吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 269-282.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230239
基于神经网络与回归分析的多孔混凝土性能预测
- 1.长安大学 特殊地区公路工程教育部重点实验室,西安 710064
2.山东高速临滕公路有限公司,山东 临沂 273400
Performance prediction of porous concrete based on neural network and regression analysis
Guang-lei QU1( ),Zong-wei YAN2,Mu-lian ZHENG1(
),Zong-wei YAN2,Mu-lian ZHENG1( ),Hong LIU2,Yue-ming YUAN2
),Hong LIU2,Yue-ming YUAN2
- 1.Key Laboratory for Special Area Highway Engineering of Ministry of Education,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.Shandong High Speed Linteng Highway Co. ,Ltd. ,Linyi 273400,China
摘要:
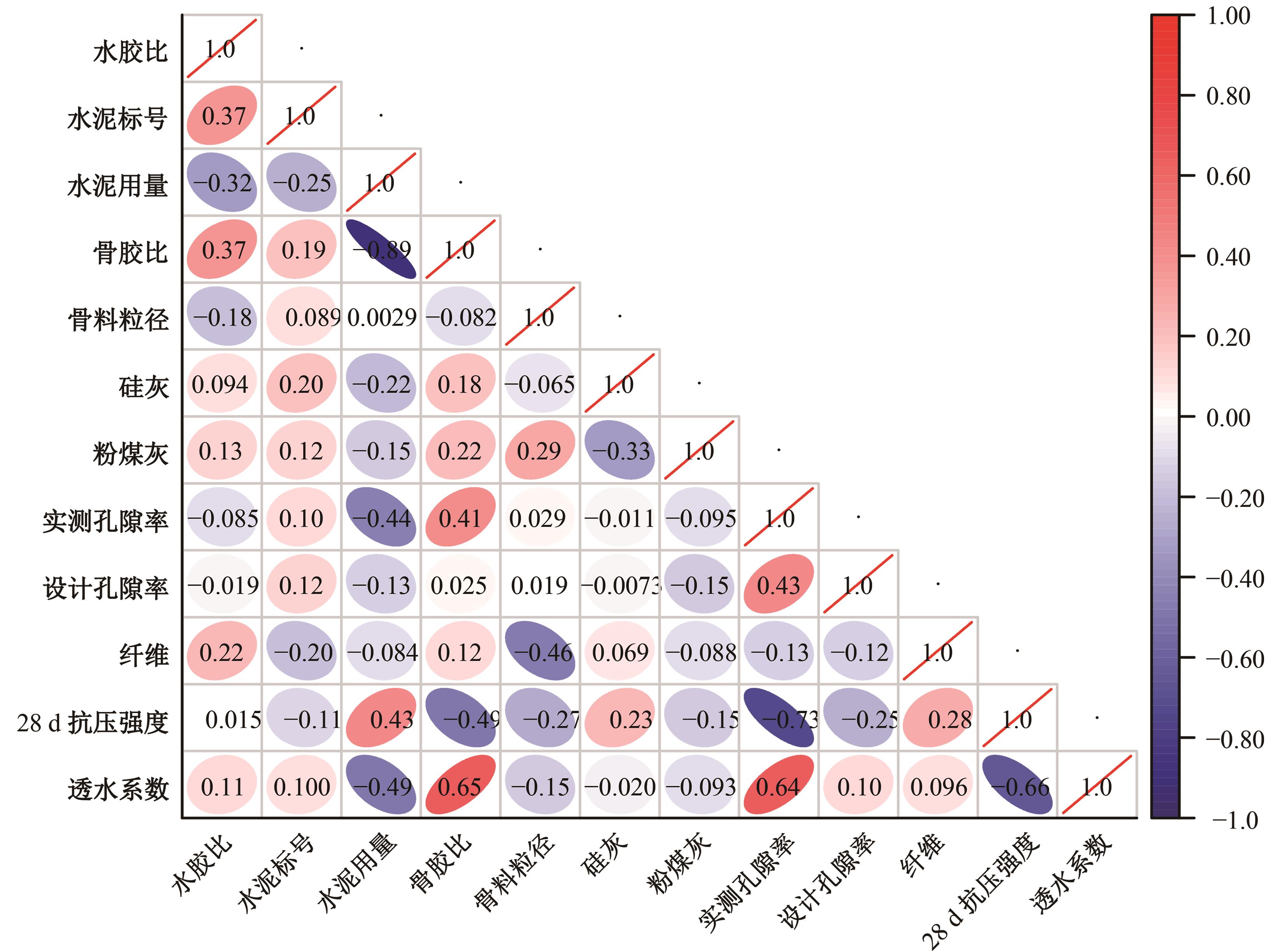
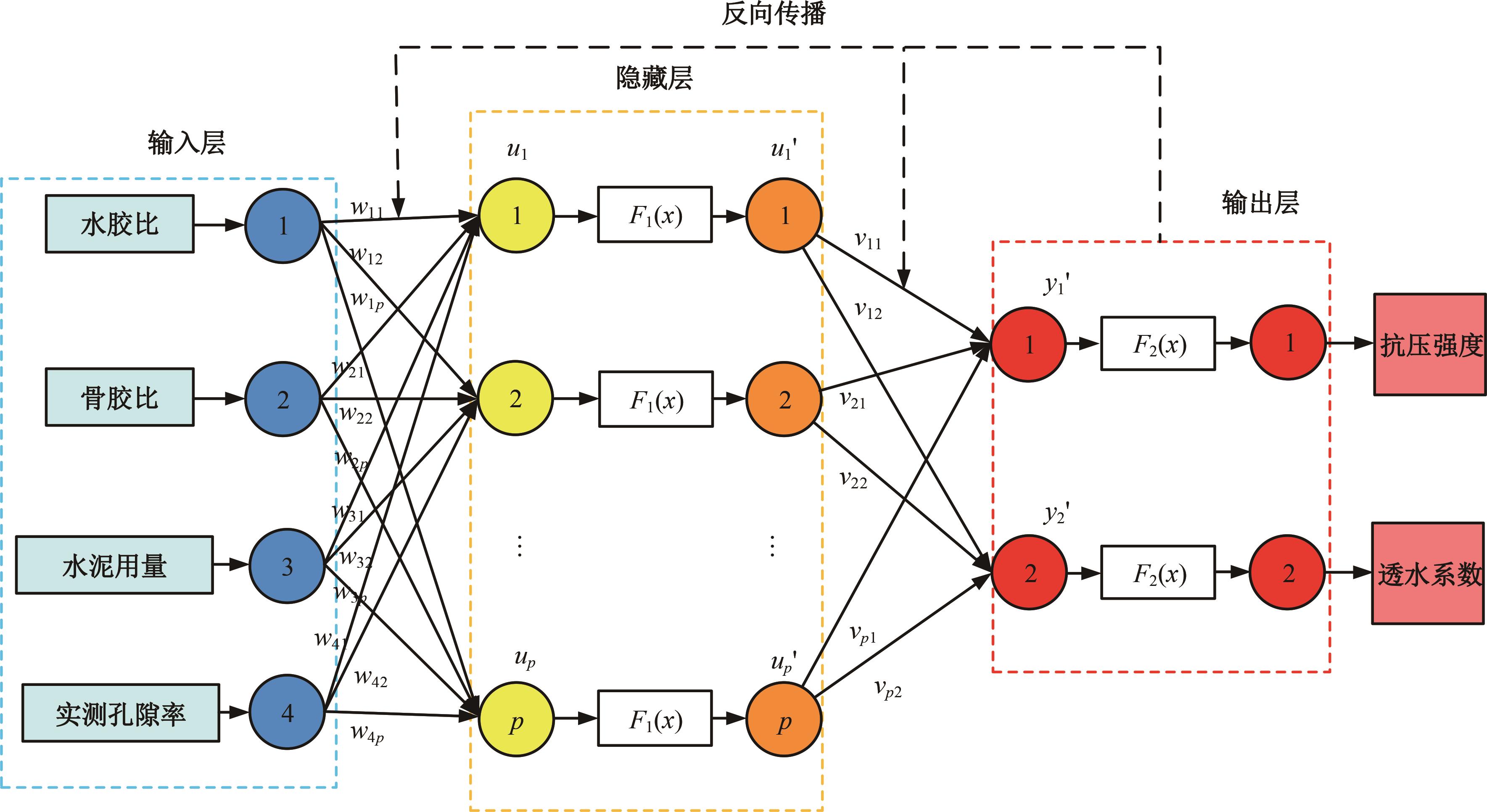
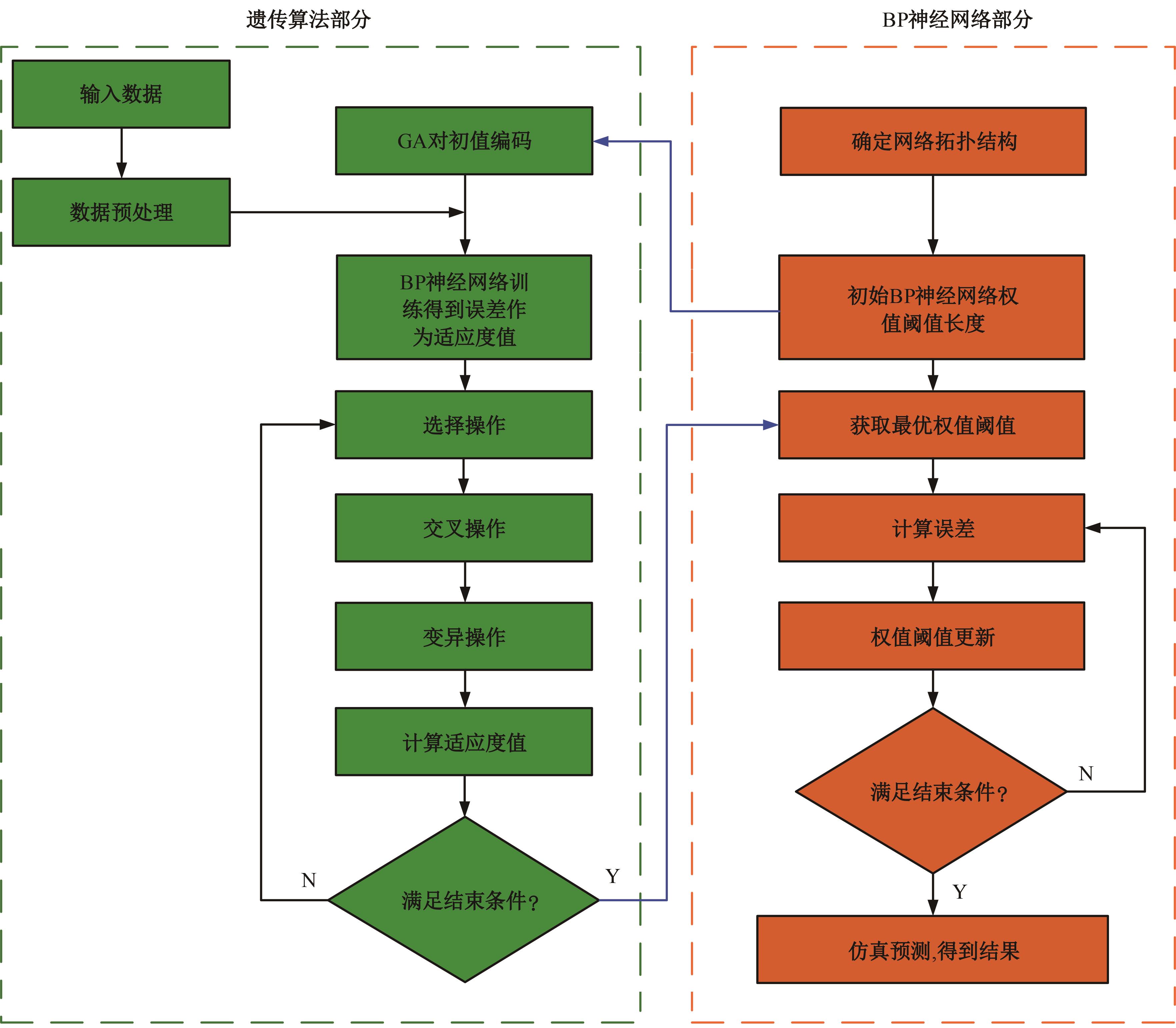
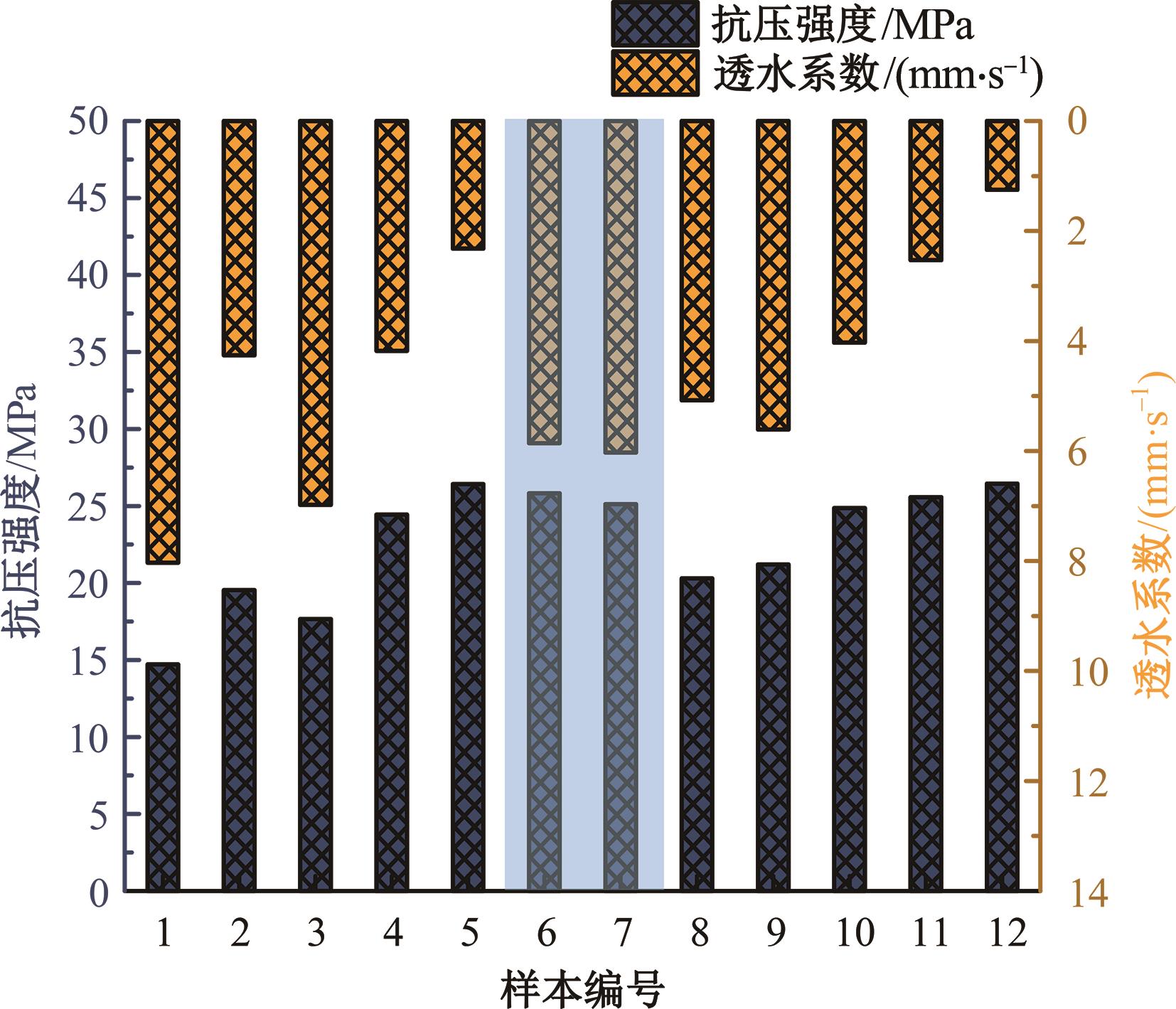
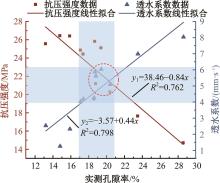
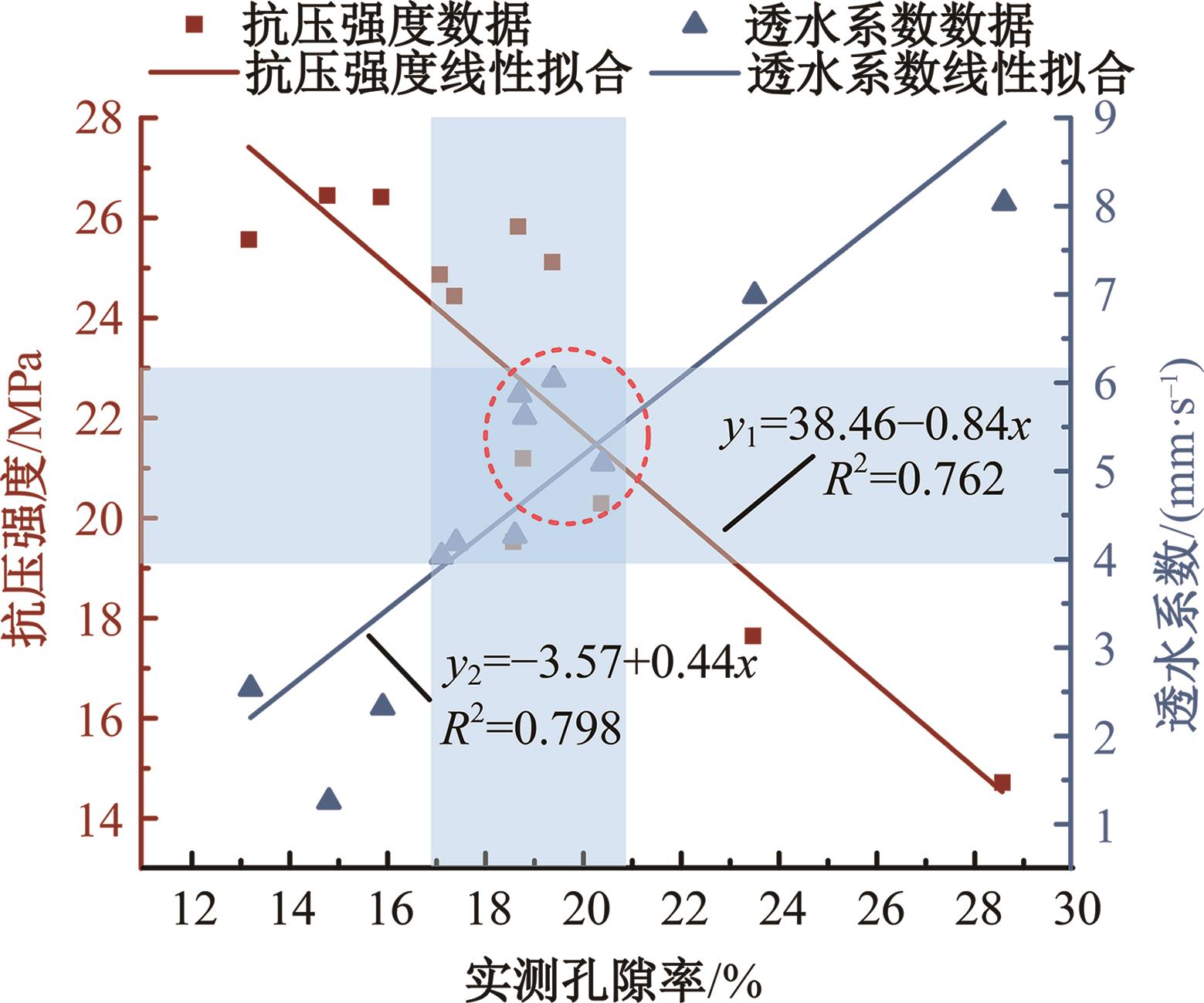
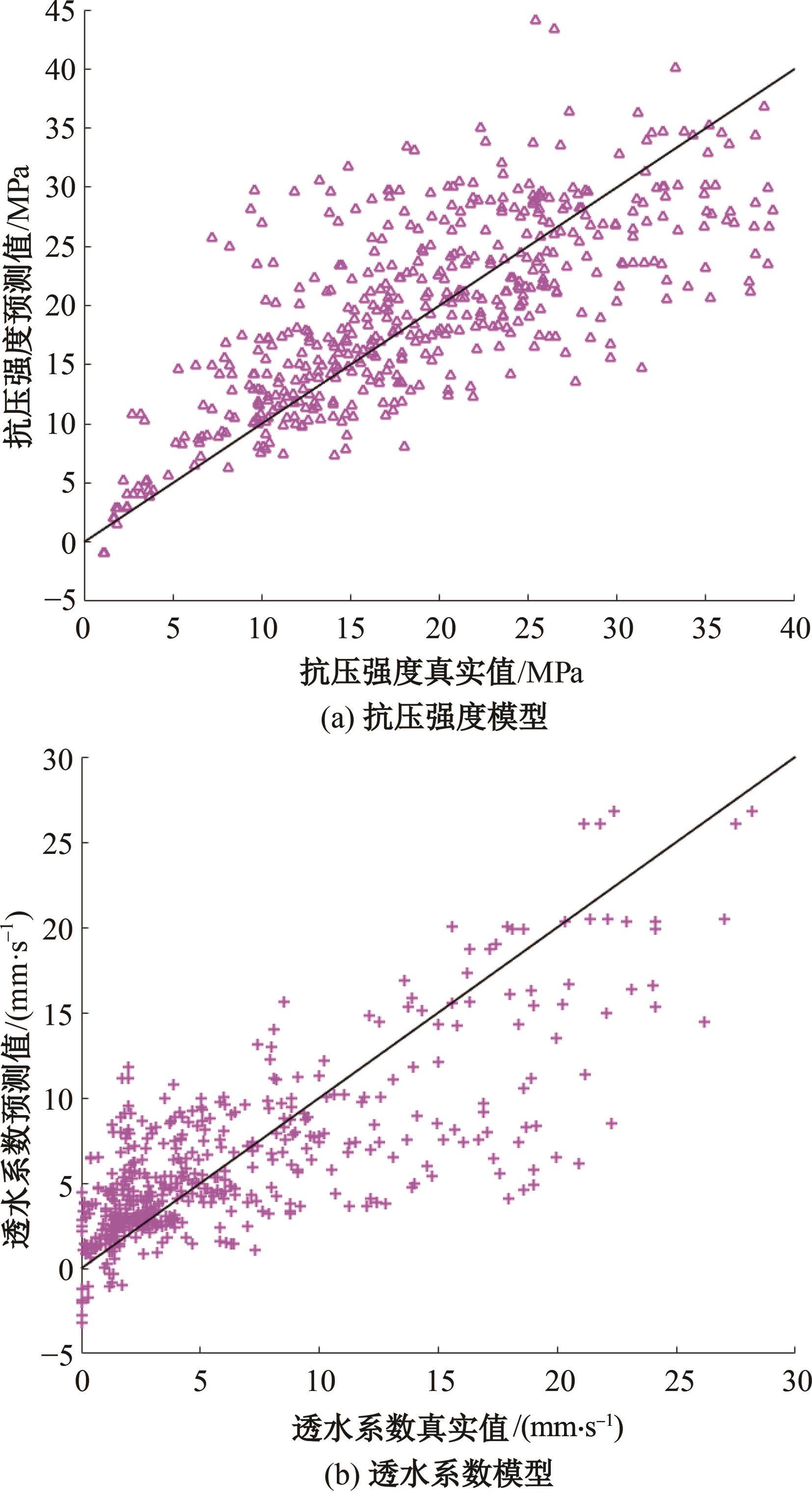
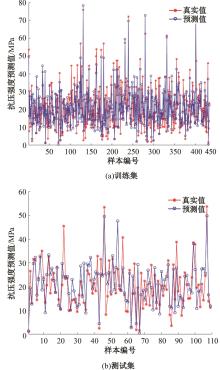
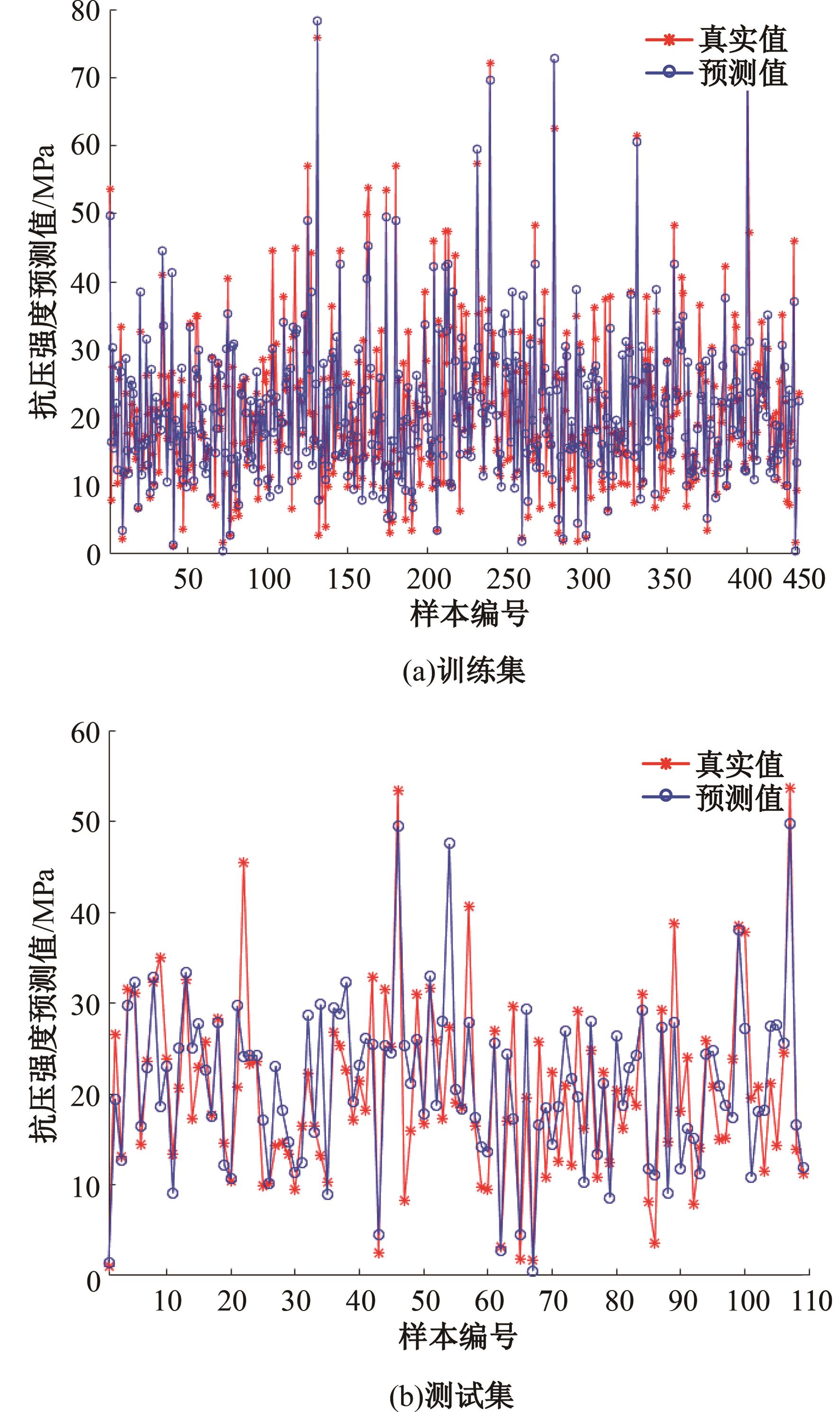
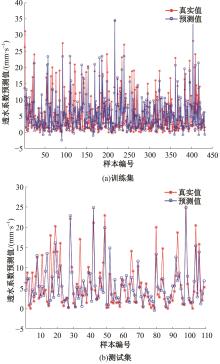
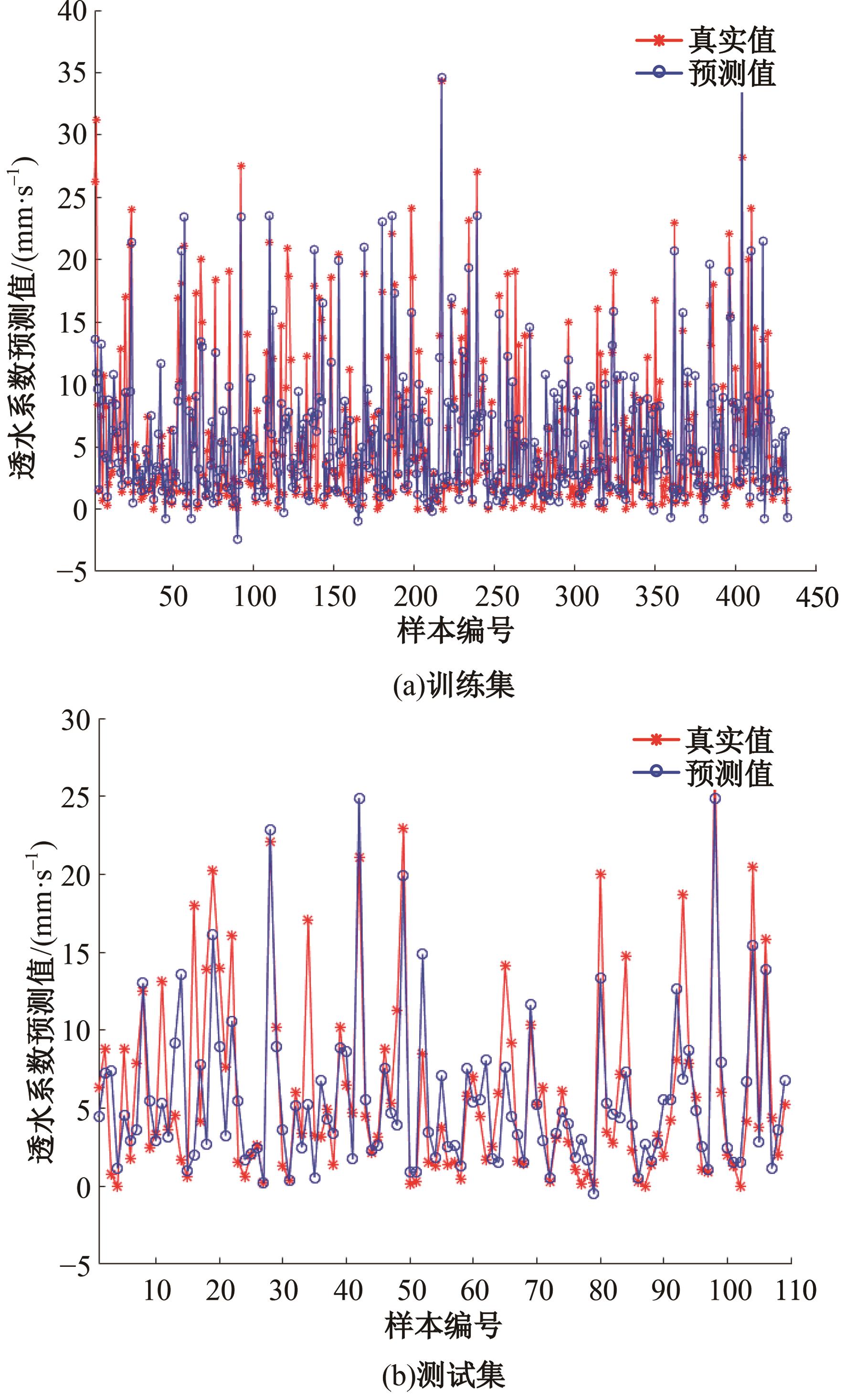
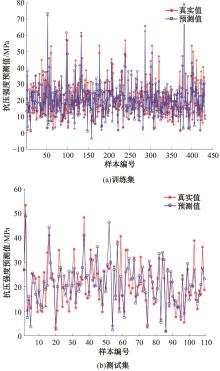
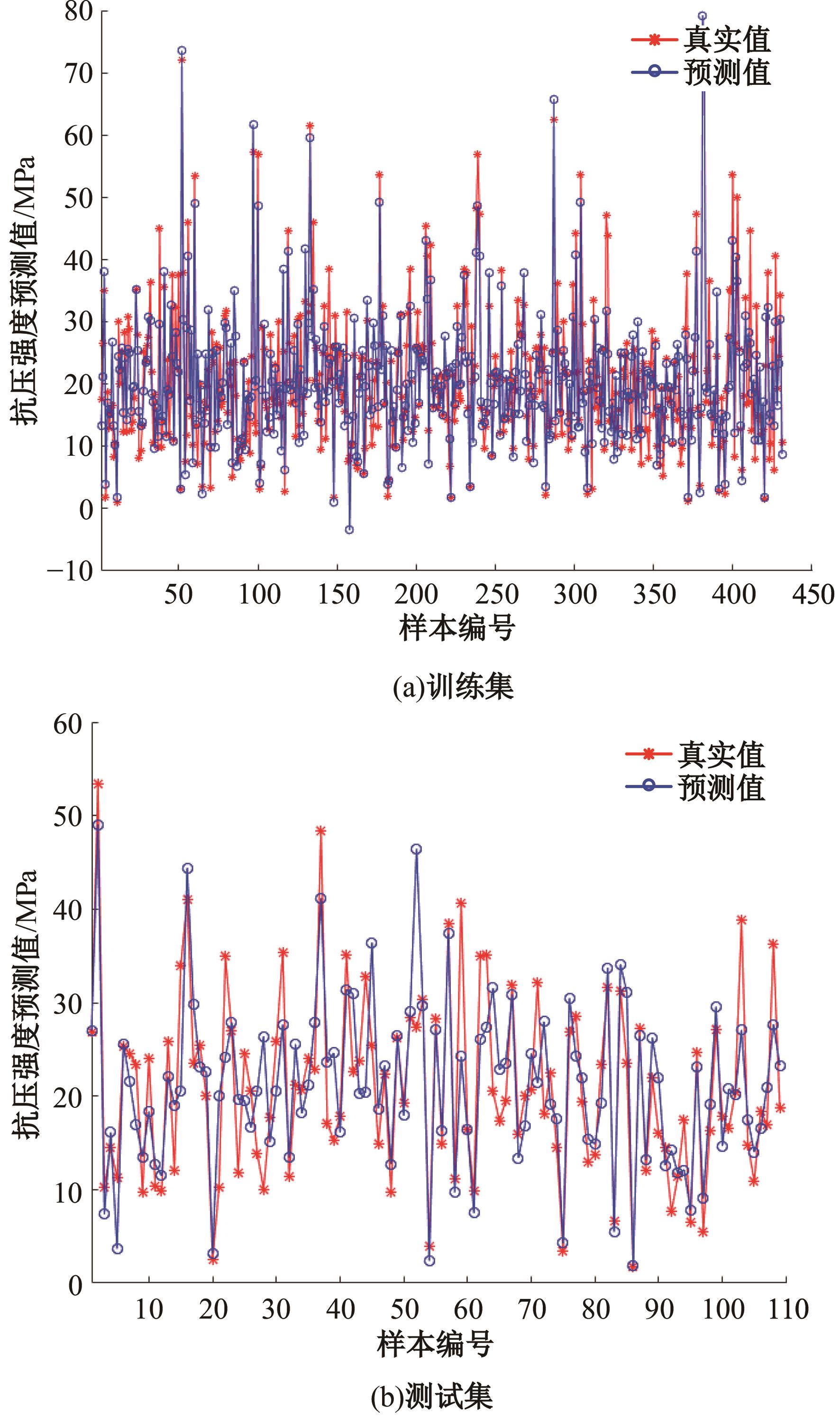
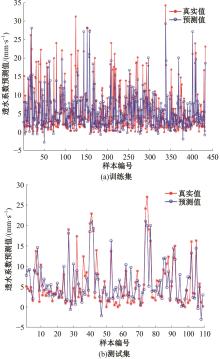
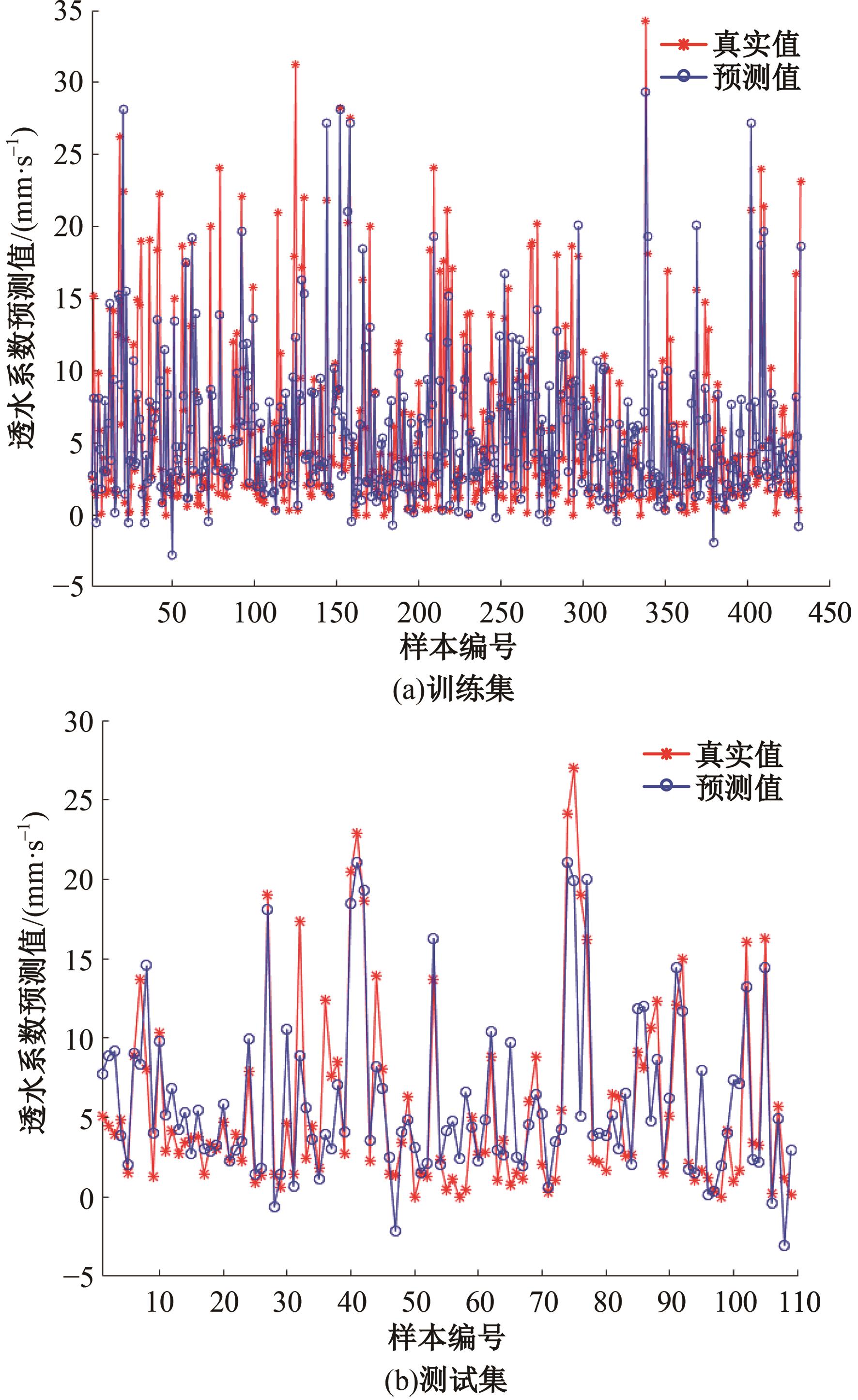
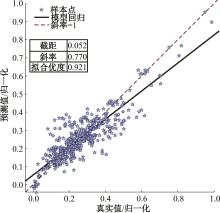
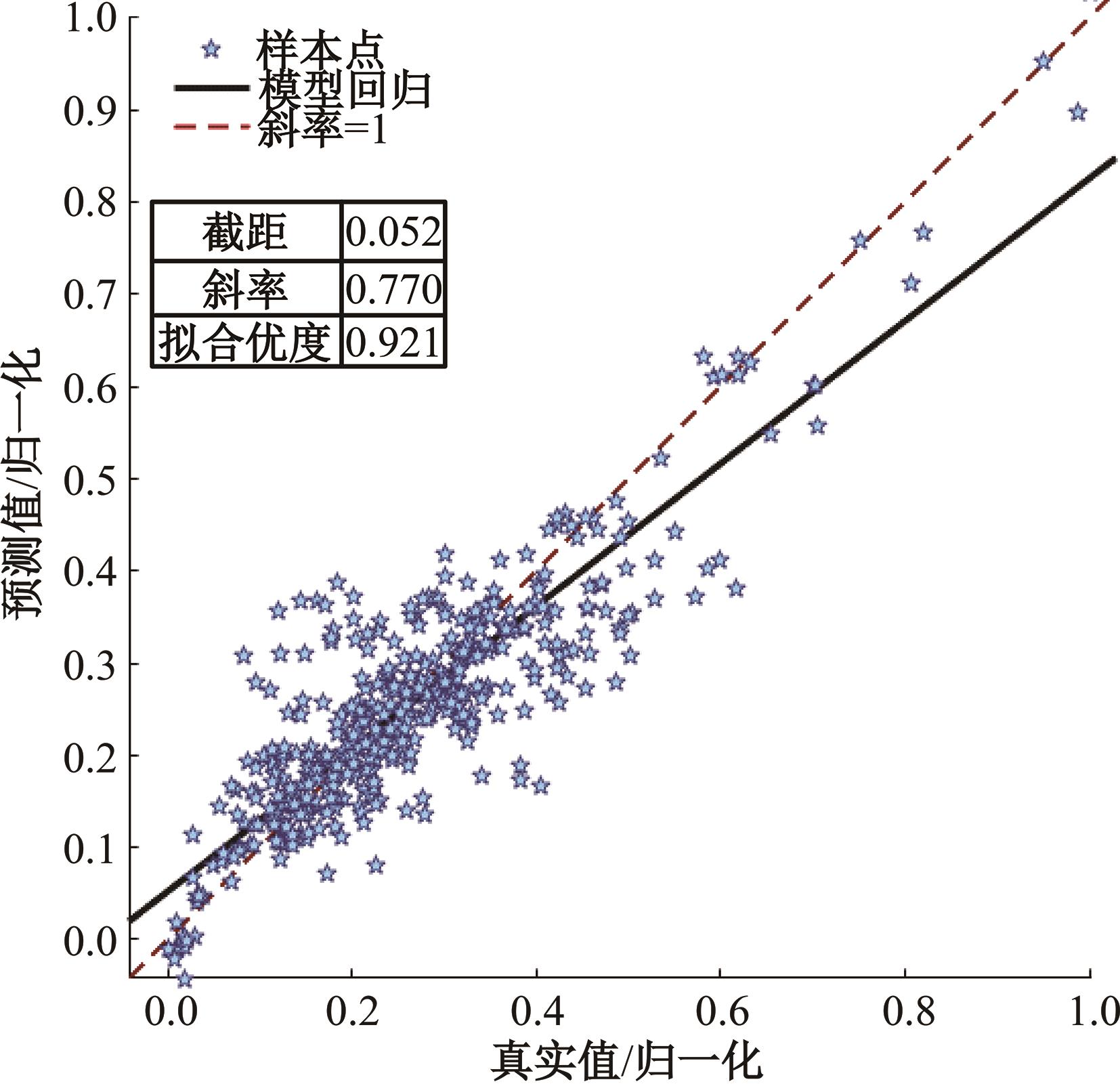
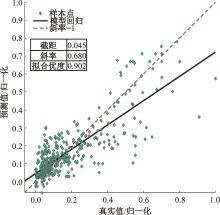
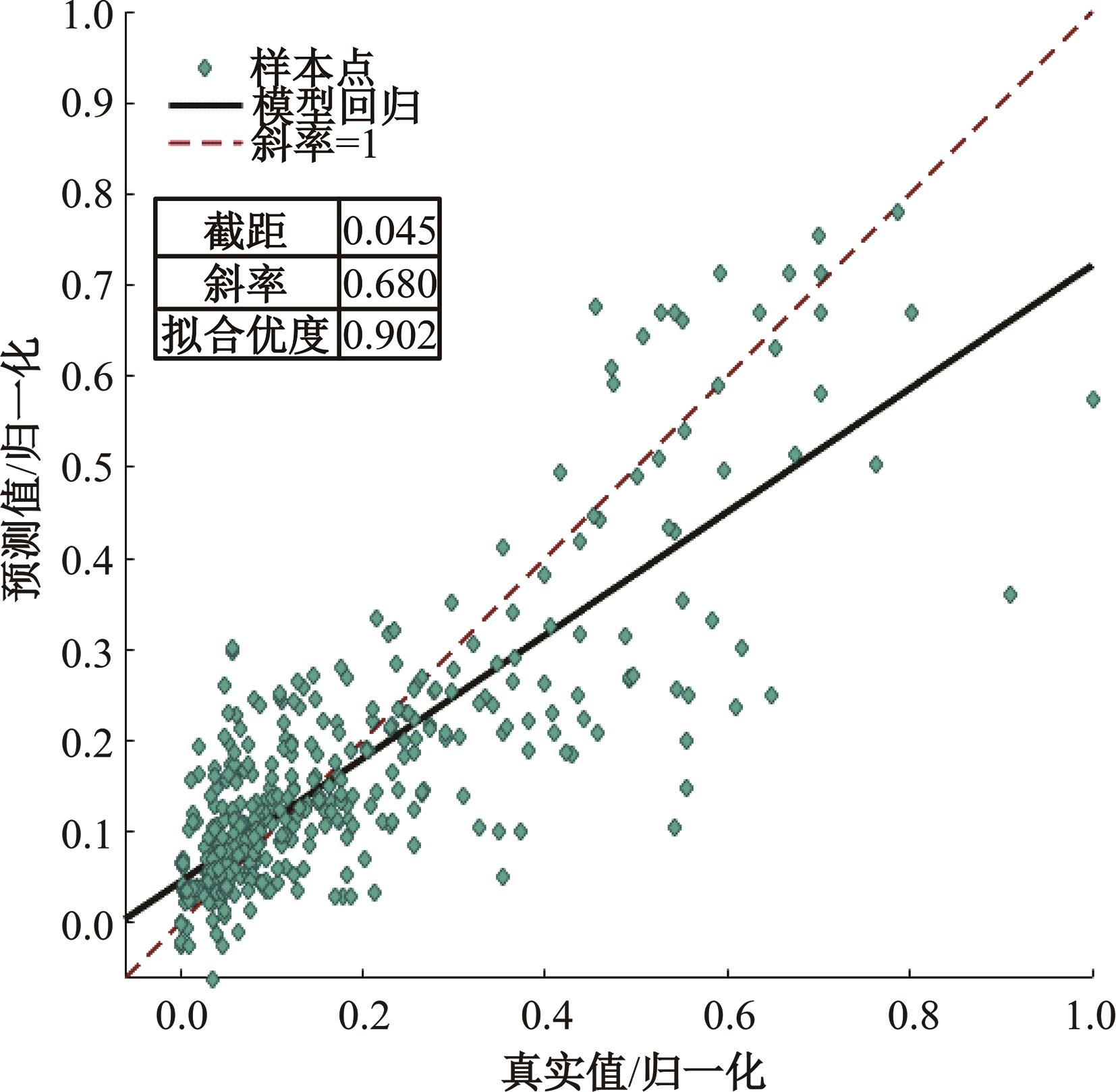
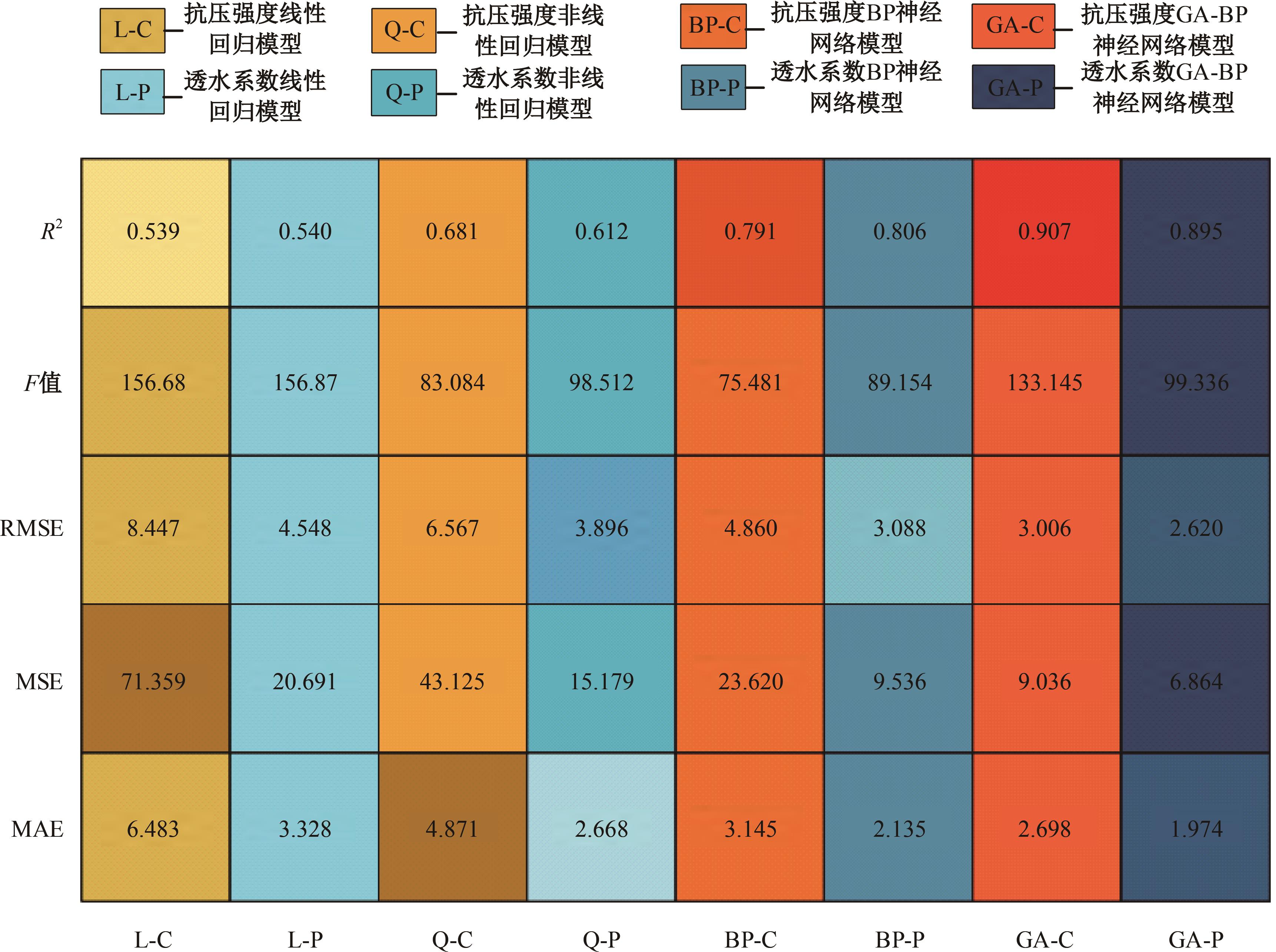
为实现对多孔混凝土28 d抗压强度和透水系数两项关键性能指标的预测,通过相关性分析确定水胶比、胶凝材料用量、骨胶比和实测孔隙率为模型输入参数,然后基于构建的数据集,采用神经网络和回归分析分别建立了4种预测模型。结果表明:两种统计回归模型的预测误差较大,对多变量的响应缺乏敏感性,其拟合优度R2均在0.681以下;两种神经网络模型更适合解决复杂、多变量的性能预测问题,其中经遗传算法优化的神经网络抗压强度预测模型的拟合优度R2达到0.9以上,体现了该预测模型的精准性和稳定性。研究成果可为多孔混凝土的配合比优化设计与性能调控提供参考和指导。
中图分类号:
- U414
| 1 | Rodin H, Rangelov M, Nassiri S, et al. Enhancing mechanical properties of pervious concrete using carbon fiber composite reinforcement [J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2018, 30(3): No.04018012. |
