吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 2984-2993.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210538
基于黏菌算法的蛋白质多序列比对
王鑫禄1,2,3( ),刘大有1,2(
),刘大有1,2( ),刘思含1,3,王征1,2,张丽伟1,2,董飒1,2
),刘思含1,3,王征1,2,张丽伟1,2,董飒1,2
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
3.吉林大学 国际教育学院,长春 130012
Multiple sequence alignment of proteins based on slime mold algorithm
Xin-lu WANG1,2,3( ),Da-you LIU1,2(
),Da-you LIU1,2( ),Si-han LIU1,3,Zheng WANG1,2,Li-wei ZHANG1,2,Sa DONG1,2
),Si-han LIU1,3,Zheng WANG1,2,Li-wei ZHANG1,2,Sa DONG1,2
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
3.College of International Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
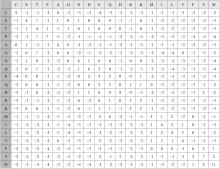
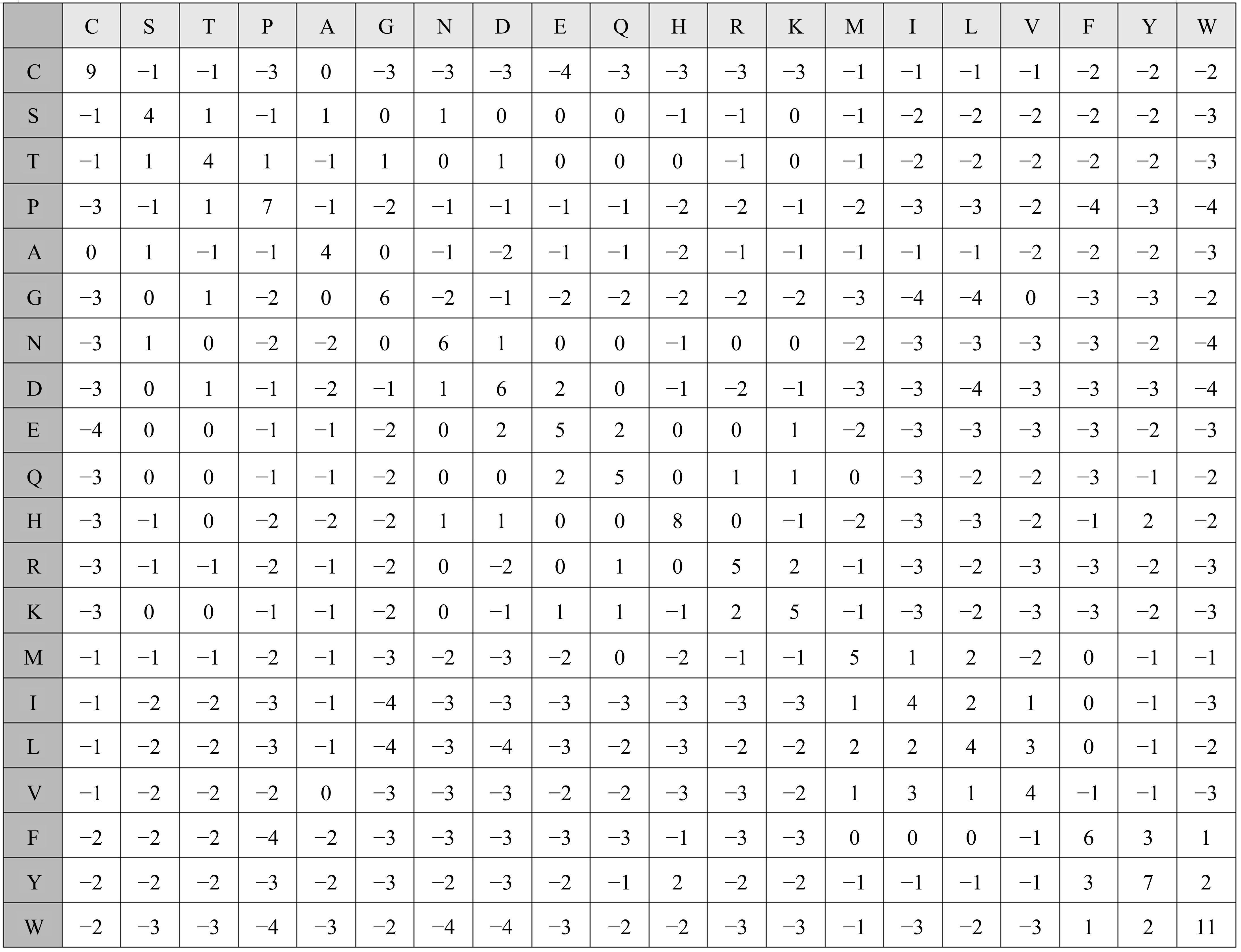
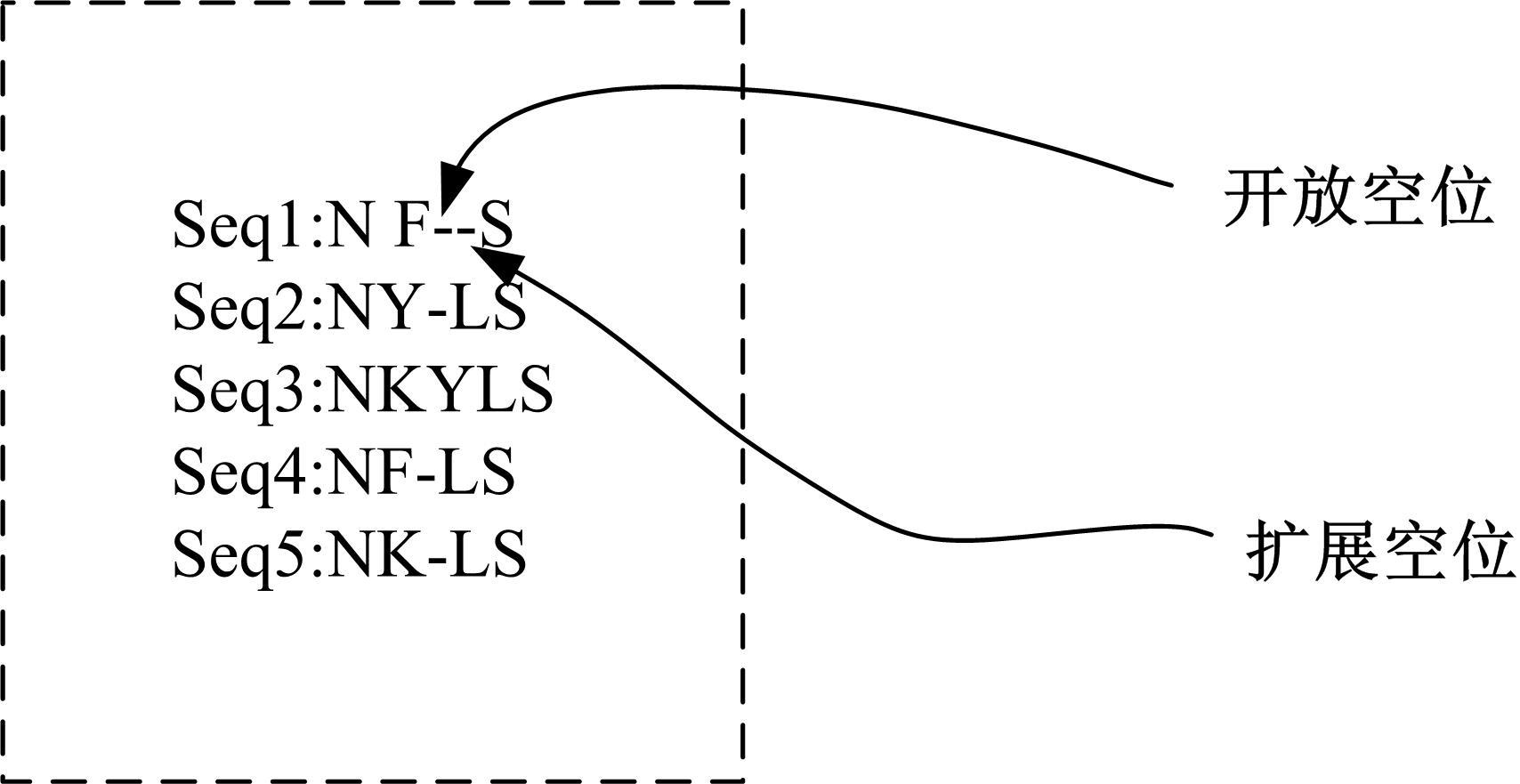
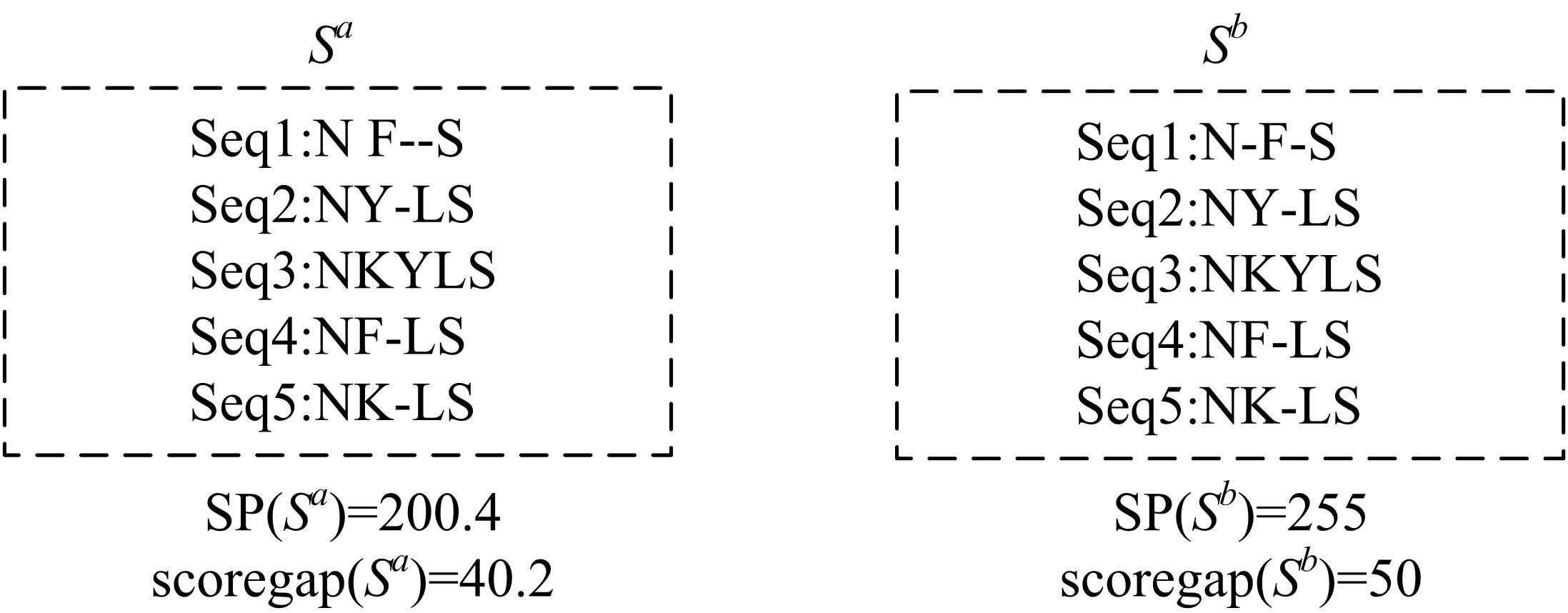
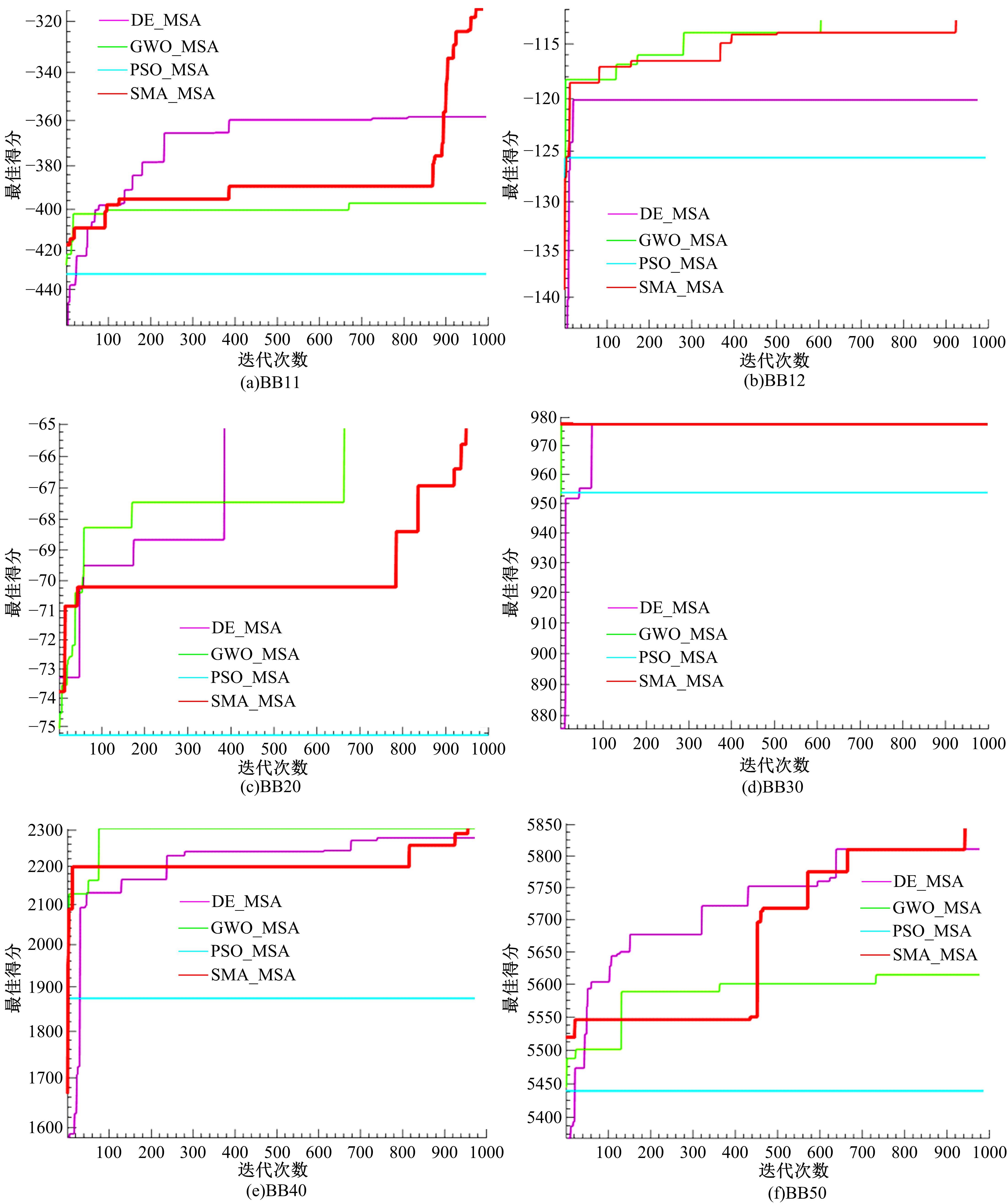
基于黏菌算法(SMA)提出了一种有效的配比模型(SMA_MSA)以辅助判断不同序列之间是否具有同源性,进而预测蛋白质结构。基于BAliBASE 3.0基准数据集,对SMA_MSA和其他经典竞争算法在6类数据集上进行了测试。结果表明:在其中的31个数据集中SMA_SMA有较好的匹配能力,说明了本文模型在蛋白质多序列比对问题中具有很大的发展潜力。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Eric S, Martinez H M. A multiple sequence alignment program[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1986(1):363-374. |
| 2 | Layeb A, Boudra A, Korichi W, et al. A new greedy randomized adaptive search procedure for multiobjective RNA structural alignment[J]. International Journal in Foundations of Computer Science & Technology, 2013, 3(1): 1-14. |
