吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1638-1649.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221511
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
非平稳极端风作用下大跨桥梁瞬态风致效应分析
冯宇1( ),郝键铭1,2(
),郝键铭1,2( ),王峰1,2,张久鹏1,黄晓明3
),王峰1,2,张久鹏1,黄晓明3
- 1.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710064
2.长安大学 风洞实验室,西安 710064
3.东南大学 交通学院,南京 211189
Analysis of transient wind⁃induced response of long⁃span bridge under nonstationary wind field
Yu FENG1( ),Jian-ming HAO1,2(
),Jian-ming HAO1,2( ),Feng WANF1,2,Jiu-peng ZHANG1,Xiao-ming HUANG3
),Feng WANF1,2,Jiu-peng ZHANG1,Xiao-ming HUANG3
- 1.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.Wind Tunnel Laboratory,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
3.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
摘要:
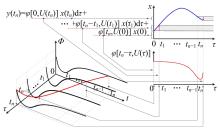
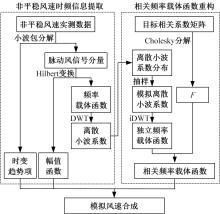
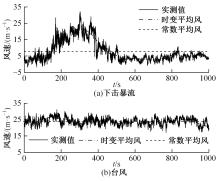
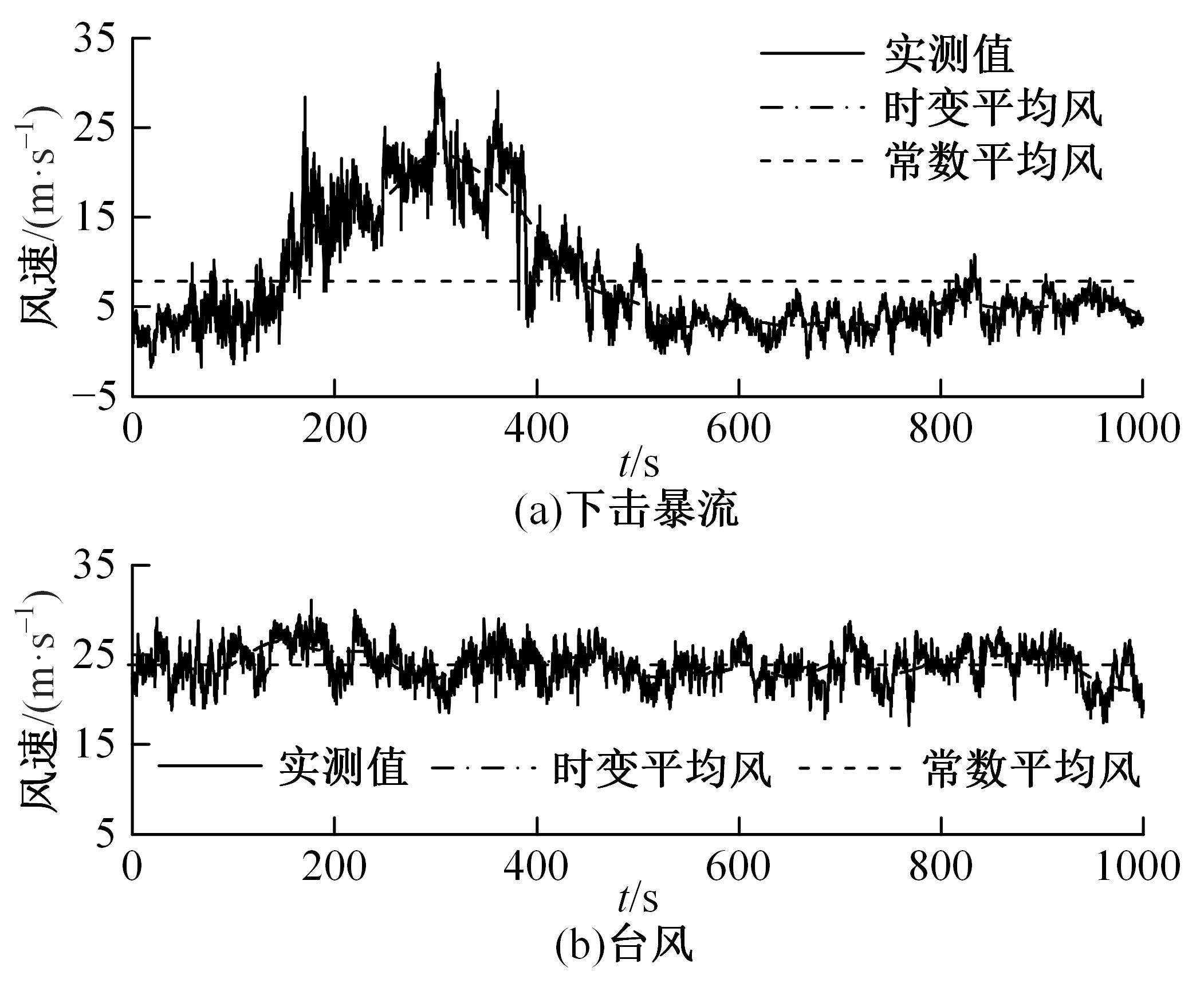
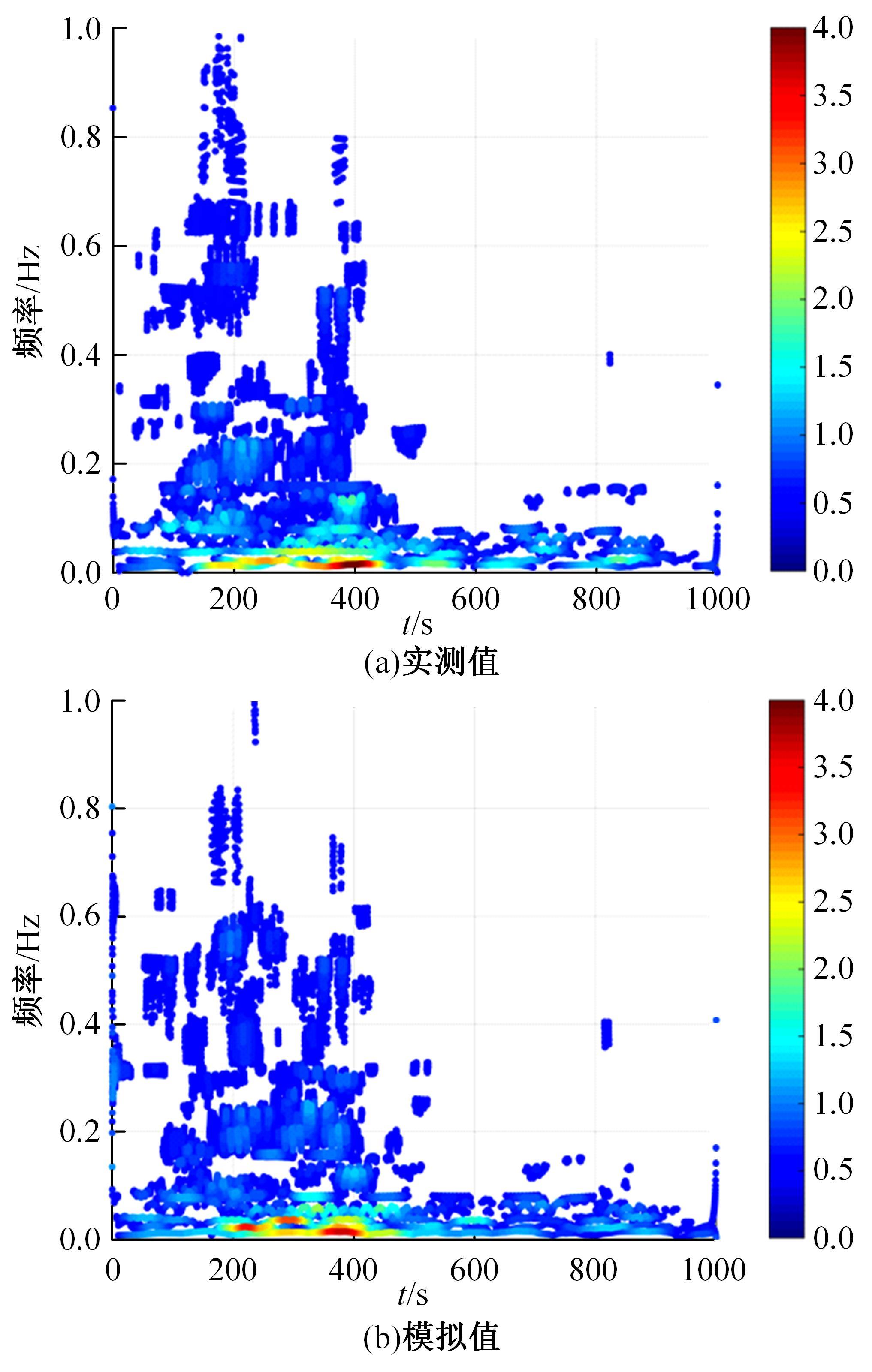
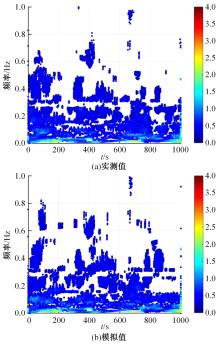
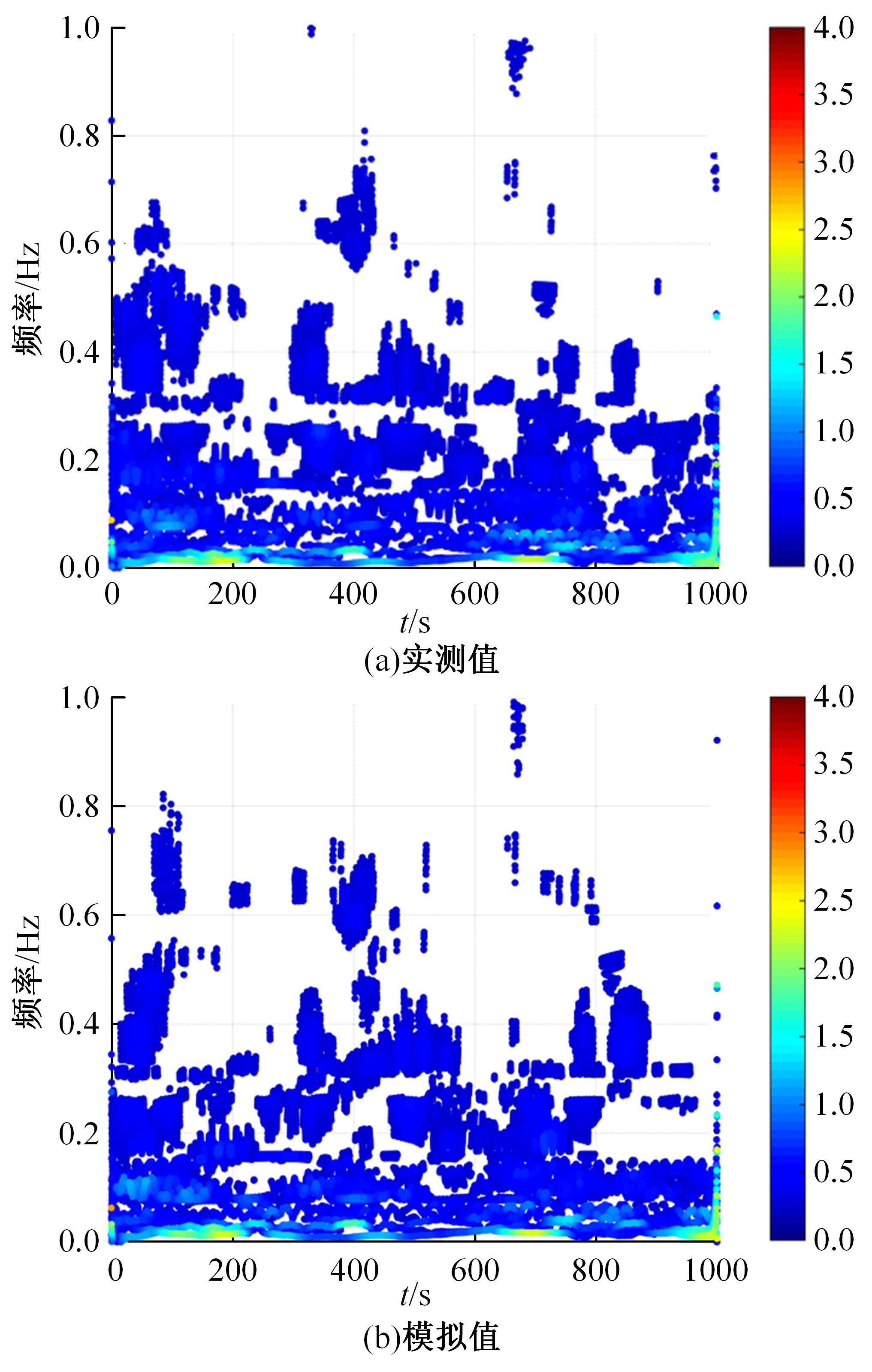
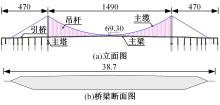
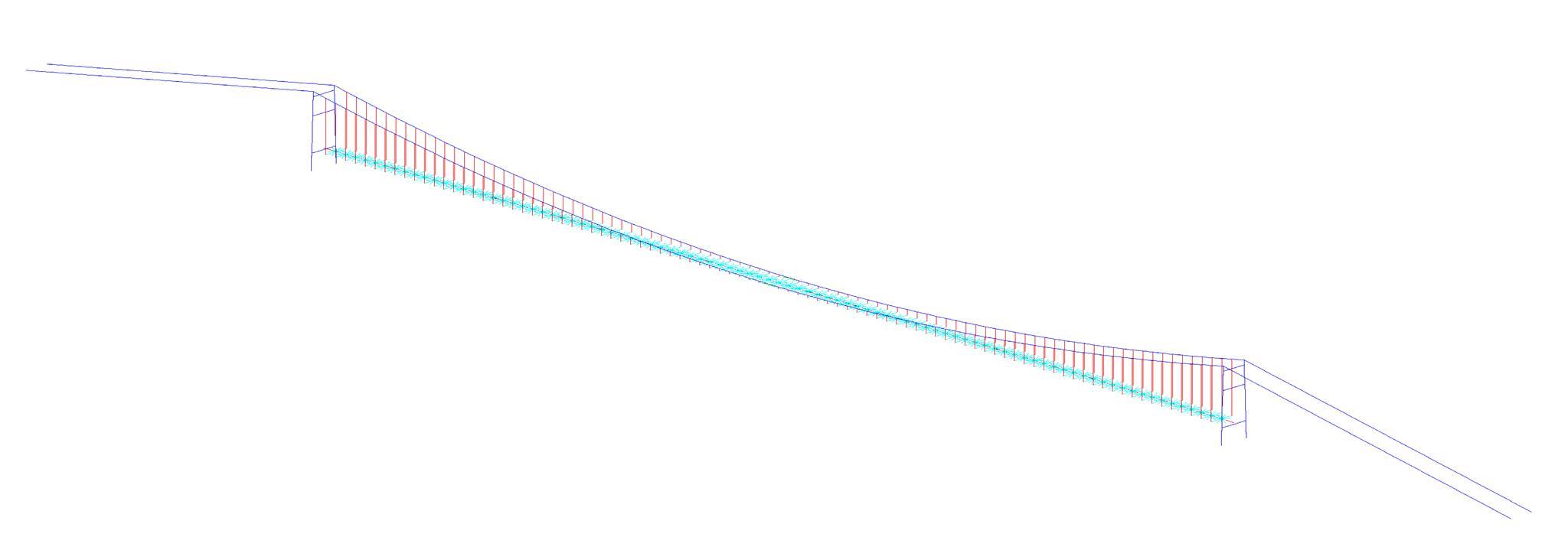
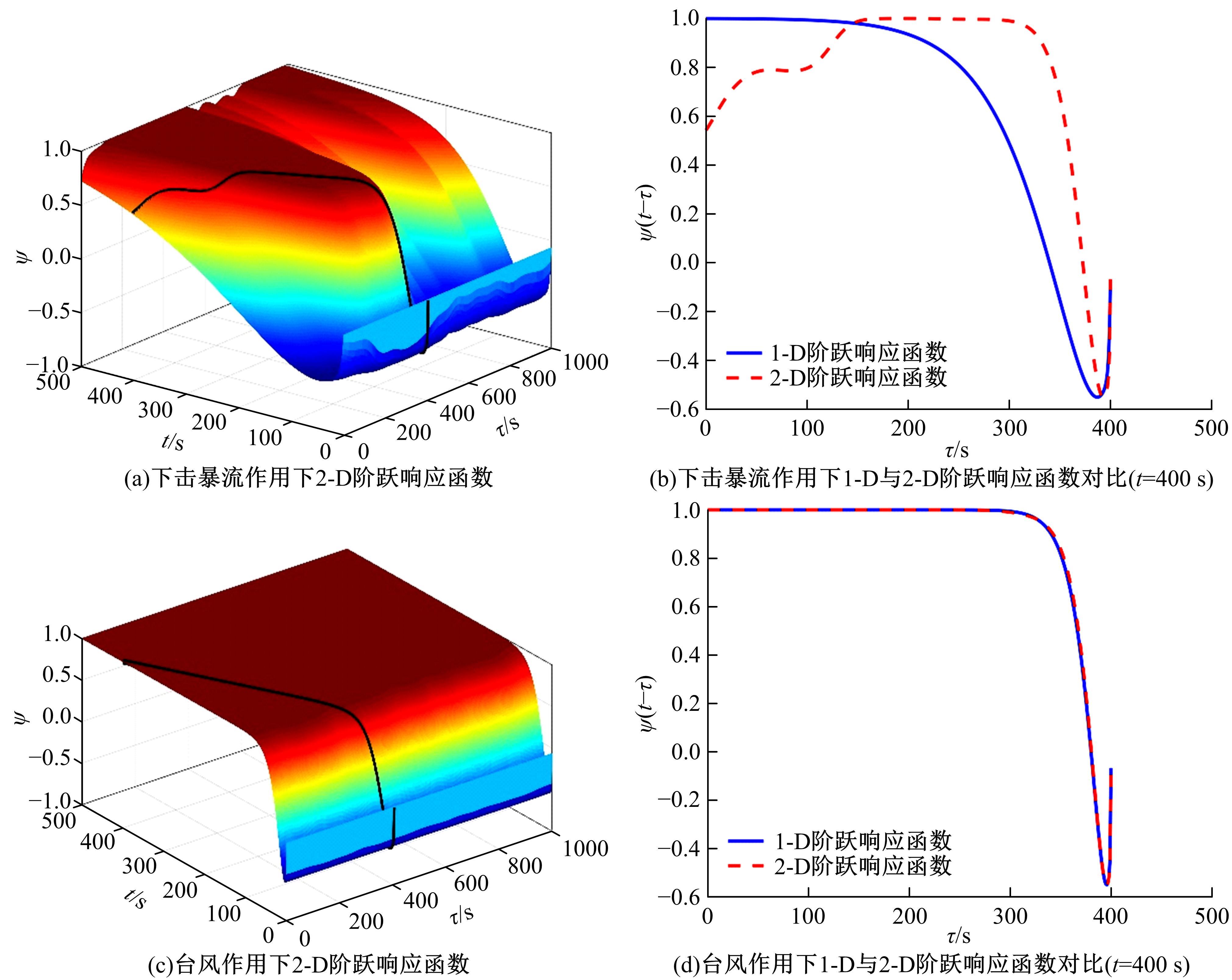
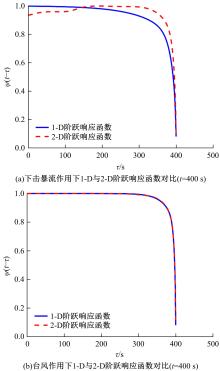