| 2 | Azad A, Saeedian A, Mousavi S F, et al. Effect of zeolite and pumice powders on the environmental and physical characteristics of green concrete filters [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 240(2020): No.117931. |
| 3 | 郑木莲,邓朝显,梁行行,等. 海绵城市透水水泥混凝土路面结构力学响应分析[J]. 路基工程, 2019, 37(2): 71-77. |
| Zheng Mu-lian, Deng Chao-xian, Liang Xing-xing, et al. Mechanical response analysis of permeability cement concrete pavenment structure in sponge city[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2019, 37(2): 71-77. | |
| 4 | Joshaghani A, Ramezanianpour A A, Ataei O, et al. Optimizing pervious concrete pavement mixture design by using the Taguchi method[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 101: 317-325. |
| 5 | Zhong R, Wille K. Influence of matrix and pore system characteristics on the durability of pervious concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 162: 132-141. |
| 6 | Amini K, Wang X, Delatte N. Statistical modeling of hydraulic and mechanical properties of pervious concrete using nondestructive tests[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2018, 30(6): No.04018077. |
| 7 | Liu J S, Ren F M, Quan H Z. Prediction model for compressive strength of porous concrete with low-grade recycled aggregate[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(14): No.3871. |
| 8 | Debnath B, Sarkar P P. Permeability prediction and pore structure feature of pervious concrete using brick as aggregate[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 213: 643-651. |
| 9 | Lian C, Zhuge Y, Beecham S. The relationship between porosity and strength for porous concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2011, 25: 4294-4298. |
| 10 | Le B A, Vu V H, Seo S Y, et al. Predicting the compressive strength and the effective porosity of pervious concrete using machine learning methods[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2022, 26(11): 466-479. |
| 11 | 杜青铉,张宇航,孙伟豪,等. 基于混合模型的煤矸石透水混凝土透水系数预测[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(): 319-323. |
| Du Qing-xuan, Zhang Yu-hang, Sun Wei-hao, et al. Prediction of permeability coefficient of coal gangue permeable concrete based on mixed model[J].Materials Reports, 2022, 36(Sup.1): 319-323. | |