| 3 | 李文. 基于k-mer相异度算法在系统进化关系中的应用[D]. 广州:华南理工大学物理与光电学院, 2019. |
| Li Wen. Application of dissimilarity algorithms based on k-mer in evolutionary relationship[D]. Guangzhou: School of Physics, South China University of Technology, 2019. | |
| 4 | Edgar R C. Muscle: a multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2004, 5(1): No.113. |
| 5 | Lassmann T, Sonnhammer E L. Kalign—an accurate and fast multiple sequence alignment algorithm[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2005, 6(1): 1-9. |
| 6 | Paolo D T, Sebastien M, Ioannis X, et al. T-Coffee: a web server for the multiple sequence alignment of protein and RNA sequences using structural information and homology extension[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, 39: W13-W17. |
| 7 | Wallace I M, Orla O, Higgins D G, et al. M-Coffee: combining multiple sequence alignment methods with T-Coffee[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2006, 34(6): 1692-1699. |
| 8 | Katoh K, Kuma K I, Miyata T, et al. Improvement in the accuracy of multiple sequence alignment program MAFFT[J]. Genome Informatics, 2005, 16(1):22-33. |
| 9 | Notredame C.Recent Evolutions of multiple sequence alignment algorithms[J]. Plos Computational Biology, 2007, 3: No.e123. |
| 10 | Ling C, Wei L, Chen J. Ant colony optimization methodfor multiple sequence alignment[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning & Cybernetics, Piscatanay, NJ, 2007: 914-919. |
