吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (1): 339-346.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230284
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
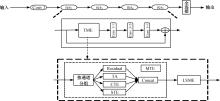
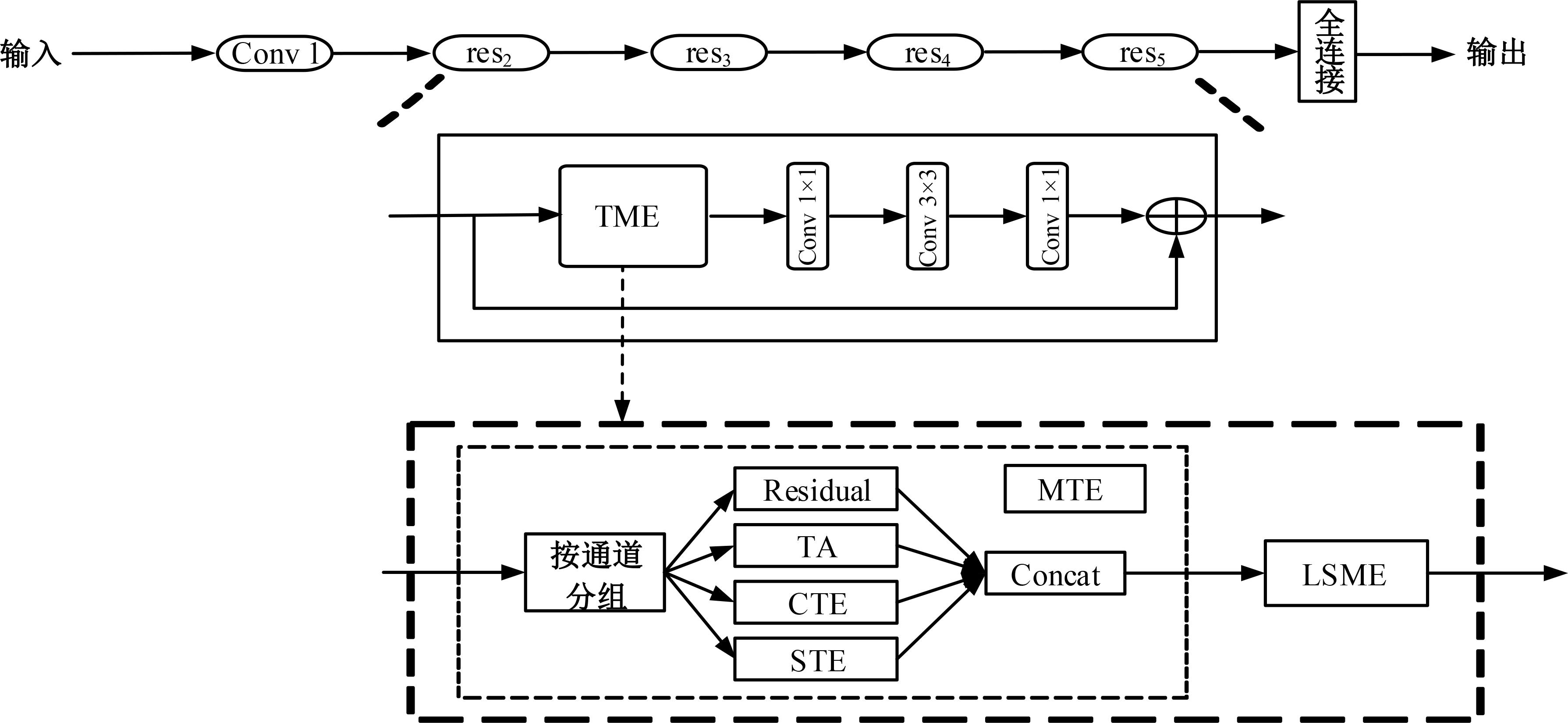
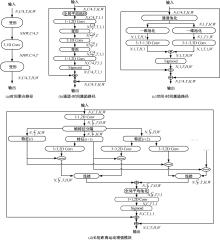
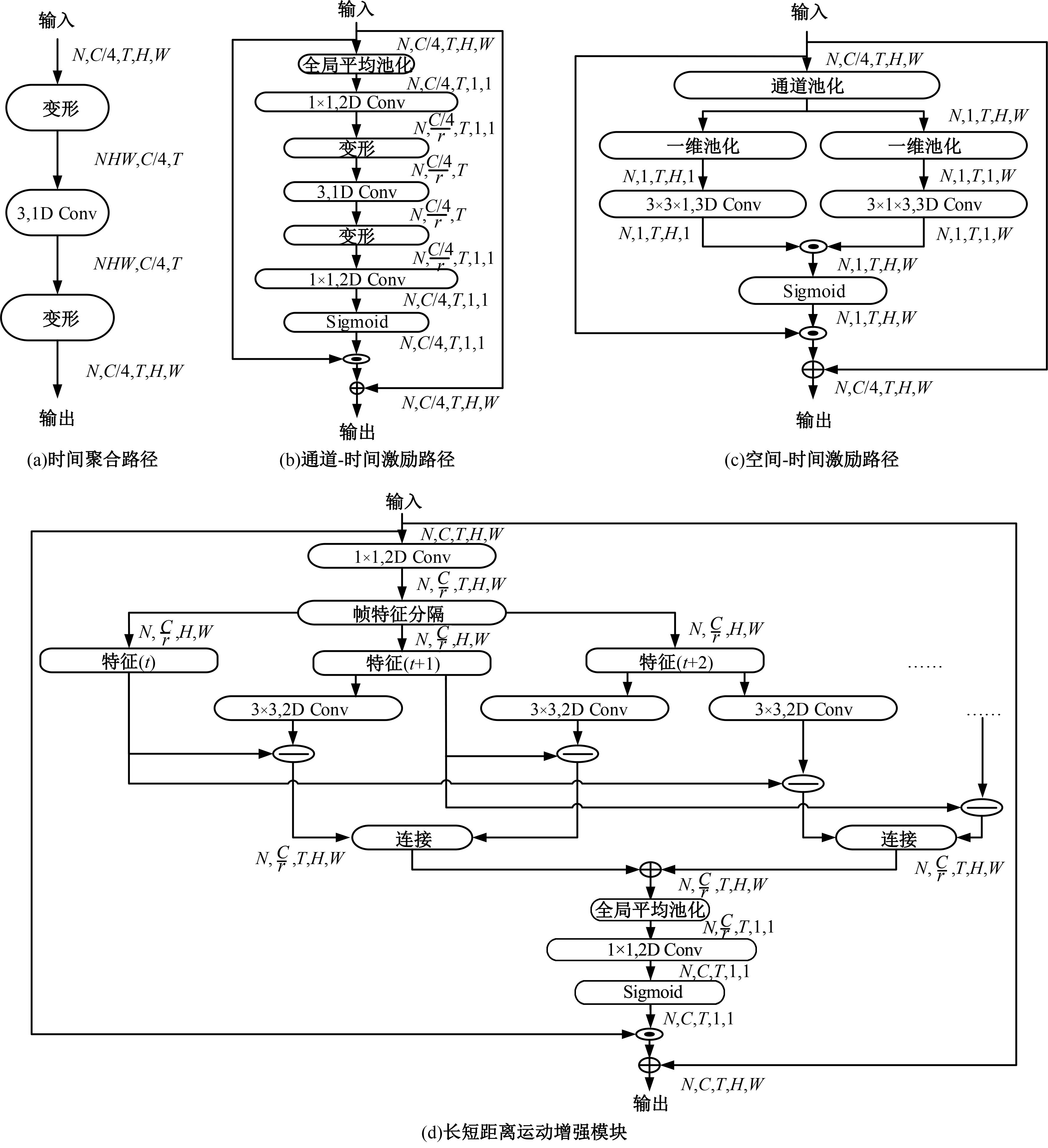
基于时间和运动增强的视频动作识别
- 1.南开大学 电子信息与光学工程学院,天津 300350
2.天津市光电传感器与传感网络技术重点实验室,天津 300350
3.南开大学 泛终端芯片交叉科学中心,天津 300350
4.南开大学 薄膜光电子技术教育部工程研究中心,天津 300350
5.桂林电子科技大学 人工智能学院,广西 桂林 541004
Temporal and motion enhancement for video action recognition
Hao WANG1,2,3,4( ),Bin ZHAO5,Guo-hua LIU1,2,3,4(
),Bin ZHAO5,Guo-hua LIU1,2,3,4( )
)
- 1.College of Electronic Information Technology and Optical Engineering,Nankai University,Tianjin 300350,China
2.Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology,Tianjin 300350,China
3.General Terminal IC Interdisciplinary Science Center,Nankai University,Tianjin 300350,China
4.Engineering Research Center of Thin Film Optoelectronics Technology,Ministry of Education,Nankai University,Tianjin 300350,China
5.School of Artificial Intelligence,Guilin University of Electronic Technology,Guilin 541004,China
摘要:
三维卷积神经网络可以通过直接融合空间和时间特征来实现良好的性能,但计算是密集的。传统的二维卷积神经网络在图像识别中表现良好,但由于无法提取时间特征,导致其在视频动作识别中表现不佳。为此,本文提出一个即插即用的时间和运动增强模块以学习视频动作的时空关系,可以插入任意二维卷积神经网络中,而额外的计算成本是相当有限的。在多个公开动作识别数据集上进行的大量实验表明,本文提出的网络以高效率优于最先进的二维卷积神经网络方法。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Diba A, Fayyaz M, Sharma V, et al. Temporal 3D convnets: new architecture and transfer learning for video classification[DB/OL]. [2023-01-29]. . |
| 2 | Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Two-stream co-nvolutional networks for action recognition in videos[DB/OL]. [2023-01-29]. . |
| 3 | Wang L, Xiong Y, Wang Z, et al. Temporal segment networks:towards good practices for deep action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands,2016: 20-36. |
| 4 | Girdhar R, Ramanan D, Gupta A, et al. Action- vlad: Learning spatio-temporal aggregation for action classification[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hawaii, USA, 2017: 971-980. |
| 5 | Zhu Y, Lan Z, Newsam S, et al. Hidden two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition[C]//Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia,2018: 363-378. |
| 6 | Tran D, Bourdev L, Fergus R, et al. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 4489-4497. |