| 12 | Azarhoosh M J, Koohmishi M. Prediction of hydraulic conductivity of porous granular media by establishment of random forest algorithm[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 366: No.130065. |
| 13 | Tian J W, Qi C C, Sun Y F, et al. Permeability prediction of porous media using a combination of computational fluid dynamics and hybrid machine learning methods[J]. Engineering with Computers, 2020, 37(4): 3455-3471. |
| 14 | Mahdi F M, Holdich R G. Using statistical and artificial neural networks to predict the permeability of loosely packed granular materials[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2016, 52(1): 1-12. |
| 15 | Chen S, Zhao Y, Bie Y. The prediction analysis of properties of recycled aggregate permeable concrete based on back-propagation neural network[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 276: No.124187. |
| 16 | Baykasoğlu A, Dereli T, Tanış S. Prediction of cement strength using soft computing techniques[J]. Cement Concrete Research, 2004, 34(11): 2083-2090. |
| 17 | Akkurt S, Ozdemir S, Tayfur G, et al. The use of GA-ANNs in the modelling of compressive strength of cement mortar[J]. Cement Concrete Research, 2003, 33(7): 973-979. |
| 18 | 王显利,曲广雷. 荷叶疏水剂对无砂透水混凝土性能的影响研究[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2017, 44(3): 11-15. |
| Wang Xian-li, Qu Gguang-lei. Study on the effects of lotus leaf hydrophobic agent on no-fines pervious concrete performance[J]. New Building Materials, 2017, 44(3): 11-15. | |
| 19 | 曲广雷. 无砂内疏水透水混凝土的研制与性能研究[D]. 吉林: 北华大学林学院, 2017. |
| Qu Guang-lei. Research on preparation and properties of no sand internal hydrophobic pervious concrete [D]. Jilin: College of Forestry, Beihua University, 2017. | |
| 20 | 郑木莲,王国清,贾献卓,等. 基于正交试验的多孔混凝土强度与空隙率影响因素分析[J]. 公路, 2015, 60(7): 230-234. |
| Zheng Mu-lian, Wang Guo-qing, Jia Xian-zhuo, et al. Analysis on the influence factors of strength and porosity based on orthogonal experiment for porous concrete[J]. Highway, 2015, 60(7): 230-234. | |
