吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 1842-1849.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210170
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于亲缘关系选择的粒子群优化算法
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学珠海学院 计算机科学与技术系,广东 珠海 519041
Particle swarm optimization algorithm based on kinship selection
Ren-chu GUAN1( ),Bao-run HE1,Yan-chun LIANG1,2,Xiao-hu SHI1(
),Bao-run HE1,Yan-chun LIANG1,2,Xiao-hu SHI1( )
)
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Computer Science and Technology Department,Zhuhai College of Jilin University,Zhuhai 519041,China
摘要:
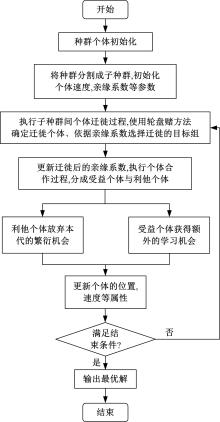
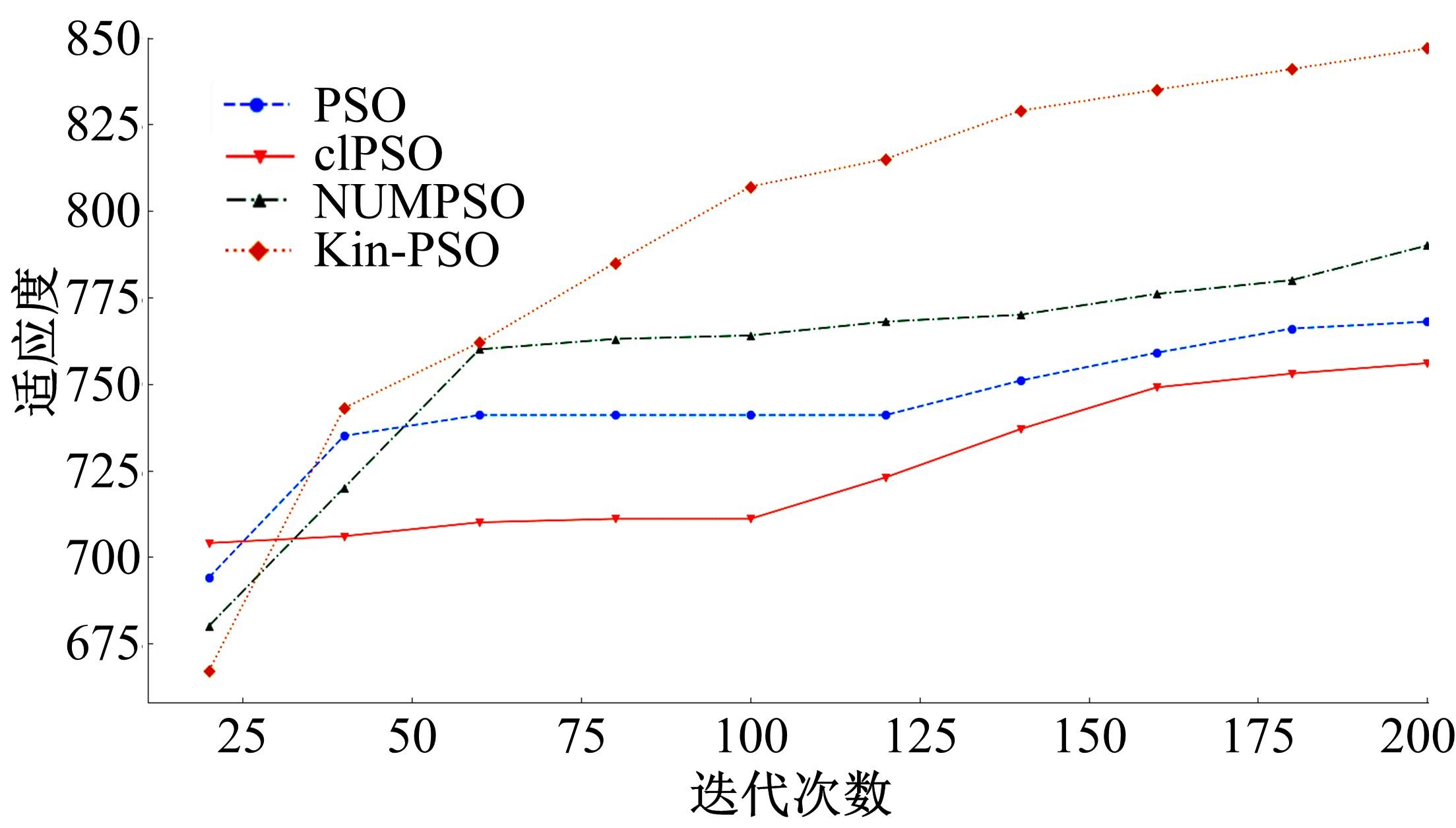
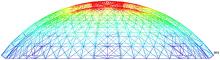
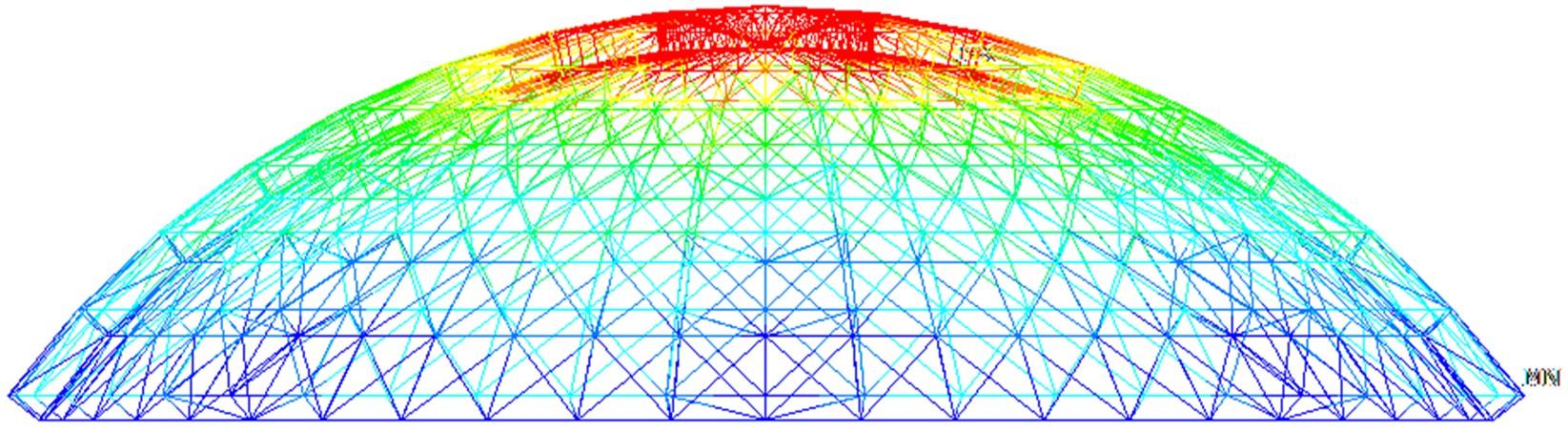
针对传统粒子群优化算法在解决最优化问题中存在早熟收敛和无法寻找到全局最优解问题,本文提出了一种基于亲缘关系选择的粒子群优化算法,提高了算法的全局搜索能力。此外,引入了多个种群的交流机制与各子种群之间的淘汰机制,有效避免了个体在寻优过程中陷入局部最优点。实验部分首先在单目标优化函数集上与传统的粒子群优化算法以及一些有竞争力的算法结果进行对比分析,发现算法在相同种群规模与评价次数的条件下,在准确性与搜索能力上有着明显的优势;然后,将新算法应用到桁架穹顶优化问题上,并与传统的粒子群优化算法进行了比较,求得了这一实际问题的一个可行解。
中图分类号:
- TP39
| 1 | 陈宝林. 最优化理论与算法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2005. |
| Chen Bao-lin. Theory and Algorithms of Optimization[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2005. | |
| 2 | Sun S, Cao Z, Zhu H, et al. A survey of optimization methods from a machine learning perspective[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(8): 3668-3681. |
| 3 | Ismail M A, Mezhuyev V, Moorthy K, et al. Optimisation of biochemical systems production using hybrid of newton method, differential evolution algorithm and cooperative coevolution algorithm[J]. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 2017, 8: 27-35. |
| 4 | Dennis J J E, Moré J J. Quasi-newton methods, motivation and theory[J]. Siam Review, 1977, 19(1): 46-89. |
| 5 | 梁艳春. 群智能优化算法理论与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009. |
| 6 | Holland J H. Genetic algorithms[J]. Scholarpedia, 2012, 7(12): 1482. |
| 7 | Kennedy J, Eberhart R. Particle swarm optimization[C]∥Proceedings of ICNN'95 International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 1995: 1942-1948. |
| 8 | Shi Y, Eberhart R. A modified particle swarm optimizer[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Proceedings, IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence, Indianaqolis,USA, 1998: 69-73. |
