吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 2192-2202.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220419
• • 上一篇
基于PSO-LSTM的质子交换膜燃料电池退化趋势预测
- 1.吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
2.吉林大学 通信工程学院,长春 130022
3.杭州电子大学 自动化学院,杭州 310018
4.大连理工大学 工业装备智能控制与优化教育部重点实验室,大连 116024
Degradation trend prediction of proton exchange membrane fuel cell based on PSO⁃LSTM
Jin-wu GAO1,2( ),Zhi-huan JIA1,2,Xiang-yang WANG1,2,Hao XING3,4
),Zhi-huan JIA1,2,Xiang-yang WANG1,2,Hao XING3,4
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Communication Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
3.School of Automation,Hangzhou Dianzi University,Hangzhou 310018,China
4.Key Laboratory of Intelligent Control and Optimization for Industrial Equipment of Ministry of Education,Dalian University of Technology,Dalian 116024,China
摘要:
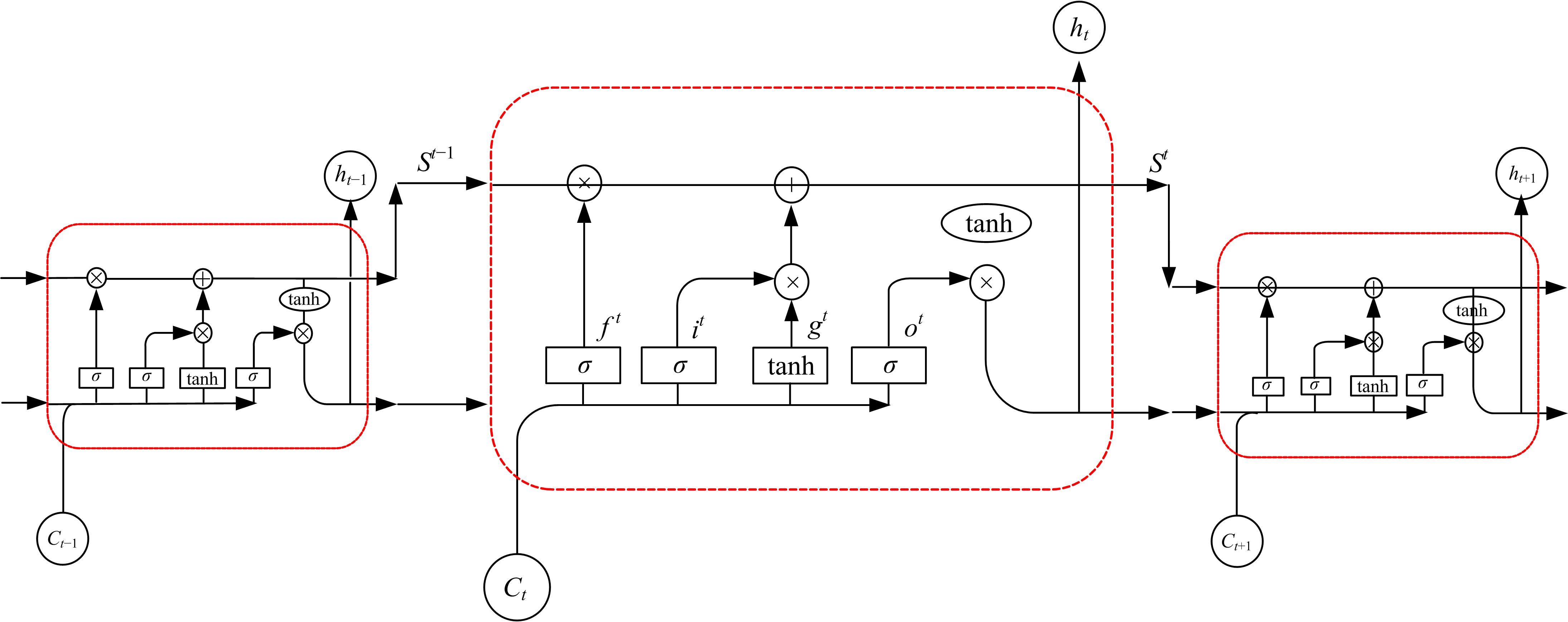
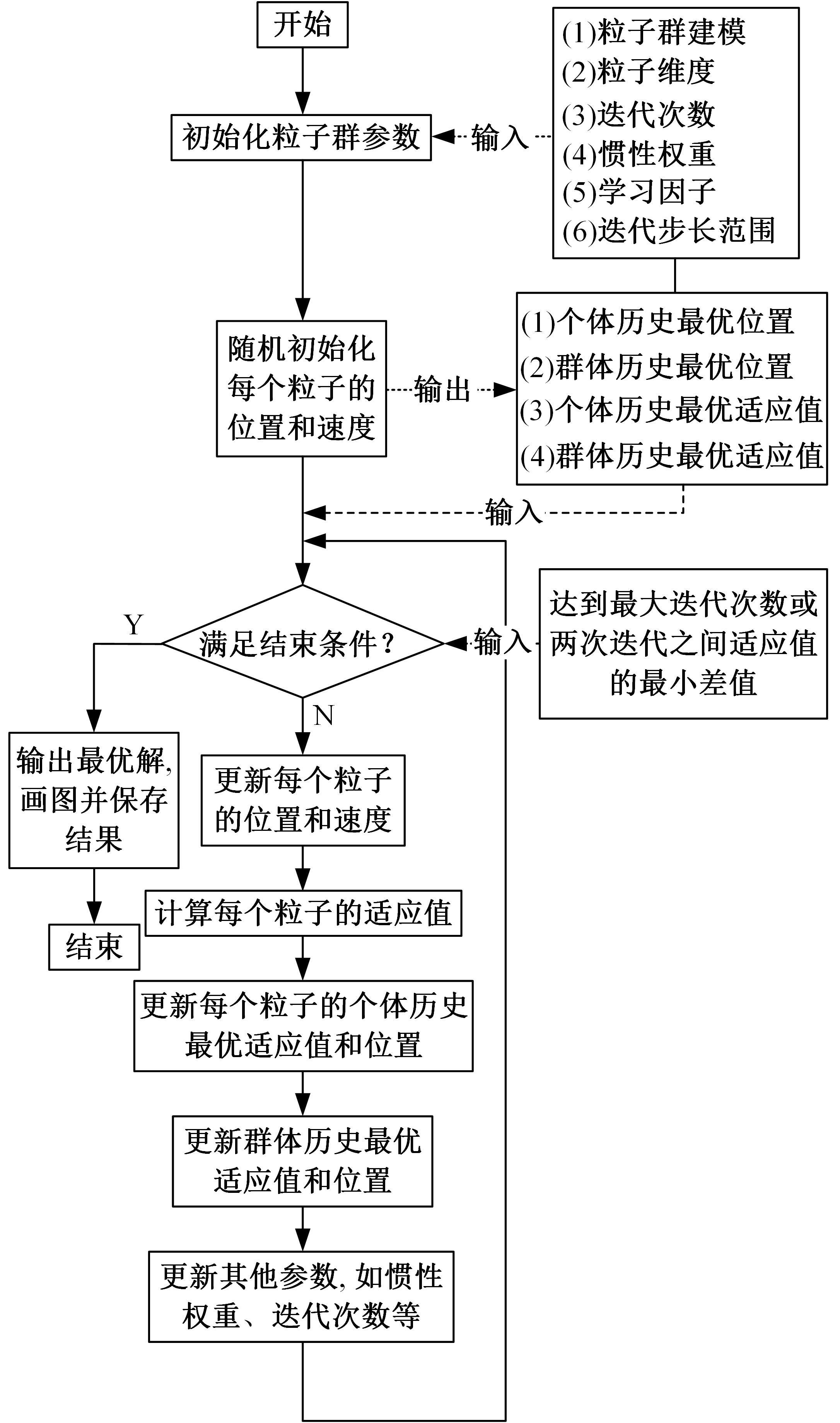
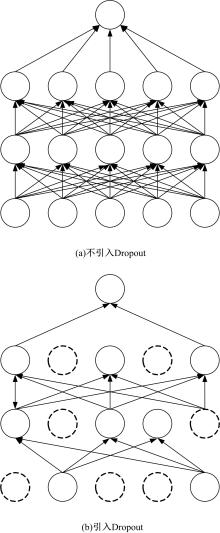
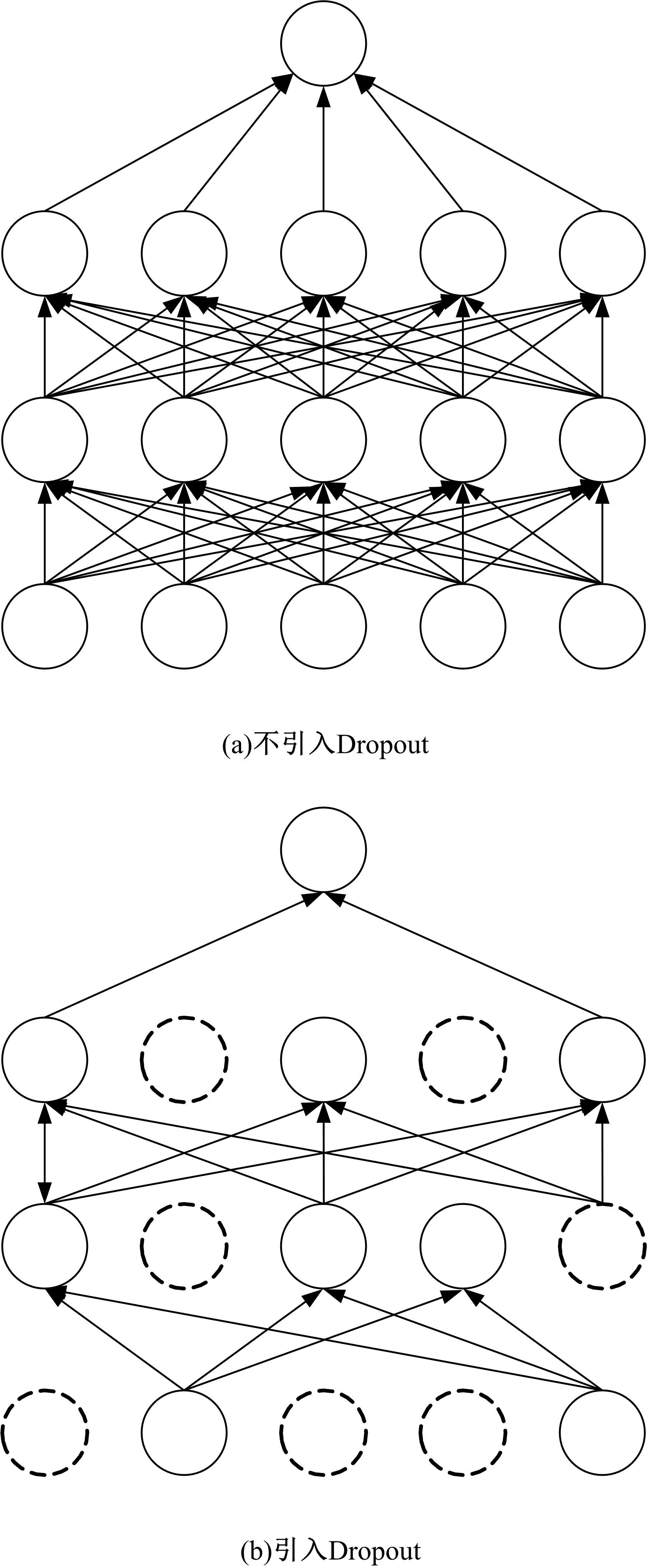
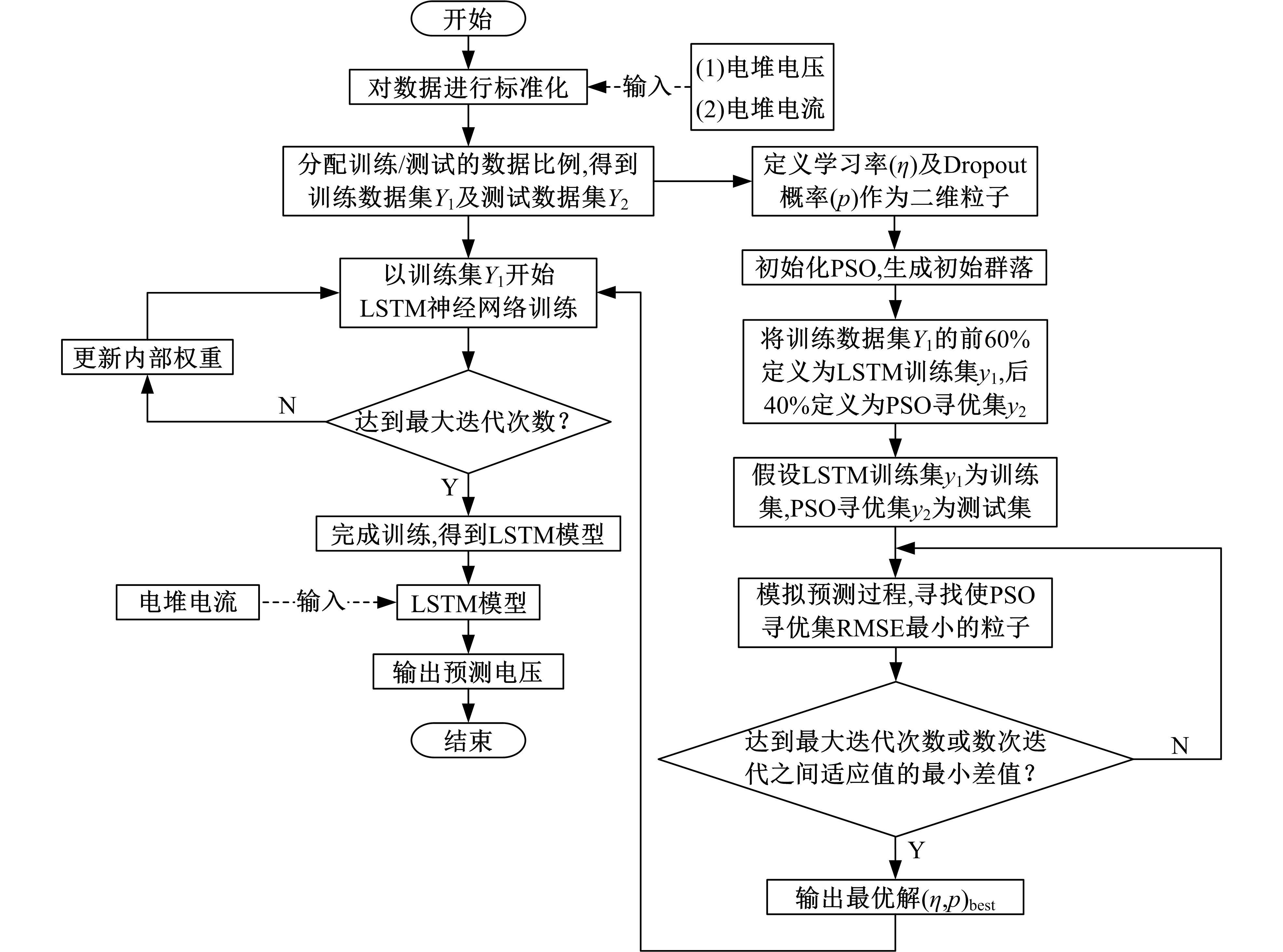
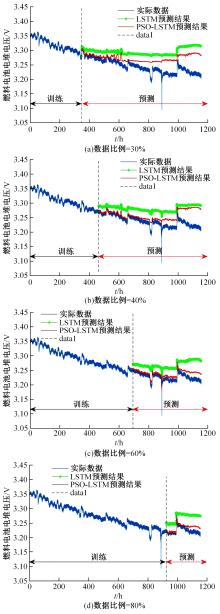
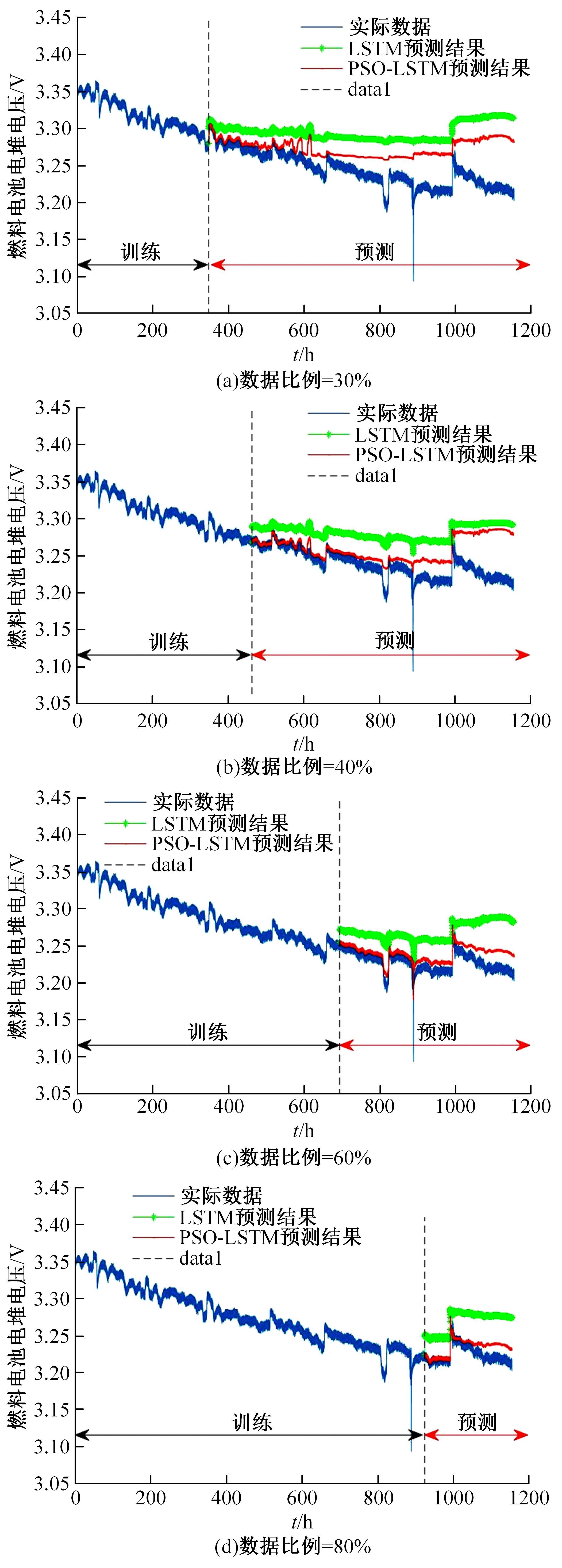
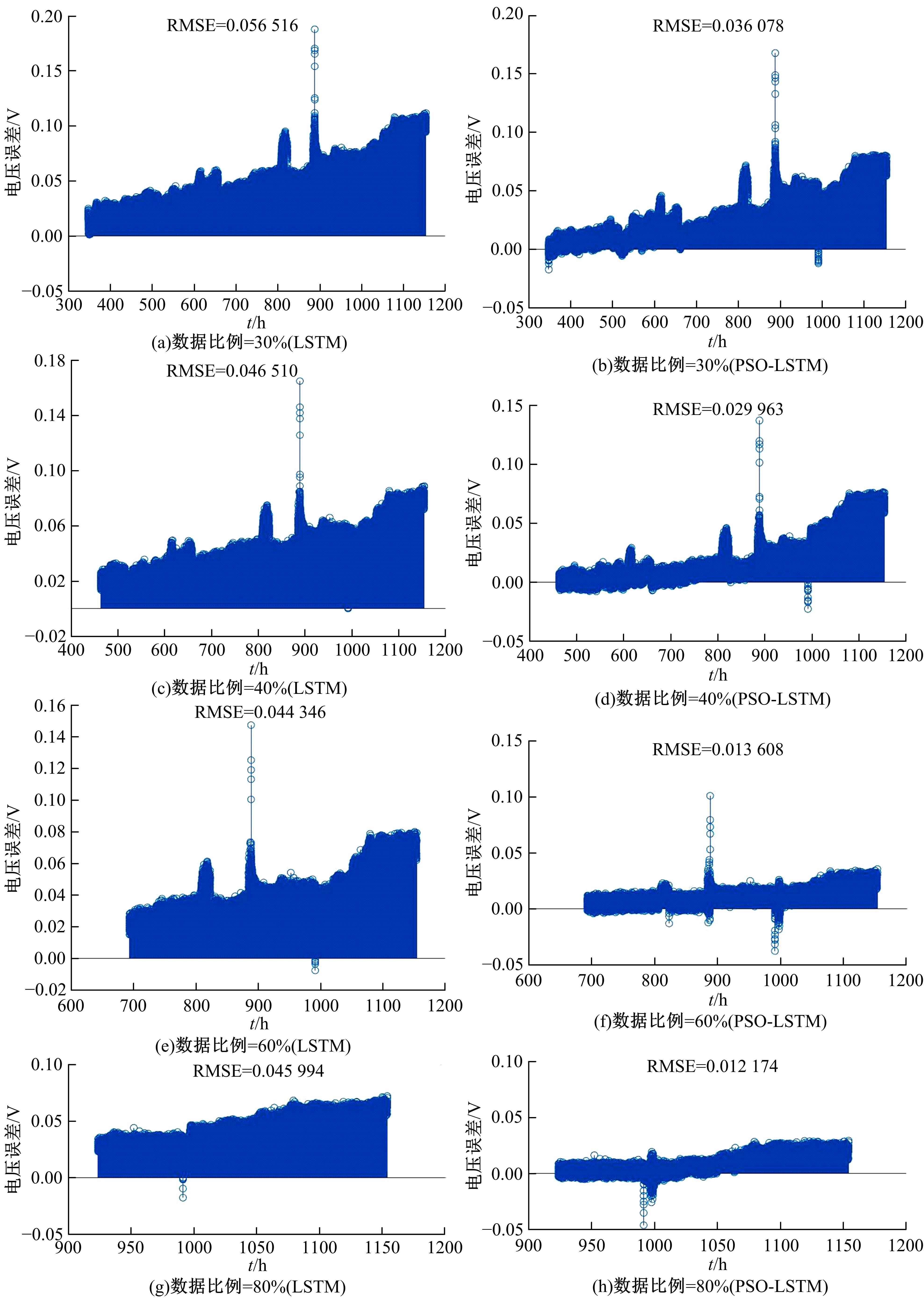
提出了一种基于粒子群优化(PSO)算法的长短期记忆网络(LSTM)方法,对质子交换膜燃料电池(PEMFC)的电堆电压进行了退化预测。首先,分析了PEMFC的退化机理。然后,应用LSTM建立了电压退化预测模型,并采用Dropout层来防止过拟合以提高模型的泛化能力。此外,使用PSO算法优化LSTM方法中的初始学习率和Dropout概率以提升预测效果。最后,使用IEEE 2014 Data Challenge Data的燃料电池实际老化数据进行验证。结果表明,本文方法可以精确地预测燃料电池的退化,相比于传统的LSTM方法,预测精度提升了50%。