| 21 | 闫楚良,郝云霄,刘克格. 基于遗传算法优化的BP神经网络的材料疲劳寿命预测[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2014, 44(6): 1710-1715. |
| Yan Chu-liang, Hao Yun-xiao, Liu Ke-ge, et al. Fatigue life prediction of materials based on BP neural networks optimized by genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(6): 1710-1715. | |
| 22 | Hatanaka S, Mishima N, Maegawa A, et al. Fundamental study on properties of small particle size porous concrete[J]. Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology, 2014, 12(1): 24-33. |
| 23 | Bhutta M A R, Tsuruta K, Mirza J. Evaluation of high-performance porous concrete properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2012, 31: 67-73. |
| 24 | Gupta M, Dudi L, Karkhanis R, et al. Determination of optimum parameters of porous concrete for adequate strength and permeability[C]∥Proceedings of the American—Society—of—Civil—Engineers(ASCE) India Conference on Urbanization Challenges in Emerging Economies—Resilience and Sustainability of Infrastructure, New Delhi, India, 2018: 12-14. |
| 25 | Liu H, Luo G, Wei H, et al. Strength, permeability, and freeze-thaw durability of pervious concrete with different aggregate sizes, porosities, and water-binder ratios[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(8): 12-17. |
| 26 | 申明昊. 基于体积法的不同目标孔隙率下透水混凝土试验研究 [D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学土木工程学院, 2021. |
| Shen Ming-hao. Study on pervious concrete with different goal porosity based on volume method[D]. Lanzhou: School of Civil Engineering, Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2021. | |
| 27 | 孙宏友. 基于正交试验法的透水混凝土配合比设计和试验研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学土木工程学院, 2016. |
| Sun Hong-you. Experimental research and mix proportion design of porous concrete based on orthogonal test method[D]. Chendu: School of Civil Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016. | |
| 28 | 王宇. 透水混凝土配合比设计及其路用性能研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学土木工程学院, 2020. |