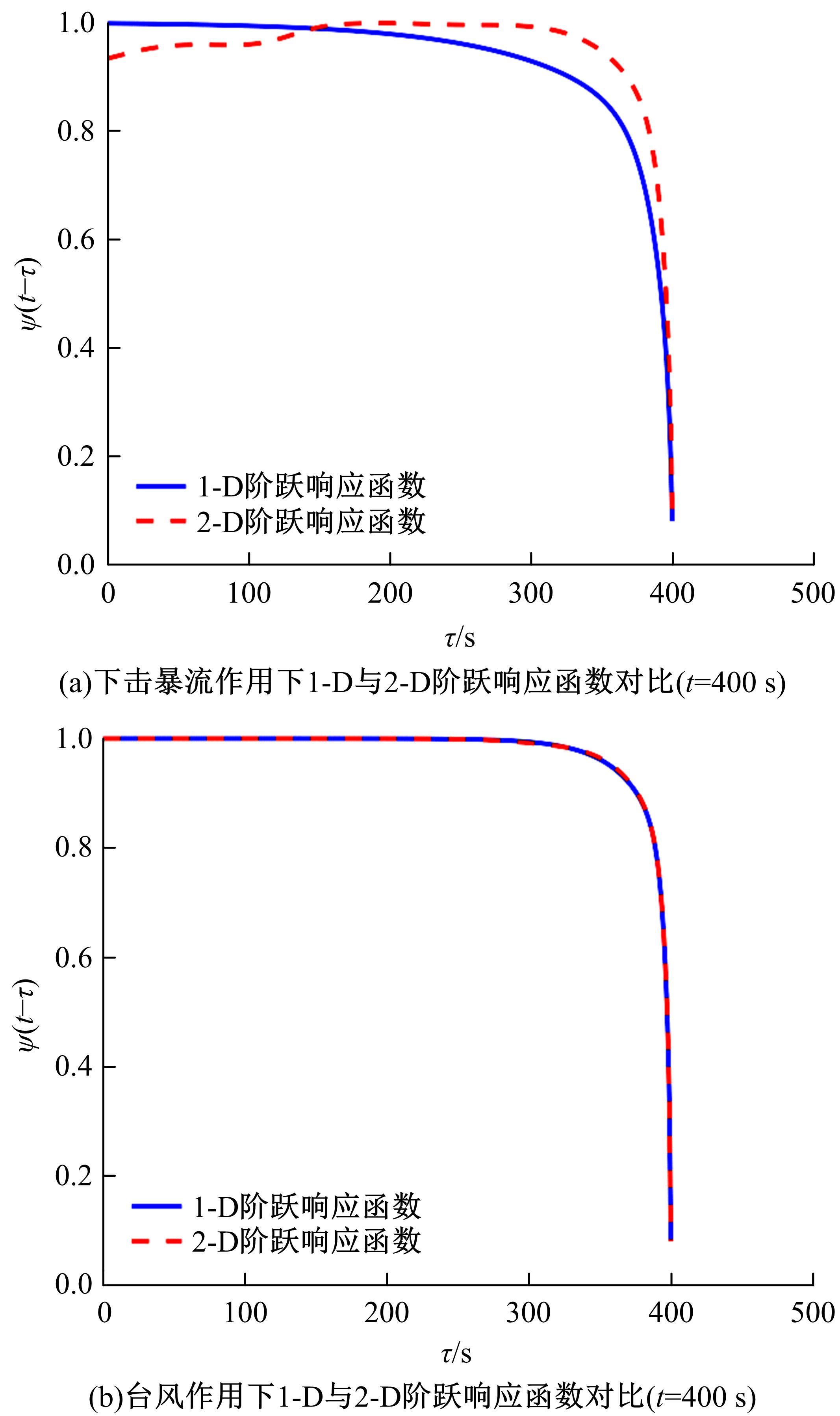
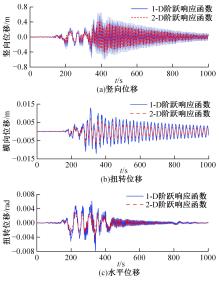
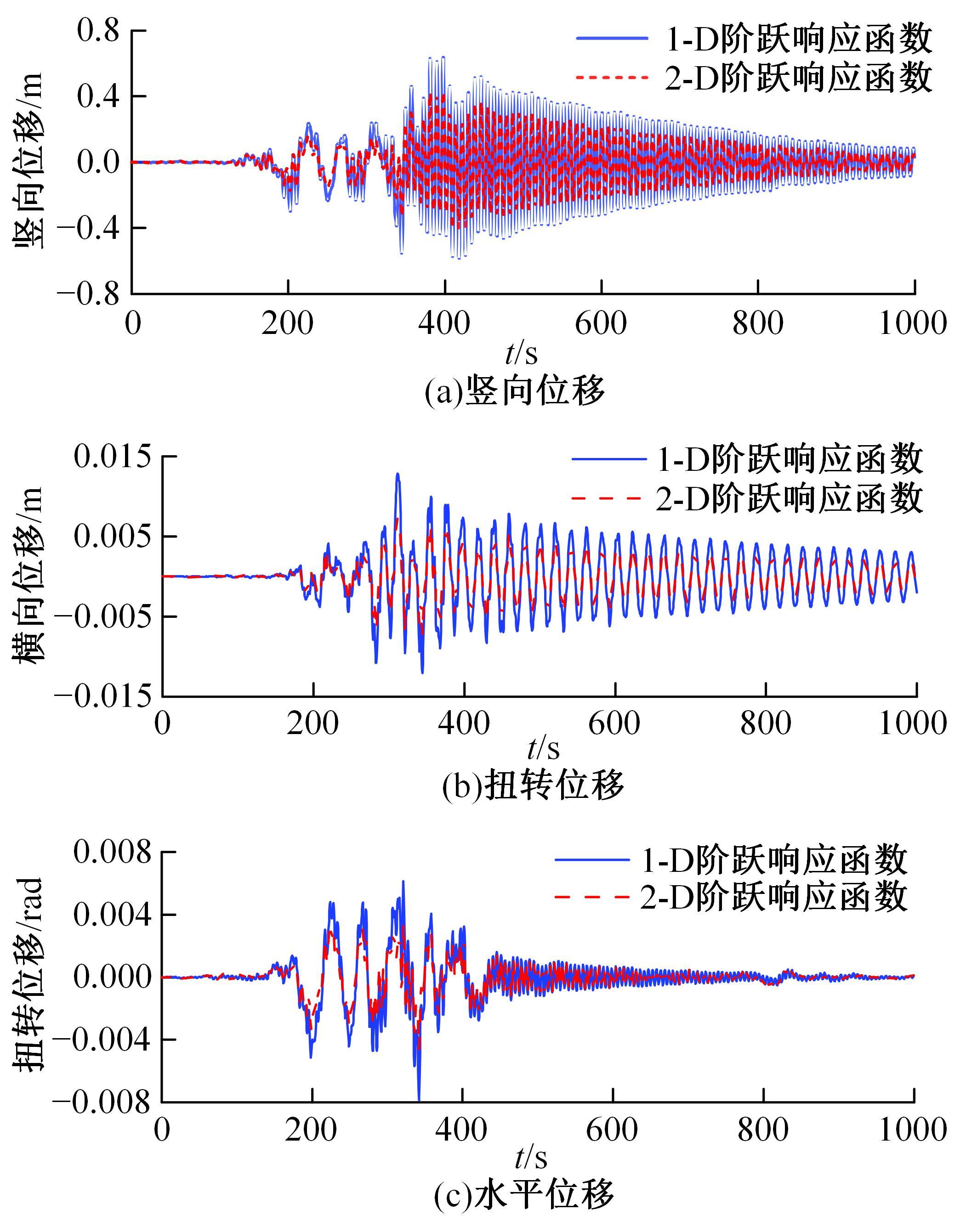
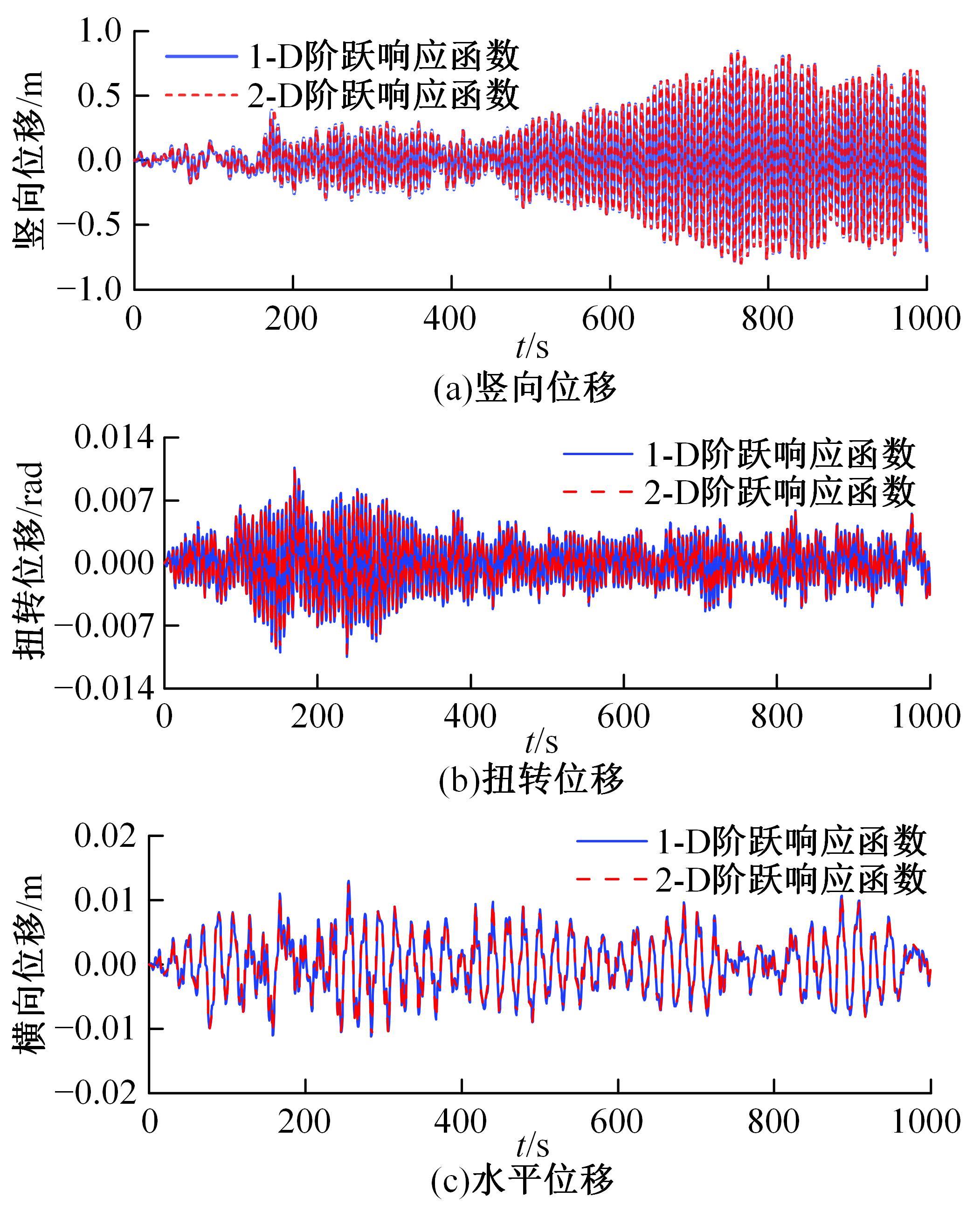
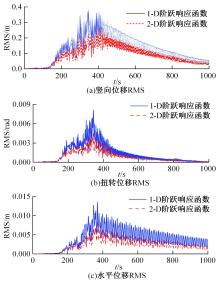
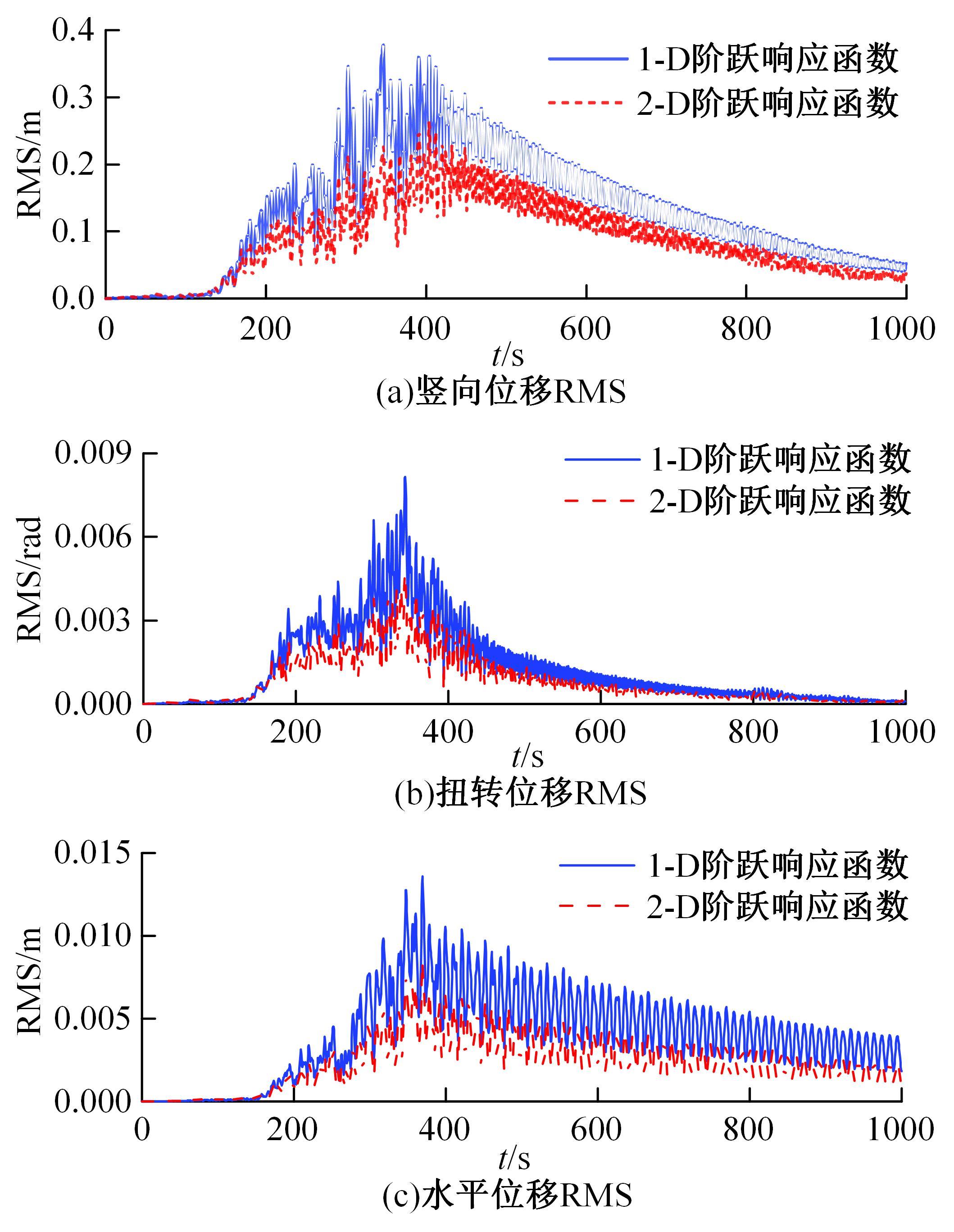
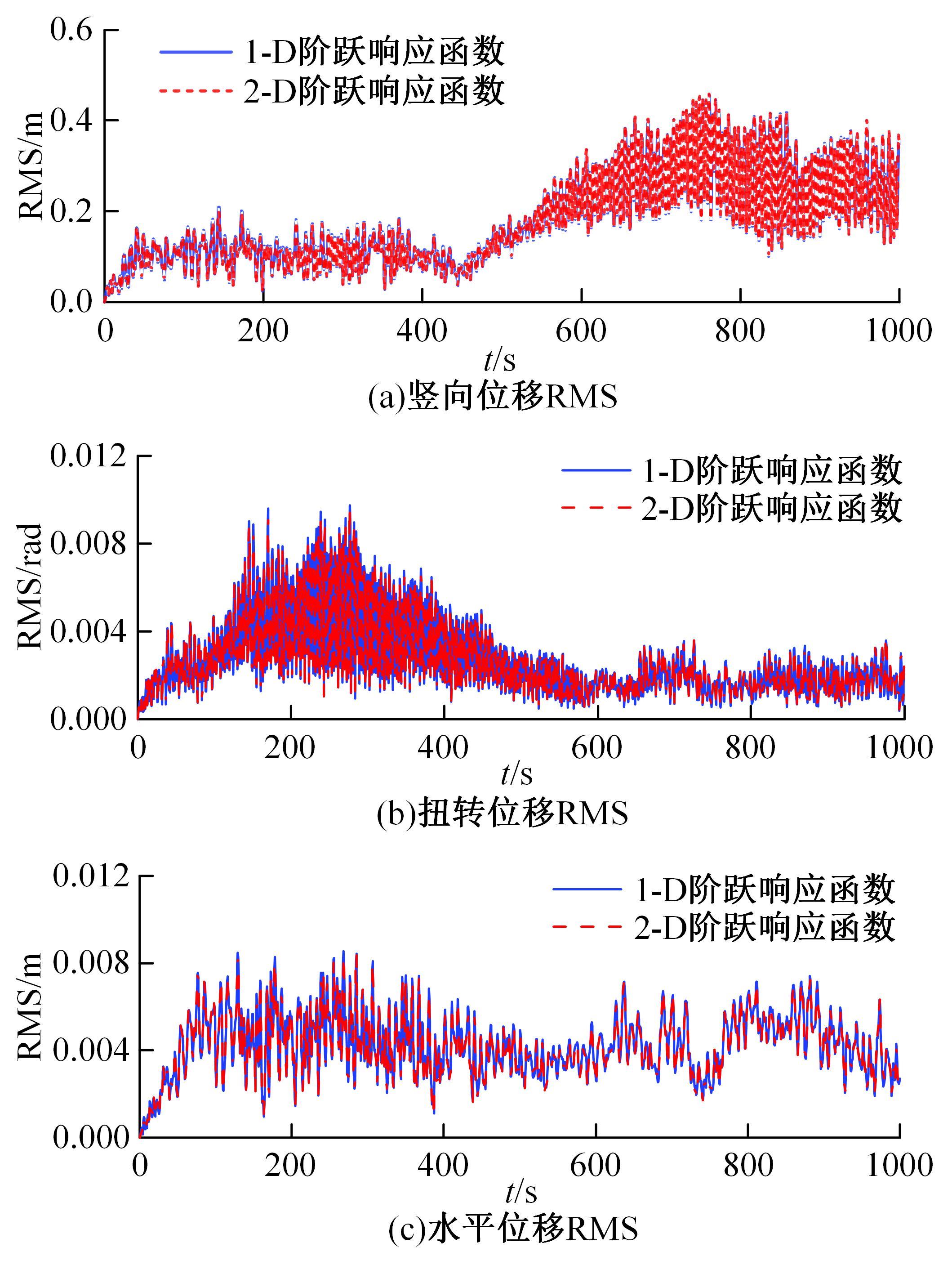
为了研究非平稳风场瞬态效应对风致桥梁响应的影响,基于Hilbert谱进行全桥非平稳风场模拟,采用Cholesky分解嵌入风场空间相性,并引入2-D阶跃响应函数建立了考虑瞬态效应的非平稳风致桥梁抖振响应分析方法。通过下击暴流和台风实测数据提取Hilbert谱,从而高精度地重现真实下击暴流/台风风场。依托某大跨度悬索桥进行非平稳抖振响应分析,探究了非平稳风场瞬态效应对桥梁气动力和抖振响应的影响。研究结果表明:下击暴流风场表现出显著的非平稳特征,时变平均风致瞬态效应明显改变了风-桥耦合系统的气动特征,使阶跃响应函数呈现出显著的时变性,进而影响大跨度桥梁的抖振响应;而在台风风场中,时变平均风致瞬态效应并不显著,对气动力和桥梁抖振响应的影响几乎可以忽略。
中图分类号:
- U442
| 1 | 陶天友, 王浩, 姚程渊. 非平稳风速的 HHS 时频状态表征[J]. 振动工程学报, 2019, 32(1): 49-55. |
| Tao Tian-you, Wang Hao, Yao Cheng-yuan. HHS-based time-frequency characterization of non-statioanry wind velocities[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2019, 32(1): 49-55. | |
| 2 | Hao J, Wu T. Downburst-induced transient response of a long-span bridge: a CFD-CSD-based hybrid approach[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2018, 179: 273-286. |
| 3 | Chen L, Letchford C W. Proper orthogonal decomposition of two vertical profiles of full-scale nonstationary downburst wind speeds[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2005, 93(3): 187-216. |
