吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 70-78.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200738
温度对车身钢铝胶铆连接结构热应力变化的影响
- 吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
Influence on thermal stress of autobody steel-aluminum clinch-adhesive connection structure
Wei-min ZHUANG( ),Shen CHEN,Nan WANG
),Shen CHEN,Nan WANG
- State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
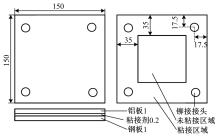
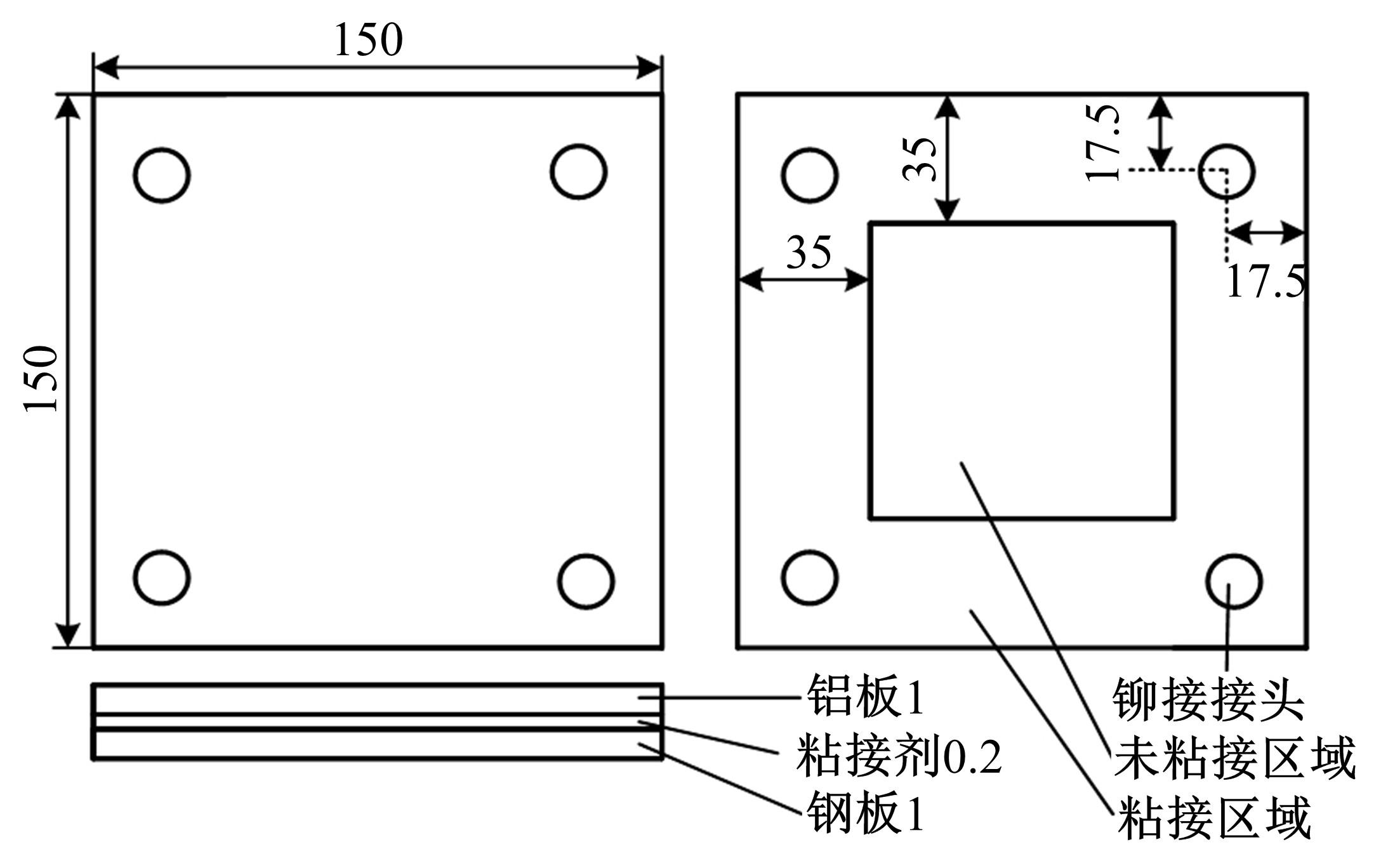
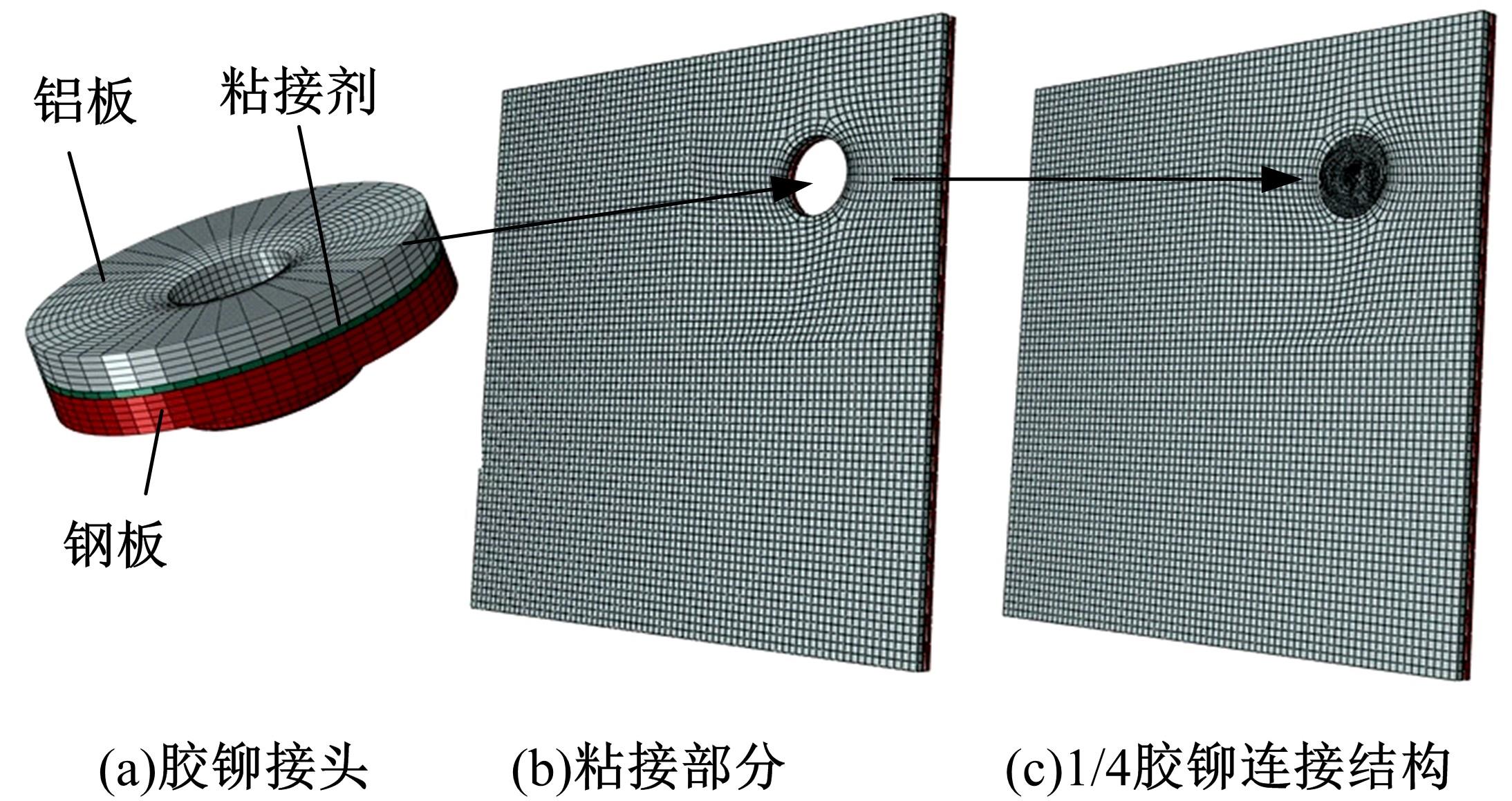
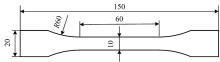
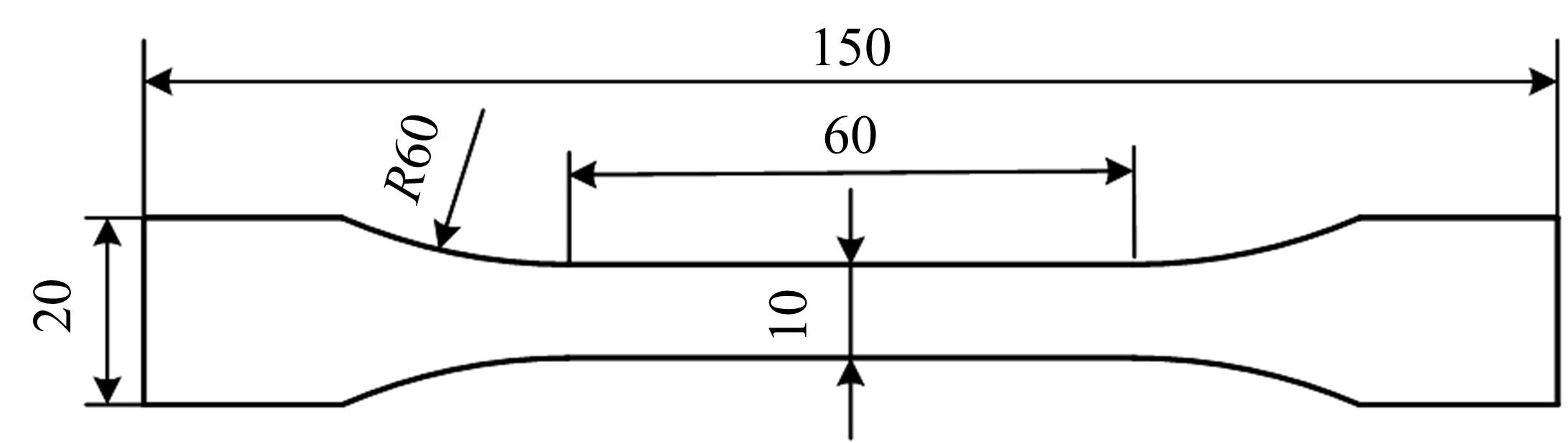
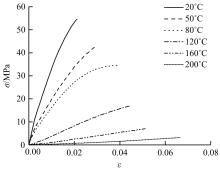
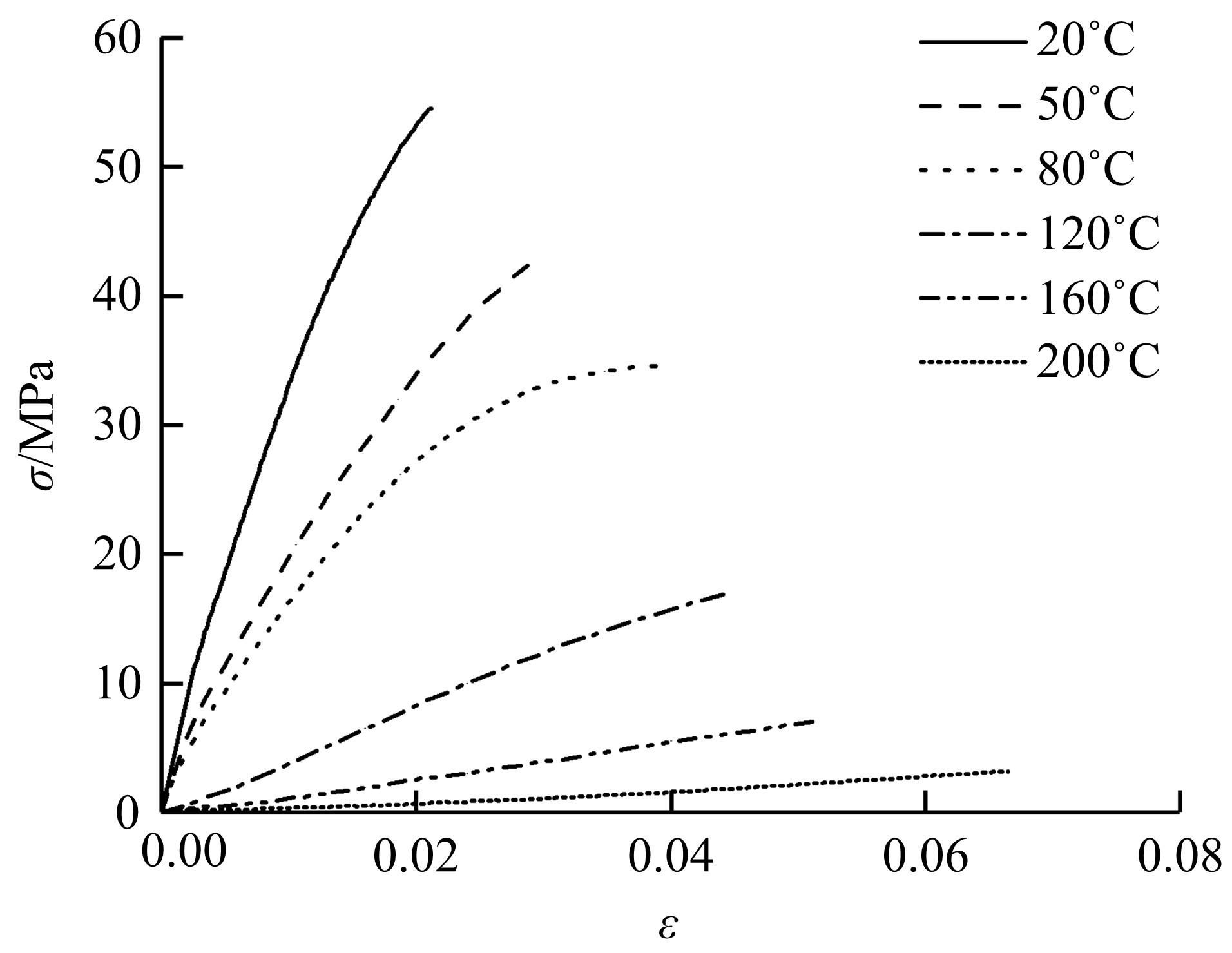
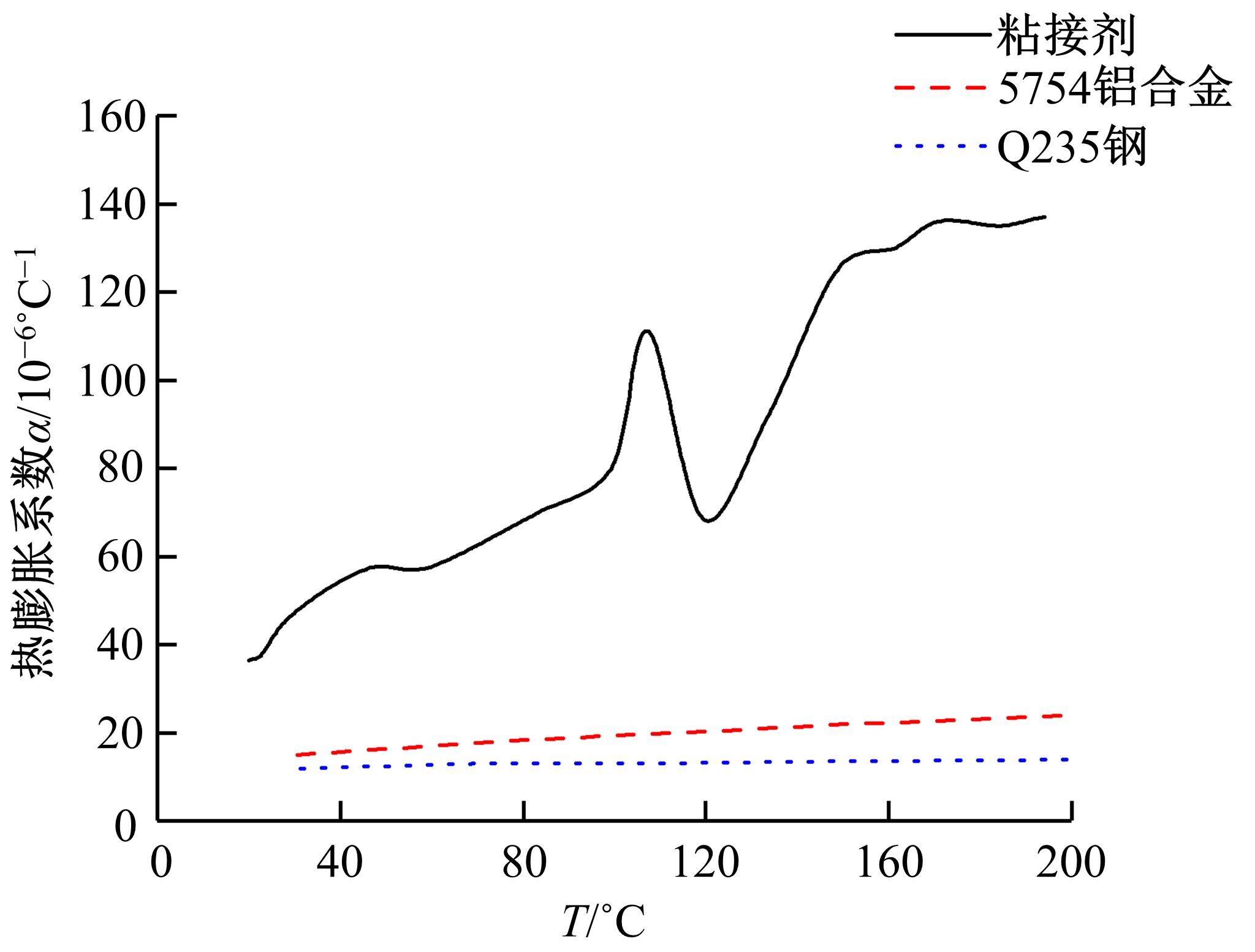
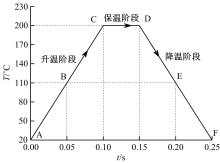
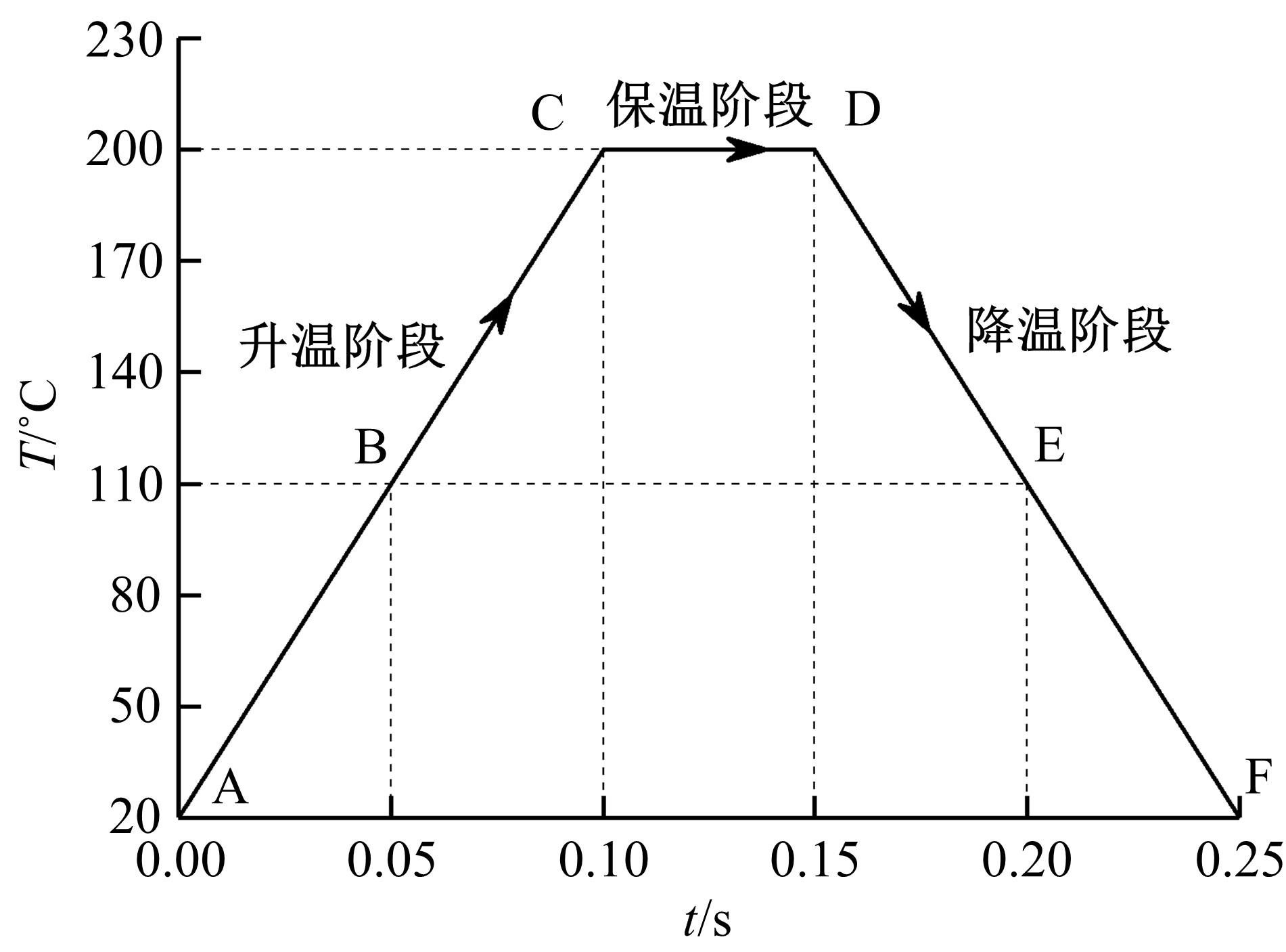
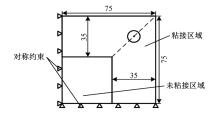