| Wang Yu. Mix design of pervious concrete and its application research on road performance[D]. Chongqing: School of Civil Engineering, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2020. | |
| 29 | 马旺坤. 成型方法和配合比对透水混凝土性能的影响研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学土木工程学院, 2020. |
| Ma Wang-kun. Research on influence of forming method and mix proportion on properties of pervious concrete [D]. Harbin: School of Civil Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. | |
| 30 | 张亚茹. 透水混凝土的基本力学性能及冻融、干湿循环试验研究[D]. 西安:西安理工大学土木建筑工程学院, 2020. |
| Zhang Ya-ru. Experimental study on the basic mechanical properties pervious concrete and freeze-thaw and dry-wet cycles[D]. Xi'an: School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Xi'an University of Technology, 2020. | |
| 31 | 刘相如. 透水砼透水系数及其力学与抗冻性能试验研究[D]. 烟台:烟台大学土木工程学院, 2019. |
| Liu Xiang-ru. Experimental study on permeability coefficient and mechanical and frost resistance of permeable concrete[D]. Yantai: School of Civil Engineering, Yantai University, 2019. | |
| 32 | 张国强. 透水混凝土试验性能研究[D]. 广州:广州大学土木工程学院, 2018. |
| Zhang Guo-qiang. An experimental study on the properties of the permeable concrete[D]. Guangzhou: School of Civil Engineering, Guangzhou University, 2018. | |
| 33 | 曲广雷,常广利,王显利,等. 透水混凝土强度与透水系数关系模型研究[J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2022 (2): 22-26. |
| Qu Guang-lei, Chang Guang-li, Wang Xian-li, et al. Study on the relationship model between pervious concrete strength and pervious coefficient[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products, 2022(2): 22-26. | |
| 34 | 胡立国. 透水混凝土的抗冻性研究[D]. 大连:大连交通大学土木与安全工程学院, 2013. |
| Hu Li-guo. The research about frost resistance of pervious concrete[D]. Dalian: School of Civil and Safety Engineering, Dalian Jiaotong University, 2013. | |
| 35 | 朱袁洁. C30透水混凝土力学性能及抗冻性能研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏科技大学土木工程与建筑学院, 2019. |
| Zhu Yuan-jie. Study on mechanical properties and frost resistance of C30 pervious concrete[D]. Zhenjiang: School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, 2019. | |