| 4 | Xu Y L, Chen J. Characterizing nonstationary wind speed using empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2004, 130(6): 912-920. |
| 5 | Huang G, Su Y, Kareem A, et al. Time-frequency analysis of nonstationary process based on multivariate empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 142(1): No.04015065. |
| 6 | Su Y, Huang G, Xu Y L. Derivation of time-varying mean for non-stationary downburst winds[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2015, 141: 39-48. |
| 7 | Priestley M B. Evolutionary spectra and non‐stationary processes[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 1965, 27(2): 204-229. |
| 8 | Deodatis G. Non-stationary stochastic vector processes: seismic ground motion applications[J]. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics, 1996, 11(3): 149-167. |
| 9 | Huang G. An efficient simulation approach for multivariate nonstationary process: hybrid of wavelet and spectral representation method[J]. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 37: 74-83. |
| 10 | Li Y, Kareem A. Simulation of multivariate nonstationary random processes by FFT[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 1991, 117(5): 1037-1058. |
| 11 | Xu Y L, Hu L, Kareem A. Conditional simulation of nonstationary fluctuating wind speeds for long-span bridges[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 140(1): 61-73. |
| 12 | Wen Y, Gu P. Description and simulation of nonstationary processes based on Hilbert spectra[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2004, 130(8): 942-951. |
| 13 | Wang H, Wu T. Hilbert-wavelet-based nonstationary wind field simulation: a multiscale spatial correlation scheme[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2018, 144(8): No.04018063. |
| 14 | Kareem A. Numerical simulation of wind effects: a probabilistic perspective[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2008, 96(10/11): 1472-1497. |
| 15 | Cao B, Sarkar P P. Numerical simulation of dynamic response of a long-span bridge to assess its vulnerability to non-synoptic wind[J]. Engineering Structures, 2015, 84: 67-75. |
| 16 | Butler K, Cao S, Kareem A, et al. Surface pressure and wind load characteristics on prisms immersed in a simulated transient gust front flow field[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2010, 98(6/7): 299-316. |