中图分类号:
- TK91
| 1 | Liu D C, Lin R, Feng B, et al. Investigation of the effect of cathode stoichiometry of proton exchange membrane fuel cell using localized electrochemical impedance spectroscopy based on print circuit board[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(14): 7564-7573. |
| 2 | Silva R E, Gouriveau R, Jemei S, et al. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell degradation prediction based on adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(21): 11128-11144. |
| 3 | Yuan H, Dai H, Wei X, et al. Model-based observers for internal states estimation and control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system: a review[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 468: No. 228376. |
| 4 | Chen H C, Xu S C, Pei P C, et al. Mechanism analysis of starvation in PEMFC based on external characteristics[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(11): 5437-5446. |
| 5 | Zhong D, Lin R, Jiang Z, et al. Low temperature durability and consistency analysis of proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack based on comprehensive characterizations[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 264: No. 114626. |
| 6 | Lin R, Che L, Shen D, et al. High durability of Pt-Ni-Ir/C ternary catalyst of PEMFC by stepwise reduction synthesis[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2020, 330: No. 135251. |
| 7 | 王哲,谢怡,臧鹏飞,等. 基于极小值原理的燃料电池客车能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(1): 36-43. |
| Wang Zhe, Xie Yi, Zang Peng-fei, et al. Energy management strategy of fuel cell bus based on Pontryagin's minimum principle[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 36-43. | |
| 8 | Lin R H, Xi X N, Wang P N, et al. Review on hydrogen fuel cell condition monitoring and prediction methods[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(11): 5488-5498. |
| 9 | Keller R, Ding S X, Müller M, et al. Fault-tolerant model predictive control of a direct methanol-fuel cell system with actuator faults[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2017, 66: 99-115. |
| 10 | Tang W, Lin R, Weng Y, et al. The effects of operating temperature on current density distribution and impedance spectroscopy by segmented fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(25): 10985-10991. |
| 11 | Gouriveau R, Hilairet M, Hissel D, et al. IEEE PHM 2014 data challenge[EB/OL]. [2022-03-02]. |
| 12 | Pukrushpan J T. Modeling and Control of fuel cell systems and fuel processors[D]. Ann Arbor, Michigan:University of Michigan, 2003. |
| 13 | Zhang X, Pisu P. Prognostic-oriented fuel cell catalyst aging modeling and its application to health-monitoring and prognostics of a PEM fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Prognostics and Health Management, 2020, 5(1): 2153-2648. |