| 9 | Engelbrecht A P. Particle swarm optimization: global best or local best?[C]∥BRICS Congress on Computational Intelligence and 11th Brazilian Congress On Computational Intelligence, Pretoria, South Africa, 2013: 124-135. |
| 10 | Sengupta S, Basak S, Peters R A. Particle swarm optimization: a survey of historical and recent developments with hybridization perspectives:1[J]. Machine Learning and Knowledge Extraction, 2019, 1(1): 157-191. |
| 11 | Lynn N, Ali M Z, Suganthan P N. Population topologies for particle swarm optimization and differential evolution[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2018, 39: 24-35. |
| 12 | Liu L, Wu J, Meng S. Analysis and improvement of neighborhood topology of particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Computational Methods in Sciences and Engineering, 2019, 19(4): 955-968. |
| 13 | Li X. Niching without niching parameters: particle swarm optimization using a ring topology[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 14(1): 150-169. |
| 14 | Miranda V, Keko H, Junior A J. Stochastic star communication topology in evolutionary particle swarms (EPSO)[J]. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Research, 2008, 4(2): 105-116. |
| 15 | West S A, Pen I, Griffin A S. Cooperation and competition between relatives[J]. Science, 2002, 296(5565): 72-75. |
| 16 | Nowak M A. Five rules for the evolution of cooperation[J]. Science, 2006, 314(5805): 1560-1563. |
| 17 | Wong K C. Evolutionary multimodal optimization: a short survey[J/OL]. [2020-08-04]. |
| 18 | Liang J J, Qin A K, Suganthan P N, et al. Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimizer for global optimization of multimodal functions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2006, 10(3): 281-295. |
| 19 | Zhao X, Gao X S, Hu Z C. Evolutionary programming based on non-uniform mutation[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2007, 192(1): 1-11. |
| 20 | Lu J, Zhou X, Ma Y, et al. A novel artificial bee colony algorithm with division of labor for solving CEC 2019 100-Digit challenge benchmark problems[C]∥IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Nanchang, China, 2019: 387-394. |
| 21 | Brest J, MaučEc M S, BošKović B. iL-SHADE: improved L-SHADE algorithm for single objective real-parameter optimization[C]∥IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Maribor, Slovenia, 2016:1188-1195. |