| 17 | Shirato H, Maeta K, Kato Y, et al. Transient drag force on 2-D bluff bodies under gusty wind condition[C]∥7th Asia-Pacific Conference on Wind Engineering, Taipei, China, 2009: 1-8. |
| 18 | Hu L, Xu Y L, Huang W F. Typhoon-induced non-stationary buffeting response of long-span bridges in complex terrain[J]. Engineering Structures, 2013, 57: 406-415. |
| 19 | Chen X. Analysis of multimode coupled buffeting response of long-span bridges to nonstationary winds with force parameters from stationary wind[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2015, 141(4): No.04014131. |
| 20 | Hao J, Wu T. Nonsynoptic wind-induced transient effects on linear bridge aerodynamics[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2017, 143(9): No. 04017092. |
| 21 | 陶天友, 王浩. 大跨度桥梁主梁节段模型非平稳抖振时域模拟与分析[J]. 振动工程学报, 2019, 32(5): 830-836. |
| Tao Tian-you, Wang Hao. Time-domain simulation and analysis of nonstationary buffeting responses of girder section model of a long-span bridge[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2019, 32(5): 830-836. | |
| 22 | Wu T, Kareem A. Revisiting convolution scheme in bridge aerodynamics: comparison of step and impulse response functions[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 140(5): No.04014008. |
