吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 1384-1395.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230740
基于注意力机制和特征融合的语义分割网络
- 1.长春理工大学 电子信息工程学院,长春 130022
2.长春理工大学 空间光电技术研究所,长春 130022
3.吉林大学第一医院 泌尿外二科,长春 130061
Semantic segmentation network based on attention mechanism and feature fusion
Hua CAI1( ),Yu-yao WANG1,Qiang FU2,Zhi-yong MA3,Wei-gang WANG3,Chen-jie ZHANG1
),Yu-yao WANG1,Qiang FU2,Zhi-yong MA3,Wei-gang WANG3,Chen-jie ZHANG1
- 1.School of Electronic Information Engineer,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.School of Opto-Electronic Engineer,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
3.No. 2 Department of Urology,The First Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun 130061,China
摘要:
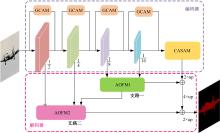
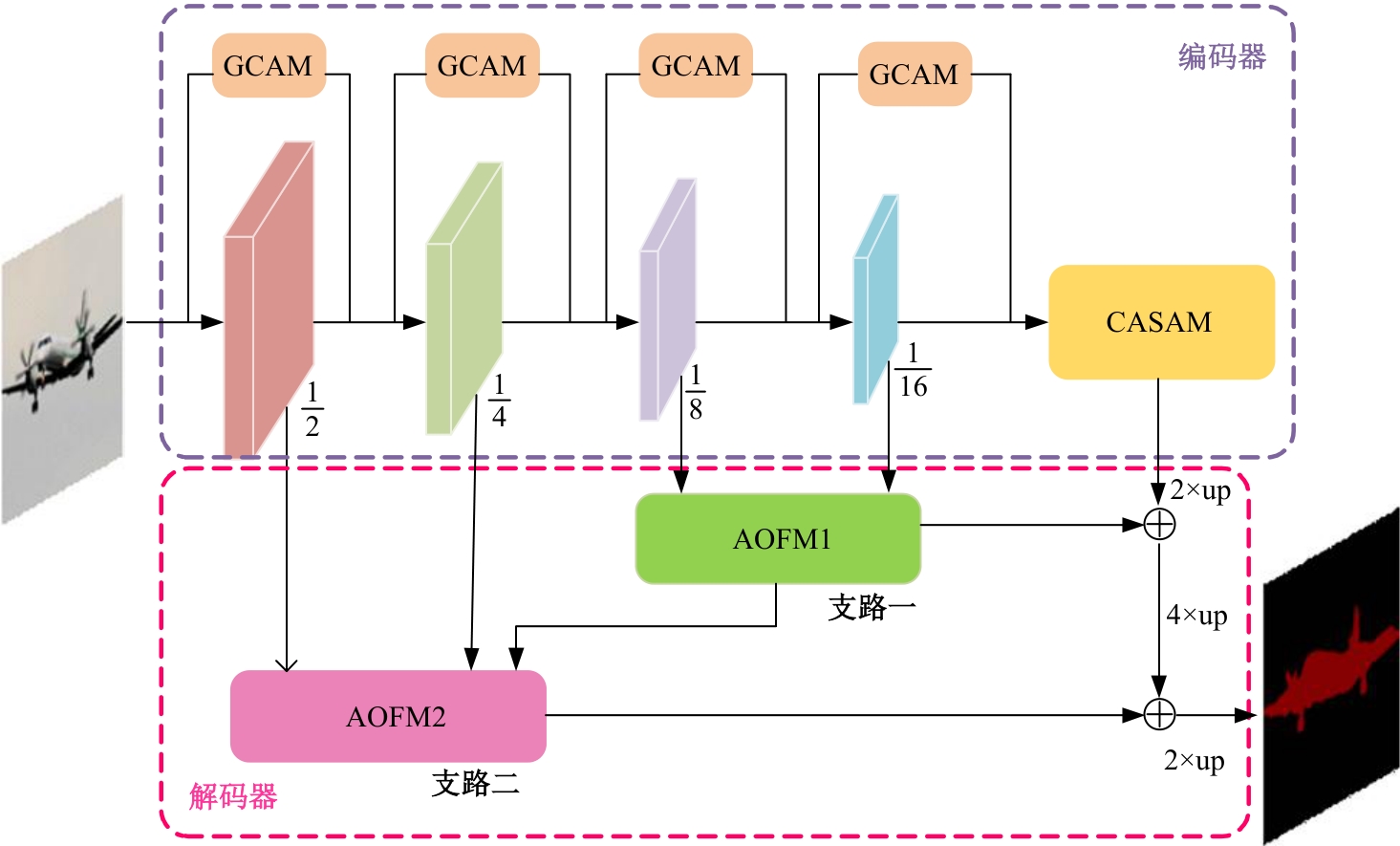
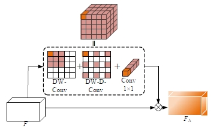
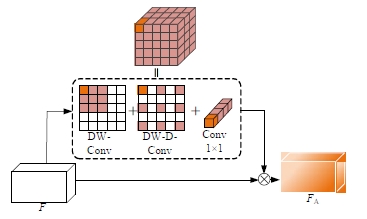
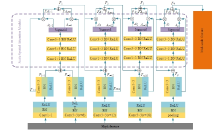
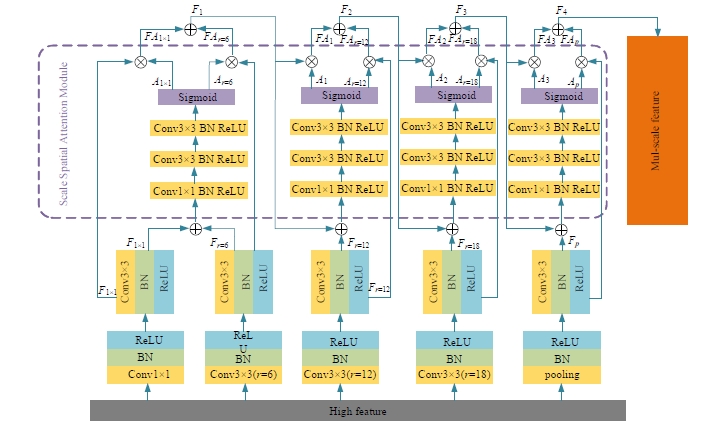
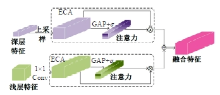
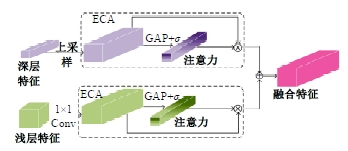
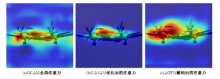
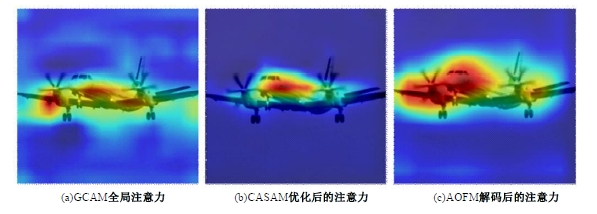
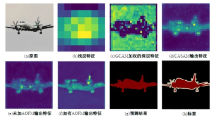
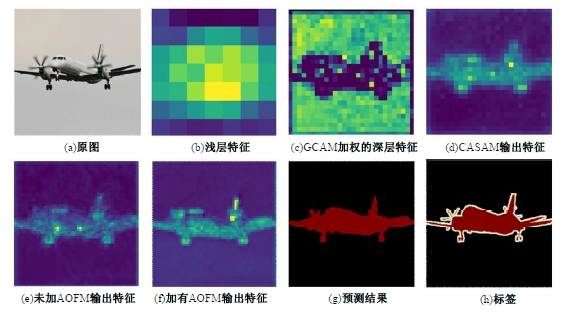
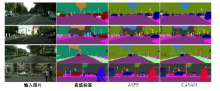
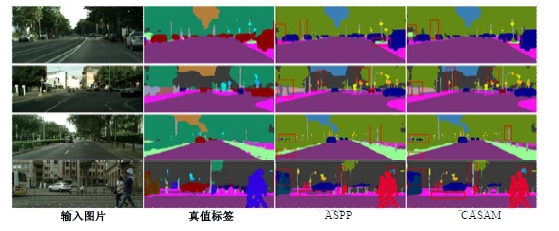
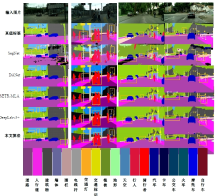
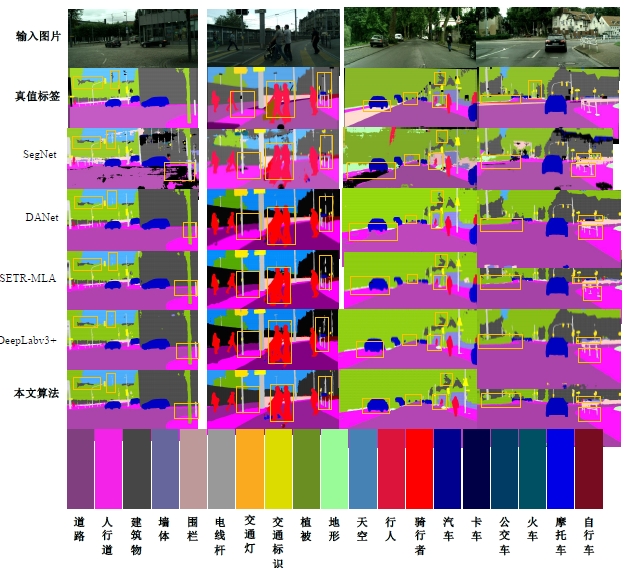
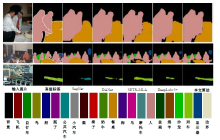
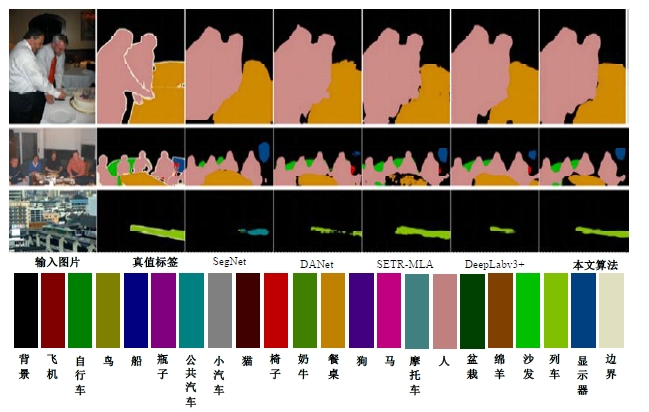
针对DeepLabv3+网络中的多尺度目标分割错误、多尺度特征图及不同阶段特征图之间关联性差的问题,提出在DeepLabv3+基础上引入全局上下文注意力模块、级联自适应尺度感知模块及注意力优化融合模块。将全局上下文注意力模块嵌入骨干网络特征提取的初始阶段,获取丰富的上下文信息;级联自适应尺度感知模块可建模多尺度特征之间的依赖性,使其更加关注目标特征;注意力优化融合模块通过多条支路融合多层特征,以此提高解码时像素的连续性。改进网络在Cityscapes数据集以及PASCAL VOC2012增强数据集上进行验证测试,实验结果表明:该网络能弥补DeepLabv3+的不足,且平均交并比分别达到76.2%、78.7%。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| [1] | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]∥Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI: The 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234-241. |
