吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 802-809.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20221254
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
基于高精度地图增强的三维目标检测算法
陶博1,2,3,4,5( ),颜伏伍1,2,3,4,5,尹智帅1,2,3,4,5(
),颜伏伍1,2,3,4,5,尹智帅1,2,3,4,5( ),武冬梅1,3,4,5
),武冬梅1,3,4,5
- 1.武汉理工大学 汽车工程学院,武汉 430070
2.先进能源科学与技术广东省实验室 佛山分中心(佛山仙湖实验室),广东 佛山 528200
3.武汉理工大学 现代汽车零部件技术湖北省重点实验室,武汉 430070
4.武汉理工大学 汽车零部件技术湖北省协同创新中心,武汉 430070
5.武汉理工大学 新能源与智能网联汽车湖北省工程技术研究中心,武汉 430070
3D object detection based on high⁃precision map enhancement
Bo TAO1,2,3,4,5( ),Fu-wu YAN1,2,3,4,5,Zhi-shuai YIN1,2,3,4,5(
),Fu-wu YAN1,2,3,4,5,Zhi-shuai YIN1,2,3,4,5( ),Dong-mei WU1,3,4,5
),Dong-mei WU1,3,4,5
- 1.School of Automotive Engineering,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430070,China
2.Foshan Xianhu Laboratory of the Advanced Energy Science and Technology Guangdong Laboratory,Foshan 528200,China
3.Hubei Key Laboratory of Advanced Technology for Automotive Components,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430070,China
4.Hubei Collaborative Innovation Center for Automotive Components Technology,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430070,China
5.Hubei Research Center for New Energy & Intelligent Connected Vehicle,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430070,China
摘要:
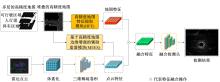
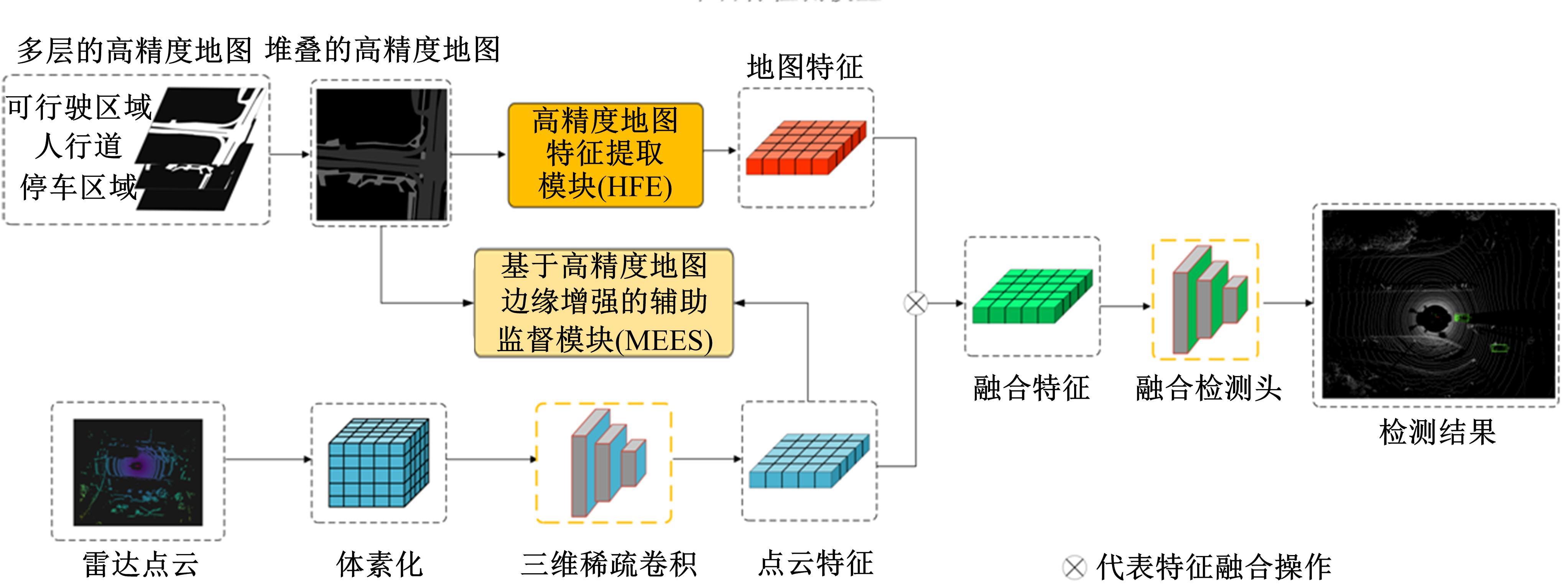
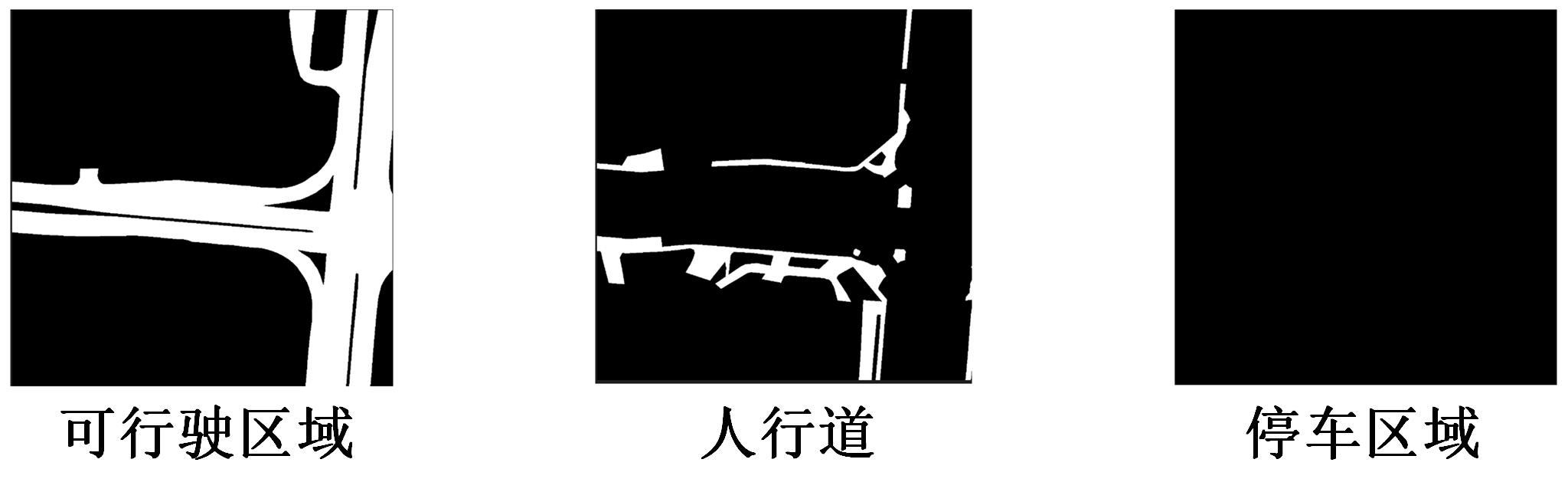
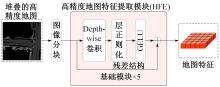
