吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 1714-1721.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230785
基于级联嵌套U-Net的红外小目标检测
- 1.南京航空航天大学 自动化学院,南京 210000
2.上海机电工程研究所,上海 201109
Infrared small target detection based on cascaded nested U-Net
Ya-li XUE1( ),Tong-an YU1,Shan CUI2,Li-zun ZHOU1
),Tong-an YU1,Shan CUI2,Li-zun ZHOU1
- 1.College of Automation Engineering,Nanjing Univercity of Aeronautics and Astronautics,Nanjing 210000,China
2.Shanghai Electro-Mechanical Engineering Institute,Shanghai 201109,China
摘要:
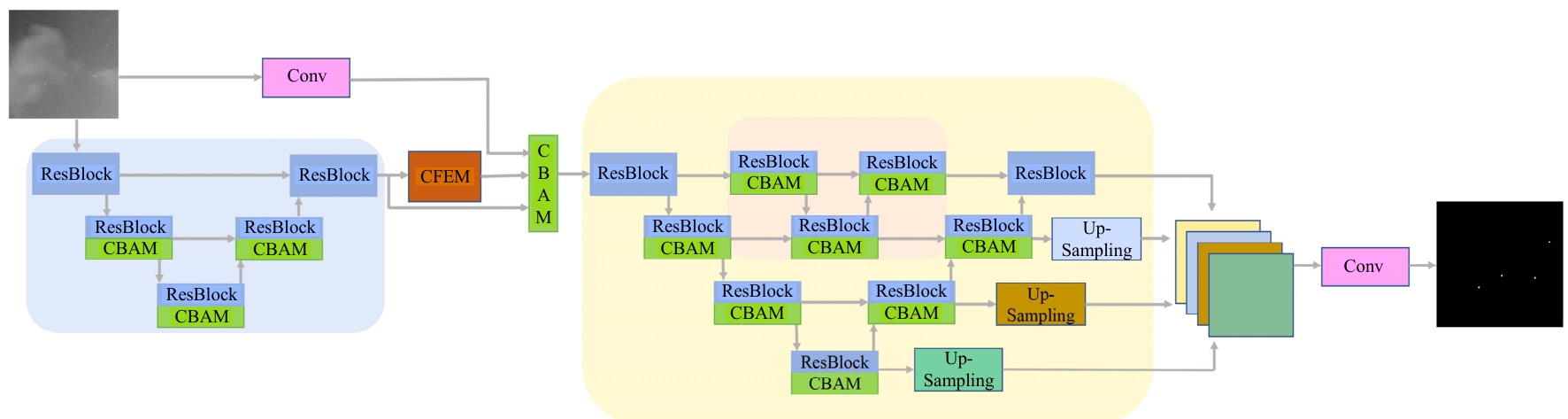
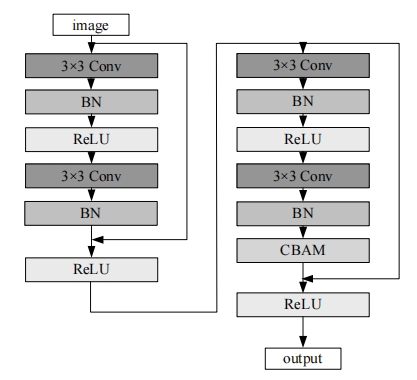
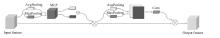
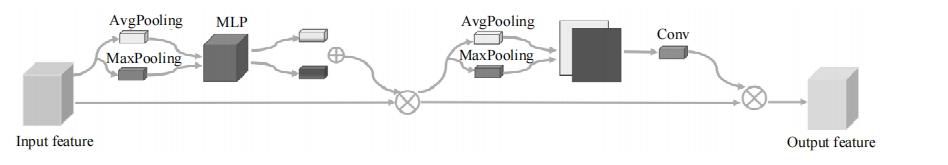
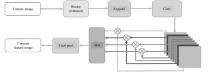
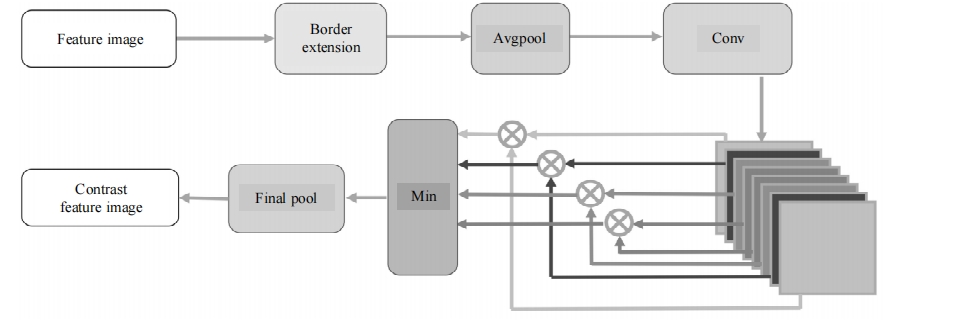
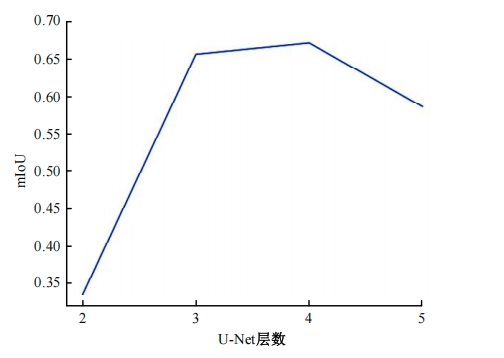
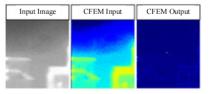
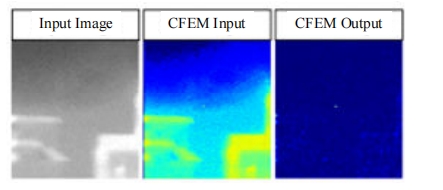
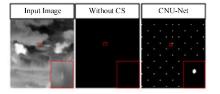
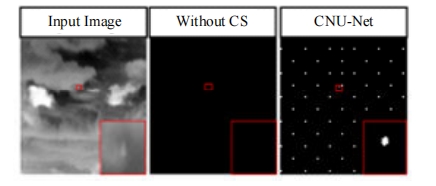
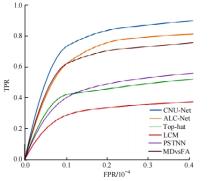
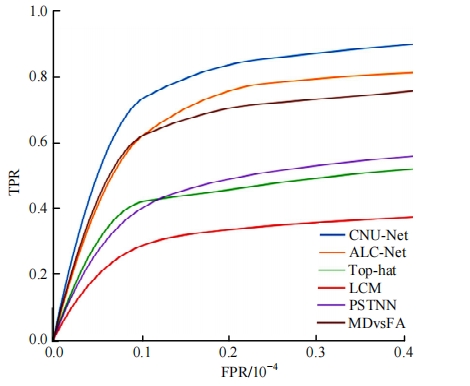
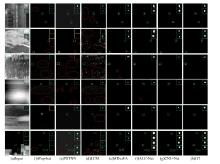
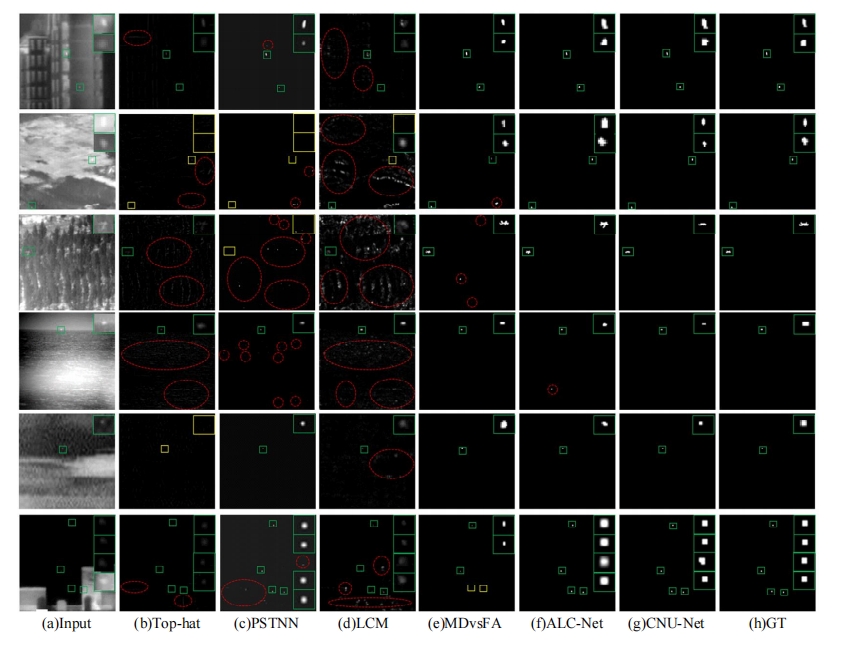
针对复杂场景下红外小目标尺寸差异大、检测效果欠佳的问题,提出了一种基于级联嵌套U-Net的红外小目标检测方法。首先,为解决不同场景下小目标尺寸差异大的问题,搭建了3种深度的U-Net网络,并将3个U-Net网络以级联嵌套的方式组成检测模型;其次,引入对比度信息抽取模块,以进一步丰富特征信息,抑制密集背景噪声的干扰;最后,将所提出的算法与5种主流的算法进行比较。实验结果表明:本文算法性能优于其他算法,并且平均交并比、精确率和召回率分别达到了78.61%、93.36%和81.78%。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| [1] | 查月, 汤晔. 红外海面小目标检测算法综述[J]. 宇航计测技术, 2022, 42(6): 57-65. |
| Zha Yue, Tang Ye. Review of infrared sea surface small target detection algorithm [J]. Journal of Astronautic Metrology and Measurement, 2022, 42(6): 57-65. | |
| [2] | Rivest J F, Fortin R. Detection of dim targets in digital infrared imagery by morphological image processing[J]. Optical Engineering, 1996, 35(7): 1886-1893. |
| [3] | Chen C L P, Li H, Wei Y, et al. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 52(1): 574-581. |