| [2] | Chen J, Lu Y, Yu Q, et al. Transunet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation[J/OL]. [2023-07-02].arXiv preprint arXiv: 2102. 04306v1. |
| [3] | Zhao T Y, Xu J D, Chen R, et al. Remote sensing image segmentation based on the fuzzy deep convolutional neural network[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2021, 42(16): 6264-6283. |
| [4] | Yuan X H, Shi J F, Gu L C. A review of deep learning methods for semantic segmentation of remote sensing imagery[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 169: No.114417. |
| [5] | Xu Z Y, Zhang W, Zhang T X, et al. Efficient transformer for remote sensing image segmentation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(18): No.3585. |
| [6] | Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. Segnet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. |
| [7] | Yu C, Gao C, Wang J, et al. Bisenet v2: bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129: 3051-3068. |
| [8] | Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA,2015: 3431-3440. |
| [9] | Chen L C, Papandreou G Kokkinos I, et al. Deeplab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 40(4): 834-848. |
| [10] | Chen L C, Papandreou G, Schroff F, et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[J/OL].[2023-07-03]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1706. 05587v3. |
| [11] | Chen L C, Zhu Y, Papandreou G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV),Munich, Germany,2018: 833-851. |
| [12] | Wang J, Sun K, Cheng T, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 43(10): 3349-3364. |
| [13] | Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, et al. Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision,Montreal, Canada, 2021: 10012-10022. |