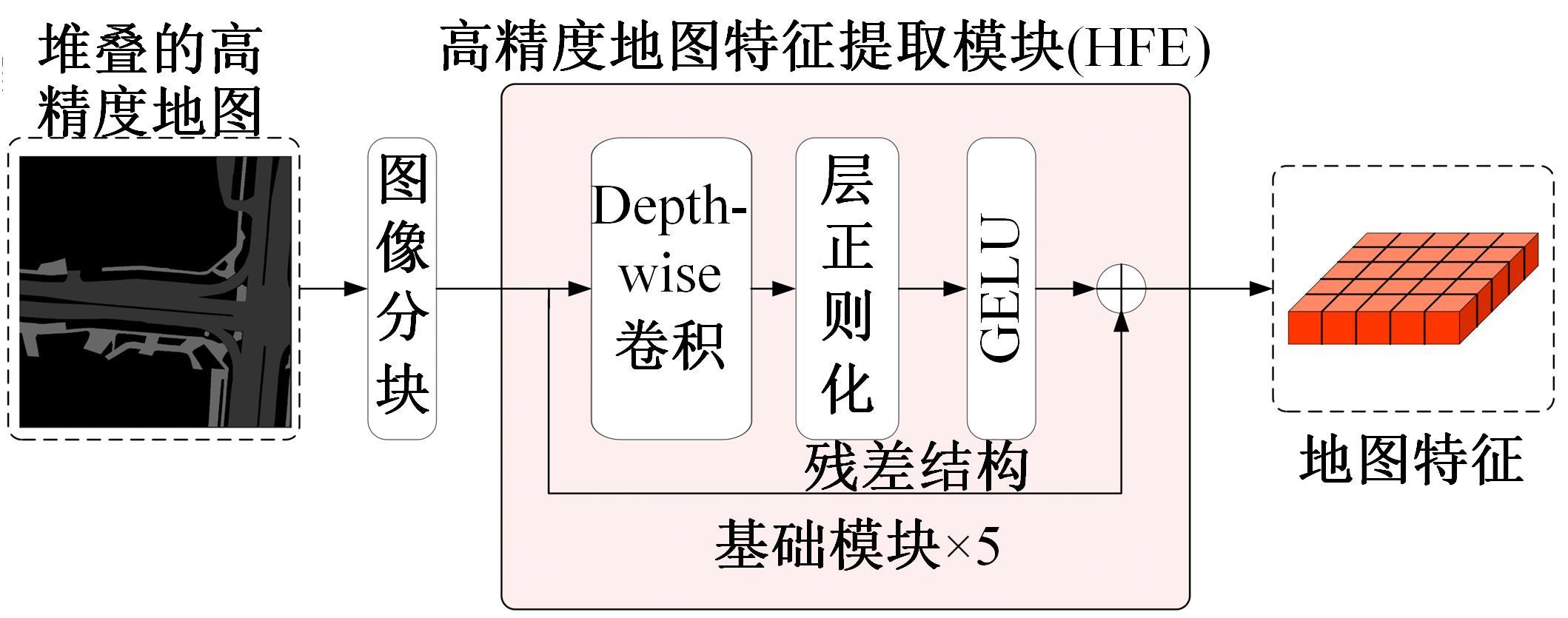
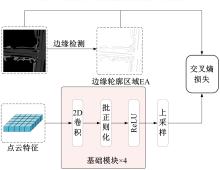
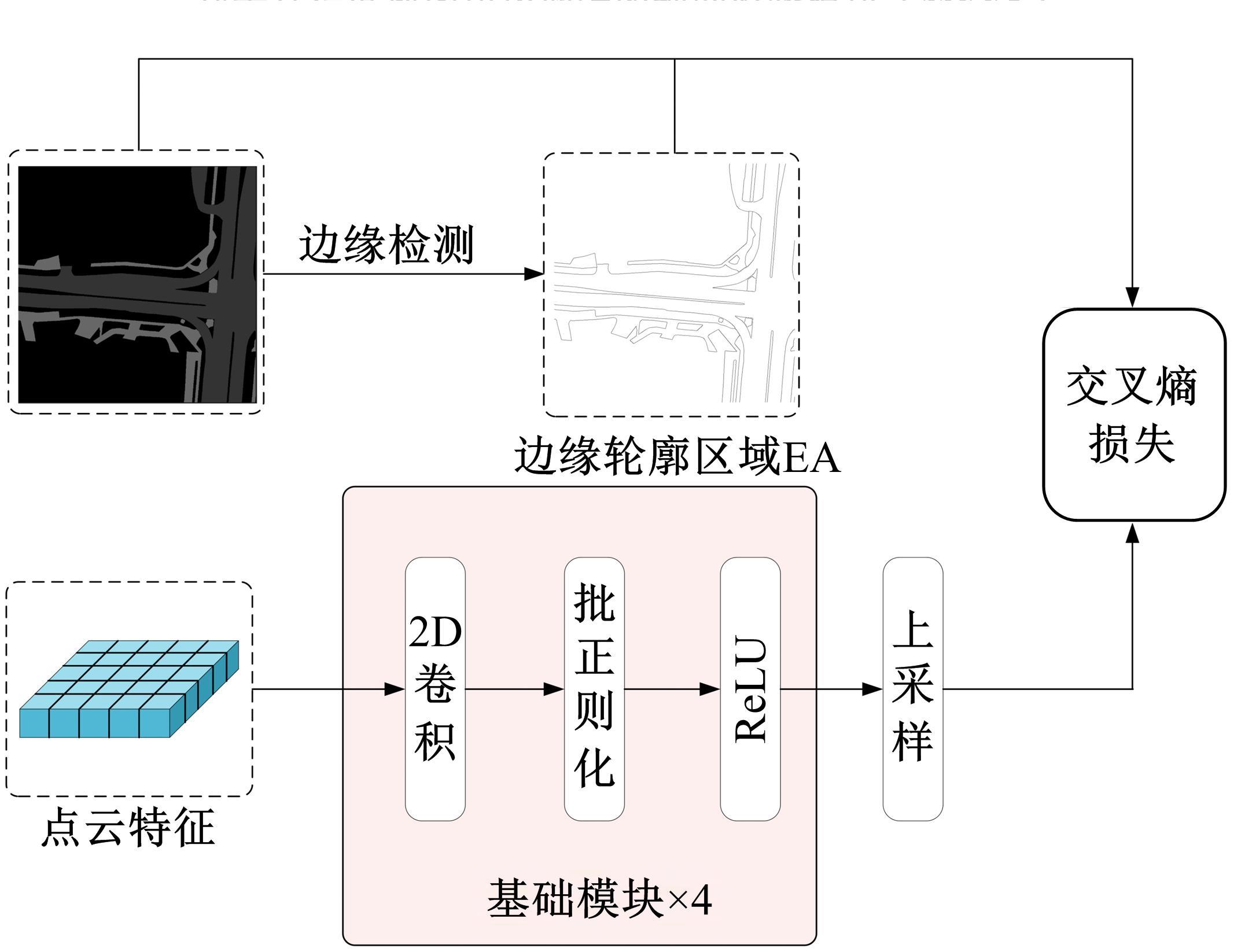
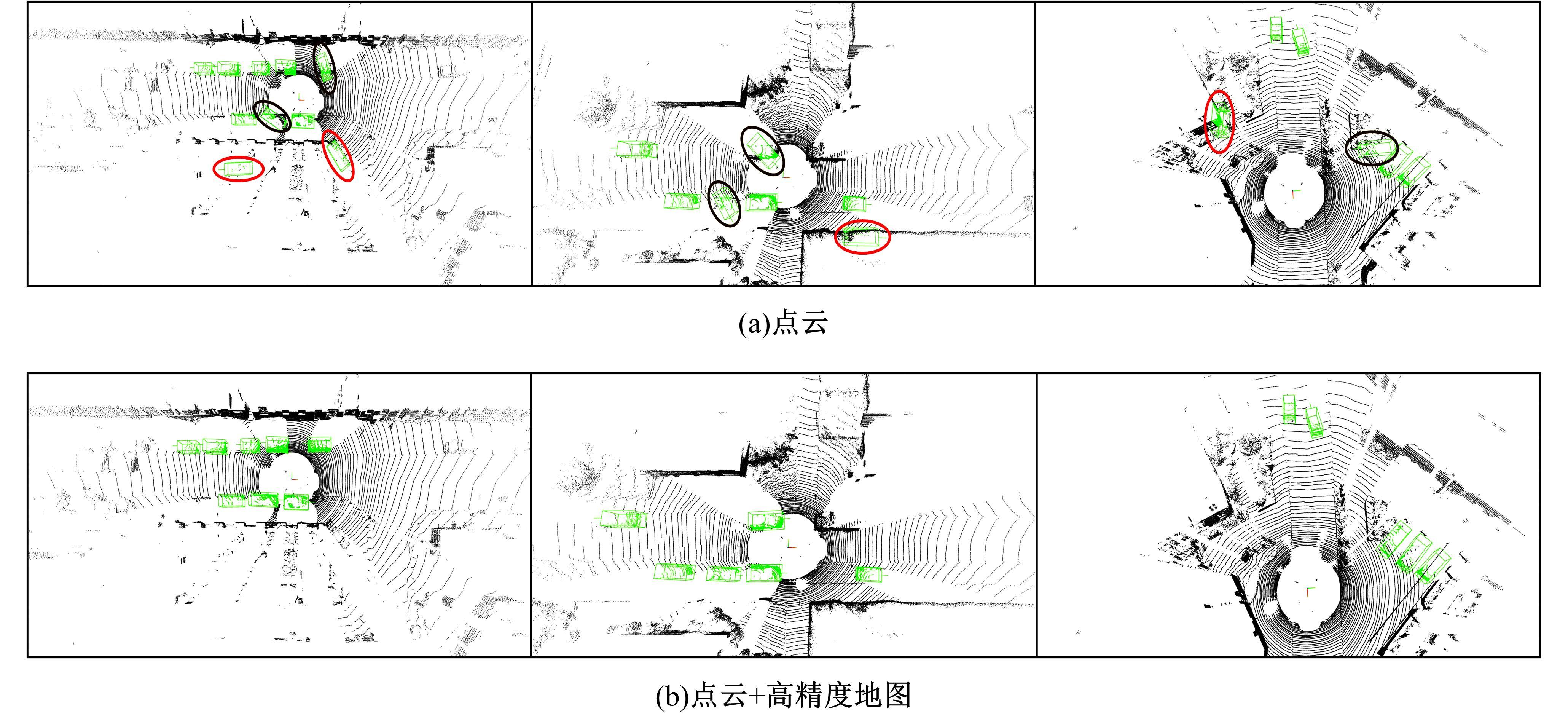
将高精度地图信息融入主干检测网络中提出了基于高精度地图增强的三维目标检测算法(HME3D)。结合传统卷积和Transformer构建了新颖的地图特征提取模块(HFE)以实现地图特征的高效提取。此外,利用基于地图边缘增强的辅助监督网络(MEES)提升三维目标检测主任务的性能。最后,在具有挑战性的nuScenes数据集上验证了本文模型的优势,它相对纯点云基线模型精度提升了2.81 mAP。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Levinson J, Askeland J, Becker J, et al. Towards fully autonomous driving: systems and algorithms[C]∥2011 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Baden-Baden, Germany, 2011: 163-168. |
| 2 | Tan M, Pang R, Le Q V. Efficientdet: scalable and efficient object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 2020: 10781-10790. |
| 3 | Lin T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 2117-2125. |
| 4 | Zhao Q, Sheng T, Wang Y, et al. M2det: a single-shot object detector based on multi-level feature pyramid network[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2019: 9259-9266. |
| 5 | Cai Z, Vasconcelos N. Cascade R-CNN: high quality object detection and instance segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 43(5): 1483-1498. |
| 6 | Shi S, Wang Z, Shi J, et al. From points to parts: 3D object detection from point cloud with part-aware and part-aggregation network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 43(8): 2647-2664. |
| 7 | He C, Zeng H, Huang J, et al. Structure aware single-stage 3D object detection from point cloud[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 2020: 11873-11882. |
