能及改性机理。采用流变仪分别进行不同掺量(3%、5%、8%)下两种高黏沥青的多重应力蠕变恢复试验(MSCR)、温度扫描试验和动态频率扫描试验,并采用Cross模型和Carreau模型对动态频率扫描结果进行拟合,得到沥青60 ℃零剪切黏度(ZSV)。进一步对高黏沥青胶结料试验指标与车辙动稳定度进行灰色关联分析。结果表明:树脂类高黏改性沥青主要由内部形成的结晶体起到增黏效果,弹性体改性沥青由改性剂与基质沥青形成的三维弹性结构起到增黏效果;树脂类高黏改性沥青在线性弹性区间有很好的改性效果,但在非线性弹性区间由于结晶体熔化,改性效果不如弹性体高黏沥青;Cross模型得到的ZSV拟合值大于Carreau模型;高黏沥青软化点和蠕变恢复率与沥青混合料车辙动稳定度有显著相关性,可以很好地评价高温路用性能,而不可恢复蠕变柔量和相位角的相关性较差。
中图分类号:
- U414.1
| 1 | 祝斯月,陈拴发,秦先涛,等. 透水性沥青路面高粘改性沥青动态力学性能[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2012, 34(12): 52-56. |
| Zhu Si-yue, Chen Shuan-fa, Qin Xian-tao, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties of high viscosity modified asphalt for permeable asphalt pavements[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2012, 34(12): 52-56. | |
| 2 | özen H, Aksoy A, Tayfur S, et al. Laboratory performance comparison of the elastomer-modified asphalt mixtures[J]. Building and Environment, 2008, 43(7): 1270-1277. |
| 3 | Yan K, Tian S, Chen J, et al. High temperature rheological properties of APAO and EVA compound modified asphalt[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2020, 233: No.117246. |
| 4 | Qin X, Zhu S, He X, et al. High temperature properties of high viscosity asphalt based on rheological methods[J]. Construction & Building Materials,2018, 186: 476-483. |
| 5 | Liao M, Chen J. Zero shear viscosity of bitumen-filler mastics[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2011, 23(12): 1672-1680. |
| 6 | Morea F, Agnusdei J O, Zerbino R. Comparison of methods for measuring zero shear viscosity in asphalts[J]. Materials and Structures, 2010, 43(4): 499-507. |
| 7 | Morea F, Morea F, Agnusdei J O, et al. The use of asphalt low shear viscosity to predict permanent deformation performance of asphalt concrete[J]. Materials and Structures, 2011, 44(7): 1241-1248. |
| 8 | Morea F, Morea F, Zerbino R, et al. Improvements on asphalt mixtures rutting performance characterization by the use of low shear viscosity[J]. Materials and Structures, 2013, 46(1): 267-276. |
| 9 | D'Angelo J. The Relationship of the MSCR test to rutting[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2009, 10: 61-80. |
| 10 | Huang W, Tang N. Characterizing SBS modified asphalt with sulfur using multiple stress creep recovery test[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2015, 93: 514-521. |
| 11 | Yan C, Huang W, Lin P, et al. Chemical and rheological evaluation of aging properties of high content SBS polymer modified asphalt[J]. Fuel (Guildford), 2019, 252: 417-426. |
| 12 | 银花,李凯. 沥青零剪切黏度与高温流变参数灰色关联分析[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(1): 108-113. |
| Yin Hua, Li Kai. Gray correlation analysis of asphalt zero shear viscosity and high temperature rheological parameters[J]. Journal of Construction Materials, 2020, 23(1): 108-113. | |
| 13 | 韩海峰,何桂平,吕伟民. 沥青混合料永久变形特性对结合料广义动态剪切模量的响应[J]. 公路交通科技,2004, 21(3): 1-5. |
| Han Hai-feng, He Gui-ping, Lv Wei-min. Response of permanent deformation properties of asphalt mixtures to the generalized dynamic shear modulus of the binding material[J]. Road Traffic Science and Technology, 2004, 21(3): 1-5. | |
| 14 | 金磊,钱振东,郑彧. 基于DMA方法的浇注式沥青胶浆高温性能及评价指标[J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 44(5): 1062-1067. |
| Jin Lei, Qian Zhen-dong, Zheng Yu. High temperature performance and evaluation index of cast asphalt mastic based on DMA method[J]. Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition), 2014, 44(5): 1062-1067. | |
