吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 2906-2915.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210414
基于双孪生网络的可见光热红外目标实时鲁棒跟踪
符磊1( ),顾文彬1(
),顾文彬1( ),艾勇保2,李伟3,郑南1,王留洋1
),艾勇保2,李伟3,郑南1,王留洋1
- 1.陆军工程大学 野战工程学院,南京 210007
2.军事科学院 国防科技创新研究院,北京 100071
3.中国人民解放军 93182部队,沈阳 110000
Real⁃time robust RGB⁃T target tracking based on dual Siamese network
Lei FU1( ),Wen-bin GU1(
),Wen-bin GU1( ),Yong-bao AI2,Wei LI3,Nan ZHENG1,Liu-yang WANG1
),Yong-bao AI2,Wei LI3,Nan ZHENG1,Liu-yang WANG1
- 1.College of Field Engineering,Army Engineering University of PLA,Nanjing 210007,China
2.National Academy of Defense Science and Technology Innovation,Academy of Military Sciences,Beijing 100071,China
3.93182 PLA Troops,Shenyang 110000,China
摘要:
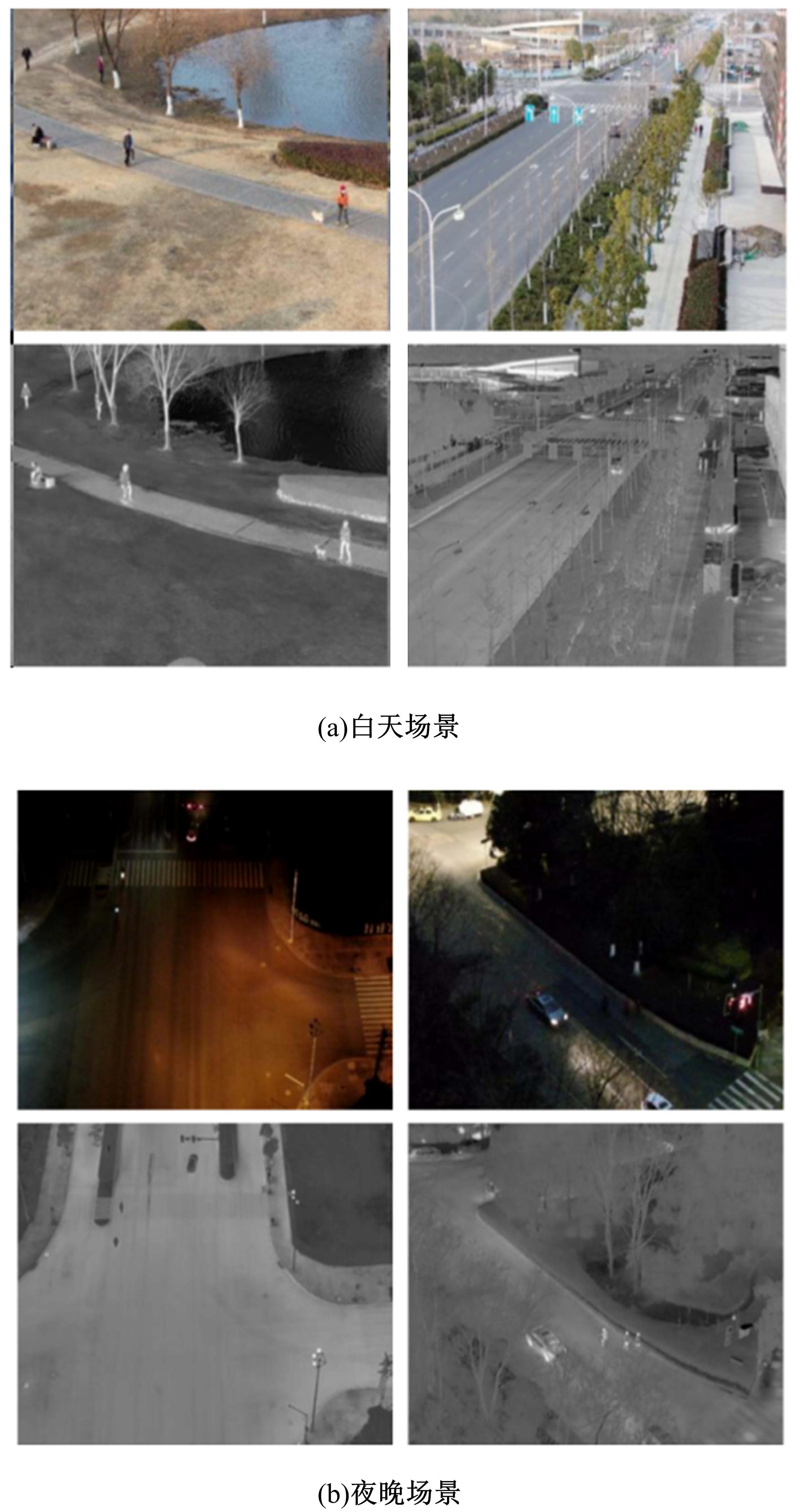
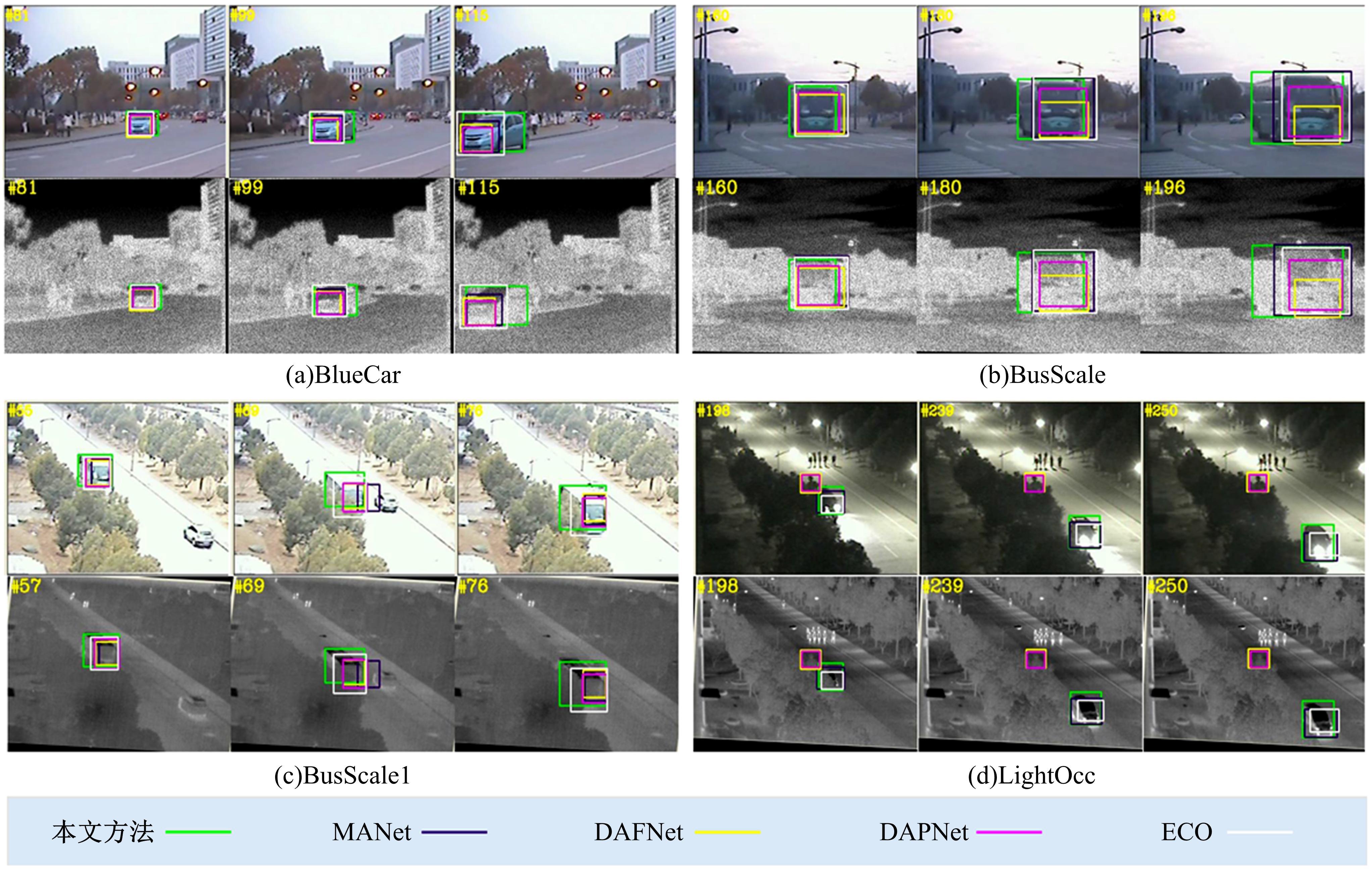
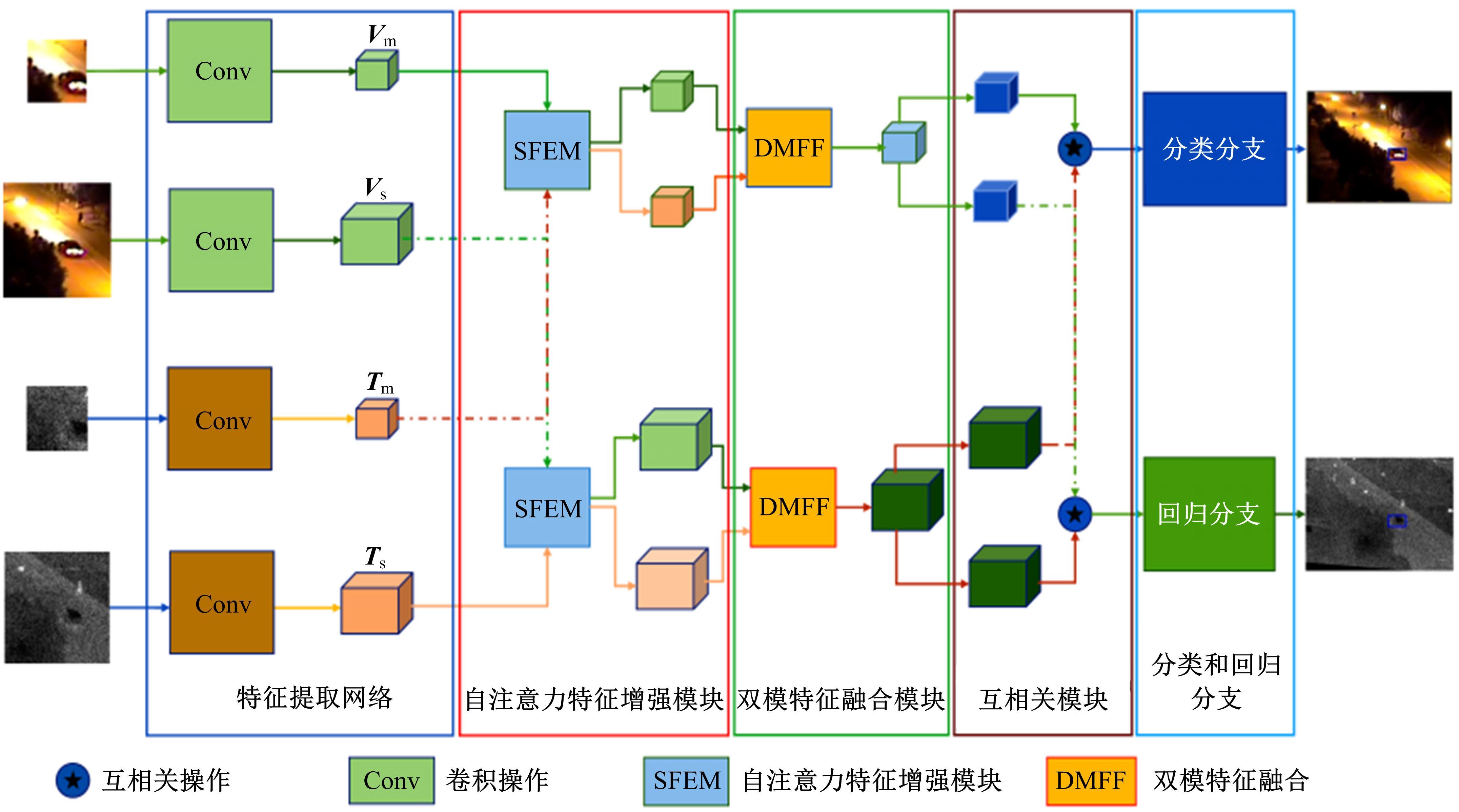
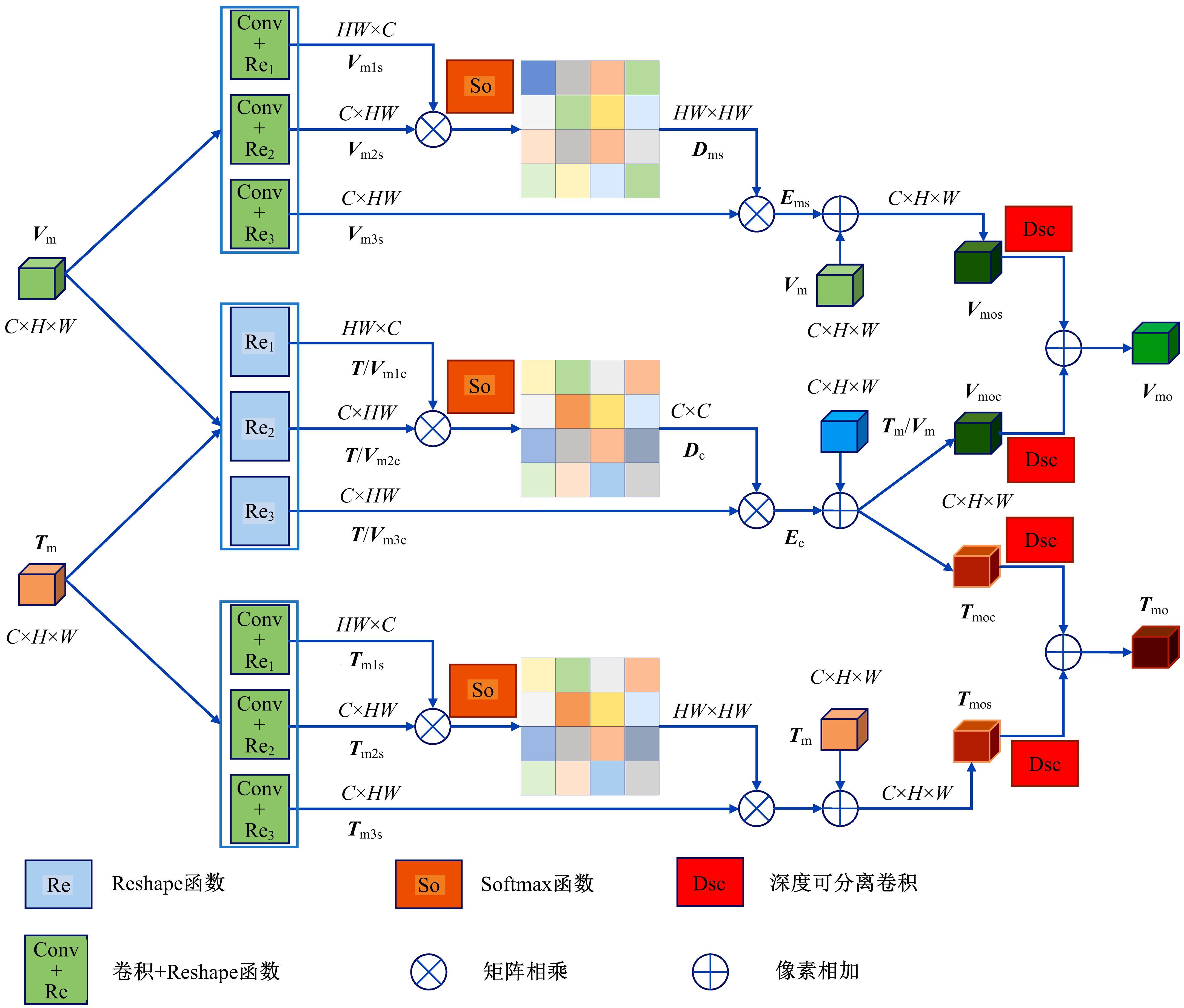