| 8 | Zhou Y, Tuzel O. Voxelnet: end-to-end learning for point cloud based 3D object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2018: 4490-4499. |
| 9 | Yin T, Zhou X, Krahenbuhl P. Center-based 3D object detection and tracking[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA,2021: 11784-11793. |
| 10 | Lang A H, Vora S, Caesar H, et al. Pointpillars: fast encoders for object detection from point clouds[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 12697-12705. |
| 11 | Qi C R, Su H, Mo K, et al. Pointnet: deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 652-660. |
| 12 | Chen X, Ma H, Wan J, et al. Multi-view 3D object detection network for autonomous driving[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017: 1907-1915. |
| 13 | Ku J, Mozifian M, Lee J, et al. Joint 3D proposal generation and object detection from view aggregation[C]∥2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 2018: 1-8. |
| 14 | Liang M, Yang B, Wang S, et al. Deep continuous fusion for multi-sensor 3D object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 641-656. |
| 15 | Liang M, Yang B, Chen Y, et al. Multi-task multi-sensor fusion for 3D object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 2019: 7345-7353. |
| 16 | Xu D, Anguelov D, Jain A. Pointfusion: deep sensor fusion for 3D bounding box estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2018: 244-253. |
| 17 | Xie L, Xiang C, Yu Z, et al. PI-RCNN: an efficient multi-sensor 3D object detector with point-based attentive cont-conv fusion module[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 2020: 12460-12467. |
| 18 | Pang S, Morris D, Radha H. CLOCs: Camera- L i D A R object candidates fusion for 3D object detection[C]∥2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2020: 10386-10393. |
| 19 | Seif H G, Hu X. Autonomous driving in the iCity—HD maps as a key challenge of the automotive industry[J]. Engineering, 2016, 2(2): 159-162. |
| 20 | Chen Y F, Liu S Y, Liu M, et al. Motion planning with diffusion maps[C]∥2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea (South), 2016: 1423-1430. |
| 21 | Caesar H, Bankiti V, Lang A H, et al. Nuscenes: a multimodal dataset for autonomous driving[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 2020: 11621-11631. |
| 22 | Gong L, Wang S, Zhang Y, et al. Lightweight map-enhanced 3D object detection and tracking for autonomous driving[C]∥12th Asia-Pacific Symposium on Internetware, Singapore Singapore, 2020: 165-174. |
| 23 | Yang B, Liang M, Urtasun R. HDNet: exploiting hd maps for 3D object detection[C]∥Conference on Robot Learning,Zürich, Switzerland, 2018: 146-155. |
| 24 | Yan Y, Mao Y, Li B. Second: sparsely embedded convolutional detection[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3337-3354. |
| 25 | Liu Z, Mao H, Wu C Y, et al. A convnet for the 2020s[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2022: 11976-11986. |