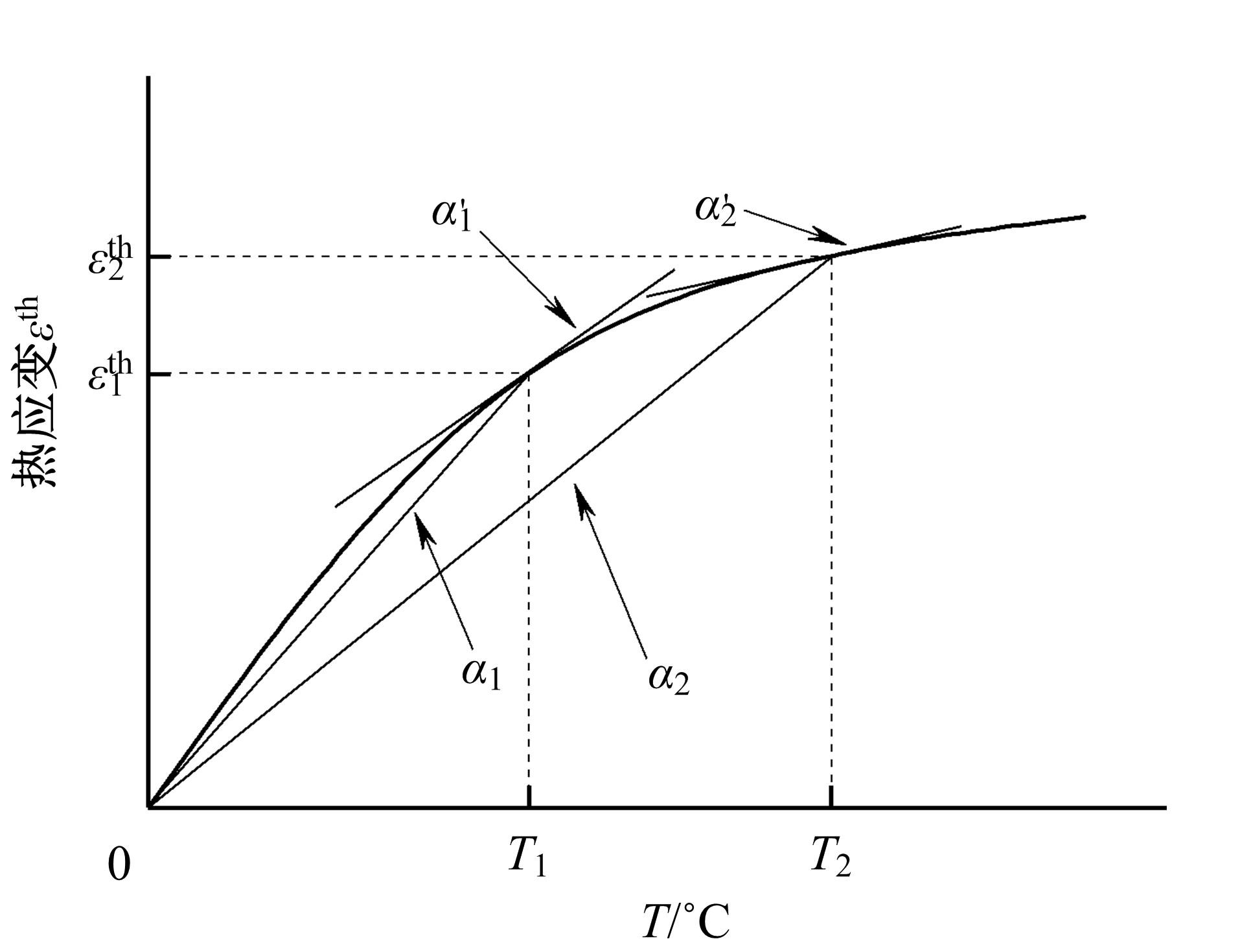
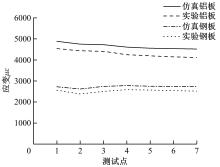
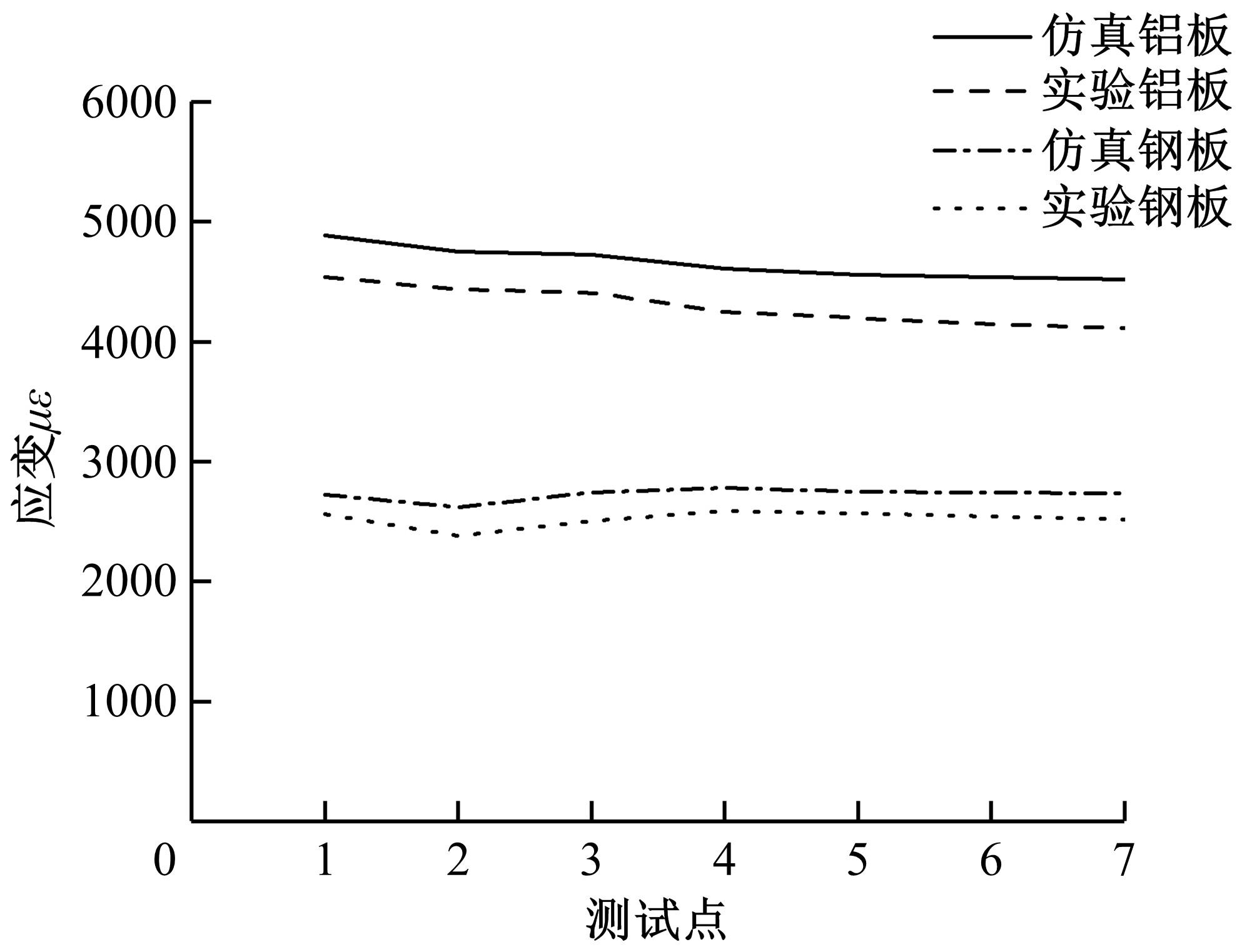
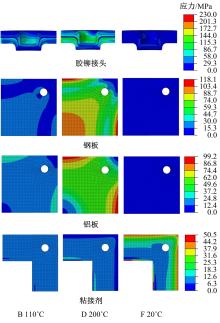
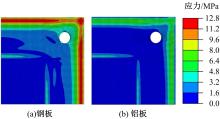
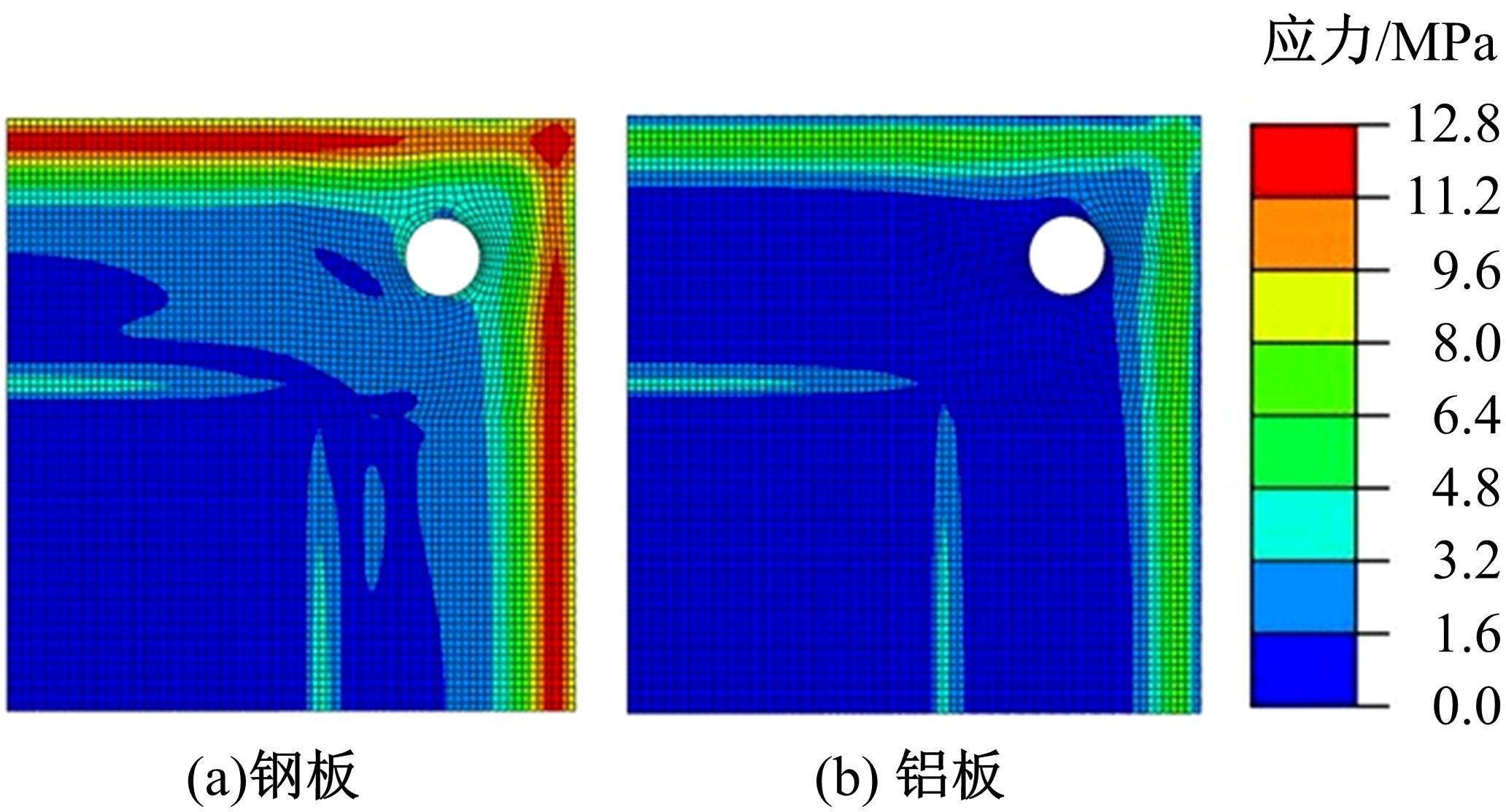
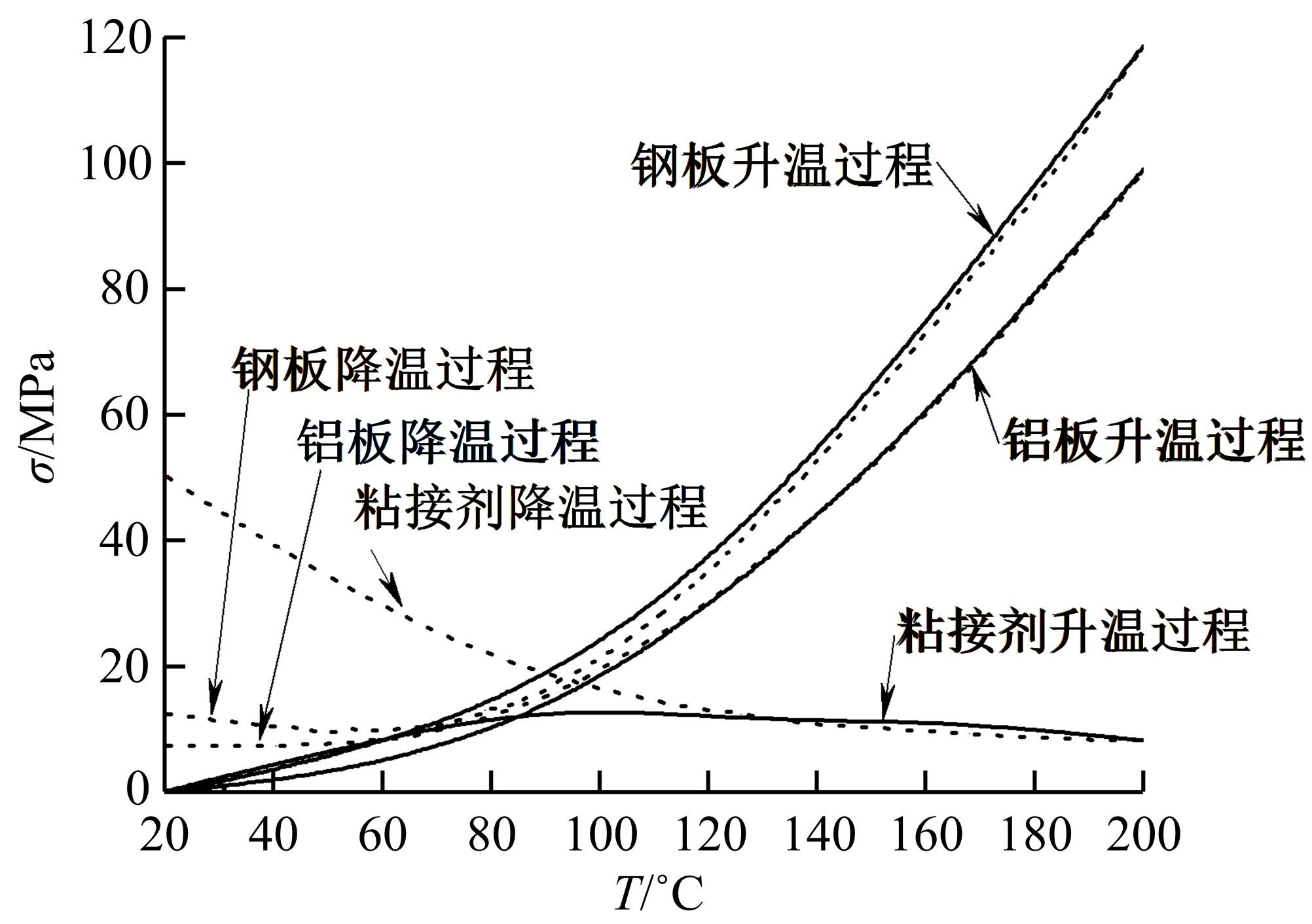
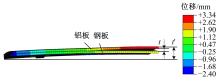
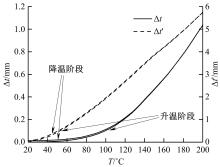
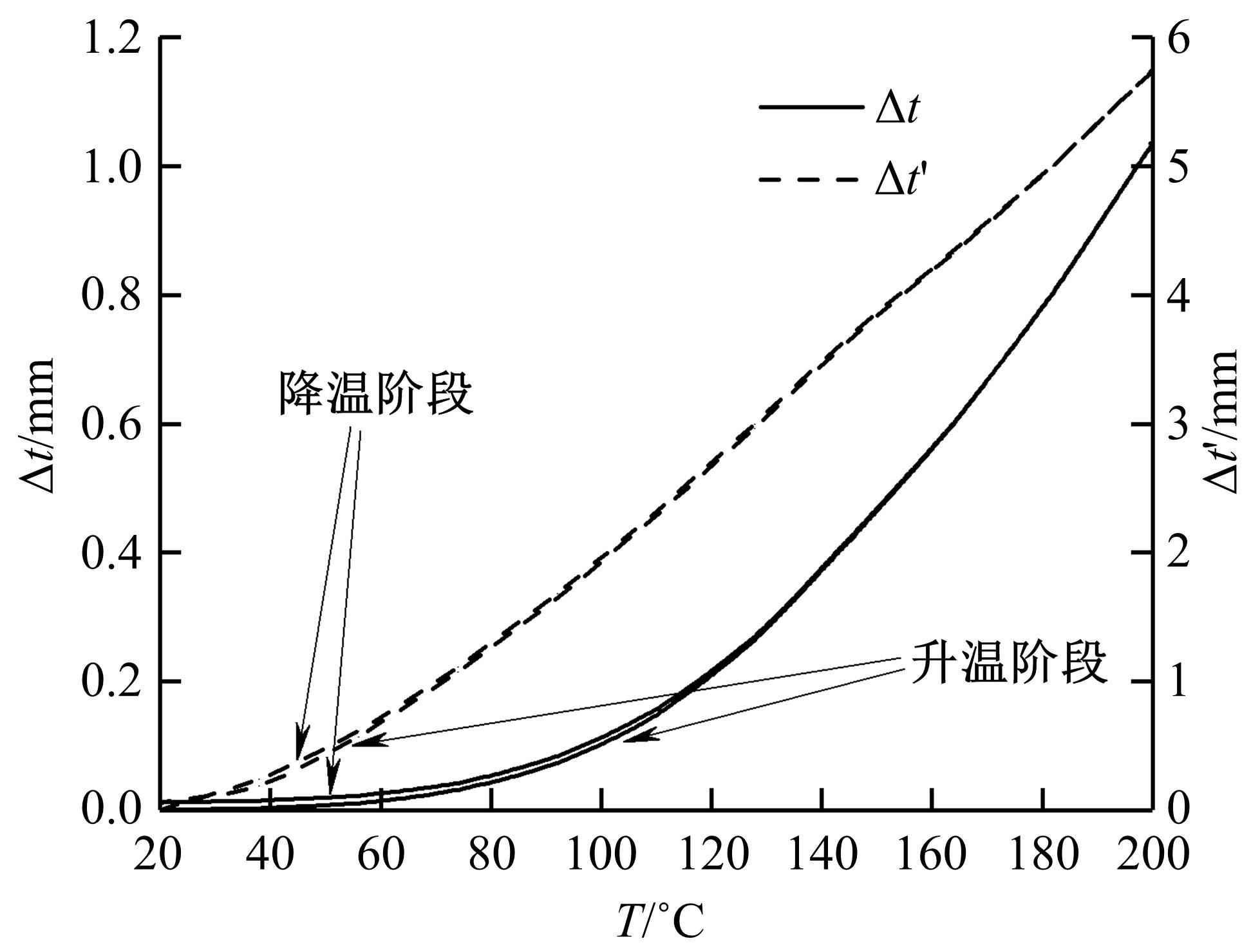
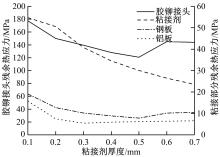
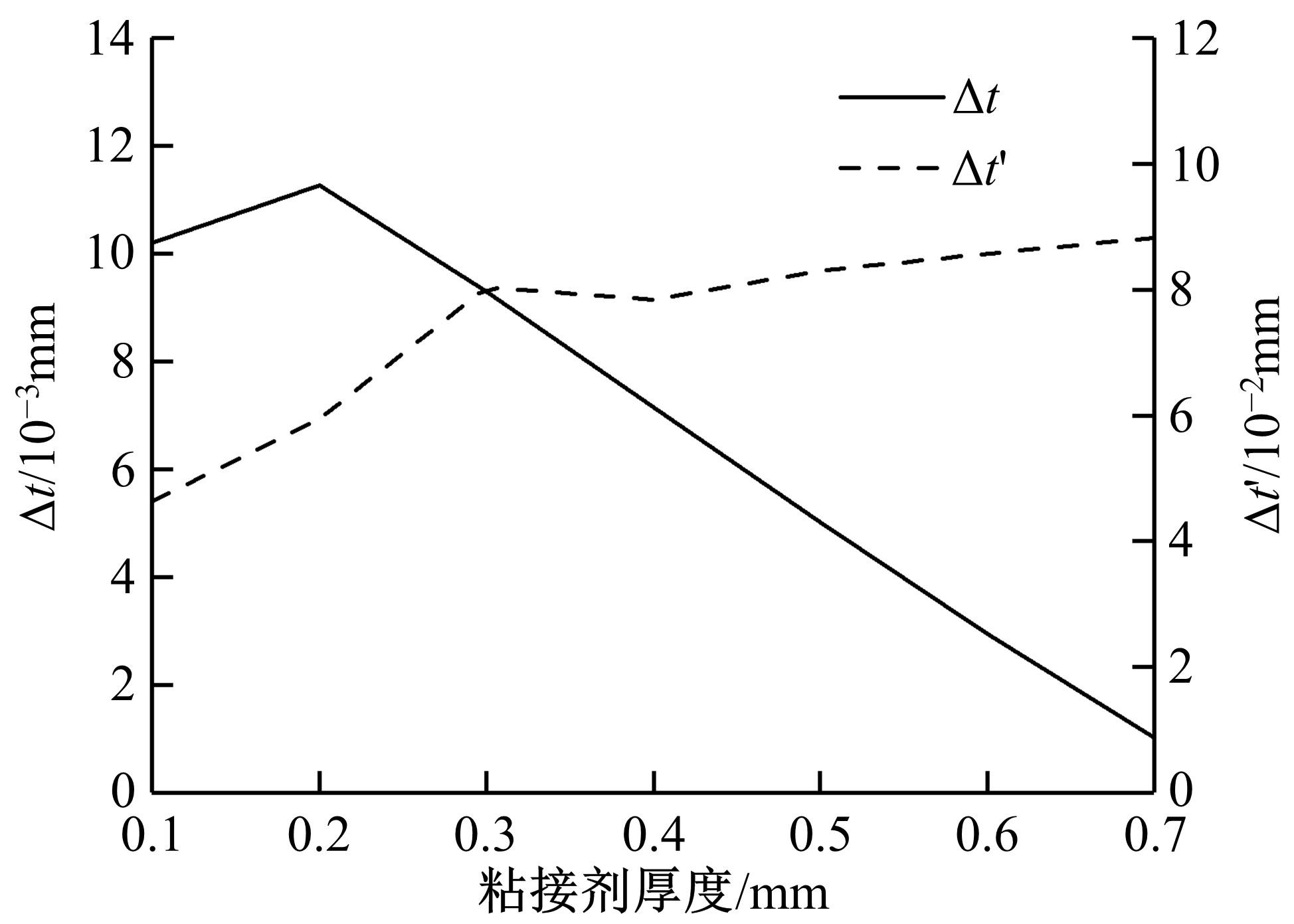
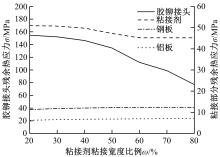
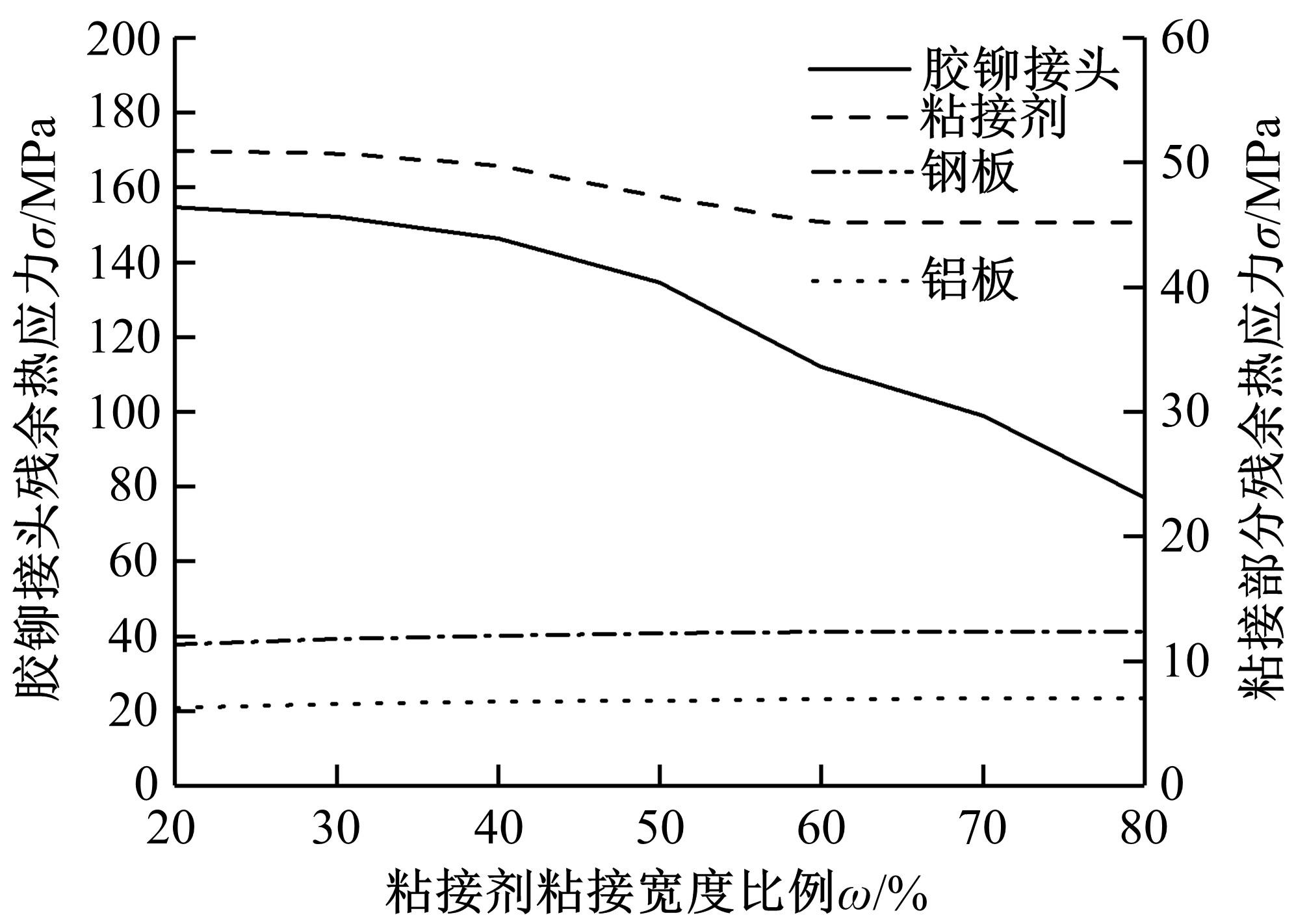
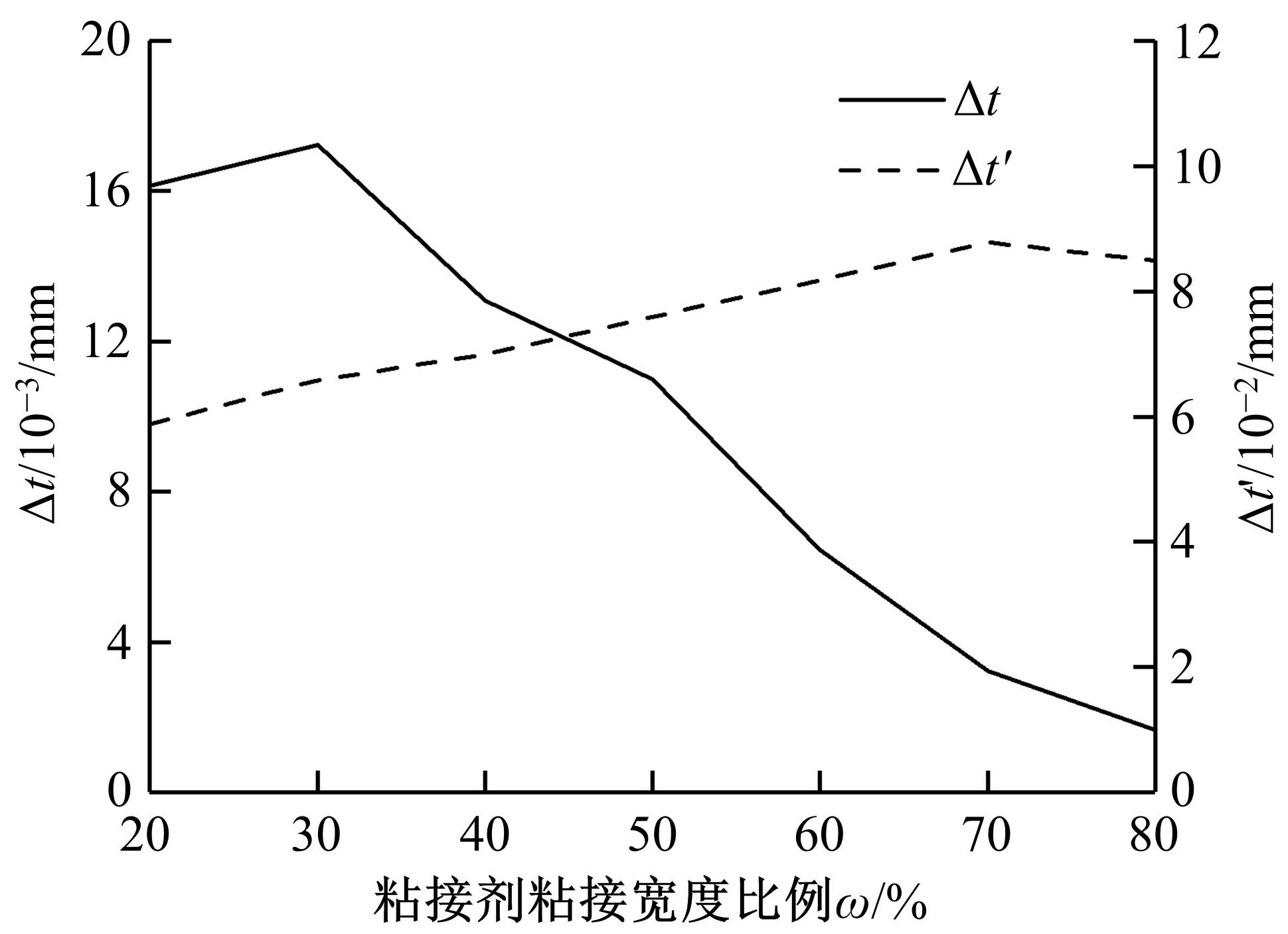
针对车身结构在涂装过程中温度变化对钢铝胶铆连接结构的影响,研究了影响结构热应力的主要因素。在钢、铝、粘接剂的单向拉伸试验和热膨胀试验基础上进行钢铝胶铆连接结构高温热膨胀试验,获得了钢板、铝板表面的应变值。建立了钢铝胶铆连接结构热膨胀有限元仿真模型,通过试验验证了仿真模型的有效性。分析胶铆结构在升温、保温、降温过程中的应力变化情况,获得了钢铝胶铆连接结构在厚度方向上尺寸随温度的变化规律。研究了粘接剂厚度、粘接宽度和金属铆接顺序对钢铝胶铆连接结构在高温作用下的影响。结果表明,钢铝胶铆连接结构在经历高温作用后会产生残余应力和热变形;适当增大粘接剂厚度可以降低胶铆连接结构的残余应力和应力集中,降低结构整体的热变形;增大粘接宽度能有效降低胶铆接头中的残余应力,但会导致钢铝胶铆连接结构塑性变形增大;铝板在上、钢板在下铆接时胶铆接头的残余应力较小。
