吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (6): 1315-1323.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210028
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
考虑安全间距的合流区可变限速协调控制方法
- 1.吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
2.厦门市城市规划设计研究院有限公司,福建 厦门 361012
Coordinated control method of variable speed limit in on⁃ramp area considering safety distance
Wen-jing WU1( ),Yong-bin ZHAN1,Li-li YANG1(
),Yong-bin ZHAN1,Li-li YANG1( ),Run-chao CHEN2
),Run-chao CHEN2
- 1.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Xiamen Urban Planning & Design Institute Co. ,Ltd. ,Xiamen 361012,China
摘要:
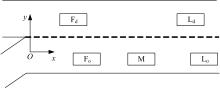
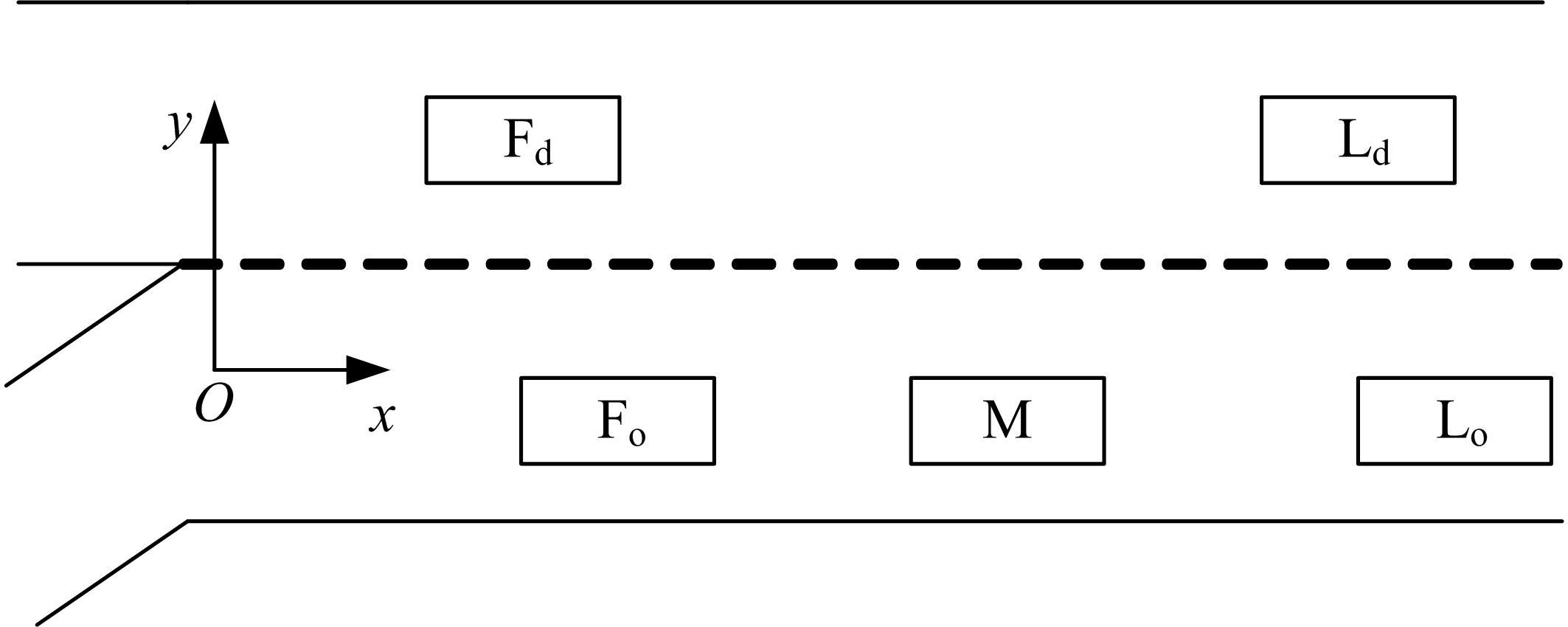
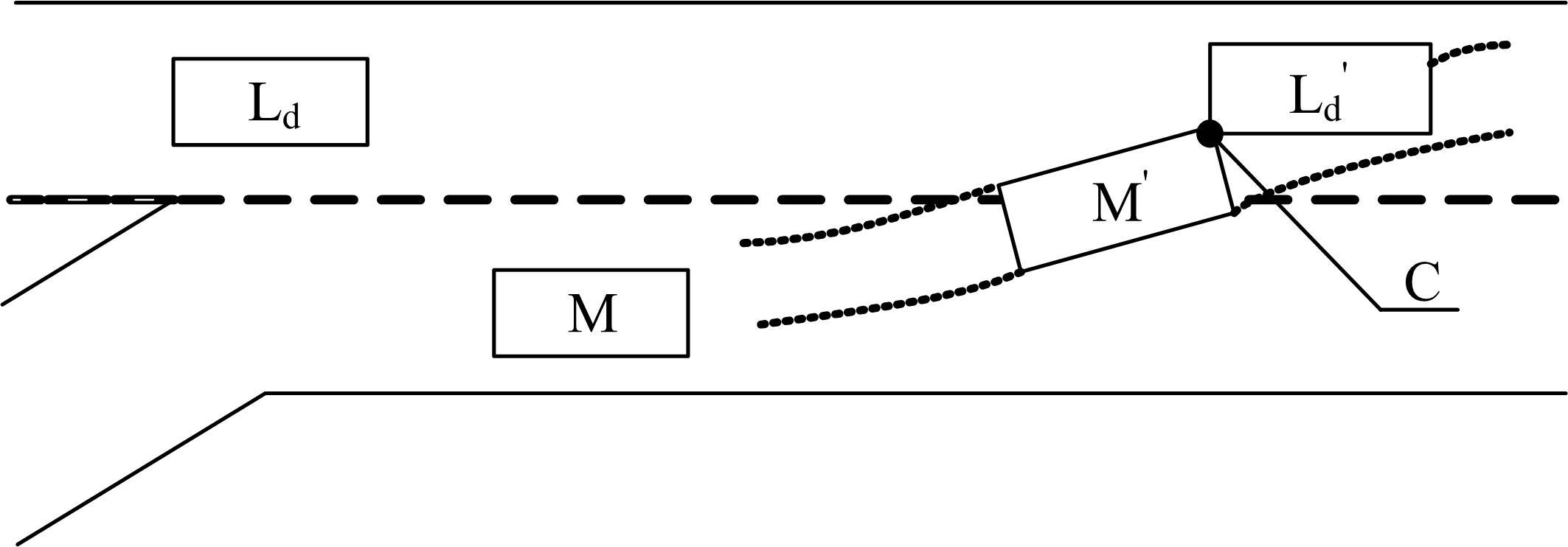
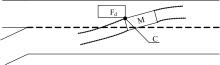
