吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 531-537.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210640
基于力学响应分析方法的导电橡胶复合路面铺装技术
- 1.吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
2.中庆建设有限责任公司,长春 130022
Conductive rubber composite pavement paving technology based on mechanical response analysis method
Hai-bin WEI1( ),Zi-peng MA1,Hai-peng BI1(
),Zi-peng MA1,Hai-peng BI1( ),Han-tao LIU2,Shuan-ye HAN1
),Han-tao LIU2,Shuan-ye HAN1
- 1.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Zhongqing Construction Co. ,Ltd. ,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
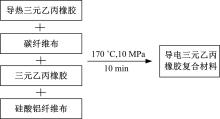
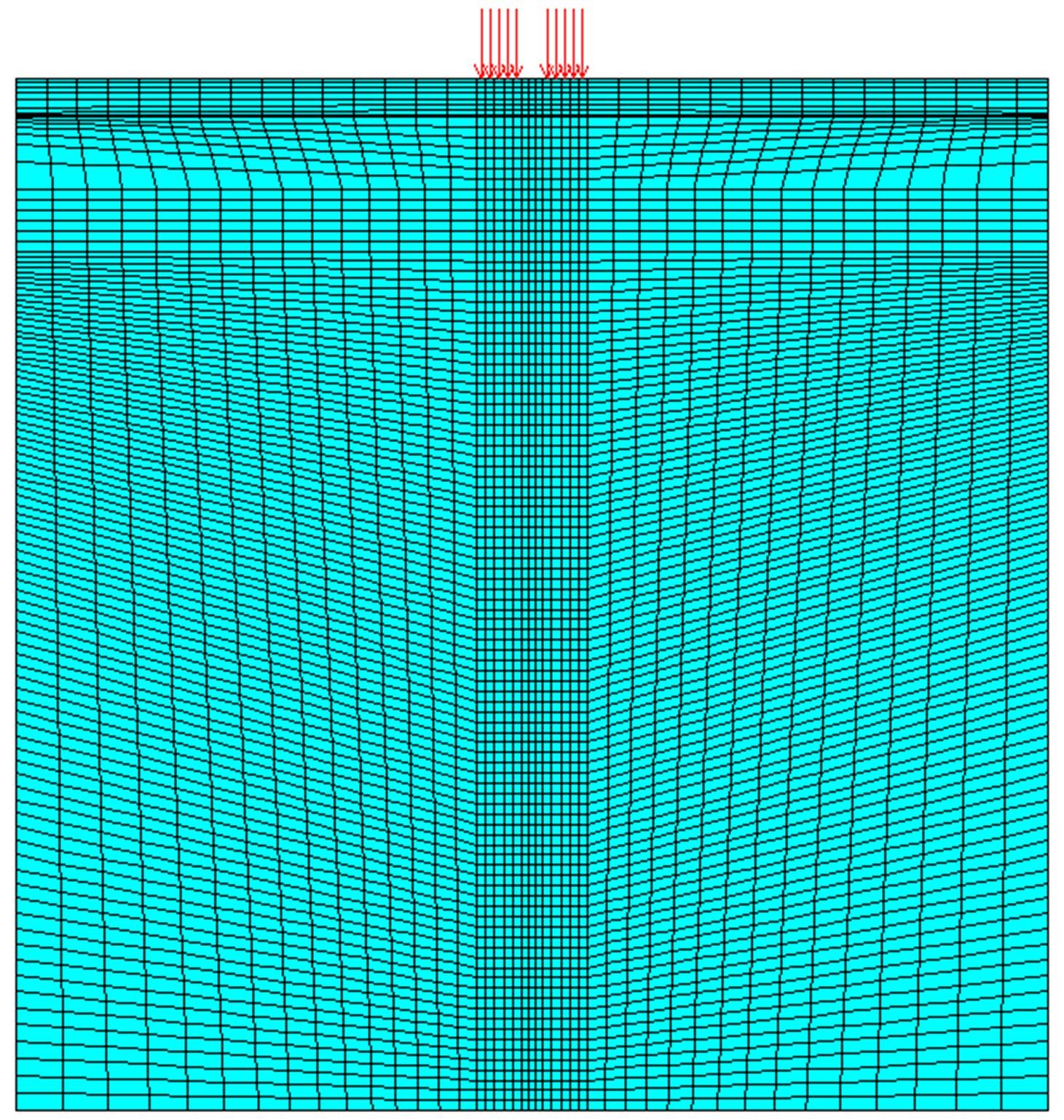
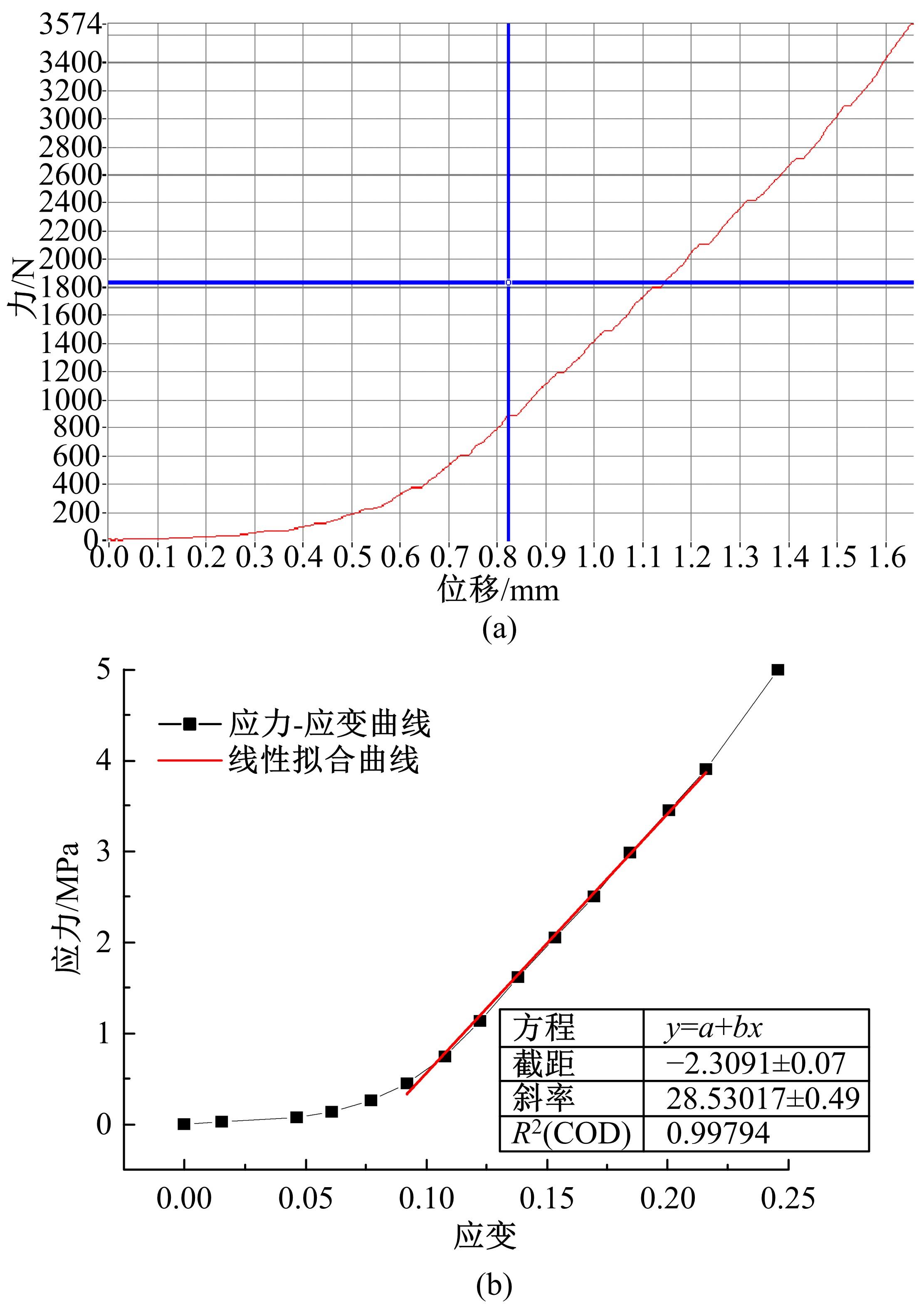
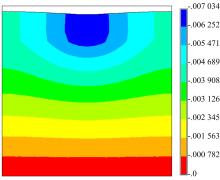
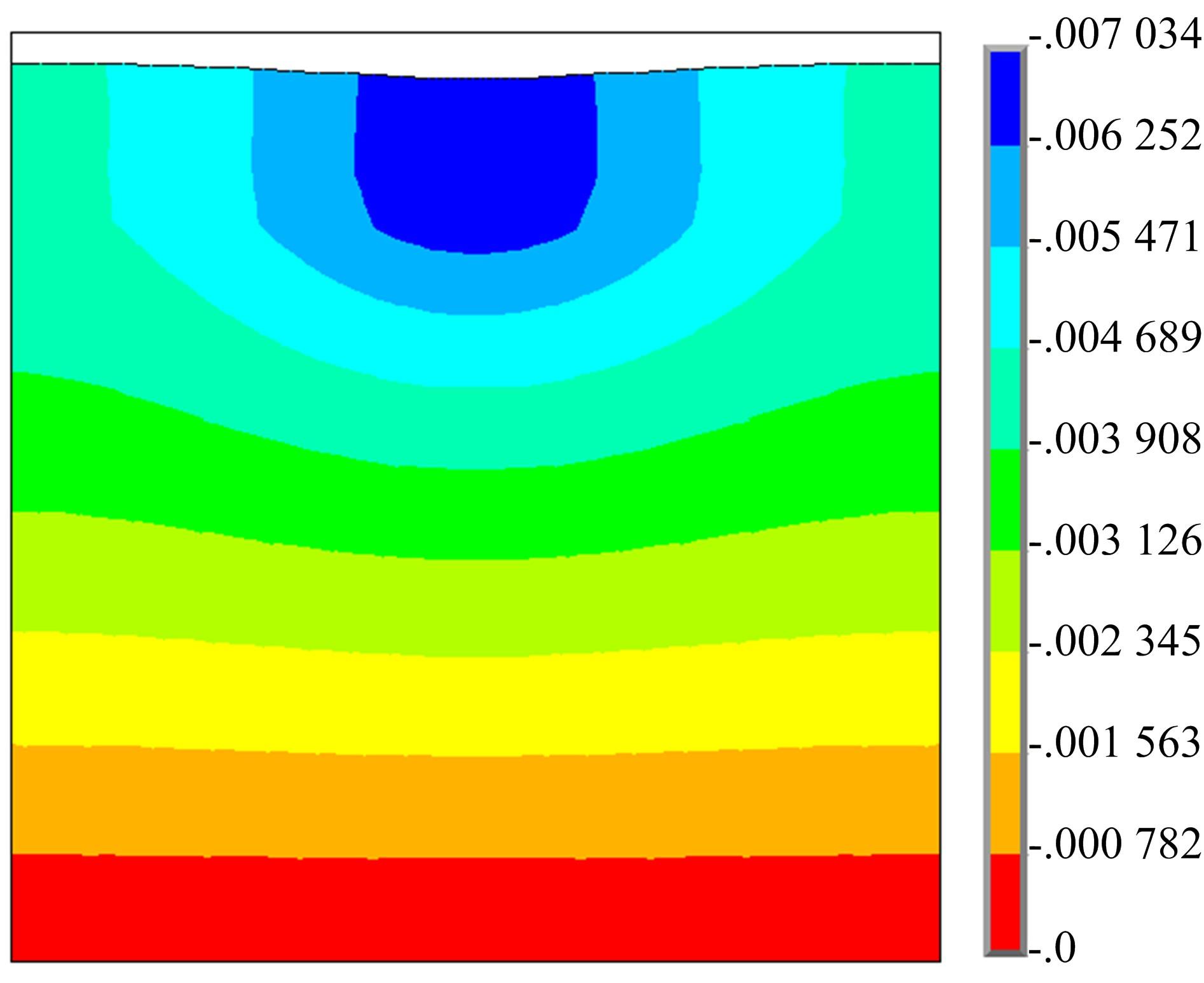
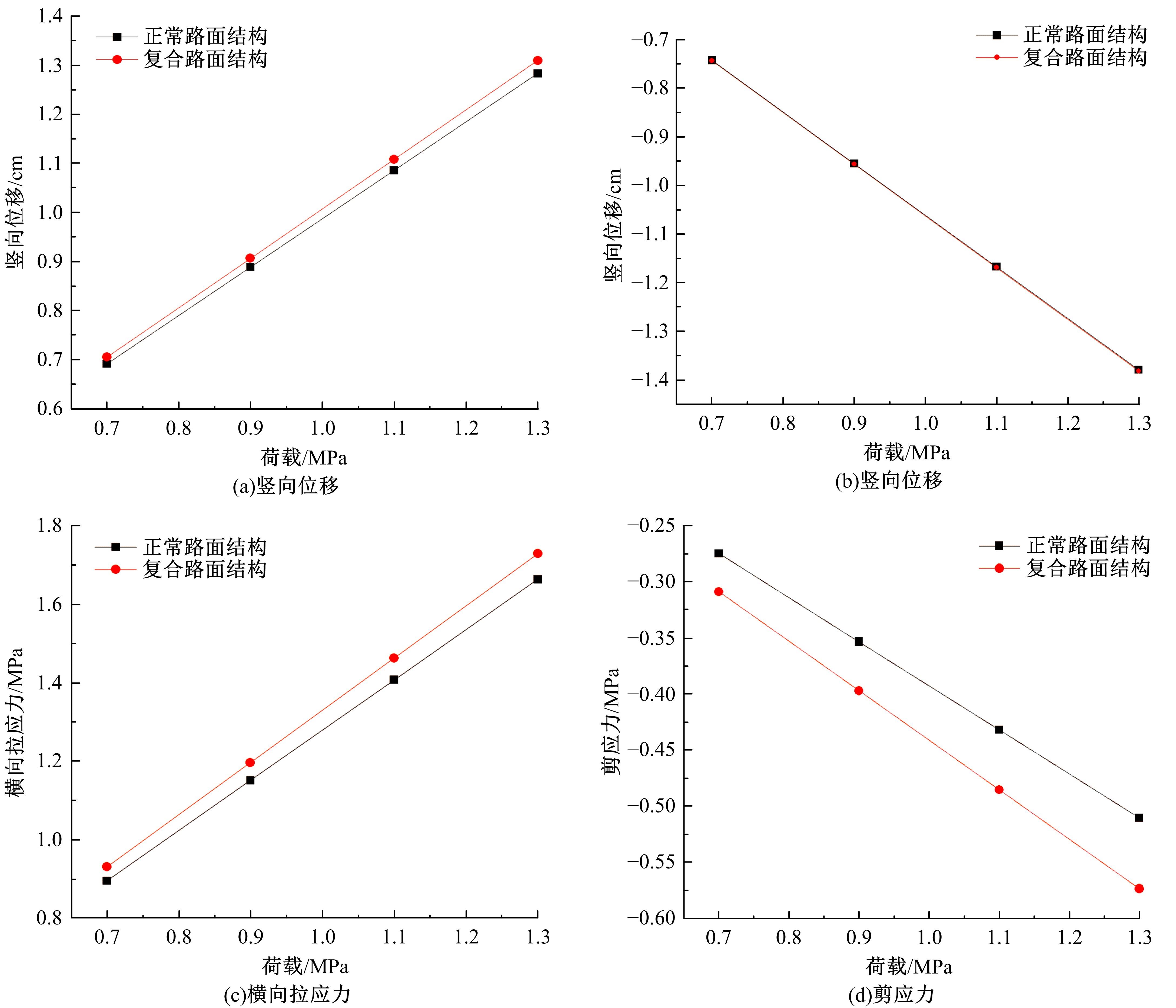
为了确定导电三元乙丙橡胶复合材料应用在路面结构中的可行性以及最佳埋设条件,通过压缩试验研究了复合材料的应力应变曲线,并通过有限元软件ANSYS建立了二维导电三元乙丙橡胶复合材料路面结构模型,分别分析了复合材料埋设位置、埋设厚度以及不同荷载作用下的复合材料路面结构力学响应,并与正常路面结构对比。压缩试验结果表明:复合材料在受力的情况下主要表现为弹性,弹性模量为30.6 MPa。力学响应结果表明:在合理假设的条件下,复合材料应用在路面结构中是可行的,最佳埋设位置为沥青下面层下,埋设厚度越小越好,在超载的情况下,需要重点考虑剪应力对复合材料路面结构的影响。本研究成果可以为复合材料实际工程应用提供参考。
中图分类号:
- U414