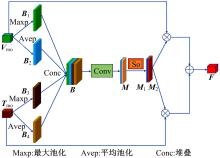
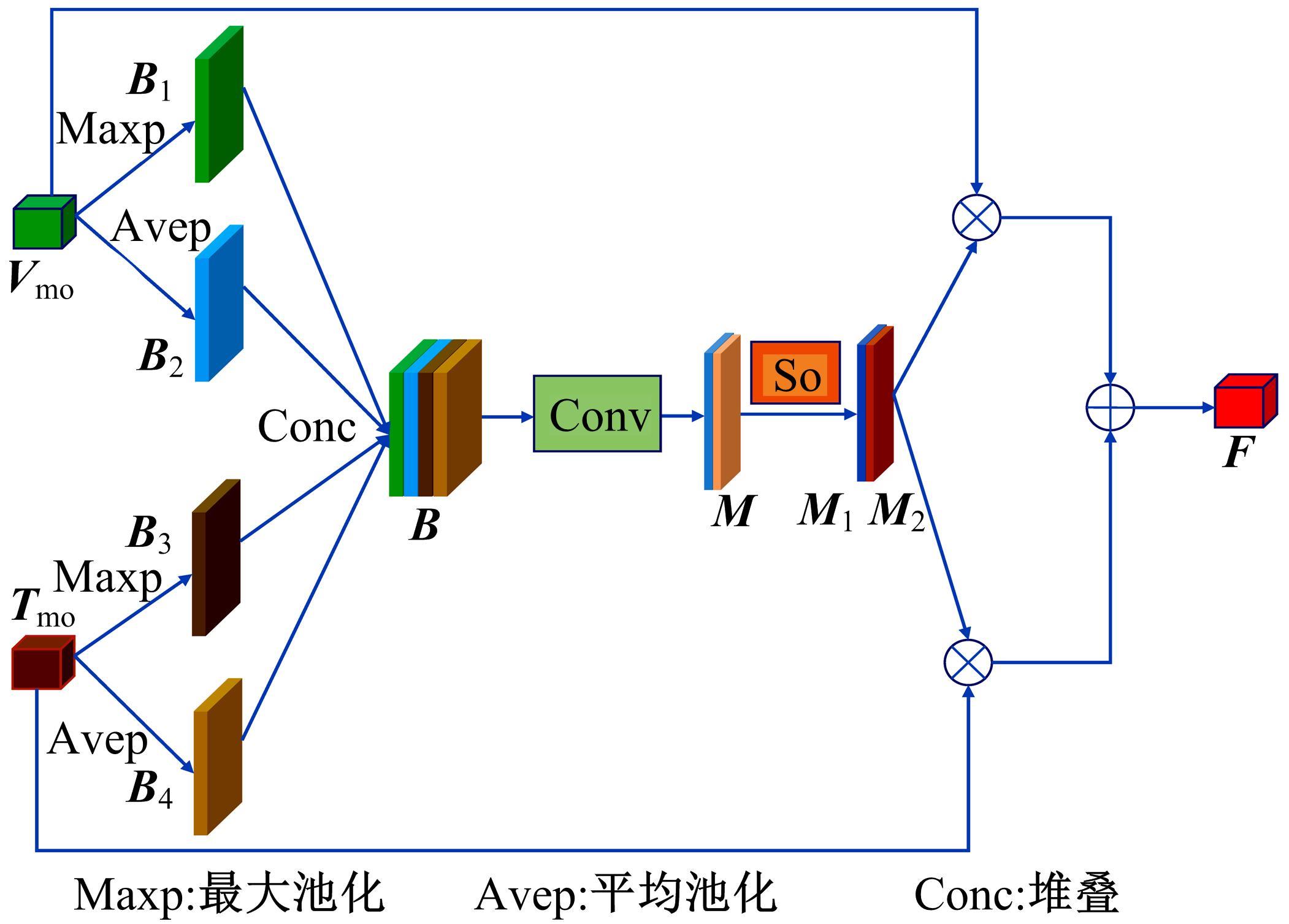
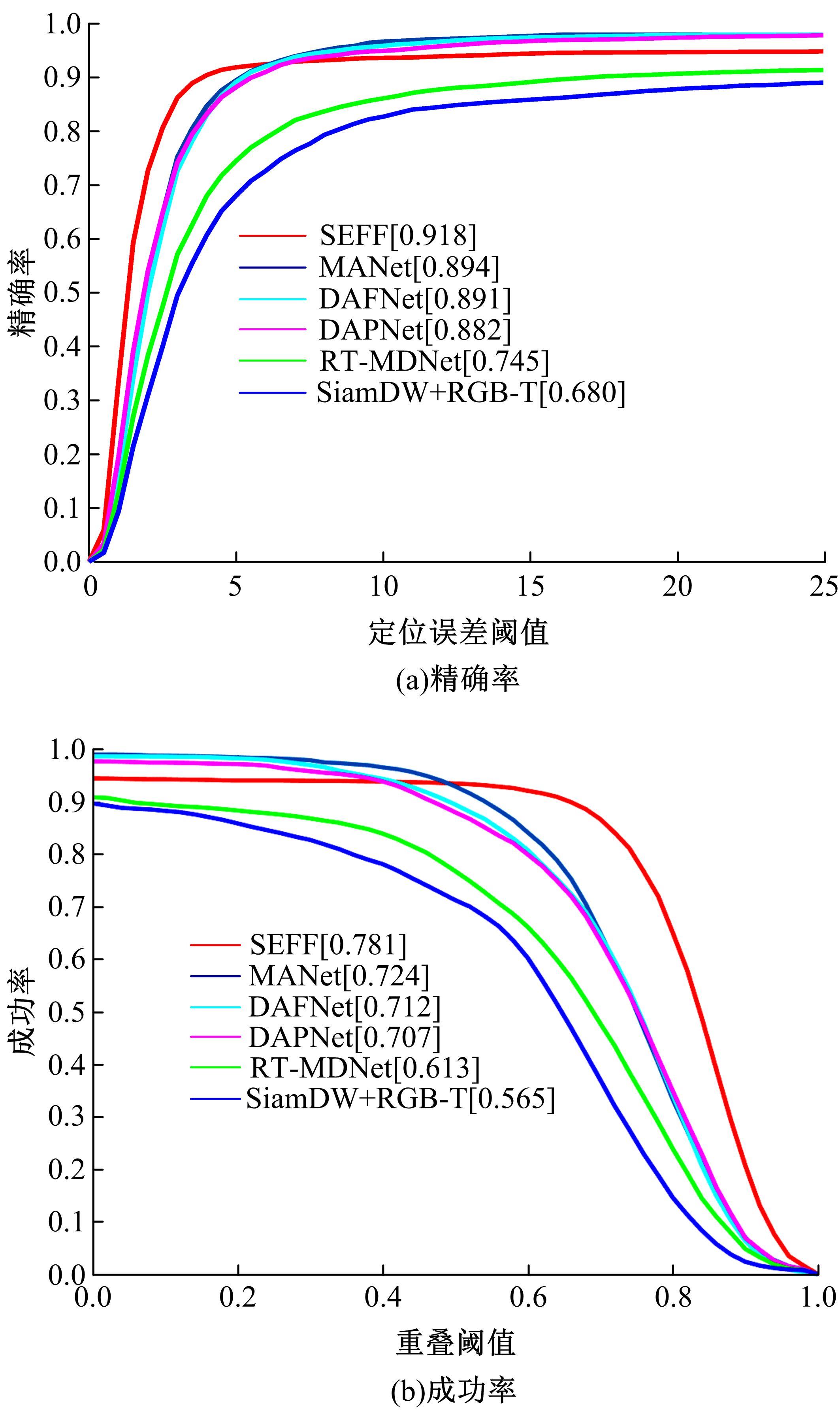
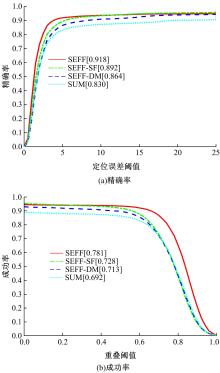
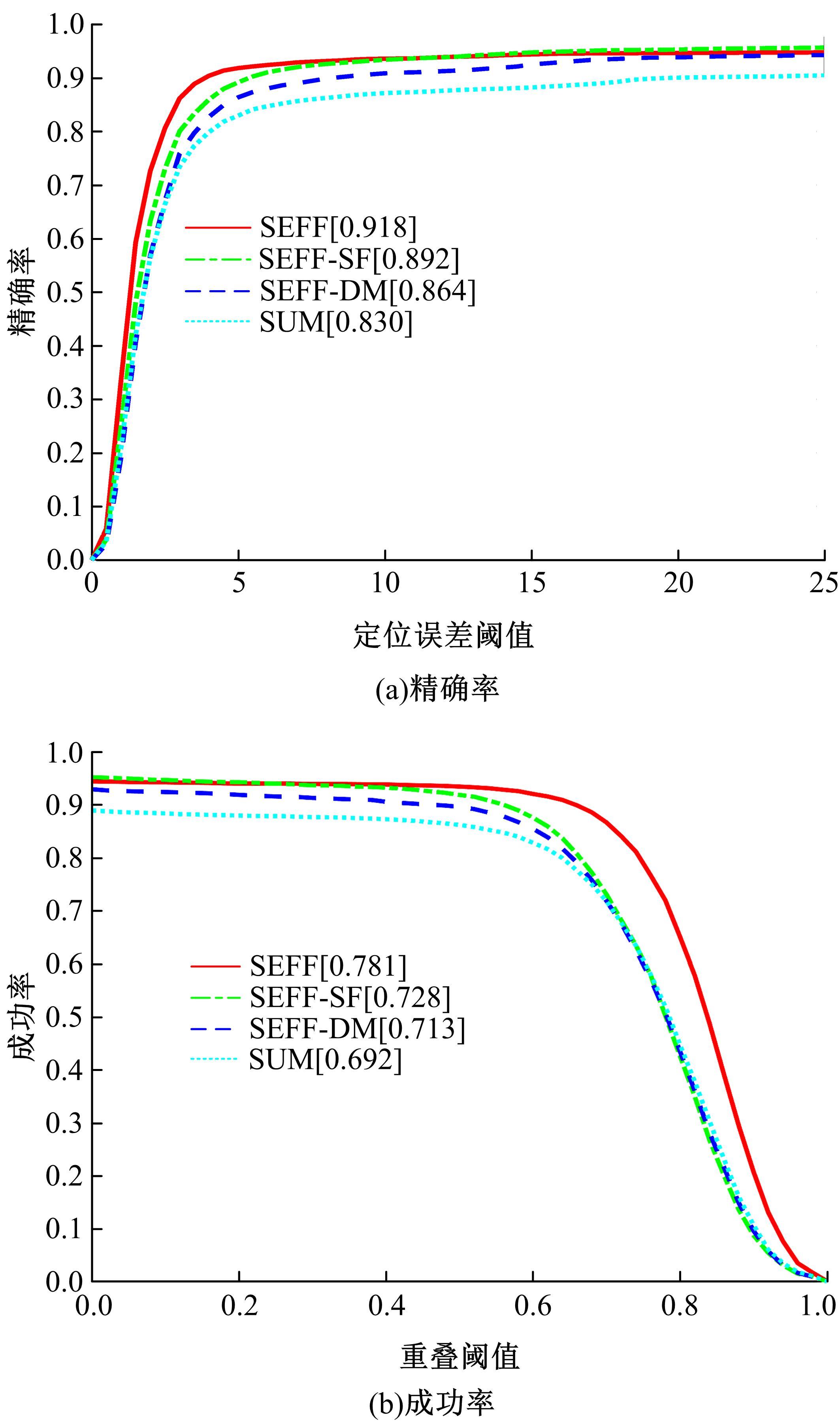
针对可见光与热红外图像融合跟踪中采用孪生网络架构进行跟踪时鲁棒性较差的问题,提出了一种基于双孪生网络特征融合的可见光热红外(RGB-T)目标实时跟踪方法。首先,采用两个孪生网络分别对可见光和红外图像的模板分支和搜索分支进行特征提取,得到两种模态特征层;然后,利用自注意力特征增强模块(SFEM)对两种模态的特征进行增强,并使用双模特征融合(DMFF)模块对模板分支和搜索分支增强后的特征分别进行融合;最后,将融合后的模板分支和搜索分支进行特定任务的互相关操作,并通过分类和回归分支得到目标位置,从而完成跟踪。在灰度热红外目标跟踪数据集(GTOT)上的测试结果表明,本文方法的精确率(PR)为91.8%,成功率(SR)为78.1%,运行速度为60 f/s。与其他RGB-T融合跟踪方法相比,本文方法能够在保持实时处理速度的同时具备较高的鲁棒性。
中图分类号:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Lu Z, Rathod V, Votel R, et al. Retinatrack: online single stage joint detection and tracking[C]∥Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 14656-14666. |
| 2 | 徐涛, 马克, 刘才华. 基于深度学习的行人多目标跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(1): 27-38. |
