吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 722-730.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230508
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于先验知识优化的医学图像候选区域生成方法
- 吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
A method for generating proposals of medical image based on prior knowledge optimization
Meng-xue ZHAO( ),Xiang-jiu CHE(
),Xiang-jiu CHE( ),Huan XU,Quan-le LIU
),Huan XU,Quan-le LIU
- College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
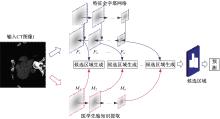
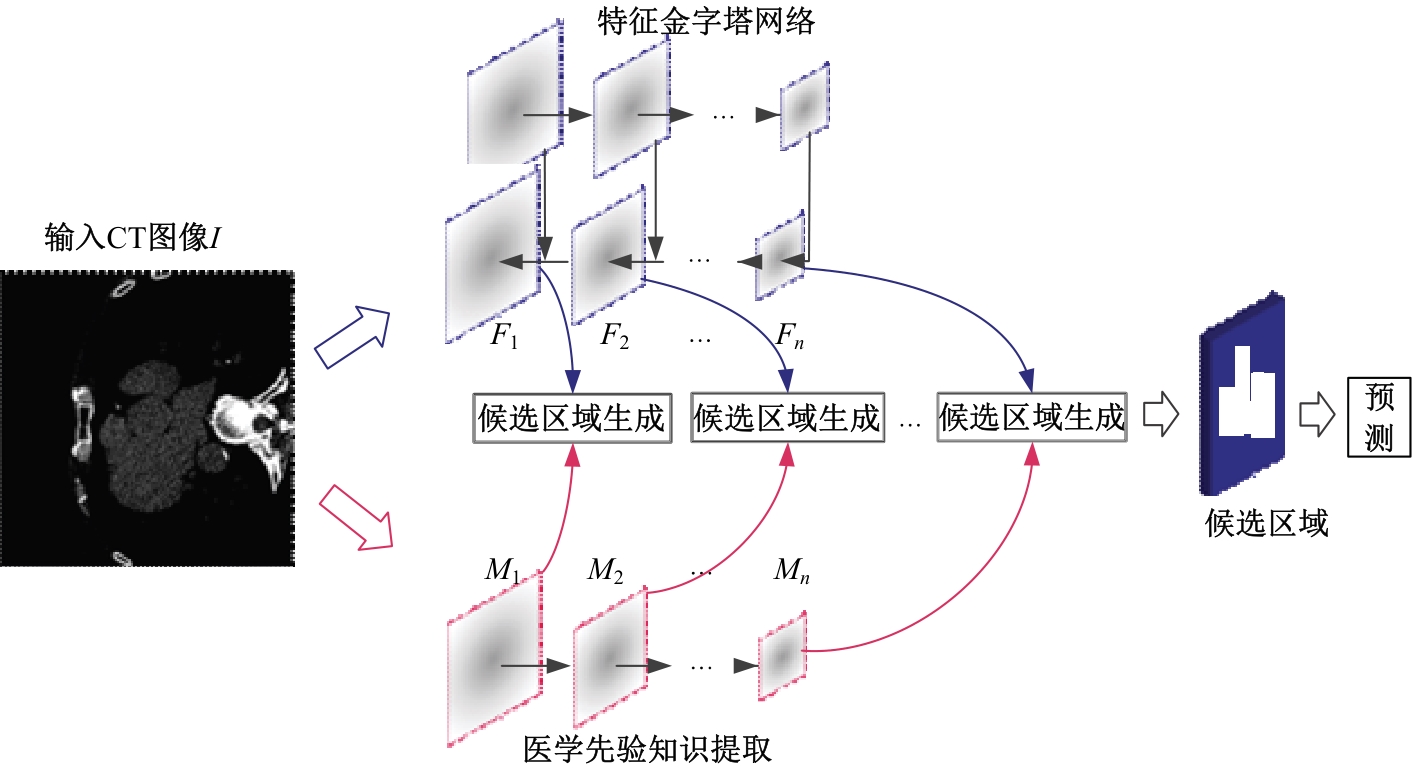
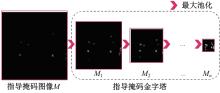
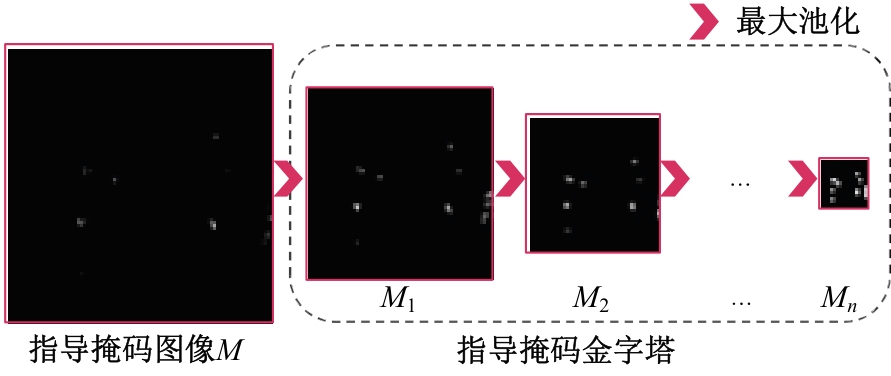
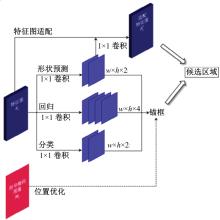
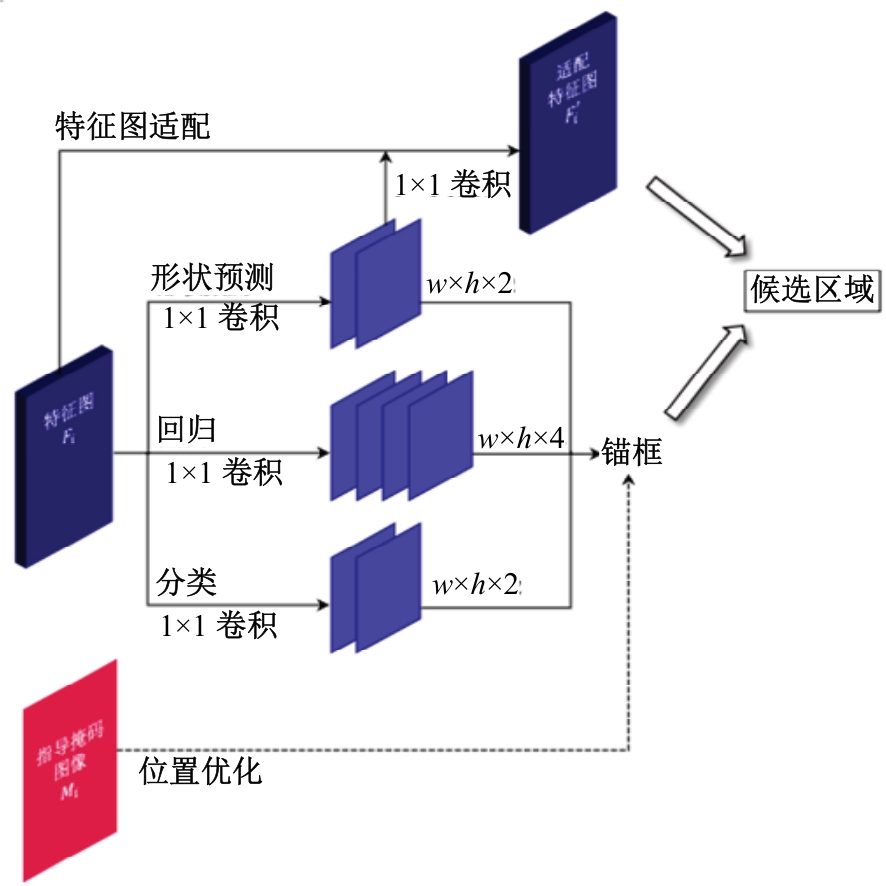
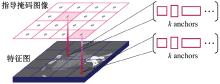
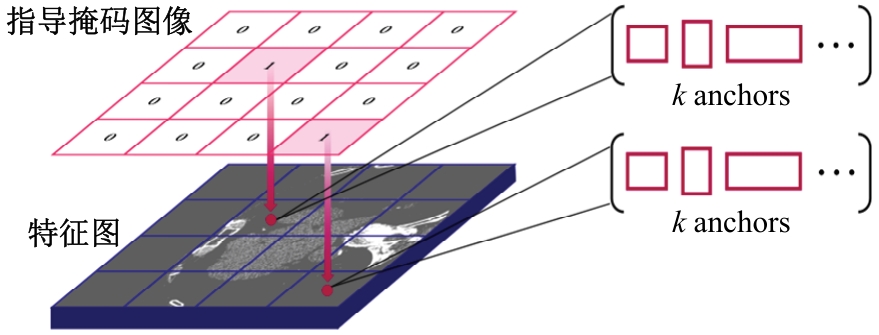
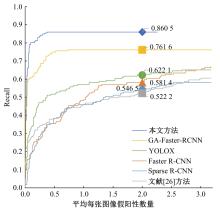
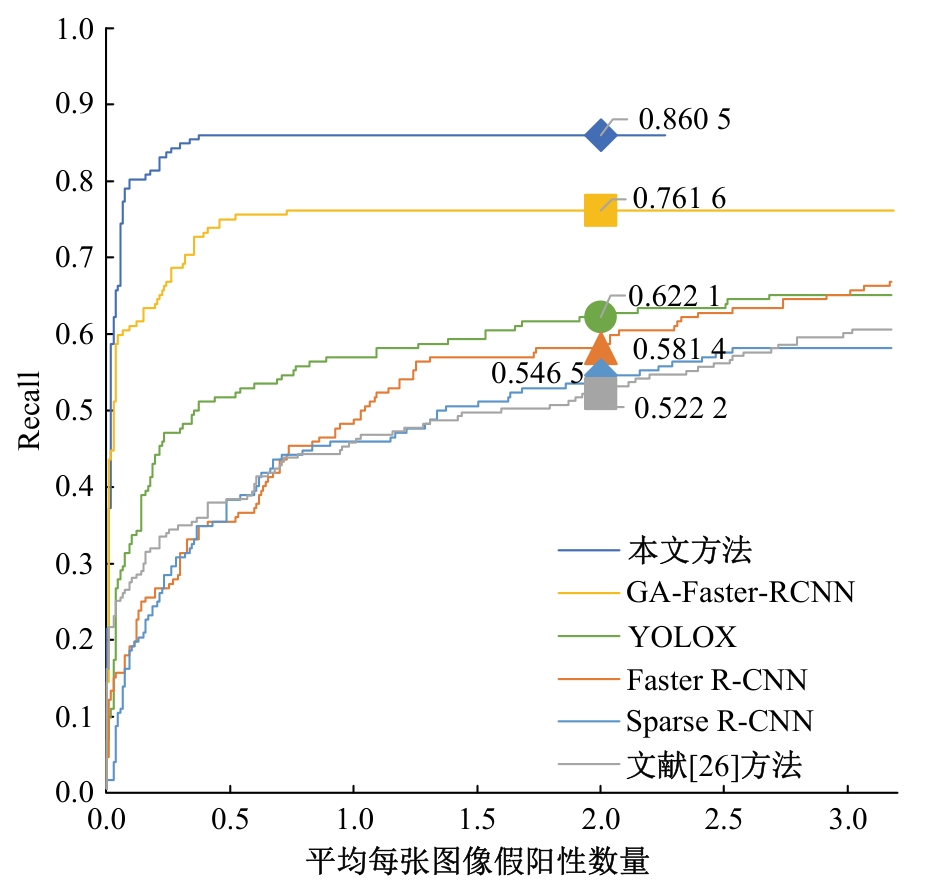
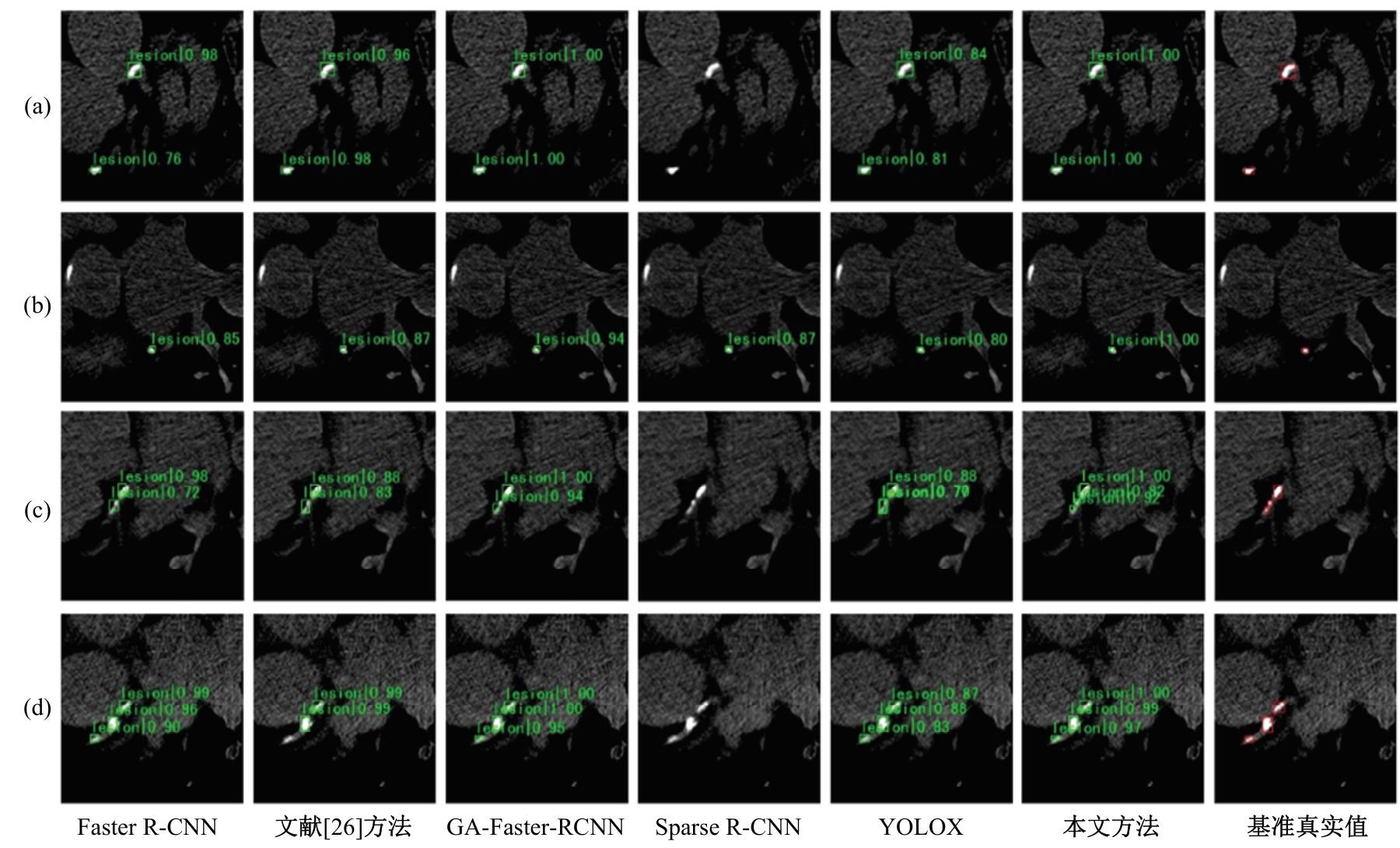
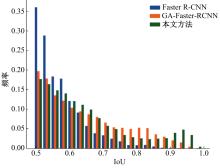
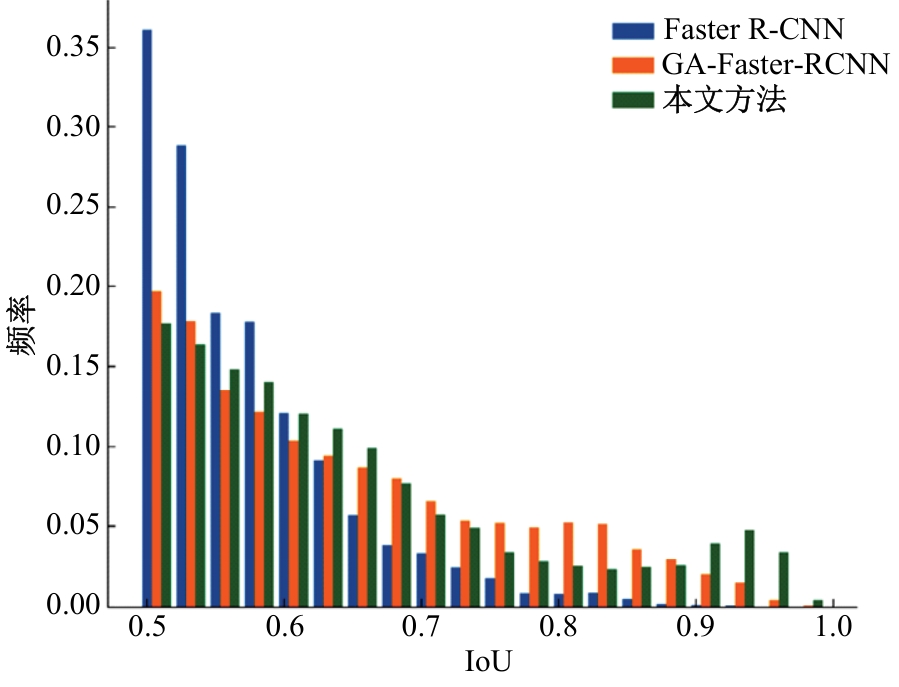
针对钙化斑块区域小、与非斑块区域易混淆的特点,本文提出一种医学先验知识引导的候选区域生成优化方法。该方法基于目标检测网络Faster R-CNN,通过锚框的位置与形状两方面优化候选区域生成。利用钙化斑块定义生成指导掩码图像,筛选候选区域生成位置。采用锚框形状预测分支生成候选区域形状。针对特征金字塔网络中不同尺度的特征图,提出多尺度的指导掩码金字塔。在CCTA图像中检测钙化斑块的实验结果表明:与集成标准RPN的Faster R-CNN模型相比,本文方法的AP与Recall分别提高12.8%与25.7%;在平均每张图像假阳性数量为2的情况下,本文方法Recall值达到86.05%。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Naghavi M, Wang H, Lozano R, et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013[J]. The Lancet, 2015, 385(9963): 117-171. |