| 15 | Mohammad R, Ellie H, Asce M, et al. Rutting characteristics of styrene-ethylene/propylene-styrene polymer modifier asphalt[J]. American Society Civil Engineers, 2015, 27(4): 1-5. |
| 16 | Shi J, Fan W, Qian C, et al. Effect of high viscosity modifier on rheological properties and microstructure of high viscosity asphalt[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2020, 2258(1):1-10. |
| 17 | Chen J, Liao M, Shiah M. Asphalt modified by styrene-butadiene-styrene triblock copolymer: morphology and model[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2002, 14(3): 224-229. |
| 18 | He Xiao-ming, Eldouma I B. Experimental study to determine the most preferred additive for improving asphalt performance using polypropylene, crumb rubber, and tafpack super in medium and high-temperature range[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(8): 1567. |
| 19 | Yan C, Huang W, Ma J, et al. Characterizing the SBS polymer degradation within high content polymer modified asphalt using ATR-FTIR[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2020, 233:No.117708. |
| 20 | Iwanski M, Mazurek G. Rheological characteristics of synthetic wax-modified asphalt binders[J]. Polimery, 2012, 57(9): 661-664. |
| 21 | Zhang X R, L Z Q. Study on one new grey simi-larity correlation degree model and its applications[J]. Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(6): 1406-1411. |
| 22 | Wang Z. Correlation analysis of sequences with interval grey numbers based on the kernel and greyness degree[J]. Kybernetes, 2013, 42(2): 309-317. |
| 23 | Fen Y, Kong Z, J X. Evaluation of shear performance of flexible waterproof-adhesive layer in concrete bridge pavement based on grey correlation analysis[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2009, 10(Sup.1): 349-360. |
| [1] | 杨柳,王创业,王梦言,程阳. 设置自动驾驶小客车专用车道的六车道高速公路交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2043-2052. |
| [2] | 马涛,马源,黄晓明. 基于多元非线性回归的智能压实关键参数最优解[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2067-2077. |
| [3] | 魏海斌,韩栓业,毕海鹏,刘琼辉,马子鹏. 智能感知道路主动除冰雪系统及实验技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1411-1417. |
| [4] | 谢超,王起才,于本田,李盛,林晓旭,鲁志铭. 聚氨酯涂膜弹性模量的AFM测定及微观结构分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1322-1330. |
| [5] | 郑睢宁,何锐,路天宇,徐紫祎,陈华鑫. RET/胶粉复合改性沥青制备及其混合料性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1381-1389. |
| [6] | 关博文,邸文锦,王发平,吴佳育,张硕文,贾治勋. 干湿循环与交变荷载作用下混凝土硫酸盐侵蚀损伤[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1112-1121. |
| [7] | 杨帆,李琛琛,李盛,刘海伦. 温缩作用下双层连续配筋混凝土路面配筋率设计参数对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1122-1132. |
| [8] | 魏海斌,马子鹏,毕海鹏,刘汉涛,韩栓业. 基于力学响应分析方法的导电橡胶复合路面铺装技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 531-537. |
| [9] | 刘状壮,张有为,季鹏宇,Abshir Ismail Yusuf,李林,郝亚真. 电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 523-530. |
| [10] | 郭庆林,刘强,吴春利,李黎丽,李懿明,刘富春. 导电沥青及混合料裂缝局部温度场及愈合效果[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1386-1393. |
| [11] | 时成林,王勇,吴春利,宋文祝. 路堤挡土墙主动土压力计算方法修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1394-1403. |
| [12] | 姚玉权,仰建岗,高杰,宋亮. 基于性能-费用模型的厂拌再生沥青混合料优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 585-595. |
| [13] | 夏全平,高江平,罗浩原,张其功,李志杰,杨飞. 用于高模量沥青砼的复合改性硬质沥青低温性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 541-549. |
| [14] | 杨海吉,何佳龙,李国发,王立鼎,王思远. 改进失效模式和影响分析方法在加工中心主轴系统风险分析中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 345-352. |
| [15] | 叶奋,胡诗园. 考虑旧水泥路面接缝传荷能力的超薄罩面力学特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2636-2643. |
|
||