吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 2333-2342.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20211094
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于实时交通信息的电动汽车充换电路径规划方法
- 1.北京邮电大学 经济管理学院,北京 100876
2.北京信息科技大学 经济管理学院,北京 100192
3.陆军炮兵防空兵学院 郑州校区,郑州 450052
Charging and battery swapping route planning for electric vehicles based on real-time traffic information
Bi-da ZHANG1( ),Qiang YAN1,Lin ZHANG2,Hai-rui ZHANG3
),Qiang YAN1,Lin ZHANG2,Hai-rui ZHANG3
- 1.School of Economics and Management, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
2.School of Economics and Management, Beijing Information Science and Technology University, Beijing 100192, China
3.Zhengzhou Campus, CPLA Army Academy of Artillery and Air Defense Forces, Zhengzhou 450052, China
摘要:
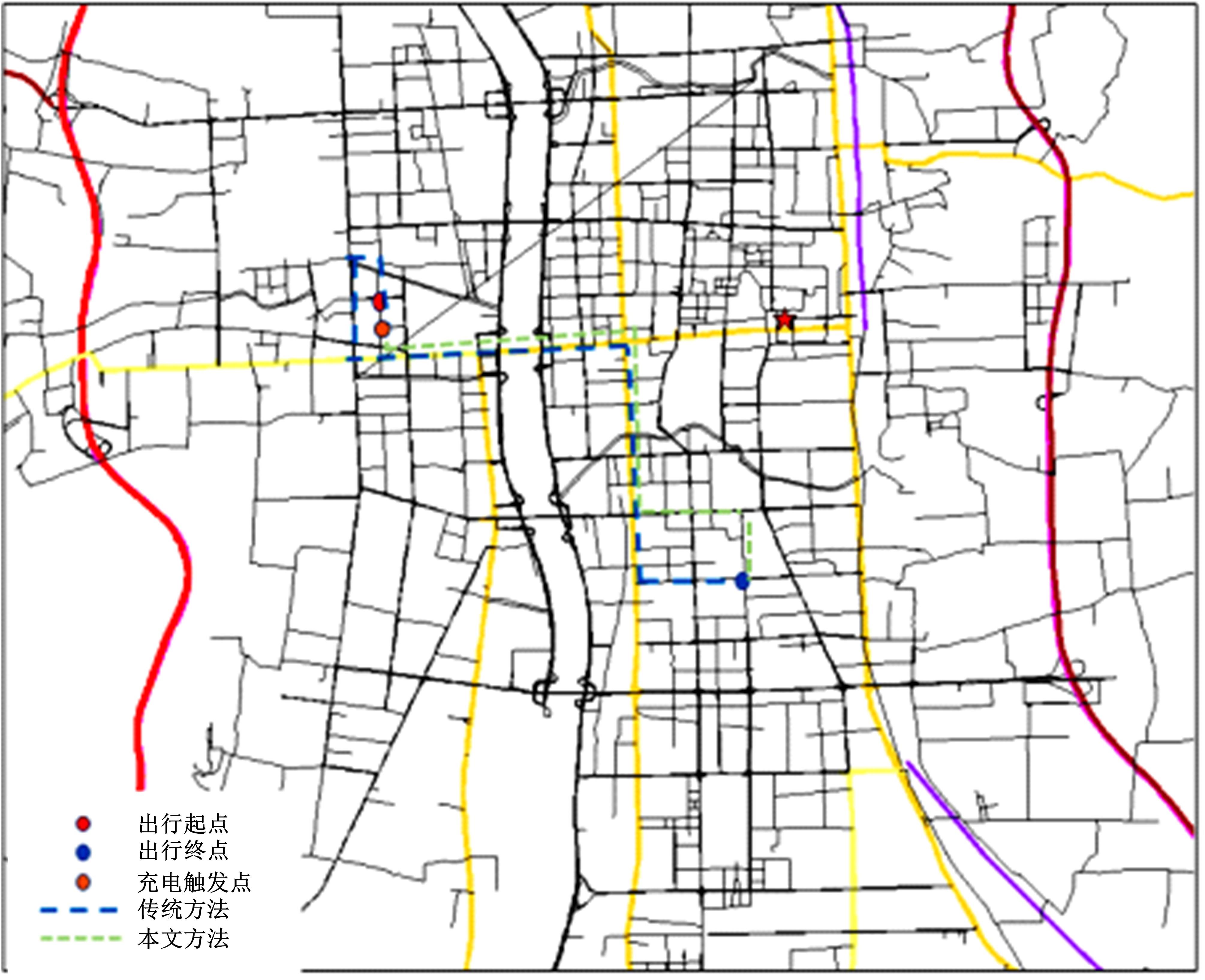
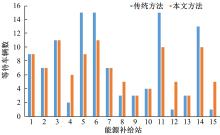
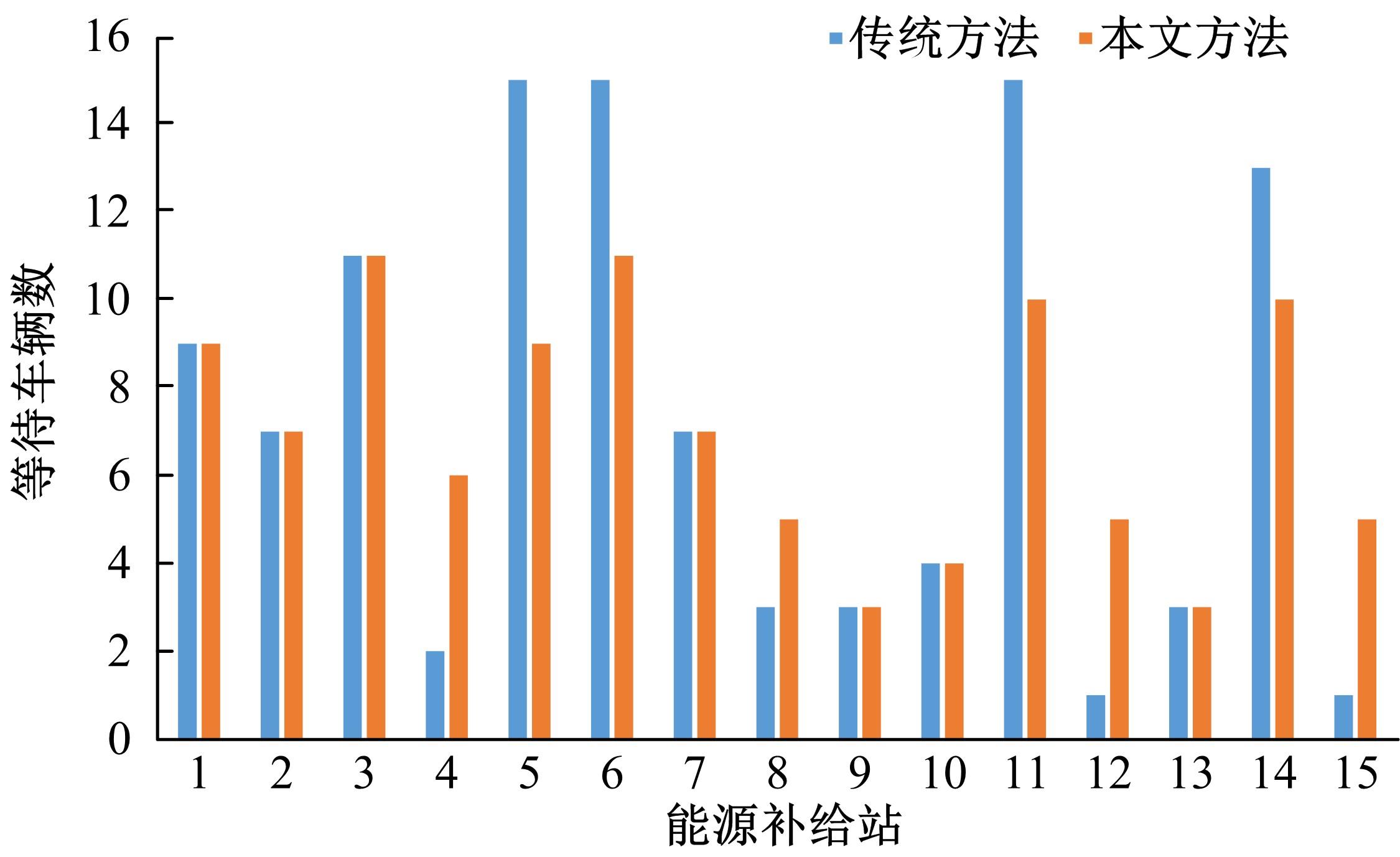
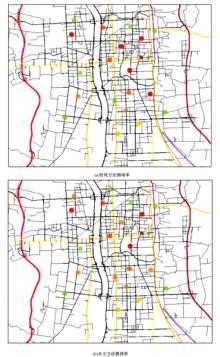
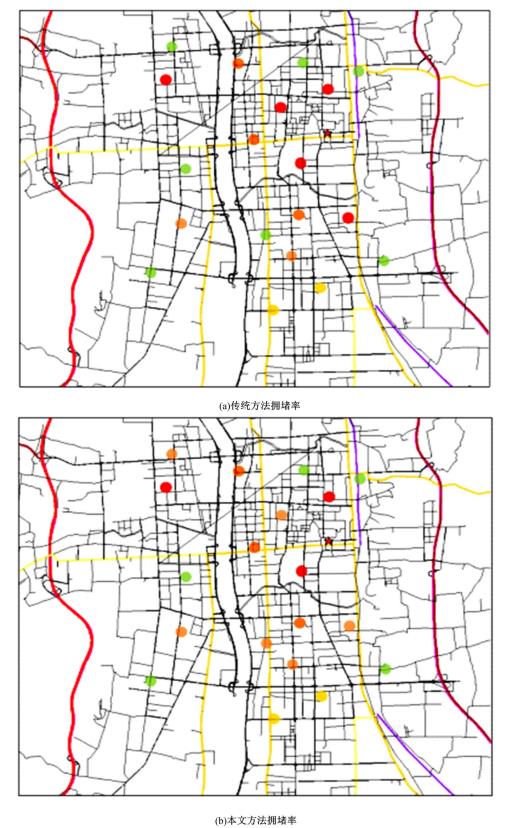
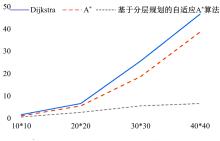
基于实时的路网信息,构建了一种充分考虑行驶时间、能源补给站点情况以及绕行指数的电动汽车充电、换电联合路径规划模型,通过改进的基于分层规划的自适应A*算法能够在动态路网中及时对导航路径进行修正。案例仿真表明,本文提出的导航策略能够选择最优的能源补给站点并进行相应的路径规划、平衡路网中各个能源补给站点的电动汽车数量,不仅缩短了行驶的整体时间、缓解了由于充换电站附近车辆聚集导致的拥堵,而且还提高了充换电站点的运营效率;改进算法通过构建一种分层路网结构,能够根据路网的实时路阻变化对模型进行高效求解,可有效提升搜索效率、降低计算时间。
中图分类号:
- U469.72
| 1 | Rahman I, Vasant P M, Singh B S M, et al. Review of recent trends in optimization techniques for plug-in hybrid, and electric vehicle charging infrastructures[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 58: 1039-1047. |
| 2 | 邵尹池,穆云飞,林佳颖,等.“车-站-网”多元需求下的电动汽车快速充电引导策略[J]. 电力系统自动化,2019,43(18):1-8. |
| Shao Yin-chi, Mu Yun-fei, Lin Jia-ying,et al.Fast charging guidance strategy for electric vehicles under the multiple demands of "Vehicle-Station-Network"[J]. Power System Automation,2019,43(18):1-8. | |