| 14 | Hu Zun-yan, Xu Liang-fei, Li Jian-qiu, et al. A reconstructed fuel cell life-prediction model for a fuel cell hybrid city bus[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 156: 723-732. |
| 15 | Lu L G, Ouyang M G, Huang H Y, et al. A semi-empirical voltage degradation model for a low-pressure proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack under bus city driving cycles[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2007, 164(1): 306-314. |
| 16 | Jouin M, Gouriveau R, Hissel D, et al. Degradations analysis and aging modeling for health assessment and prognostics of PEMFC[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2016, 148: 78-95. |
| 17 | Javed K, Gouriveau R, Zerhouni N, et al. Prognostics of proton exchange membrane fuel cells stack using an ensemble of constraints based connectionist networks[J]. Journal Power Sources, 2016, 324: 745-757. |
| 18 | Silva R E, Gouriveau R, Jemei S, et al. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell degradation prediction based on adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy inference systems[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(21): 11128-11144. |
| 19 | Morando S, Jemei S, Hissel D, et al. Proton exchange membrane fuel cell ageing forecasting algorithm based on echo state network[J].International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(2): 1472-1480. |
| 20 | Wu Y M, Breaz E, Gao F, et al. Nonlinear performance degradation prediction of proton exchange membrane fuel cells using relevance vector machine[J]. IEEE Trans Energy Convers, 2016, 31(4): 1570-1582. |