| 2 | Hutcheson J D, Goettsch C, Bertazzo S, et al. Genesis and growth of extracellular-vesicle-derived microcalcification in atherosclerotic plaques[J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(3): 335-343. |
| 3 | Išgum I, Van G B, Viergever M A. Automatic detection of calcifications in the aorta from abdominal CT scans[J]. International Congress Series, 2003, 1256(C): 1037-1042. |
| 4 | Isgum I, Prokop M, Niemeijer M, et al. Automatic coronary calcium scoring in low-dose chest computed tomography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2012, 31(12): 2322-2334. |
| 5 | Wolterink J M, Leiner T, Takx R A P, et al. Automatic coronary calcium scoring in non-contrast-enhanced ECG-triggered cardiac CT with ambiguity detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2015, 34(9): 1867-1878. |
| 6 | Wolterink J M, Leiner T, Devos B D, et al. Automatic coronary artery calcium scoring in cardiac CT angiography using paired convolutional neural networks[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2016, 34: 123-136. |
| 7 | Tourassi G D, Armato S G, Lessmann N, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for automatic coronary calcium scoring in a screening study with low-dose chest CT[J].Medical Imaging 2016:Computer-Aided Diagnosis,2016, 9785: 255-260. |
| 8 | Liu J, Lu L, Yao J, et al. Pelvic artery calcification detection on CT scans using convolutional neural networks[J]. Conference on Computer-Aided Diagnosis,2017, 10134: 319-325. |