| 3 | Shao Sai, Wei Guan, Bi Jun.Electric vehicle-routing problem with charging demands and energy consumption[J].IET Intelligent Transport Systems,2018, 12(3):202-212. |
| 4 | 邢强,陈中,冷钊莹,等.基于实时交通信息的电动汽车路径规划和充电导航策略[J].中国电机工程学报,2020,40(2):534-549. |
| Xing Qiang, Chen Zhong, Leng Zhao-ying,et al.Route planning and charging navigation strategy for electric vehicles based on real-time traffic information[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2020,40(2): 534-549. | |
| 5 | Rossetti G, Pappalardo L, Pedreschi D, et al. Tiles: an online algorithm for community discovery in dynamic social networks[J]. Machine Learning, 2016, 106(8): 1213-1241. |
| 6 | 王志坚,韩伟一,李一军.具有多条最短路径的最短路问题[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报,2010,42(9):1428-1431. |
| Wang Zhi-jian, Han Wei-yi, Li Yi-jun.Shortest path problem with multiple shortest paths[J].Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2010,42(9):1428-1431. | |
| 7 | 邵成成,李徐亮,钱涛,等.基于交通均衡的电动汽 车快速充电负荷模拟[J].中国电机工程学报,2021,41(4):1368-1376. |
| Shao Cheng-cheng, Li Xu-liang, Qian Tao,et al.Simulation of EV fast charging load based on traffic equilibrium[J].Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021,41(4):1368-1376. | |
| 8 | 邵尹池,穆云飞,余晓丹,等.“车-路-网”模式下电 动汽车充电负荷时空预测及其对配电网潮流的影响[J].中国电机工程学报,2017,37(18):5207-5218. |
| Shao Yin-chi, Mu Yun-fei, Yu Xiao-dan,et al.Temporal and spatial prediction of charging loads of electric vehicles under "Vehicle-Road-Network" mode and its influence on power flow of distribution network[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2017,37(18): 5207-5218. | |
| 9 | Xing Q, Chen Z, Zhang Z,et al.Charging demand forecasting model for electric vehicles based on online ride-hailing trip data[J]. IEEE Access, 2019(7): 137390-137409. |