| 21 | Ma R, Yang T, Breaz E, et al. Data-driven proton exchange membrane fuel cell degradation predication through deep learning method[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 231: 102-115. |
| 22 | Pan R, Yang D, Wang Y J, et al. Performance degradation prediction of proton exchange membrane fuel cell using a hybrid prognostic approach[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(55): 30994-31008. |
| 23 | Liu H, Chen J, Hou M, et al. Data-based short-term prognostics for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(32): 20791-20808. |
| 24 | Zhou D, Gao F, Breaz E, et al. Degradation prediction of PEM fuel cell using a moving window based hybrid prognostic approach[J]. Energy, 2017, 138: 1175-1186. |
| 25 | Zuo B, Cheng J S, Zhang Z H. Degradation prediction model for proton exchange membrane fuel cells based on long short-term memory neural network and Savitzky-Golay filter[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(29): 15928-15937. |
| 26 | Dong S J, Luo T H. Bearing degradation process prediction based on the PCA and optimized LS-SVM model[J]. Measurement: Journal of the International Measurement Confederation, 2013, 46(9): 3143-3152. |
| 27 | Chen J, Jing H, Chang Y, et al. Gated recurrent unit based recurrent neural network for remaining useful life prediction of nonlinear deterioration process[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2019, 185: 372-382. |