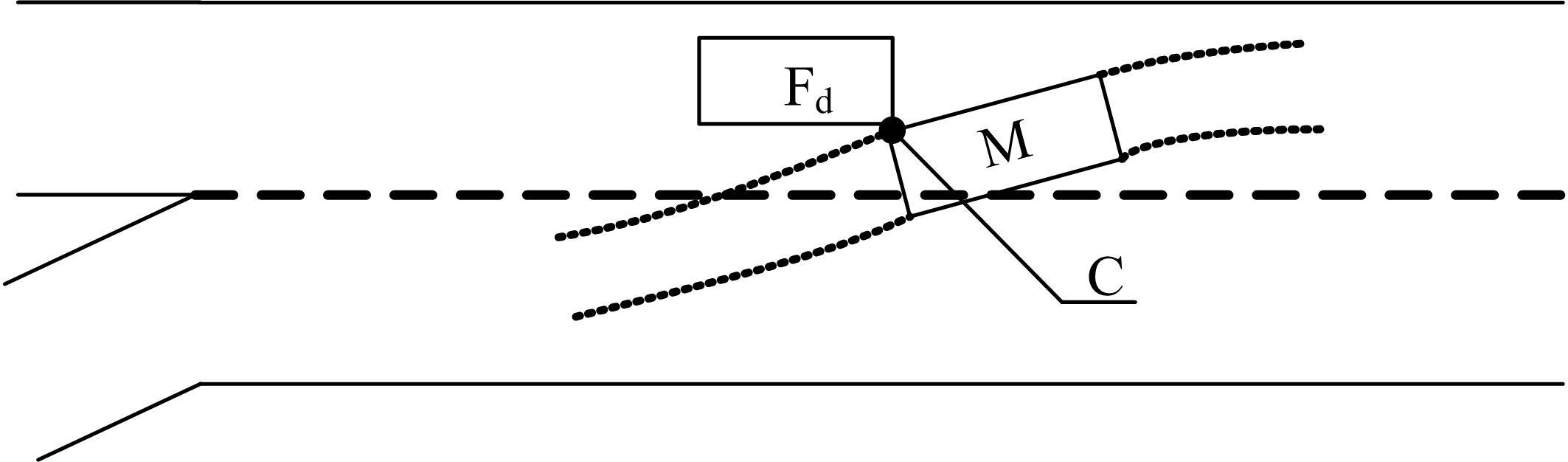
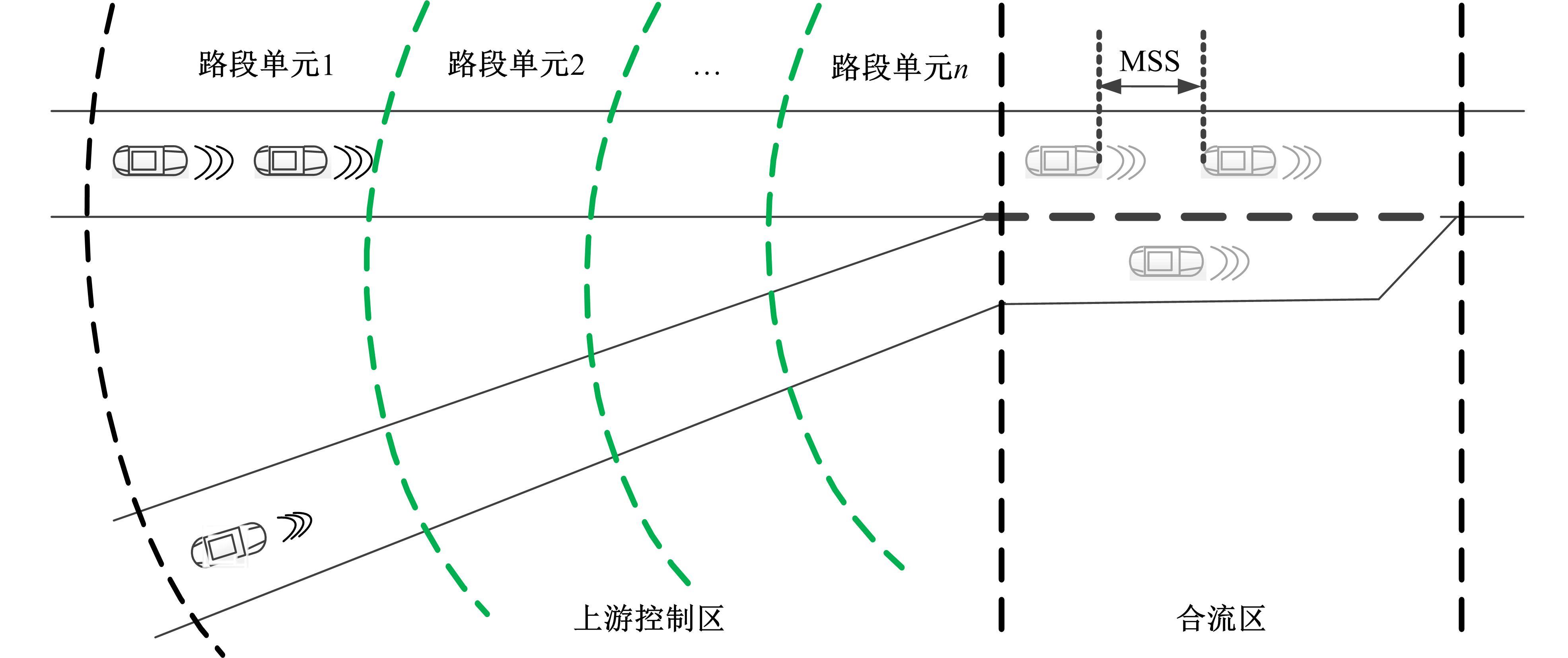
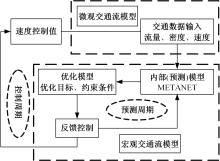
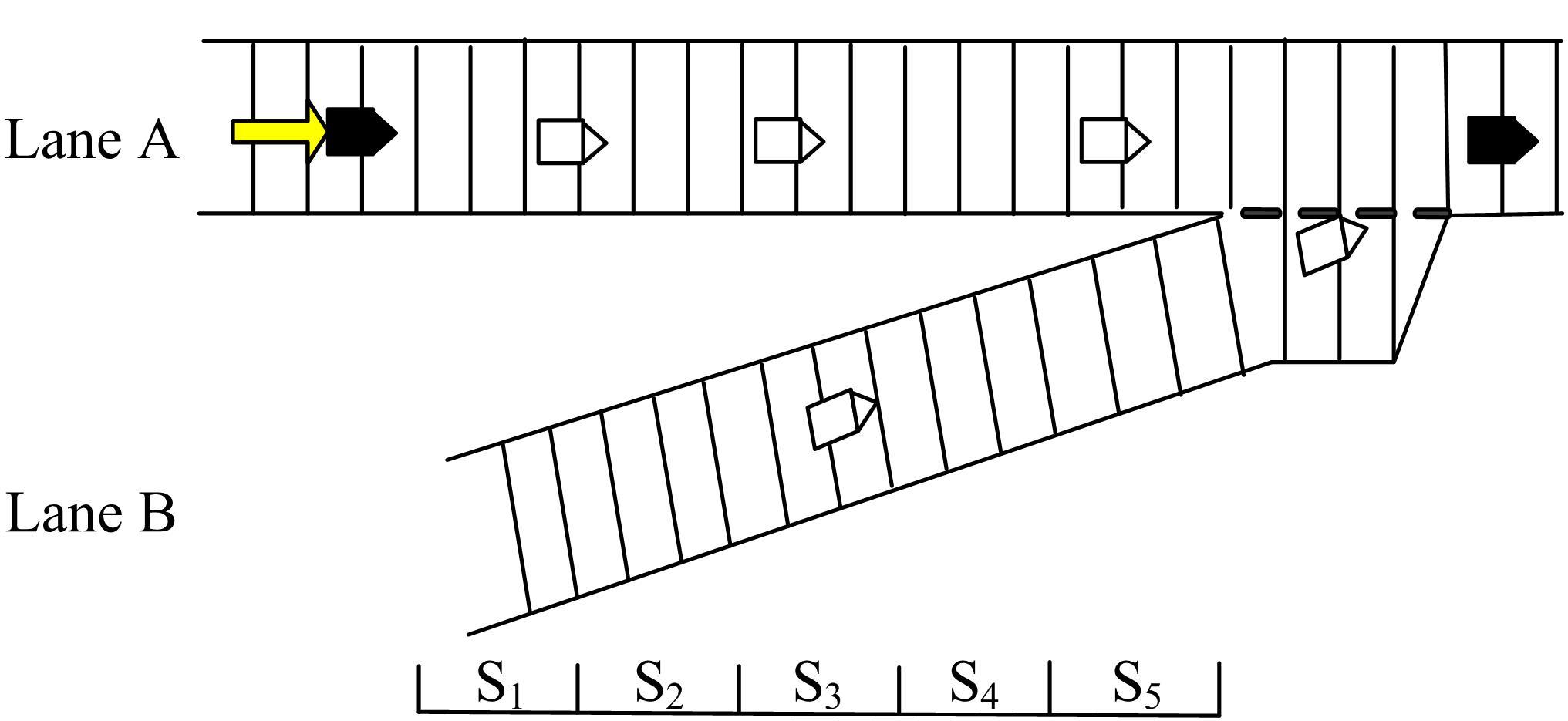
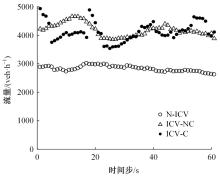
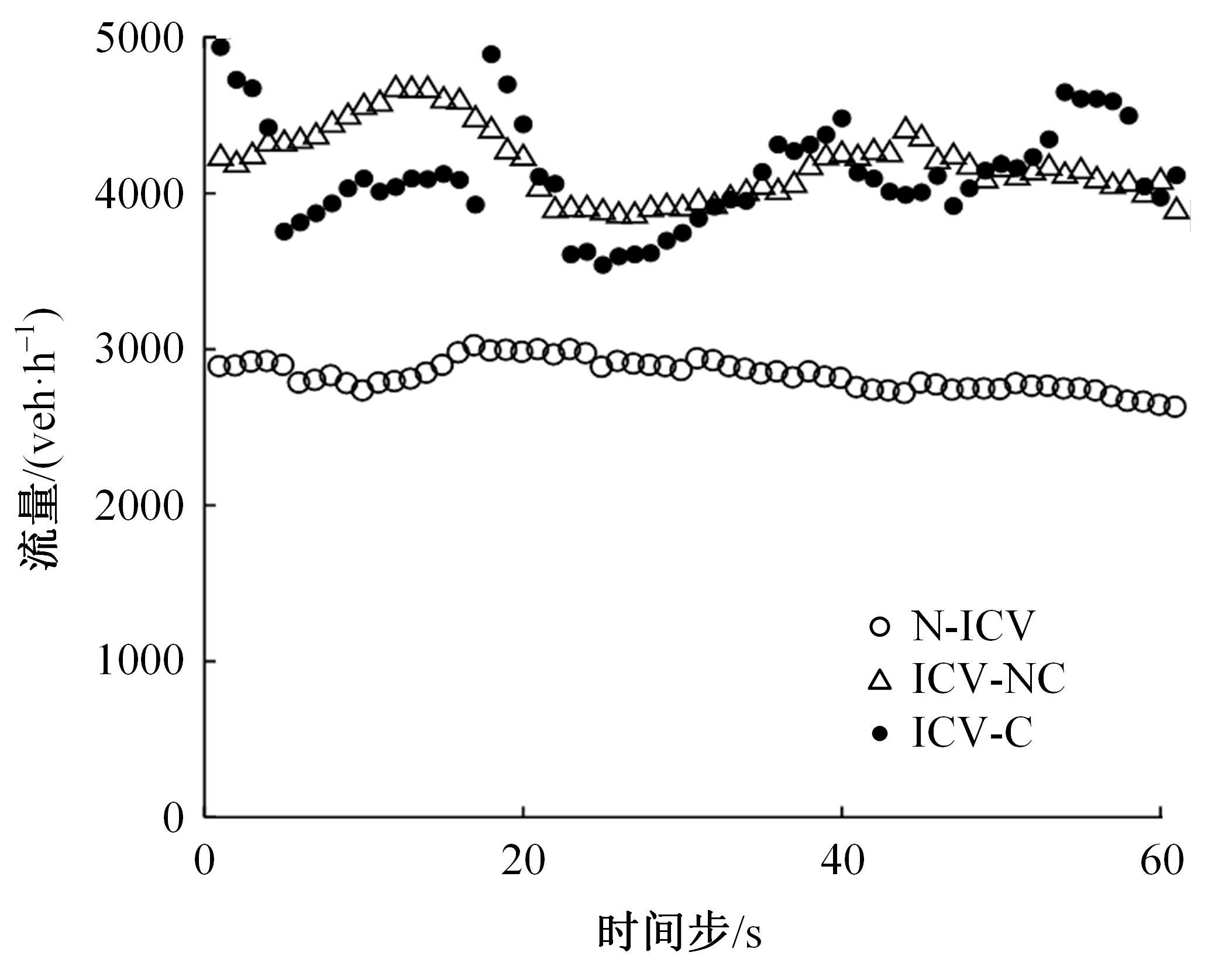
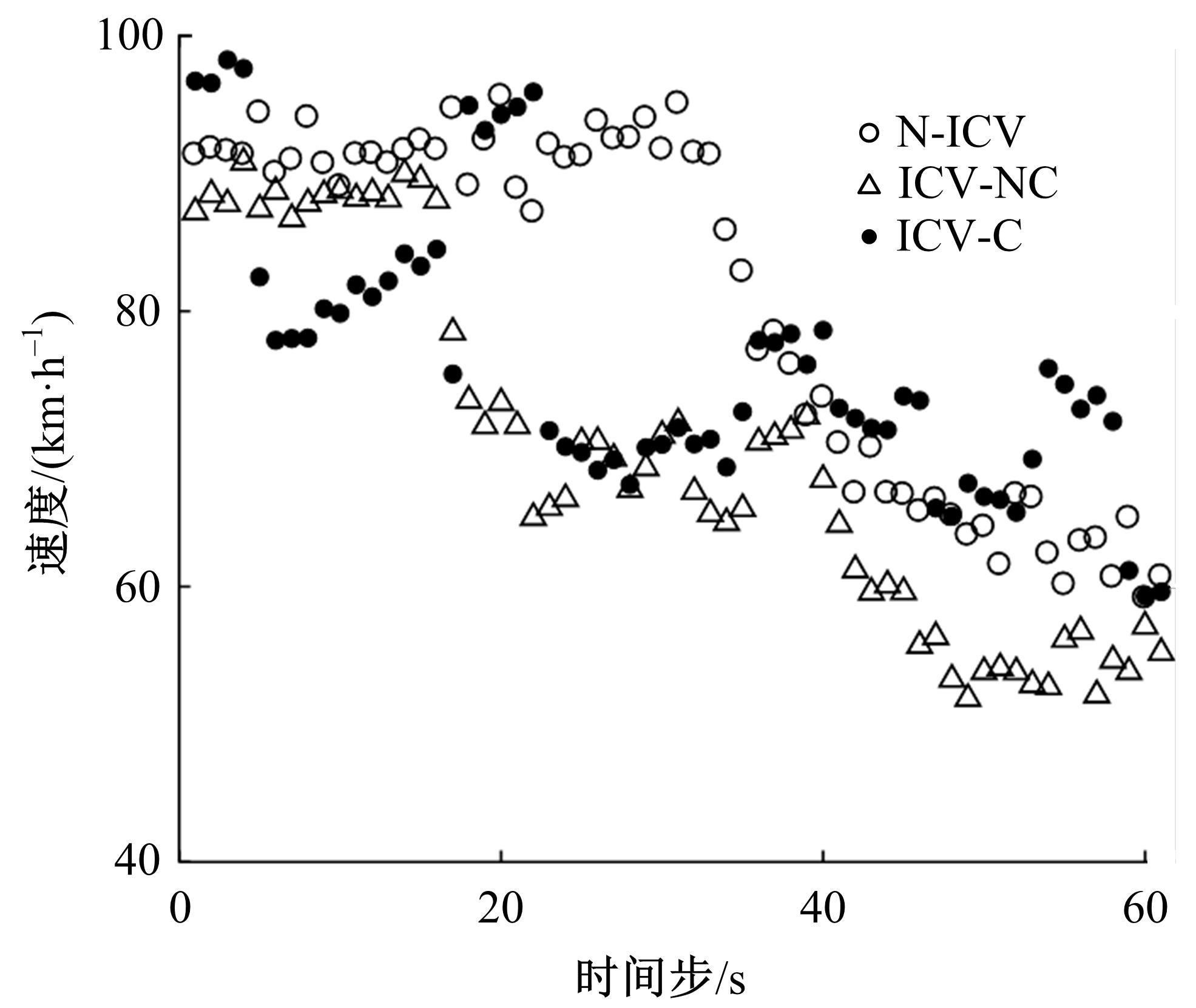
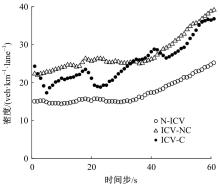
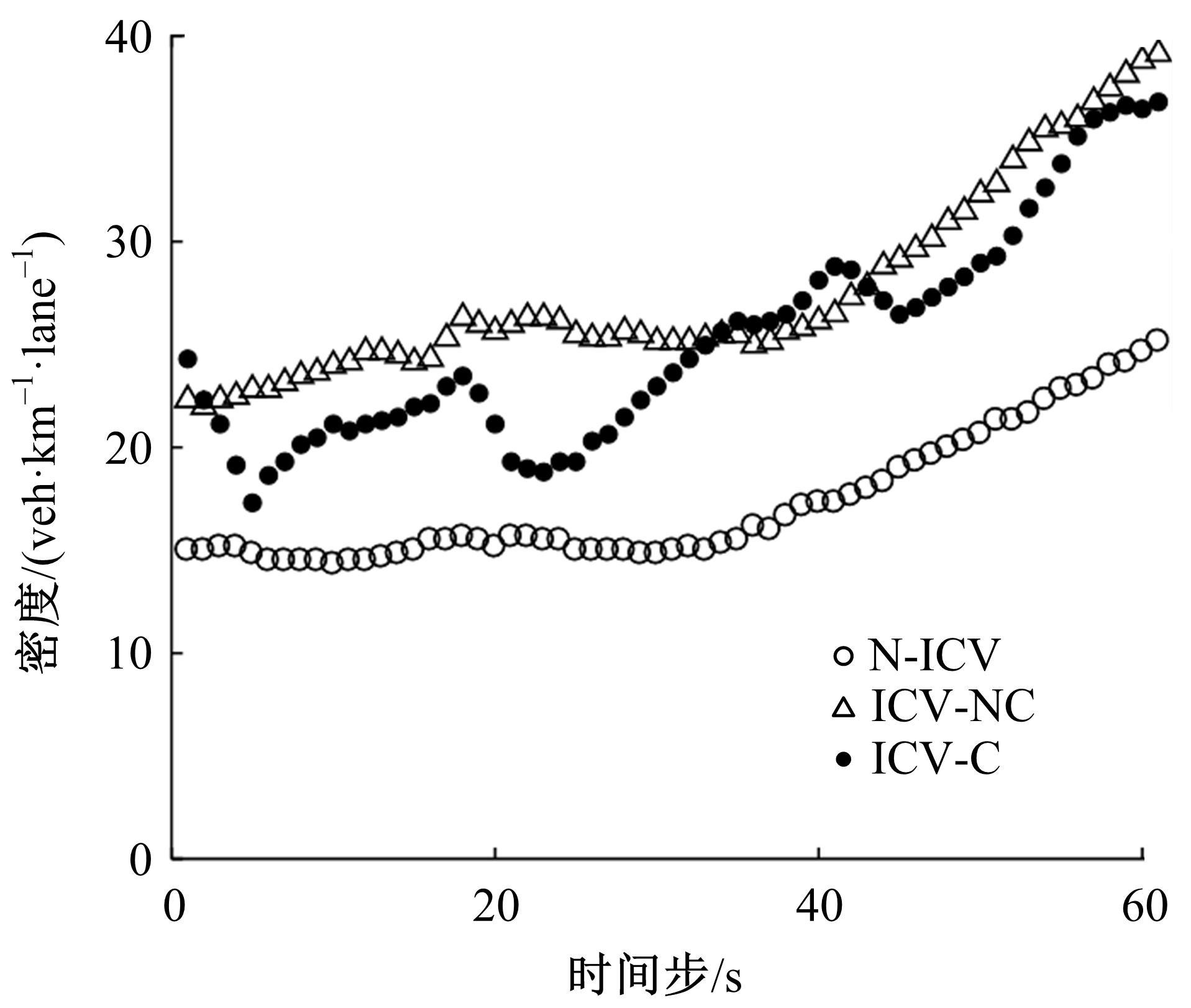
针对匝道合流冲突的问题,分析了合流区车辆换道特性及运动轨迹,提出了满足车辆合流需求的车辆安全间距计算模型。首先,将其纳入可变限速的控制框架中,运用模型预测控制方法,建立了网联环境下合流区可变限速协调控制方法和模型。然后,利用元胞自动机搭建仿真环境,实现了网联车在上游控制区的速度协调控制。最后,将匝道与主道车辆到达率按照低、中、高进行27个场景的设置,选取交通量、速度、密度、行程时间作为评价指标,通过仿真分析了控制策略下的合流区交通状况。仿真结果表明:匝道车辆到达率会影响控制策略的实施效果,低密度时,效果不显著;中密度时,控制策略优势得以体现;高密度时,策略失效。
中图分类号:
- U491.4
| 1 | Kang K P, Chang G L, Zou N. Optimal dynamic speed-limit control for highway work zone operations[C]∥Venue: Hilton DFW Lakes Executive Conference Center, Grapevine, Texas, USA, 2004: 77-84. |