| 10 | 严弈遥,罗禹贡,朱陶,等.融合电网和交通网信息的电动车辆最优充电路径推荐策略[J].中国电机工程学报,2015,35(2):310-318. |
| Yan Yi-yao, Luo Yu-gong, Zhu Tao,et al.Optimal charging path recommendation strategy for electric vehicles based on information of power grid and traffic network[J].Proceedings of the CSEE,2015,35(2): 310-318. | |
| 11 | Cedric De Cauwer, Verbeke Wouter,van Mierlo Joeri, et al.A model for range estimation and energy-efficient routing of electric vehicles in real-world conditions[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2020,21(7):2787-2800. |
| 12 | 苏粟,杨恬恬,李玉璟,等.考虑实时动态能耗的电 动汽车充电路径规划[J].电力系统自动化,2019,43(7): 136-143. |
| Su Su, Yang Tian-tian, Li Yu-jing,et al.Electric vehicle charging path planning considering real-time dynamic energy consumption[J]. Power System Automation, 2019,43(7):136-143. | |
| 13 | 杨洪明,李明,文福拴,等.利用实时交通信息感知的电动汽车路径选择和充电导航策略[J].电力系统自动化,2017,41(11):106-113. |
| Yang Hong-ming, Li Ming, Wen Fu-shuan,et al.Route selection and charging navigation strategy for electric vehicles based on real-time traffic information perception[J].Power System Automation,2017,41(11): 106-113. | |
| 14 | 黄晶,杨健维,王湘.下一目的地导向下的电动汽车充电引导策略[J].电网技术,2017,41(7):2173-2181. |
| Huang Jing, Yang Wei-jian, Wang Xiang,et al.Charging guidance strategy for electric vehicles under the next destination orientation[J].Power System Technology, 2017,41(7):2173-2181. | |
| 15 | Pacaci A, Tamer O M. Experimental analysis of streaming algorithms for graph partitioning[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Management of Data, Amsterdam, Netherlands,2019: 1375-1392. |
| 16 | Zhang Z H, Qian J, Fang Z X, et al. Dynamic division of traffic control sub areas based on community discovery algorithm[J]. Journal of Yangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 23 (4): 73-78. |