| 26 | Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, et al. Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021: 10012-10022. |
| 27 | Ba J L, Kiros J R, Hinton G E. Layer normalization[J/OL]. [2022-09-20]. |
| 28 | Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning, Lile, France, 2015: 448-456. |
| 29 | Glorot X, Bordes A, Bengio Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks[J/OL].[2022-09-20]. .net/publication/215616967_Deep_Spars⁃e_Rectifier_Neural_Networks |
| 30 | Canny J. A computational approach to edge detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1986, 10(6): 679-698. |
| 31 | Zhang Z, Sabuncu M. Generalized cross entropy loss for training deep neural networks with noisy labels[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2018, 31(5): 135-146. |
| 32 | Loshchilov I, Hutter F. Decoupled weight decay regularization[J/OL]. [2022-09-23]. |
| 33 | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 34 | 杨怀江, 王二帅, 隋永新, 等. 简化型残差结构和快速深度残差网络[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(6): 1413-1421. |
| Yang Huai-jiang, Wang Er-shuai, Sui Yong-xin, et al. Simplified residual structure and fast deep residual networks[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1413-1421. | |
| 35 | 申铉京, 张雪峰, 王玉, 等. 像素级卷积神经网络多聚焦图像融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| Shen Xuan-jing, Zhang Xue-feng, Wang Yu, et al. Multi⁃focus image fusion algorithm based on pixel⁃level convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| [1] | 何科,丁海涛,赖宣淇,许男,郭孔辉. 基于Transformer的轮式里程计误差预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [2] | 吴振宇,刘小飞,王义普. 基于DKRRT*-APF算法的无人系统轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 781-791. |
| [3] | 潘弘洋,刘昭,杨波,孙庚,刘衍珩. 基于新一代通信技术的无人机系统群体智能方法综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 629-642. |
| [4] | 朱冰,范天昕,赵健,张培兴,孙宇航. 基于危险边界搜索的自动驾驶系统加速测试方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 704-712. |
| [5] | 郭鹏,赵文超,雷坤. 基于改进Jaya算法的双资源约束柔性作业车间调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 480-487. |
| [6] | 刘近贞,高国辉,熊慧. 用于脑组织分割的多尺度注意网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 576-583. |
| [7] | 时小虎,吴佳琦,吴春国,程石,翁小辉,常志勇. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| [8] | 祁贤雨,王巍,王琳,赵玉飞,董彦鹏. 基于物体语义栅格地图的语义拓扑地图构建方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 569-575. |
| [9] | 周丰丰,朱海洋. 基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法SEE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1834-1841. |
| [10] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [11] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [12] | 赵宏伟,张健荣,朱隽平,李海. 基于对比自监督学习的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1850-1856. |
| [13] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [14] | 胡丹,孟新. 基于时变网格的对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1896-1903. |
| [15] | 王军,徐彦惠,李莉. 低能耗支持完整性验证的数据融合隐私保护方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1657-1665. |
|
||