| [14] | Wang W, Xie E, Li X, et al. Pyramid vision transformer: a versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision,Montreal, Canada, 2021: 568-578. |
| [15] | Zheng S, Lu J, Zhao H, et al. Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA,2021: 6881-6890. |
| [16] | Xie E, Wang W, Yu Z, et al. SegFormer: simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021, 34: 12077-12090. |
| [17] | Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[J/OL]. [2023-07-04].arXiv preprint arXiv: 2010. 11929v2. |
| [18] | Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2881-2890. |
| [19] | Hou Q, Zhang L, Cheng M M, et al. Strip pooling: rethinking spatial pooling for scene parsing[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Seattle, USA, 2020: 4003-4012. |
| [20] | Peng C, Zhang X, Yu G, et al. Large kernel matters-improve semantic segmentation by global convolutional network[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4353-4361. |
| [21] | Ding X, Zhang X, Han J, et al. Scaling up your kernels to 31×31: revisiting large kernel design in CNNs[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,New Orleans, USA, 2022: 11963-11975. |
| [22] | Guo M H, Lu C Z, Liu Z N, et al. Visual attention network[J/OL]. [2023-07-04].arXiv preprint arXiv:. |
| [23] | Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132-7141. |
| [24] | Wang Q, Wu B, Zhu P, et al. ECA-Net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Seattle, USA, 2020: 11534-11542. |
| [25] | Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3146-3154. |
| [26] | Cordts M, Omran M, Ramos S, et al. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 3213-3223. |
| [27] | Everingham M, Eslami S M A, Van Gool L, et al. The pascal visual object classes challenge: a retrospective[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 111: 98-136. |