| 1 | 苗广营,沈建青,仲玮年. 沥青路面除冰雪技术研究进展[J].筑路机械与施工机械化,2019,36(9): 18-22. |
| Miao Guang-ying, Shen Jian-qing, Zhong Wei-nian. Progress of research on deicing and snow removal technology for asphalt pavement[J]. Road Machinery & Construction Mechanization, 2019, 36(9): 18-22. | |
| 2 | 谭忆秋,张驰,徐慧宁,等. 主动除冰雪路面融雪化冰特性及路用性能研究综述[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(4): 1-17. |
| Tan Yi-qiu, Zhang Chi, Xu Hui-ning, et al. Snow melting and deicing characteristics and pavement performance of active deicing and snow melting pavement[J]. Chinese Journal of Highways, 2019, 32(4): 1-17. | |
| 3 | 程刚,韩萍,杜素军. 融雪剂概况及存在的问题[J]. 山西交通科技, 2004(5): 45-46. |
| Cheng Gang, Han Ping, Du Su-jun. The discussion on the conditions and main problem of the deicer[J]. Shanxi science & Technology of communications, 2004(5): 45-46. | |
| 4 | 肖劲松,邹孟秋. 物理-化学综合融雪除冰沥青混合料研究[J]. 公路, 2017, 62(8): 248-252. |
| Xiao Jin-song, Zou Meng-qiu. Study of asphalt mixture for melting snow and ice by physical-chemical[J]. Highway, 2017, 62(8): 248-252. | |
| 5 | 冯新军,查旭东,程景. PAN基碳纤维导电沥青混凝土的制备及性能[J]. 中国公路学报, 2012, 25(2): 27-32. |
| Feng Xin-jun, Zha Xu-dong, Cheng Jing.Preparation and performance of PAN-based carbon fiber conductive asphalt concrete[J]. Chinese Journal of Highways, 2012, 25(2):27-32. | |