| 9 | Mohri M, Rostamizadeh A, Talwalkar A. Foundations of Machine Learning[M]. London: MIT Press, 2018. |
| 10 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012, 25: 1097-1105. |
| 11 | Lin T Y, Maire M, Belongie S, et al. Microsoft coco: common objects in context[J]. Computer Vision, 2014, 8693: 740-755. |
| 12 | Acharya U R, Meiburger K M, Koh J E W, et al. Automated detection of calcified plaque using higher-order spectra cumulant technique in computer tomography angiography images[J]. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 2020, 30: 285-297. |
| 13 | Li Y C, Shen T Y, Chen C C, et al. Automatic detection of atherosclerotic plaque and calcification from intravascular ultrasound images by using deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2021, 68(5): 1762-1772. |
| 14 | Chen C, Biffi C, Tarroni G, et al. Learning shape priors for robust cardiac mr segmentation from multi-view images[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2019, 11765: 523-531. |
| 15 | Yue Q, Luo X, Ye Q, et al. Cardiac segmentation from LGE MRI using deep neural network incorporating shape and spatial priors[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2019, 11765: 559-567. |
| 16 | Mirikharaji Z, Hamarneh G. Star shape prior in fully convolutional networks for skin lesion segmentation[C]∥Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, Granada, Spain, 201: 737-745. |