| 11 | Rubio-Largo A, Vega-Rodríguez M A, González-Álvarez D L. A hybrid multiobjective memetic metaheuristic for multiple sequence alignment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2016, 20(4): 499-514. |
| 12 | Liu Y, Schmidt B, Maskell D L. Msaprobs: multiple sequence alignment based on pair hidden Markov models and partition function posterior probabilities[J]. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26: 1958-1964. |
| 13 | Gao Y X. A multiple sequence alignment algorithm based on inertia weights particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Bionanoence, 2014, 8(5): 400-404. |
| 14 | Rani R R, Ramyachitra D. Multiple sequence alignment using multi-objective based bacterial foraging optimization algorithm[J]. Biosystems, 2016, 150: 177-189. |
| 15 | Sun J, Wu X, Wei F, et al. Multiple sequence alignment using the hidden markov model trained by an improved quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization[J]. Information Sciences, 2012, 182(1): 93-114. |
| 16 | Öztürk C, Aslan S. A new artificial bee colony algorithm to solve the multiple sequence alignment problem[J]. International Journal of Data Mining & Bioinformatics, 2016, 14(4): 332-353. |
| 17 | Zhu H, He Z, Jia Y. A novel approach to multiple sequence alignment using multiobjective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical & Health Informatics, 2016, 20(2): No.717. |