| 2 | Zhang Yi-hang, Sirmatel I I, Alasiri F. Comparison of feedback linearization and model predictive techniques for variable speed limit control[C]∥2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Maui, HI, USA, 2018: 3000-3005. |
| 3 | Zhang C B, Nasser R. Optimisation of lane-changing advisory at the motorway lane drop bottleneck[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2019, 106(7): 303-316. |
| 4 | Zhang Yao-zong, Ma Ming-hui, Liang Shi-dong. Dynamic control cycle speed limit strategy for improving traffic operation at freeway bottlenecks[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2021, 25(2): 692-704. |
| 5 | 陈永恒,刘鑫山,熊帅,等. 冰雪条件下快速路汇流区可变限速控制[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2018, 48(3): 677-687. |
| Chen Yong-heng, Liu Xin-shan, Xiong Shuai, et al. Variable speed limit control under snow and ice conditions for urban expressway in junction bottleneck area[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(3): 677-687. | |
| 6 | Hu Xiang-wang, Sun Jian. Trajectory optimization of connected and autonomous vehicles at a multilane freeway merging area[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 101(2): 111-125. |
| 7 | Ntousakis I A, Nikolos I K, Papageorgiou M. Optimal vehicle trajectory planning in the context of cooperative merging on highways[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 71: 464-488. |
| 8 | Xu Ling-hui, Lu Jia, Wang Chong, et al. Cooperative merging control strategy of connected and automated vehicles on highways[J]. Journal of Southeast University(English Edition), 2019, 35(2): 220-227. |