| 17 | Liao W, Rosenhahn B, Shuai L, et al. Natural language guided visual relationship detection[J]. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2019, 6: 444-453. |
| 18 | Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580-587. |
| 19 | Yang G, Chen Y, Ning X, et al. Automatic coronary calcium scoring using noncontrast and contrast CT images[J]. Medical Physics, 2016, 43(5): 2174-2186. |
| 20 | Durlak F, Wels M, Schwemmer C, et al. Growing a random forest with fuzzy spatial features for fully automatic artery-specific coronary calcium scoring[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2017, 10541: 27-35. |
| 21 | Zhang Y, Wang S, Zhao H, et al. CT image classification based on convolutional neural network[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 33(14): 8191-8200. |
| 22 | Gao K, Su J, Jiang Z, et al. Dual-branch combination network (DCN): towards accurate diagnosis and lesion segmentation of COVID-19 using CT images[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2021, 67: 101836. |
| 23 | Liang X, Li N, Zhang Z, et al. Incorporating the hybrid deformable model for improving the performance of abdominal CT segmentation via multi-scale feature fusion network[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2021, 73: 102156. |
| 24 | Fan J, Cao X, Yap P T, et al. BIRNet: brain image registration using dual-supervised fully convolutional networks[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2019, 54: 193-206. |