| 28 | Mao L, Jackson L, Davies B. Effectiveness of a novel sensor selection algorithm in PEM fuel cell on-line diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (1982), 2018, 65(9): 7301-7310. |
| 29 | Pei P C, Chen D F, Wu Z Y, et al. Nonlinear methods for evaluating and online predicting the lifetime of fuel cells[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 254: No. 113730. |
| 30 | Revankar S T, Majumdar P. Fuel cells: Principles, Design, and Analysis[M]. Boca Raton:CRC Press, 2014. |
| 31 | Huang S Y, Ganesan P, Jung H, et al. Development of supported bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts and corrosion-resistant gas diffusion layer for unitized regenerative fuel cell applications[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 198: 23-29. |
| 32 | Xing L, Hossain M A, Tian M, et al. Platinum electro-dissolution in acidic media upon potential cycling[J]. Electrocatalysis-US, 2014, 5(1): 96-112. |
| 33 | Zhang S S, Yuan X Z, Hin J N C, et al. A review of platinum-based catalyst layer degradation in proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 194(2): 588-600. |
| 34 | Ma R, Yang T, Breaz E, et al. Data-driven proton exchange membrane fuel cell degradation predication through deep learning method[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 231: 102-115. |
| 35 | Curtin D E, Lousenberg R D, Henry T J, et al. Advanced materials for improved PEMFC performance and life[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2004, 131(1/2): 41-48. |
| 36 | Yuan Xiao-zi, Li Hui, Zhang Sheng-sheng, et al. A review of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell durability test protocols[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2011, 196(22): 9107-9116. |
| 37 | Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, et al. Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1): 1929-1958. |
| 38 | van den Bergh F, Engelbrecht A P. A study of particle swarm optimization particle trajectories[J]. Information Sciences, 2006, 176(8): 937-971. |
| 39 | 张慧斌, 王鸿斌, 胡志军. PSO 算法全局收敛性分析[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2011, 47(34): 61-63. |
| Zhang Hui-bin, Wang Hong-bin, Hu Zhi-jun. Analysis of particle swarm optimization algorithm global convergence method[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2011, 47(34): 61-63. | |
| 40 | Kingma D P, Ba L J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[C]∥International Conference on Learning Representations,San Diego,California,USA 2015: No.13. |
| [1] | 刘继宗,吴小平,孔维华. 基于鱼群优化算法的有轨电车用燃料电池混合动力系统参数配置[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2004-2013. |
| [2] | 曹起铭,闵海涛,孙维毅,于远彬,蒋俊宇. 质子交换膜燃料电池低温启动水热平衡特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2139-2146. |
| [3] | 杨子荣,李岩,冀雪峰,刘芳,郝冬. 质子交换膜燃料电池运行工况参数敏感性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1971-1981. |