| 6 | Ullah S, Yang C, Cao L P, et al. Material design and performance improvement of conductive asphalt concrete incorporating carbon fiber and iron tailings[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 303: 124446. |
| 7 | Mohammad A N, Arabzadeh A, Ceylan H, et al. Effect of carbon-fiber properties on volumetrics and ohmic heating of electrically conductive asphalt concrete[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2019, 31(9): 04019200. |
| 8 | 武海琴. 发热电缆用于路面融雪化冰的技术研究[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学建筑工程学院, 2005. |
| Wu Hai-qin.A study of applied technology in deicing and melting snow on road surface by electric heating cable[D].Beijing:College of Architecture and Civil Engineering,Beijing University of Technology, 2005. | |
| 9 | 李荣清,王超,朱耀庭,等. 碳纤维发热线桥面铺装融雪化冰试验研究[J]. 中外公路, 2019, 39(6): 241-244. |
| Li Rong-qing, Wang Chao, Zhu Yao-ting, et al. Experimental study on snow melting and ice melting in carbon fiber hair hotline bridge deck paving[J]. Zhongwai Highway, 2019, 39(6): 241-244. | |
| 10 | Xin S, Yong L, Yan L, et al. Research of deicing and melting snow on airport asphalt pavement by carbon fiber heating wire[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2020: 5209350. |
| 11 | 袁玉卿,许海铭,张永健. 导电沥青混凝土发热性能实验研究[J]. 华中科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 42(10): 128-132. |
| Yuan Yu-qing, Xu Hai-ming, Zhang Yong-jian. Experimental study on warming performance of conductive asphalt concrete[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(10): 128-132. | |
| 12 | Zhao H M, Wu Z M, Wang S G, et al. Concrete pavement deicing with carbon fiber heating wires[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2010, 65(3): 413-420. |
| 13 | Wei H B, Ma Z P, He X,et al. Structural response analysis of conductive ethylene-propylene-diene monomer rubber composite pavement under validated temperature field[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 328: 127094. |
| 14 | Wei H B, Ma Z P, Han L L, et al. Durability of conductive ethylene-propylene-diene monomer rubber composite with active deicing and snow melting under vehicle load[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2022, 34(5): 04022055. |
| 15 | . 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶压缩应力应变性能的测定 [S]. |