| 23 | Scanlan R H, Béliveau J G, Budlong K S. Indicial aerodynamic functions for bridge decks[J]. Journal of the Engineering Mechanics Division, 1974, 100(4): 657-672. |
| 24 | Gabor D. Theory of communication. Part 1: the analysis of information[J]. Journal of the Institution of Electrical Engineers-part III: Radio and Communication Engineering, 1946, 93(26): 429-441. |
| 25 | Boashash B. Estimating and interpreting the instantaneous frequency of a signal. I. Fundamentals[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1992, 80(4): 520-538. |
| 26 | Olhede S, Walden A. The Hilbert spectrum via wavelet projections[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2004, 460(2044): 955-975. |
| 27 | Wang L, Mccullough M, Kareem A. A data-driven approach for simulation of full-scale downburst wind speeds[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2013, 123: 171-190. |
| 28 | Huang N E, Shen Z, Long S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995. |
| 29 | Wu T. Simulation of nonstationary wind velocity field utilizing multi-scale spatial correlation nested Hilbert-wavelet scheme[C]∥14th International Conference on Wind Engineering, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2015: 1-16. |
| 30 | Zhang S, Solari G, De Gaetano P, et al. A refined analysis of thunderstorm outflow characteristics relevant to the wind loading of structures[J]. Probabilistic Engineering Mechanics, 2018, 54: 9-24. |
| 31 | Song L, Chen W, Wang B, et al. Characteristics of wind profiles in the landfalling typhoon boundary layer[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2016, 149: 77-88. |
| 32 | Chen L, Letchford C. Numerical simulation of extreme winds from thunderstorm downbursts[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2007, 95(9-11): 977-990. |
| 33 | 陈艾荣. 润扬长江公路大桥悬索桥抗风性能试验研究[R]. 上海:同济大学土木工程防灾国家重点实验室,2001. |
| 34 | Jones R T. The unsteady lift of a wing of finite aspect ratio[R]. Washington DC: National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics, 1940. |
| [1] | 吴春利,黄诗茗,李魁,顾正伟,黄晓明,张炳涛,杨润超. 基于数值仿真和统计分析的洪水作用下桥墩作用效应分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1612-1620. |
| [2] | 谭国金,孔庆雯,何昕,张攀,杨润超,朝阳军,杨忠. 基于动力特性和改进粒子群优化算法的桥梁冲刷深度识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1592-1600. |
| [3] | 江辉,李新,白晓宇. 桥梁抗震结构体系发展述评:从延性到韧性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1550-1565. |
| [4] | 刘子玉,陈士通,支墨墨,黄晓明,陈哲心. 可“临-永”转换抢修钢墩应急使用极限承载力[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1601-1611. |