| 18 | Zambrano-Vega C, Nebro A J, Durillo J, et al. Multiple sequence alignment with multiobjective metaheuristics. a comparative study[J]. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2017, 32(8): 843-861. |
| 19 | Mokaddem A, Hadj A B, Elloumi M. Refin-align: new refinement algorithm for multiple sequence alignment[J]. Informatica, 2019, 43(4):527-534. |
| 20 | Bonizzoni P, Vedova G D. The complexity of multiple sequence alignment with SP-score that is a metric[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2001, 259(1/2):63-79. |
| 21 | Needleman S B, Wunsch C D. A general method applicable to search for similarities in amino acid sequence of 2 proteins[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1970, 48(3): 443-453. |
| 22 | Thompson J D, Higgins D G, Gibson T J. Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 1994, 22(22): 1673-1680. |
| 23 | Notredame C, Holm L, Higgins D G. Coffee: an objective function for multiple sequence alignments[J]. Bioinformatics, 1998(5): 407-422. |
| 24 | Notredame C, Higgins D G, Heringa J . et al. T-Coffee: a novel method for fast and accurate multiple sequence alignment[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2000, 302(1): 205-217. |
| 25 | O'Sullivan O, Karsten S, Chantal A, et al. 3Dcoffee: combining protein sequences and structures within multiple sequence alignments[J]. Journal of molecular biology, 2004, 340(2): 385-395. |
| 26 | Naznin F, Sarker R, Essam D. Progressive alignment method using genetic algorithm for multiple sequence alignment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2012, 16: 615-631. |
| 27 | Naznin F, Sarker R, Essam D. Vertical decomposition with genetic algorithm for multiple sequence alignment[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2011, 12: No. 353. |
| 28 | Henikoff H. Amino acid substitution matrices from protein blocks[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1992, 89(22):10915-10919. |
| 29 | Li S, Chen H, Wang M, et al. Slime mould algorithm: a new method for stochastic optimization[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 111: 300-323. |
| 30 | Venter G, Jaroslaw S S. Particle swarm optimization[J]. AIAA Journal, 2003, 41(8): 129-132. |
| 31 | Mirjalili S, Mirjalili S, Lewis A. Grey wolf optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69: 46-61. |
| 32 | Das S S P N. Differential evolution: a survey of the state-of-the-art[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2011, 15(1): 4-31. |
| 33 | Thompson J D, Koehl P, Ripp R, et al. Balibase 3.0: latest developments of the multiple sequence alignment benchmark.[J]. Proteins-structure Function & Bioinformatics, 2010, 61(1): 127-136. |