| 16 | 姬豪杰,谢海巍,刘尊青. 基于有限元ANSYS的半刚性基层沥青路面力学响应分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(12): 5092-5097. |
| Ji Hao-jie, Xie Hai-wei, Liu Zun-qing. Mechanical response analysis of semi-rigid asphalt pavement based on finite element ANSYS[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021, 21(12): 5092-5097. | |
| 17 | . 公路沥青路面设计规范 [S]. |
| 18 | 吴玉,蒋鑫,梁雪娇,等. 轮载作用下典型沥青路面结构力学行为分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2017, 52(3): 563-570. |
| Wu Yu, Jiang Xin, Liang Xue-jiao, et al. Mechanical behaviours of typical asphalt pavement structures under wheel loads[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017, 52(3): 563-570. |
| [1] | 刘状壮,张有为,季鹏宇,Abshir Ismail Yusuf,李林,郝亚真. 电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 523-530. |
| [2] | 肖阳,王洁,刘孟军,杨发庆,张天瑶,兰巍. 质子交换膜燃料电池气体扩散层的力学改进模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2147-2155. |
| [3] | 陈昭明,邹劲松,王伟,石明全. 改进粒子群神经网络融合有限元分析的铸锻双控动态成型多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1524-1533. |
| [4] | 杨国俊,田骐玮,吕明航,杜永峰,唐光武,韩宗健,伏一多. 大跨度悬索桥隧道式锚碇力学特性研究综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1245-1263. |