| 7 | Feichtenhofer C, Fan H, Malik J, et al. Slowfast networks for video recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 6202-6211. |
| 8 | Qiu Z, Yao T, Mei T. Learning spatio-temporal representation with pseudo-3D residual networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice,Italy, 2017: 5533-5541. |
| 9 | Tran D, Wang H, Torresani L, et al. A closer look at spatiotemporal convolutions for action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA,2018: 6450⁃6459. |
| 10 | Xie S, Sun C, Huang J, et al. Rethinking spatiotemporal feature learning: speed-accuracy trade-offs in video classification[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany,2018: 305-321. |
| 11 | Carreira J, Zisserman A.Quo vadis, action recognition? a new model and the kinetics dataset[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA,2017:6299-6308. |
| 12 | Lin J, Gan C, Han S. TSM: temporal shift module for efficient video understanding[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 7083-7093. |
| 13 | Li Y, Ji B, Shi X, et al. Tea: temporal excitation and aggregation for action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Online, 2020: 909-918. |
| 14 | Jiang B, Wang M, Gan W, et al. Stm: spatiotemporal and motion encoding for action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Online, 2019: 2000-2009. |
| 15 | Liu Z, Luo D, Wang Y, et al. Teinet: towards an efficient architecture for video recognition[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020(34): 11669-11676. |
| 16 | Liu Z, Wang L, Wu W, et al. Tam: temporal adaptive module for video recognition[DB/OL].[2021-08-18]. . |
| 17 | Zhou B, Andonian A, Oliva A, et al. Temporal relational reasoning in videos[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany,2018: 803-818. |
| 18 | Lee M, Lee S, Son S, et al. Motion feature network: fixed motion filter for action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich,Germany,2018: 387-403. |
| 19 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 20 | Karpathy A, Toderici G, Shetty S, et al. Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA,2014: 1725-1732. |
| 21 | Zolfaghari M, Singh K, Brox T. Eco: efficient convolutional net- work for online video understanding[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 695-712. |
| 22 | Wang Z, She Q, Smolic A.Action-net: multipath excitation for action recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 2021: 13214-13223. |