| 25 | Prasoon A, Petersen K, Igel C, et al. Deep feature learning for knee cartilage segmentation using a triplanar convolutional neural network[J]. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2013, 8150: 246-253. |
| 26 | Chellamuthu K, Liu J, Yao J, et al. Atherosclerotic vascular calcification detection and segmentation on low dose computed tomography scans using convolutional neural networks[C]∥IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, Melbourne, Australia, 2017: 388-391. |
| 27 | Gernaat S A M, Van S G M, Koh V, et al. Automatic quantification of calcifications in the coronary arteries and thoracic aorta on radiotherapy planning CT scans of Western and Asian breast cancer patients[J]. Radiotherapy and Oncology, 2018, 127(3): 487-492. |
| 28 | Lessmann N, Van Ginneken B, Zreik M, et al. Automatic calcium scoring in low-dose chest CT using deep neural networks with dilated convolutions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(2): 615-625. |
| 29 | Zreik M, Van H R W, Wolterink J M, et al. A recurrent CNN for automatic detection and classification of coronary artery plaque and stenosis in coronary CT angiography[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(7): 1588-1598. |
| 30 | Fischer A M, Eid M, Dececco C N, et al. Accuracy of an artificial intelligence deep learning algorithm implementing a recurrent neural network with long short-term memory for the automated detection of calcified plaques from coronary computed tomography angiography[J]. Journal of Thoracic Imaging, 2020, 35: 49-57. |