| 17 | Ji Zhen-ya, Huang Xue-liang.Plug-in electric vehicle charging infrastructure deployment of China towards 2020: policies, methodologies, and challenges[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2018,90:710-727. |
| [1] | 赵又群,李宇昊,邓汇凡,林涛,林棻. 基于Popov超稳定性的分布式电动汽车稳定性控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2225-2233. |
| [2] | 李明,薛庆峰,张可欣,吕然,韦长华. 电动汽车热泵空调系统性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1943-1952. |
| [3] | 张家旭,王晨,赵健,卜纯研. 面向狭小平行泊车位的路径规划与跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1879-1886. |
| [4] | 李浩,陈浩. 考虑充电排队时间的电动汽车混合交通路网均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1684-1691. |
| [5] | 王聪,马彦,王国光. 电动汽车充电站内的实时最优功率分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1490-1495. |
| [6] | 张家旭,王欣志,赵健,施正堂. 汽车高速换道避让路径规划及离散滑模跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1081-1090. |
| [7] | 宋强,孙丹婷,章伟. 纯电动车机械式自动变速器换挡非线性建模及控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 810-819. |
| [8] | 马苗苗,潘军军,刘向杰. 含电动汽车的微电网模型预测负荷频率控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1644-1652. |
| [9] | 韩小健,赵伟强,陈立军,郑宏宇,刘阳,宗长富. 基于区域采样随机树的客车局部路径规划算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1428-1440. |
| [10] | 席利贺,张欣,孙传扬,王泽兴,姜涛. 增程式电动汽车自适应能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1636-1644. |
| [11] | 常成,宋传学,张雅歌,邵玉龙,周放. 双馈电机驱动电动汽车变频器容量最小化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1629-1635. |
| [12] | 金立生, 谢宪毅, 高琳琳, 郭柏苍. 基于二次规划的分布式电动汽车稳定性控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1349-1359. |
| [13] | 张天时, 宋东鉴, 高青, 王国华, 闫振敏, 宋薇. 电动汽车动力电池液体冷却系统构建及其工作过程仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 387-397. |
| [14] | 孙文, 王庆年, 王军年. 基于横摆力矩控制的电动轮汽车转弯节能控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 11-19. |
| [15] | 邵赛, 毕军, 关伟. 基于电动汽车的动态需求车辆路径问题[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1688-1695. |
|
||