中图分类号:
- U270.4
| 1 | 李永兵, 马运五, 楼铭, 等. 轻量化多材料汽车车身连接技术进展[J]. 机械工程学报, 2016, 52(24): 1-23. |
| Li Yong-bing, Ma Yun-wu, Lou Ming, et al. Advances in welding and joining processes of multi-material lightweight car body[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(24): 1-23. | |
| 2 | Markus P. Manufacturing of high strength steel and aluminum for a mixed material body in white[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2005, 6-8: 109-126. |
| 3 | 庄蔚敏, 施宏达, 解东旋, 等. 钢铝异质无铆钉粘铆复合连接胶层厚度分布[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(1): 100-106. |
| Zhuang Wei-min, Shi Hong-da, Xie Dong-xuan, et al. Thickness distribution of adhesive layer in dissimilar clinch-adhesive hybrid joint with steel and aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 100-106. | |
| 4 | Meschut G, Hahn O, Janzen V, et al. Innovative joining technologies for multi-material structures[J]. Welding in the World, 2014, 58(1): 65-75. |
| 5 | Gómez S, Oñoro J, Pecharromán J. A simple mechanical model of a structural hybrid adhesive/riveted single lap joint[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 2006, 27(4): 263-267. |
| 6 | 邢保英, 何晓聪, 王玉奇, 等. 多铆钉自冲铆接头力学性能机理[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(5): 1488-1494. |
| Xing Bao-ying, He Xiao-cong, Wang Yu-qi, et al. Mechanism of mechanical properties of self-piercing riveted joints with multiple rivets[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(5): 1488-1494. | |
| 7 | Adams R D, Coppendale J, Mallick V, et al. The effect of temperature on the strength of adhesive joints[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 1992, 12(3): 185-190. |