| Xu Tao, Ma Ke, Liu Cai-hua. Multi object pedestrian tracking based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 27-38. | |
| 3 | 孟琭, 杨旭. 目标跟踪算法综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(7): 1244-1260. |
| Meng Lu, Yang Xu. A survey of object tracking algorithms[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(7): 1244-1260. | |
| 4 | 苑晶, 李阳, 董星亮, 等. 基于运动模式在线分类的移动机器人目标跟踪[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38(3): 568-577. |
| Yuan Jing, Li Yang, Dong Xing-liang, et al. Target tracking with a mobile robot based on online classification for motion patterns[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38(3): 568-577. | |
| 5 | Hao J, Zhou Y, Zhang G, et al. A review of target tracking algorithm based on UAV[C]∥Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Cyborg and Bionic Systems, Shenzhen, China, 2018: 328-333. |
| 6 | Zhang X, Ye P, Leung H, et al. Object fusion tracking based on visible and infrared images: a comprehensive review[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 63: 166-187. |
| 7 | Li C, Wu X, Zhao N, et al. Fusing two-stream convolutional neural networks for RGB-T object tracking[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 281: 78-85. |
| 8 | Zhu Y, Li C, Luo B, et al. Dense feature aggregation and pruning for RGBT tracking[C]∥The 27th ACM International Conference, Nice, France, 2019: 465-472. |
| 9 | Gao Y, Li C, Zhu Y, et al. Deep adaptive fusion network for high performance RGBT tracking[C]∥2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Soule, South Korea, 2019: 91-99. |
| 10 | Li C, Lu A, Zheng A, et al. Multi-adapter RGBT tracking[C]∥2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW), Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 2262-2270. |