| 36 | 朱仁旺. 高透水性水泥混凝土的强度性能研究[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学土木与水利工程学院, 2016. |
| Zhu Ren-wang. Strength properties research for high-permeability cement concrete[D]. Hefei: School of Civil and Hydraulic Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, 2016. | |
| 37 | 林永盛. 环境友好型透水混凝土的制备与性能研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学材料科学与工程学院, 2019. |
| Lin Yong-sheng. Study on preparation and properties of environmentally-friendly pervious concrete[D]. Nanjing: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Southeast University, 2019. | |
| 38 | 欧阳云鹏. 配合比参数对透水混凝土性能影响及其相关性研究[D]. 石家庄: 石家庄铁道大学材料科学与工程学院, 2019. |
| Ouyang Yun-peng. Study on the influence and relevance of mix ratio parameters on the permeable concrete performance[D]. Shijiazhuang: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, 2019. | |
| 39 | 朱燕飞. 不同掺合料透水混凝土性能试验研究[D]. 广州: 华南农业大学水利与土木工程学院, 2019. |
| Zhu Yan-fei. Experimental study on pervious concrete with different admixtures[D]. Guangzhou: College of Water Conservancy and Civil Engineering, South China Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| 40 | 何明. 复掺矿物掺合料透水混凝土的试验研究[D]. 鞍山: 辽宁科技大学土木工程学院, 2021. |
| He Ming. Experimental research on permeable concrete mixed with mineral admixtures[D]. Anshan: School, Civil Engineering, University of Science and Technology Liaoning, 2021. | |
| 41 | 郭桂香. 集料骨架结构对多孔混凝土性能的影响研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学料科学与工程学院, 2016. |
| Guo Gui-xiang. Study the effect of aggregate gradation on the performance of porous concrete[D]. Chongqing: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2016. | |
| 42 | 张旭东. 透水混凝土道路板配合比试验研究与组合结构形式设计[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学水利土木工程学院, 2022. |
| Zhang Xu-dong. Experimental study on mix proportion of pervious concrete pavement slab and design of composite structure form[D]. Taian: College of Water Conservancy and Civil Engineering, Shandong Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| 43 | 黄涛. 特定强度透水混凝土的透水性能研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学建筑与测绘工程学院, 2019. |