| 8 | 周江奇, 潘海涛, 楼铭, 等. 结构胶对铝钢异种金属自冲铆接工艺影响研究[J]. 汽车工程学报, 2015, 5(5): 313-320. |
| Zhou Jiang-qi, Pan Hai-tao, Lou Ming, et al. Impact of structural adhesive on self-piercing riveted aluminum to steel joints[J]. Chinese Journal of Automotive Engineering, 2015, 5(5): 313-320. | |
| 9 | Sadowski T, Kneć M, Golewski P. Experimental investigations and numerical modelling of steel adhesive joints reinforced by rivets[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 2009, 30(5): 338-346. |
| 10 | 胡平, 韩啸, 李伟东, 等. 考虑汽车车身涂装工艺影响的非平衡胶接接头强度[J]. 机械工程学报, 2012, 48(20): 93-102. |
| Hu Ping, Han Xiao, Li Wei-dong, et al. Influence of automobile body coating process on the strength of unbalanced adhesive joints[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(20): 93-102. | |
| 11 | 韩啸, 李伟东, 胡平. 非平衡胶接接头循环温度场强度退化研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2012, 48(18): 97-103. |
| Han Xiao, Li Wei-dong, Hu Ping. Research on the strength degradation of unbalanced adhesive joints subjected to cyclic-temperature environment[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(18): 97-103. | |
| 12 | Pirondi A, Moroni F. Science of clinch–adhesive joints[J]. Advanced Structured Materials, 2011, 6: 109-147. |
| 13 | da Silva L F M. Technology of mixed adhesive joints[J]. Advanced Structured Materials, 2011, 6: 283-309. |
| 14 | 干勇. 钢铁材料手册[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2009. |
| 15 | 树脂浇注体性能试验方法[S]. |
| 16 | 金属材料热膨胀特征参数的测定[S]. |
| 17 | Moroni F, Pirondi A, Kleiner F. Experimental analysis and comparison of the strength of simple and hybrid structural joints[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 2010, 30(5): 367-379. |
| 18 | Meschut G, Hahn O, Teutenberg D, et al. Influence of the curing process on joint strength of a toughened heat-curing adhesive[J]. Welding in the World, 2015, 59(2): 209-216. |