| [4] | 张文杰, 熊庆宇. 基于对比度与空间位置特征的显著性区域检测[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(5): 1709-1716. |
| Zhang Wen-jie, Xiong Qing-yu. Joint segmentation of optic cup and disc based on high resolution network [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(5): 1709-1716. | |
| [5] | Ren S, He K, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015, 28: 7485869. |
| [6] | Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779-788. |
| [7] | Wang H, Zhou L, Wang L. Miss detection vs false alarm: adversarial learning for small object segmentation in infrared images[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 8509-8518. |
| [8] | Deng C, Wang M, Liu L, et al. Extended feature pyramid network for small object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2021, 24: 1968-1979. |
| [9] | Goodfellow I, Pouget A J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014, 2: 2672-2680. |
| [10] | Wu X, Hong D, Chanussot J. UIU-Net: U-Net in U-Net for infrared small object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 32: 364-376. |
| [11] | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]// Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234-241. |
| [12] | Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2117-2125. |
| [13] | Woo S, Park J, Lee J Y, et al. Cbam: convolutional block attention module[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3-19. |
| [14] | Dai Y, Wu Y, Zhou F, et al. Asymmetric contextual modulation for infrared small target detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, USA, 2021: 950-959. |
| [15] | Li B, Xiao C, Wang L, et al. Dense nested attention network for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 32: 1745-1758. |
| [16] | Dai Y, Wu Y, Zhou F, et al. Attentional local contrast networks for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(11): 9813-9824. |