| 11 | Zhang X C, Ye P, Peng S Y, et al. SiamFT: an RGB-infrared fusion tracking method via fully convolutional Siamese networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7(1): 122122-122133. |
| 12 | 申亚丽. 基于特征融合的RGBT双模态孪生跟踪网络[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(3): 20200459. |
| Shen Ya-li. RGBT dual-modal Siamese tracking network with feature fusion[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(3): 20200459. | |
| 13 | Xu Y, Wang Z, Li Z, et al. Towards robust and accurate visual tracking with target estimation guidelines[C]∥Association for the Advance of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), New York, USA, 2020: 125491-125565. |
| 14 | Li B, Yan J, Wu W, et al. High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network[C]∥Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, USA, 2017: 8971-8980. |
| 15 | Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]∥Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1106-1164. |
| 16 | Fu J, Liu J, Tian H, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]∥Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3146-3154. |
| 17 | François C. Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]∥Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Hawai, USA, 2017: 1800-1807. |
| 18 | Lin T, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318-327. |
| 19 | Yu J, Jiang Y, Wang Z, et al. UnitBox: an advanced object detection network[C]∥ACM international conference on Multimedia, Amsterdam, Netherlands. 2016: 516-520. |
| 20 | Li C, Hui C, Hu S, et al. Learning collaborative sparse representation for grayscale-thermal tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(12): 5743-5756. |