| [1] | 段亮,宋春元,刘超,魏苇,吕成吉. 基于机器学习的高速列车轴承温度状态识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 53-62. |
| [2] | 胡兴军,张靖龙,罗雨霏,辛俐,李胜,胡金蕊,兰巍. 冷却管结构及进气方向对空冷中冷器性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1933-1942. |
| [3] | 陈剑斌,周宋泽,费峰永,陈永龙,凌国平. 过盈量及滚花方式对装配式凸轮轴压装失效的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1959-1966. |
| [4] | 罗勇,韦永恒,黄欢,肖人杰,任淋,崔环宇. 驾驶员意图识别的P2.5插混构型双离合器起步控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1575-1582. |
| [5] | 曾小华,宋美洁,宋大凤,王越. 基于车联网信息的公交客车行驶工况数据处理方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1692-1699. |
| [6] | 马超,高云凯,刘哲,段月星,田林雳. 骨架式车身多材料及梁截面形状和尺寸优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1583-1592. |
| [7] | 兰凤崇,李继文,陈吉清. 面向动态场景复合深度学习与并行计算的DG-SLAM算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1437-1446. |
| [8] | 杨建,夏琦,周海超,王国林. 修正胎体弦轮廓载重子午线轮胎的降噪机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1198-1203. |
| [9] | 龙江启,向锦涛,俞平,王骏骋. 适用于非线性主动悬架滑模控制的线性干扰观测器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1230-1240. |
| [10] | 陈鑫,于贵申,张彪,潘凯旋,杨立飞. 搅拌摩擦点焊接头拉伸-剪切行为的等效建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1190-1197. |
| [11] | 宋大凤,杨丽丽,曾小华,王星琦,梁伟智,杨南南. 基于行驶工况合成的混合动力汽车电池寿命优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 781-791. |
| [12] | 何仁,赵晓聪,杨奕彬,王建强. 基于驾驶人风险响应机制的人机共驾模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 799-809. |
| [13] | 张家旭,王欣志,赵健,施正堂. 汽车高速换道避让路径规划及离散滑模跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1081-1090. |
| [14] | 王波,何洋扬,聂冰冰,许述财,张金换. 底部爆炸条件下车内乘员的腹部损伤[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 792-798. |
| [15] | 庄蔚敏,王鹏跃,高瑞娟,解东旋. 温热成形对AA5754铝合金静态力学性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 847-854. |
|
||