| 31 | Ren S, He K, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015, 28: 91-99. |
| 32 | Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936-944. |
| 33 | Agatston A S, Janowitz W R, Hildner F J, et al. Quantification of coronary artery calcium using ultrafast computed tomography[J]. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 1990, 15(4): 827-832. |
| 34 | Wang J, Chen K, Yang S, et al. Region proposal by guided anchoring[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 2960-2969. |
| 35 | Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2999-3007. |
| 36 | Wolterink J M, Leiner T, Devos B D, et al. An evaluation of automatic coronary artery calcium scoring methods with cardiac CT using the orCaScore framework[J]. Medical Physics, 2016, 43(5): 2361-2373. |
| 37 | Zhao M, Che X, Liu H, et al. Medical prior knowledge guided automatic detection of coronary arteries calcified plaque with cardiac CT[J]. Electronics (Switzerland), 2020, 9(12): 1-14. |
| 38 | Chen K, Wang J, Pang J, et al. MMdetection: open mmlab detection toolbox and benchmark[J]. Arxiv Preprint, 2019, 6: 190607155. |
| 39 | Sun P, Zhang R, Jiang Y, et al. Sparse R-CNN: end-to-end object detection with learnable proposals[C]// 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 14454-14463. |
| 40 | Ge Z, Liu S, Wang F, et al. Yolox: exceeding yolo series in 2021[J]. Arxiv Preprint, 2017, 7: 210708430. |
| [1] | 车翔玖,武宇宁,刘全乐. 基于因果特征学习的有权同构图分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 681-686. |