| 22 | Xu P, Luo W, Lin X, et al. Hybrid of PSO and CMA-ES for global optimization[C]∥IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Hunan, China, 2019: 27-33. |
| 23 | Zhang G, Li Y, Ding B, et al. Univariate Gaussian model for multimodal inseparable problems[C]∥International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Liverpool, England, 2017: 612-623. |
| 24 | Thompson M K, Thompson J M. Ansys Mechanical Apdl for Finite Element Analysis[M]. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2017. |
| 25 | 张雄, 王天舒. 计算动力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2015. |
| [1] | 陈昭明,邹劲松,王伟,石明全. 改进粒子群神经网络融合有限元分析的铸锻双控动态成型多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1524-1533. |
| [2] | 邢海燕,刘超,徐成,陈玉环,王松弘泽. 基于粒子群优化模糊C焊缝等级磁记忆定量识别模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 525-532. |
| [3] | 罗巍,卢博,陈菲,马腾. 基于PSO-SVM及时序环节的数控刀架故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 392-399. |
| [4] | 杜常清,曹锡良,何彪,任卫群. 基于混合粒子群算法的双离合变速器参数优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1556-1564. |
| [5] | 马芳武,韩丽,吴量,李金杭,杨龙帆. 基于遗传与粒子群算法的隔振平台减振性能优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1608-1616. |
| [6] | 臧国帅, 孙立军. 基于惰性弯沉点的刚性下卧层深度设置方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1037-1044. |
| [7] | 于繁华, 刘仁云, 张义民, 张晓丽, 孙秋成. 机械零部件动态可靠性稳健优化设计的群智能算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1903-1908. |
| [8] | 孙亮, 徐海浪, 葛宏伟. 保证全局收敛的随机粒子群新算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 615-623. |
| [9] | 于繁华, 刘仁云, 张义民, 孙秋成, 张晓丽. 机械结构动态可靠性设计的智能计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1269-1275. |
| [10] | 张静, 刘向东. 混沌粒子群算法优化最小二乘支持向量机的混凝土强度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1097-1102. |
| [11] | 季彦婕, 陈晓实, 王炜, 胡波. 基于小波变换和粒子群小波神经网络组合模型的有效停车泊位短时预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 399-405. |
| [12] | 高明亮, 于生宝, 郑建波, 徐畅, 张堃, 栾卉. PSBP在高密度电阻率法二维反演中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 2026-2033. |
| [13] | 刘红,孙爽滋,王庆元,李延忠. 基于PSO的模拟电路故障信息特征提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 675-680. |
| [14] | 温涛, 李迎秋, 盛国军, 迟玉红. 不确定信息下基于改进粒子群算法的Web服务选择[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(01): 129-136. |
| [15] | 刘仁云, 于繁华. 基于层次分析粒子群算法的可靠性稳健优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 139-142. |
|
||