| [5] | 郭庆林,刘强,吴春利,李黎丽,李懿明,刘富春. 导电沥青及混合料裂缝局部温度场及愈合效果[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1386-1393. |
| [6] | 时成林,王勇,吴春利,宋文祝. 路堤挡土墙主动土压力计算方法修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1394-1403. |
| [7] | 郑植,耿波,王福敏,董俊宏,魏思斯. 既有低等级混凝土护栏防护能力提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1362-1374. |
| [8] | 庄蔚敏,陈沈,吴迪. 碳纤维增强复合材料包裹强化形式对钢管横向冲击性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 819-828. |
| [9] | 李伟,宋海生,陆浩宇,史文库,王强,王晓俊. 复合材料板簧迟滞特性线性辨识方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 829-836. |
| [10] | 姚玉权,仰建岗,高杰,宋亮. 基于性能-费用模型的厂拌再生沥青混合料优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 585-595. |
| [11] | 夏全平,高江平,罗浩原,张其功,李志杰,杨飞. 用于高模量沥青砼的复合改性硬质沥青低温性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 541-549. |
| [12] | 叶奋,胡诗园. 考虑旧水泥路面接缝传荷能力的超薄罩面力学特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2636-2643. |
| [13] | 于开锋,何小玲,李俊涛,梁策. 玄武岩纤维对不饱和聚酯树脂复合材料的增韧[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2300-2306. |
| [14] | 杨彦海,崔宏,杨野,张怀志,刘赫. 冻融循环作用对非饱和乳化沥青冷再生混合料性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2352-2359. |
| [15] | 于晓贺,罗蓉,柳子尧,黄婷婷,束裕. 沥青路面典型裂缝湿度场数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2343-2351. |
|