| Huang Tao. Study on permeability performance of pervious concrete under specific strength[D]. Ganzhou: School of Architectural and Surveying & Mapping Engineering, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2019. | |
| 44 | Li L G, Feng J J, Zhu J, et al. Pervious concrete: effects of porosity on permeability and strength[J]. Magazine of Concrete Research, 2021, 73(2): 69-79. |
| 45 | Chandrappa A K, Biligiri K P. Effect of pore structure on fatigue of pervious concrete[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design, 2018, 20(7): 1525-1547. |
| 46 | Joshi T, Dave U. Evaluation of strength, permeability and void ratio of pervious concrete with changing W/C ratio and aggregate size[J]. International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology, 2016, 7(4): 276-284. |
| 47 | Ibrahim A, Mahmoud E, Yamin M, et al. Experimental study on Portland cement pervious concrete mechanical and hydrological properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 50: 524-529. |
| 48 | Liu H, Luo G, Wang L, et al. Laboratory evaluation of eco-friendly pervious concrete pavement material containing silica fume[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 9(1): 73-87. |
| 49 | Pradhan S K, Behera N. Performance assessment of pervious concrete road on strength and permeability by using silica fume[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Sustainable Materials and Practices for Built Environment (SMPBE), Jaipur, India, 2021: 25-26. |
| 50 | Claudino G O, Rodrigues G G O, Rohden A B, et al. Mix design for pervious concrete based on the optimization of cement paste and granular skeleton to balance mechanical strength and permeability[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 347: No.128620. |
| 51 | Torres A, Hu J, Ramos A. The effect of the cementitious paste thickness on the performance of pervious concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 95: 850-859. |