| [1] | 祁贤雨,王巍,王琳,赵玉飞,董彦鹏. 基于物体语义栅格地图的语义拓扑地图构建方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 569-575. |
| [2] | 时小虎,吴佳琦,吴春国,程石,翁小辉,常志勇. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| [3] | 郭鹏,赵文超,雷坤. 基于改进Jaya算法的双资源约束柔性作业车间调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 480-487. |
| [4] | 刘近贞,高国辉,熊慧. 用于脑组织分割的多尺度注意网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 576-583. |
| [5] | 赵宏伟,张健荣,朱隽平,李海. 基于对比自监督学习的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1850-1856. |
| [6] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [7] | 胡丹,孟新. 基于时变网格的对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1896-1903. |
| [8] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [9] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [10] | 周丰丰,朱海洋. 基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法SEE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1834-1841. |
| [11] | 周丰丰,张亦弛. 基于稀疏自编码器的无监督特征工程算法BioSAE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1645-1656. |
| [12] | 王军,徐彦惠,李莉. 低能耗支持完整性验证的数据融合隐私保护方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1657-1665. |
| [13] | 康耀龙,冯丽露,张景安,陈富. 基于谱聚类的高维类别属性数据流离群点挖掘算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1422-1427. |
| [14] | 王文军,余银峰. 考虑数据稀疏的知识图谱缺失连接自动补全算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1428-1433. |
| [15] | 陈雪云,贝学宇,姚渠,金鑫. 基于G⁃UNet的多场景行人精确分割与检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 925-933. |
|