| [4] | 胡云峰,于彤,杨惠策,孙耀. 低温环境下燃料电池启动优化控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2034-2043. |
| [5] | 都京,赵洪辉,王宇鹏,丁天威,魏凯,王恺,韩令海. 基于AMESim模型的燃料电池发动机排氢策略优化及整车搭载验证[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2069-2076. |
| [6] | 张冲,胡云峰,宫洵,孙耀. 燃料电池阴极流量无模型自适应滑模控制器设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2085-2095. |
| [7] | 隗海林,王泽钊,张家祯,刘洋. 基于Avl-Cruise的燃料电池汽车传动比及能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2119-2129. |
| [8] | 肖阳,王洁,刘孟军,杨发庆,张天瑶,兰巍. 质子交换膜燃料电池气体扩散层的力学改进模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2147-2155. |
| [9] | 刘岩,丁天威,王宇鹏,都京,赵洪辉. 基于自适应控制的燃料电池发动机热管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2168-2174. |
| [10] | 张佩,王志伟,杜常清,颜伏伍,卢炽华. 车用质子交换膜燃料电池空气系统过氧比控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1996-2003. |
| [11] | 高金武,王义琳,刘华洋,王艺达. 基于滑模观测器的质子交换膜燃料电池阴极进气系统解耦控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2156-2167. |
| [12] | 陈凤祥,张俊宇,裴冯来,侯明涛,李其朋,李培庆,王洋洋,张卫东. 质子交换膜燃料电池氢气供应系统的建模及匹配设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1982-1995. |
| [13] | 刘镇宁,江柯,赵韬韬,樊文选,卢国龙. 大功率质子交换膜燃料电池测试系统的开发及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2025-2033. |
| [14] | 池训逞,侯中军,魏伟,夏增刚,庄琳琳,郭荣. 基于模型的质子交换膜燃料电池系统阳极气体浓度估计技术综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [15] | 裴尧旺,陈凤祥,胡哲,翟双,裴冯来,张卫东,焦杰然. 基于自适应LQR控制的质子交换膜燃料电池热管理系统温度控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2014-2024. |
|
||