| [17] | Sun Y, Yang J, An W. Infrared dim and small target detection via multiple subspace learning and spatial-temporal patch-tensor model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 59(5): 3737-3752. |
| [1] | 田丽,贾煜辉. 改进YOLOv5s算法的高光谱遥感图像目标检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1742-1748. |
| [2] | 侯越,郭劲松,林伟,张迪,武月,张鑫. 分割可跨越车道分界线的多视角视频车速提取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1692-1704. |
| [3] | 张汝波,常世淇,张天一. 基于深度学习的图像信息隐藏方法综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1497-1515. |
| [4] | 王军,司昌馥,王凯鹏,付强. 融合集成学习技术和PSO-GA算法的特征提取技术的入侵检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1396-1405. |
| [5] | 张彬桥,吴健. 基于跟踪-学习-检测算法的四旋翼无人机自主降落姿态控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1419-1425. |
| [6] | 聂为之,尹斐,苏毅珊. 任务驱动下成像声呐水下目标识别方法综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1163-1175. |
| [7] | 才华,王玉瑶,付强,马智勇,王伟刚,张晨洁. 基于注意力机制和特征融合的语义分割网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1384-1395. |
| [8] | 郭宁,胡小晨,董德存. 基于改进YOLO算法的地铁车厢客流检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1258-1265. |
| [9] | 程光,李沛霖. 基于MSE改进BiLSTM网络算法的工业互联网异常流量时空融合检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1406-1411. |
| [10] | 张河山,范梦伟,谭鑫,郑展骥,寇立明,徐进. 基于改进YOLOX的无人机航拍图像密集小目标车辆检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1307-1318. |
| [11] | 孙淑琴,祁鑫,袁正海,李再华,唐晓骏. 基于耦合混沌系统阵列的电力系统微弱谐波检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 1082-1092. |
| [12] | 李学军,权林霏,刘冬梅,于树友. 基于Faster-RCNN改进的交通标志检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 938-946. |
| [13] | 李扬,李现国,苗长云,徐晟. 基于双分支通道先验和Retinex的低照度图像增强算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 1028-1036. |
| [14] | 张兰芳,李根泽,刘婷宇,余博. 局部多车影响下跟驰行为机理及建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 963-973. |
| [15] | 单泽彪,薛泓垚,刘小松,姚瑞广,陈广秋. Alpha稳定分布噪声下基于近似l0范数稀疏重构的波达方向估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 1093-1102. |
|