| 21 | Li C, Liang X, Lu Y, et al. RGB-T object tracking: benchmark and baseline[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019: 96: No. 106977. |
| 22 | Jung I, Son J, Beak M, et al. Real-time MDNet[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 89-104. |
| 23 | Zhang Z, Peng H. Deeper and wider Siamese networks for real-time visual tracking[C]∥Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4591-4600. |
| [1] | 祁贤雨,王巍,王琳,赵玉飞,董彦鹏. 基于物体语义栅格地图的语义拓扑地图构建方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 569-575. |
| [2] | 时小虎,吴佳琦,吴春国,程石,翁小辉,常志勇. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| [3] | 郭鹏,赵文超,雷坤. 基于改进Jaya算法的双资源约束柔性作业车间调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 480-487. |
| [4] | 刘近贞,高国辉,熊慧. 用于脑组织分割的多尺度注意网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 576-583. |
| [5] | 赵宏伟,张健荣,朱隽平,李海. 基于对比自监督学习的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1850-1856. |
| [6] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [7] | 胡丹,孟新. 基于时变网格的对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1896-1903. |
| [8] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [9] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [10] | 周丰丰,朱海洋. 基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法SEE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1834-1841. |
| [11] | 周丰丰,张亦弛. 基于稀疏自编码器的无监督特征工程算法BioSAE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1645-1656. |
| [12] | 王军,徐彦惠,李莉. 低能耗支持完整性验证的数据融合隐私保护方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1657-1665. |
| [13] | 康耀龙,冯丽露,张景安,陈富. 基于谱聚类的高维类别属性数据流离群点挖掘算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1422-1427. |
| [14] | 王文军,余银峰. 考虑数据稀疏的知识图谱缺失连接自动补全算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1428-1433. |
| [15] | 陈雪云,贝学宇,姚渠,金鑫. 基于G⁃UNet的多场景行人精确分割与检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 925-933. |
|