| 9 | Hyun W, Jorge A. Combined ramp-metering and variable speed limit system for capacity drop control at merge bottlenecks[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 2020, 146(6): No. 04020033. |
| 10 | 杨敏, 王立超, 张健, 等. 面向智慧高速的合流区协作车辆冲突解脱协调方法[J].交通运输工程学报, 2020, 20(3): 217-224. |
| Yang Min, Wang Li-chao, Zhang Jian, et al. Collaborative method of vehicle conflict resolution in merging area for intelligent expressway[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2020, 20(3): 217-224. | |
| 11 | Du W D, Abbas-Turki A, Koukam A, et al. On the V2X speed synchronization at intersections: Rule based System for extended virtual platooning[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2018, 141: 255-262. |
| 12 | Yang M M, Wang X S, Quddus M. Examining lane change gap acceptance, duration and impact using naturalistic driving data[J]. Transportation Research, Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 104(7): 317-331. |
| 13 | 张良,陈诗慧,张伟. 驾驶员换道执行持续时间研究[J]. 工业工程与管理,2014,19(4):109-114. |
| Zhang Liang, Chen Shi-hui, Zhang Wei. Study on lane change duration[J]. Industrial Engineering and Management, 2014, 19(4):109-114. | |
| 14 | 马明辉, 杨庆芳, 梁士栋. 高速公路主线可变限速控制方法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2015, 47(9): 107-111. |
| Ma Ming-hui, Yang Qing-fang, Liang Shi-dong.A method of variable speed limit control for traffic flow on freeway mainline[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015, 47(9): 107-111. | |
| 15 | Ye L H, Yamamoto T. Modeling connected and autonomous vehicles in heterogeneous traffic flow[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2018, 490: 269-277. |