| 52 | Huang J, Luo Z, Khan M B E. Impact of aggregate type and size and mineral admixtures on the properties of pervious concrete: an experimental investigation[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 265:No. 120759. |
| 53 | Akbarpour H, Mohajeri M, Moradi M. Investigation on the synthesis conditions at the interpore distance of nanoporous anodic aluminum oxide: a comparison of experimental study, artificial neural network, and multiple linear regression[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2013, 79: 75-81. |
| [1] | 汪豪,赵彬,刘国华. 基于时间和运动增强的视频动作识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 339-346. |
| [2] | 胡宏宇,张争光,曲优,蔡沐雨,高菲,高镇海. 基于双分支和可变形卷积网络的驾驶员行为识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 93-104. |
| [3] | 商蕾,杨萍,杨祥国,潘建欣,杨军,张梦如. 基于APSO-BP-PID控制的质子交换膜燃料电池热管理系统温度控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2401-2413. |
| [4] | 杨军,韩鹏飞. 采用神经网络架构搜索的高分辨率遥感影像目标检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2646-2657. |
| [5] | 赵宏伟,武鸿,马克,李海. 基于知识蒸馏的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2307-2312. |
| [6] | 张锦洲,姬世青,谭创. 融合卷积神经网络和双边滤波的相贯线焊缝提取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2313-2318. |
| [7] | 特木尔朝鲁朝鲁,张亚萍. 基于卷积神经网络的无线传感器网络链路异常检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2295-2300. |
| [8] | 朱圣杰,王宣,徐芳,彭佳琦,王远超. 机载广域遥感图像的尺度归一化目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2329-2337. |
| [9] | 汪恩良,任志凤,王储,刘君巍,刘兴超,田野,邹猛,卢孜筱,张伟伟,姜生元. 基于灰色关联分析模拟月壤抗压强度性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 2015-2025. |
| [10] | 魏晓辉,王晨洋,吴旗,郑新阳,于洪梅,岳恒山. 面向脉动阵列神经网络加速器的软错误近似容错设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1746-1755. |
| [11] | 李祖仲,李梦园,刘卫东,庞萧萧,唐豪,张学磊,马晨杨. 蔗渣纤维表面改性及其沥青混合料路用性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1738-1745. |
| [12] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [13] | 李光保,高栋,路勇,平昊,周愿愿. 基于改进神经网络和Fluent的气液固技术的内表面处理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1537-1547. |
| [14] | 张玺君,余光杰,崔勇,尚继洋. 基于聚类算法和图神经网络的短时交通流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1593-1600. |
| [15] | 张西广,张龙飞,马钰锡,樊银亭. 基于密度峰值的海量云数据模糊聚类算法设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1401-1406. |
|
||