| [2] | 蔡晓东,周青松,张言言,雪韵. 基于动静态和关系特征全局捕获的社交推荐模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 700-708. |
| [3] | 徐慧智,蒋时森,王秀青,陈爽. 基于深度学习的车载图像车辆目标检测和测距[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 185-197. |
| [4] | 郭晓然,王铁君,闫悦. 基于局部注意力和本地远程监督的实体关系抽取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 307-315. |
| [5] | 汪豪,赵彬,刘国华. 基于时间和运动增强的视频动作识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 339-346. |
| [6] | 刘元宁,臧子楠,张浩,刘震. 基于深度学习的核糖核酸二级结构预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 297-306. |
| [7] | 张磊,焦晶,李勃昕,周延杰. 融合机器学习和深度学习的大容量半结构化数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2631-2637. |
| [8] | 李路,宋均琦,朱明,谭鹤群,周玉凡,孙超奇,周铖钰. 基于RGHS图像增强和改进YOLOv5网络的黄颡鱼目标提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2638-2645. |
| [9] | 赵宏伟,武鸿,马克,李海. 基于知识蒸馏的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2307-2312. |
| [10] | 张云佐,郑宇鑫,武存宇,张天. 基于双特征提取网络的复杂环境车道线精准检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1894-1902. |
| [11] | 乔百友,武彤,杨璐,蒋有文. 一种基于BiGRU和胶囊网络的文本情感分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 2026-2037. |
| [12] | 郭昕刚,何颖晨,程超. 抗噪声的分步式图像超分辨率重构算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 2063-2071. |
| [13] | 张丽平,刘斌毓,李松,郝忠孝. 基于稀疏多头自注意力的轨迹kNN查询方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1756-1766. |
| [14] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [15] | 李延风,刘名扬,胡嘉明,孙华栋,孟婕妤,王奥颖,张涵玥,杨华民,韩开旭. 基于梯度转移和自编码器的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1777-1787. |
|
||