| [5] | 张玥,刘传森,宋飞. 桥台背墙对连续梁桥地震易损性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1372-1380. |
| [6] | 兰树伟,周东华,陈旭,莫南明. 双柱式高墩桥梁整体稳定性的实用算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1105-1111. |
| [7] | 孙琪凯,张楠,刘潇,周子骥. 基于Timoshenko梁理论的钢-混组合梁动力折减系数[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 488-495. |
| [8] | 叶华文,段智超,刘吉林,周渝,韩冰. 正交异性钢⁃混组合桥面的轮载扩散效应[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1808-1816. |
| [9] | 王立峰,肖子旺,于赛赛. 基于Bayesian网络的多塔斜拉桥挂篮系统风险分析的新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 865-873. |
| [10] | 张彦玲,王灿,张旭,王昂洋,李运生. 不同吊杆形式悬索桥人致振动分析及舒适度评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2644-2652. |
| [11] | 钟昌均,王忠彬,柳晨阳. 悬索桥主索鞍承载力影响因素及结构优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2068-2078. |
| [12] | 陈巍,万田保,王忠彬,厉萱,沈锐利. 悬索桥主缆除湿的内部送气管道设计与性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1749-1755. |
| [13] | 郭殊伦,钟铁毅,闫志刚. 大跨度斜拉桥拉索的抖振响应计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1756-1762. |
| [14] | 高凯,刘纲. 全局临界强度分枝-约界法的有效强度改进[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 597-603. |
| [15] | 宫亚峰,宋加祥,谭国金,毕海鹏,刘洋,单承新. 多车桥梁动态称重算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 583-596. |
|
||