| [28] | 王雪, 李占山, 吕颖达. 基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| Wang Xue, Li Zhan-shan, Ying-da Lyu. Medical image segmentation algorithm based on multi-scale perception and semantic adaptation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 640-647. |
| [1] | 薛雅丽,俞潼安,崔闪,周李尊. 基于级联嵌套U-Net的红外小目标检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1714-1721. |
| [2] | 程光,李沛霖. 基于MSE改进BiLSTM网络算法的工业互联网异常流量时空融合检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1406-1411. |
| [3] | 张河山,范梦伟,谭鑫,郑展骥,寇立明,徐进. 基于改进YOLOX的无人机航拍图像密集小目标车辆检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1307-1318. |
| [4] | 李学军,权林霏,刘冬梅,于树友. 基于Faster-RCNN改进的交通标志检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 938-946. |
| [5] | 程德强,刘规,寇旗旗,张剑英,江鹤. 基于自适应大核注意力的轻量级图像超分辨率网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 1015-1027. |
| [6] | 李扬,李现国,苗长云,徐晟. 基于双分支通道先验和Retinex的低照度图像增强算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 1028-1036. |
| [7] | 张兰芳,李根泽,刘婷宇,余博. 局部多车影响下跟驰行为机理及建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 963-973. |
| [8] | 刘元宁,臧子楠,张浩,刘震. 基于深度学习的核糖核酸二级结构预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 297-306. |
| [9] | 郭晓然,王铁君,闫悦. 基于局部注意力和本地远程监督的实体关系抽取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 307-315. |
| [10] | 李路,宋均琦,朱明,谭鹤群,周玉凡,孙超奇,周铖钰. 基于RGHS图像增强和改进YOLOv5网络的黄颡鱼目标提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2638-2645. |
| [11] | 郭昕刚,程超,沈紫琪. 基于卷积网络注意力机制的人脸表情识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2319-2328. |
| [12] | 余萍,赵康,曹洁. 基于优化A-BiLSTM的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2156-2166. |
| [13] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [14] | 高云龙,任明,吴川,高文. 基于注意力机制改进的无锚框舰船检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1407-1416. |
| [15] | 李晓旭,安文娟,武继杰,李真,张珂,马占宇. 通道注意力双线性度量网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 524-532. |
|