| [1] | 冯天军,孙学路,黄家盛,田秀娟,宋现敏. 基于三种过街方式的两相位信号交叉口延误[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 550-556. |
| [2] | 李兴华,冯飞宇,成诚,王洧,唐鹏程. 网约拼车服务选择偏好分析及建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 578-584. |
| [3] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [4] | 尹超英,邵春福,黄兆国,王晓全,王晟由. 基于梯度提升决策树的多尺度建成环境对小汽车拥有的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 572-577. |
| [5] | 贾洪飞,邵子函,杨丽丽. 终点不确定条件下网约车合乘匹配模型及算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 564-571. |
| [6] | 贾彦峰,曲大义,林璐,姚荣涵,马晓龙. 基于运行轨迹的网联混合车流速度协调控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2051-2060. |
| [7] | 薛锋,何传磊,黄倩,罗建. 多式轨道交通网络的耦合协调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2040-2050. |
| [8] | 陆文琦,周天,谷远利,芮一康,冉斌. 基于张量分解理论的车道级交通流数据修复算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1708-1715. |
| [9] | 卢凯,吴蔚,林观荣,田鑫,徐建闽. 基于KNN回归的客运枢纽聚集人数组合预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1241-1250. |
| [10] | 彭博,张媛媛,王玉婷,唐聚,谢济铭. 基于自动编码机-分类器的视频交通状态自动识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 886-892. |
| [11] | 张健,吴坤润,杨敏,冉斌. 智能网联环境下交叉口双环自适应控制模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 541-548. |
| [12] | 王殿海,沈辛夷,罗小芹,金盛. 车均延误最小情况下的相位差优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 511-523. |
| [13] | 何德峰,罗捷,舒晓翔. 自主网联车辆时滞反馈预测巡航控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 349-357. |
| [14] | 贾超,徐洪泽,王龙生. 基于多质点模型的列车自动驾驶非线性模型预测控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1913-1922. |
| [15] | 宋现敏,张明业,李振建,王鑫,张亚南. 动态公交专用道的设置及其仿真分析评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1677-1686. |
|
||