| 23 | Goyal R, Ebrahimi Kahou S, Michalski V, et al. The “something-something” video database for learning and evaluating visual common sense[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5842-5850. |
| 24 | Kuehne H, Jhuang H, Garrote E,et al. Hmdb: a large video database for human motion recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 2011:2556-2563. |
| 25 | Soomro K, Zamir A R, Shah M. Ucf101: a dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild[J/OL]. [2012-12-03]. . |
| 26 | Wang X, Girshick R, Gupta A, et al. Non-local neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018:7794-7803. |
| 27 | Contributors M.OpenMMLab's Next Generation Video Understanding Toolbox and Benchmark[DB/OL].[2020-12-26]. . |
| [1] | 郭晓然,王铁君,闫悦. 基于局部注意力和本地远程监督的实体关系抽取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 307-315. |
| [2] | 刘元宁,臧子楠,张浩,刘震. 基于深度学习的核糖核酸二级结构预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 297-306. |
| [3] | 李路,宋均琦,朱明,谭鹤群,周玉凡,孙超奇,周铖钰. 基于RGHS图像增强和改进YOLOv5网络的黄颡鱼目标提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2638-2645. |
| [4] | 赵宏伟,武鸿,马克,李海. 基于知识蒸馏的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2307-2312. |
| [5] | 张锦洲,姬世青,谭创. 融合卷积神经网络和双边滤波的相贯线焊缝提取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2313-2318. |
| [6] | 特木尔朝鲁朝鲁,张亚萍. 基于卷积神经网络的无线传感器网络链路异常检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2295-2300. |
| [7] | 朱圣杰,王宣,徐芳,彭佳琦,王远超. 机载广域遥感图像的尺度归一化目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2329-2337. |
| [8] | 张云佐,郑宇鑫,武存宇,张天. 基于双特征提取网络的复杂环境车道线精准检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1894-1902. |
| [9] | 魏晓辉,王晨洋,吴旗,郑新阳,于洪梅,岳恒山. 面向脉动阵列神经网络加速器的软错误近似容错设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1746-1755. |
| [10] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [11] | 李延风,刘名扬,胡嘉明,孙华栋,孟婕妤,王奥颖,张涵玥,杨华民,韩开旭. 基于梯度转移和自编码器的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1777-1787. |
| [12] | 张丽平,刘斌毓,李松,郝忠孝. 基于稀疏多头自注意力的轨迹kNN查询方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1756-1766. |
| [13] | 夏超,王梦佳,朱剑月,杨志刚. 基于分层卷积自编码器的钝体湍流流场降阶分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 874-882. |
| [14] | 梁礼明,周珑颂,尹江,盛校棋. 融合多尺度Transformer的皮肤病变分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1086-1098. |
| [15] | 张云佐,郭威,李文博. 遥感图像密集小目标全方位精准检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1105-1113. |
|
||